堆排序(python实现)
堆排序是利用最大最或最小堆,废话不多说:
先给出几个概念:
二叉树:二叉树是每个节点最多有两个子树的树结构。通常子树被称作“左子树”(left subtree)和“右子树”
完全二叉树:除最后一层外,每一层上的节点数均达到最大值;在最后一层上只缺少右边的若干结点。
满二叉树: 除最后一层无任何子节点外,每一层上的所有结点都有两个子结点。
堆:堆是一种数据结构,类似树根结构,如图,但是不一定是二叉树。
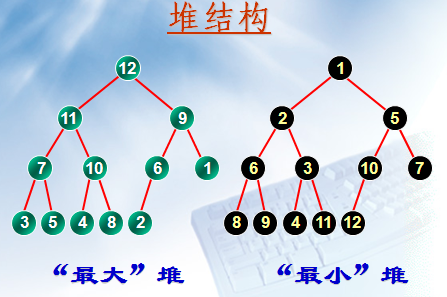
二叉堆:二叉堆是一种特殊的堆,二叉堆是完全二元树(二叉树)或者是近似完全二元树(二叉树),包括最大堆和最小堆。
最大堆:父结点的键值总是大于或等于任何一个子节点的键值,即根节点为最大数字
最小堆:父结点的键值总是大于或等于任何一个子节点的键值,即根节点为最小数字
堆排序步骤:
1.将数据构建成堆,这里的堆指完全二叉树(不一定是满二叉树)
2.将堆调整为最小堆或最大堆
3.此时堆顶已经为最大数或最小数,可以对下面的分支堆再进行调堆即可,此处采用的是将堆顶数取出,再调堆
本人愚钝,网上代码不慎明了,根据自己的思路写了一下,不足之处,请多多指教
1.首先实现将数组按照堆打印
def PrintArrayTree(arr):
frontRowSum=1 #Number of digits in front of n-1 rows
row=1 #row n(start from 1)
for i in range(0,len(arr)):
if i==frontRowSum:
frontRowSum=frontRowSum+2**row #Number of digits in front of n rows
print("\n")#the next row
row=row+1
print (arr[i],end=" ") #print digits
print("Over") arr=[10,9,8,7,6,5,4,3,2,1,234,562,452,23623,565,5,26]
PrintArrayTree(arr)
运行结果如下:
10
9 8
7 6 5 4
3 2 1 234 562 452 23623 565
5 26
print Over
2.构建完了堆,我想实现在堆内任意查找,找到他的子节点和父节点,代码如下:
def FindNode(arr,row,cloumn):
if row<1 or cloumn<1:
print("the number of row and column must be greater than 1")
return
if cloumn>2**(row-1):
print("this row just ",2**(row-1),"numbers")
return
frontRowSum=0
CurrentRowSum=0
for index in range(0,row-1):
CurrentRowSum=2**index #the number of digits in current row
frontRowSum=frontRowSum+CurrentRowSum #the number of digits of all rows
NodeIndex=frontRowSum+cloumn-1 #find the location of the node in the array by row and cloumn
if NodeIndex>len(arr)-1:
print("out of this array")
return
currentNode=arr[NodeIndex]
childIndex=NodeIndex*2+1
print("Current Node:",currentNode)
if row==1: #row 1 have no parent node
print("no parent node!")
else: #the parent node ofcurrent node
parentIndex=int((NodeIndex-1)/2)
parentNode=arr[parentIndex]
print("Parent Node:",parentNode)
if childIndex+1>len(arr): #print leftChild node
print("no left child node!")
else:
leftChild=arr[childIndex]
print("Left Child Node:",leftChild)
if childIndex+1+1>len(arr): #print rightChild node
print("no left right node!")
else:
rightChild=arr[childIndex+1]
print("Right Child Node:",rightChild)
print("\n")
arr=[10,9,8,7,6,5,4,3,2,1,234,562,452,23623,565,5,26]
FindNode(arr,1,1)
FindNode(arr,2,2)
FindNode(arr,4,1)
代码运行结果如下:
Current Node: 10
no parent node!
Left Child Node: 9
Right Child Node: 8
Current Node: 8
Parent Node: 10
Left Child Node: 5
Right Child Node: 4
Current Node: 3
Parent Node: 7
Left Child Node: 5
Right Child Node: 26
此代码在堆排序中没有直接用到,但是提供了一些思路
3.按照堆排序步骤,建堆之后需要进行堆调整,接下来进行堆调整,先实现单个叉(某个节点及其子孩子)的进行排序,直接借鉴FindNode里面的代码,将当前节点分别与其左右孩子比较就行了,本文意在实现最小堆,即将小的节点作为父节点
def MinSort(arr,row,cloumn):
if row<1 or cloumn<1:
print("the number of row and column must be greater than 1")
return
if cloumn>2**(row-1):
print("this row just ",2**(row-1),"numbers")
return
frontRowSum=0
CurrentRowSum=0
for index in range(0,row-1):
CurrentRowSum=2**index #the number of digits in current row
frontRowSum=frontRowSum+CurrentRowSum #the number of digits of all rows
NodeIndex=frontRowSum+cloumn-1 #find the location of the node in the array by row and cloumn
if NodeIndex>len(arr)-1:
print("out of this array")
return
currentNode=arr[NodeIndex]
childIndex=NodeIndex*2+1
print("Current Node:",currentNode)
if row==1:
print("no parent node!")
else:
parentIndex=int((NodeIndex-1)/2)
parentNode=arr[parentIndex]
print("Parent Node:",parentNode)
if childIndex+1>len(arr):
print("no left child node!")
else:
leftChild=arr[childIndex]
print("Left Child Node:",leftChild)
if currentNode>leftChild:
print("swap currentNode and leftChild")
temp=currentNode
currentNode=leftChild
leftChild=temp
arr[childIndex]=leftChild
if childIndex+1>=len(arr):
print("no right child node!")
else:
rightChild=arr[childIndex+1]
print("Right Chile Node:",rightChild)
if currentNode>rightChild:
print("swap rightCild and leftChild")
temp=rightChild
rightChild=currentNode
currentNode=temp
arr[childIndex+1]=rightChild
arr[NodeIndex]=currentNode
arr=[10,9,8,7,6,5,4,3,2,1,234,562,452,23623,565,5,26]
print("initial array:",arr)
MinSort(arr,1,1)
print("result array:",arr)
运行结果如下,可以看出对于第一个节点,其自孩子为9,8,已经实现将节点与最小的自孩子进行交换,保证父节点小于任何一个子孩子
initial array: [10, 9, 8, 7, 6, 5, 4, 3, 2, 1, 234, 562, 452, 23623, 565, 5, 26]
Current Node: 10
no parent node!
Left Child Node: 9
swap currentNode and leftChild
Right Chile Node: 8
swap rightCild and leftChild
result array: [8, 10, 9, 7, 6, 5, 4, 3, 2, 1, 234, 562, 452, 23623, 565, 5, 26]
4.已经实现对单个节点和子孩子进行比较,保证父节点小于孩子,将堆内所有拥有孩子的节点进行排序,即可调整为最小堆,代码如下:
def MinHeap(arr):
frontRowSum=1
row=1
for i in range(0,len(arr)):
if i==frontRowSum:
frontRowSum=frontRowSum+2**row #the number of digits of all rows
print("\n") # next row
row=row+1
print (arr[i],end=" ")
print("row",row)
rowIndex=row-1 #the last row have no child node
print("rowIndex",rowIndex)
column=2**(rowIndex-1) #the number of digits of current row
print("column",column)
number=len(arr)
while rowIndex>0: #sort the nodes that have child nodes from the last number to the first number
if number<=2**(rowIndex-1):
rowIndex=rowIndex-1
column=2**(rowIndex-1)
print("sort",rowIndex,column)
MinSort(arr,rowIndex,column)
number=number-1
column=column-1
arr=[10,9,8,7,6,5,4,3,2,1,234,562,452,23623,565,5,26]
print("initial array:",arr)
PrintArrayTree(arr)
MinHeap(arr)
print("result array:",arr)
PrintArrayTree(arr)
运行结果如下,可以看到最小数字已经位于顶端,实现最小堆
initial array: [10, 9, 8, 7, 6, 5, 4, 3, 2, 1, 234, 562, 452, 23623, 565, 5, 26]
10
9 8
7 6 5 4
3 2 1 234 562 452 23623 565
5 26
print Over
.......
result array: [1, 10, 4, 9, 2, 8, 5, 7, 3, 6, 234, 562, 452, 23623, 565, 5, 26]
1
10 4
9 2 8 5
7 3 6 234 562 452 23623 565
5 26
print Over
4.最小值已经到顶端,将最小值依次取出,然后再调整堆,再取出,就完成堆排序。代码如下:
def HeapSort(arr):
arr2=[]
for i in range(0,len(arr)):
MinHeap(arr)
arr2.append(arr[0])
del arr[0]
return arr2 arr=[10,9,8,7,6,5,4,3,2,1,234,562,452,23623,565,5,26]
print("initial array:",arr)
PrintArrayTree(arr)
resultArr=HeapSort(arr)
print("result array:",resultArr)
PrintArrayTree(resultArr)
运行结果如下:
initial array: [10, 9, 8, 7, 6, 5, 4, 3, 2, 1, 234, 562, 452, 23623, 565, 5, 26]
10
9 8
7 6 5 4
3 2 1 234 562 452 23623 565
5 26
print Over
10
9 8
7 6 5 4
3 2 1 234 562 452 23623 565
5 26
.........
result array: [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 26, 234, 452, 562, 565, 23623]
1
2 3
4 5 5 6
7 8 9 10 26 234 452 562
565 23623
print Over
5.后续工作:
1)代码需要优化
2)感觉堆排序有点类似冒泡排序
3)需要检查代码的健壮性
4)后续需要计算分析代码的复杂度
1)优化之后的程序如下:写法还能再优化,但继续优化会影响可读性
def MinSort(arr,start,end):
import math
arrHeight=0
for index in range(0,end-start):
if index==2**(arrHeight+1)-1:
arrHeight=arrHeight+1 for NodeIndex in range(2**(arrHeight)-2,-1,-1):
currentNode=arr[NodeIndex+start]
childIndex=NodeIndex*2+1+start if childIndex+1>len(arr):
continue
else:
leftChild=arr[childIndex] if currentNode>leftChild:
temp=currentNode
currentNode=leftChild
leftChild=temp
arr[childIndex]=leftChild
arr[NodeIndex+start]=currentNode if childIndex+1>=len(arr):
continue
else:
rightChild=arr[childIndex+1]
if currentNode>rightChild: temp=rightChild
rightChild=currentNode
currentNode=temp
arr[childIndex+1]=rightChild
arr[NodeIndex+start]=currentNode def HeapSort(arr):
for i in range(0,len(arr)-1):
MinSort(arr,i,len(arr)) arr=[10,9,8,7,6,5,4,3,2,1,234,562,452,23623,565,5,26] print("Initial array:\n",arr)
HeapSort(arr)
print("Result array:\n",arr)
运行结果:
Initial array:
[10, 9, 8, 7, 6, 5, 4, 3, 2, 1, 234, 562, 452, 23623, 565, 5, 26]
Result array:
[1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 26, 234, 452, 562, 565, 23623]
堆排序(python实现)的更多相关文章
- 高速排序,归并排序,堆排序python实现
高速排序的时间复杂度最好情况下为O(n*logn),最坏情况下为O(n^2),平均情况下为O(n*logn),是不稳定的排序 归并排序的时间复杂度最好情况下为O(n*logn),最坏情况下为O(n*l ...
- 堆排序python实现
def MAX_Heapify(heap,HeapSize,root):#在堆中做结构调整使得父节点的值大于子节点 left = 2*root+1 right = left + 1 larger = ...
- 简单的堆排序-python
AA = raw_input().strip().split(' ') A = [] ###############初始化大堆############### def fixUp(A): k = len ...
- 排序NB三人组
排序NB三人组 快速排序,堆排序,归并排序 1.快速排序 方法其实很简单:分别从初始序列“6 1 2 7 9 3 4 5 10 8”两端开始“探测”.先从右往左找一个小于6的数,再从左往 ...
- 3、计数排序,电影top100
1.计数排序 # -*- coding: utf-8 -*- # @Time : 2018/07/31 0031 11:32 # @Author : Venicid def count_sort(li ...
- 数据结构:堆排序 (python版) 小顶堆实现从大到小排序 | 大顶堆实现从小到大排序
#!/usr/bin/env python # -*- coding:utf-8 -*- ''' Author: Minion-Xu 小堆序实现从大到小排序,大堆序实现从小到大排序 重点的地方:小堆序 ...
- 你需要知道的九大排序算法【Python实现】之堆排序
六.堆排序 堆排序是一种树形选择排序,是对直接选择排序的有效改进. 堆的定义下:具有n个元素的序列 (h1,h2,...,hn),当且仅当满足(hi>=h2i,hi>=2i+1)或(h ...
- python下实现二叉堆以及堆排序
python下实现二叉堆以及堆排序 堆是一种特殊的树形结构, 堆中的数据存储满足一定的堆序.堆排序是一种选择排序, 其算法复杂度, 时间复杂度相对于其他的排序算法都有很大的优势. 堆分为大头堆和小头堆 ...
- 算法导论 第六章 堆排序(python)
6.1堆 卫星数据:一个带排序的的数通常是有一个称为记录的数据集组成的,每一个记录有一个关键字key,记录的其他数据称为卫星数据. 原地排序:在排序输入数组时,只有常数个元素被存放到数组以外的空间中去 ...
- Python八大算法的实现,插入排序、希尔排序、冒泡排序、快速排序、直接选择排序、堆排序、归并排序、基数排序。
Python八大算法的实现,插入排序.希尔排序.冒泡排序.快速排序.直接选择排序.堆排序.归并排序.基数排序. 1.插入排序 描述 插入排序的基本操作就是将一个数据插入到已经排好序的有序数据中,从而得 ...
随机推荐
- JavaScript权威设计--JavaScript变量,作用域,声明提前(简要学习笔记四)
1.宿主对象与宿主环境 宿主对象:由ECMAScript实现的宿主环境提供的对象,可以理解为:浏览器提供的对象.所有的BOM和DOM都是宿主对象. 宿主环境:一般宿主环境由外壳程序创建与维护,只要 ...
- 1、Python基础知识
输出print “houkai”,3.0版本后print修改为函数,print(‘houkai’) 数学运算:默认整数整除1/2=0而1.0/2=0.5,可以使用from __future__ imp ...
- 【转】c#、wpf 字符串,color,brush之间的转换
转自:http://www.cnblogs.com/wj-love/archive/2012/09/14/2685281.html 1,将#3C3C3C 赋给background this.selec ...
- 多行文本溢出显示省略号(…) text-overflow: ellipsis
详解text-overflow 语法: text-overflow:clip | ellipsis 默认值:clip 适用于:块级容器元素 继承性:无 动画性:否 计算值:指定值 取值: clip:当 ...
- AngularJS Resource:与 RESTful API 交互
REST(表征性状态传输,Representational State Transfer)是Roy Fielding博士在2000年他的博士论文中提出来的一种软件架构风格.RESTful风格的设计不仅 ...
- MySQL binlog中的事件类型
MySQL binlog记录的所有操作实际上都有对应的事件类型的,譬如STATEMENT格式中的DML操作对应的是QUERY_EVENT类型,ROW格式下的DML操作对应的是ROWS_EVENT类型. ...
- 用H5中的Canvas等技术制作海报
在去年的时候也实现过合成海报的功能,不过当时时间仓促,实现的比较简单. 就一个旋转功能,图片也不能拖动放大,也不能裁剪. 去年的实现可以参考<移动图片操作--上传>和<移动图片操作- ...
- SQL Tuning 基础概述05 - Oracle 索引类型及介绍
一.B-Tree索引 三大特点:高度较低.存储列值.结构有序 1.1利用索引特性进行优化 外键上建立索引:不但可以提升查询效率,而且可以有效避免锁的竞争(外键所在表delete记录未提交,主键所在表会 ...
- docker对数据卷容器进行备份
转载请注明出处 官网的数据以及各大博客都没有对这个的具体说明,本人也是理解了好久. 我们使用docker的过程中,使用共享的数据卷是经常的,那么.我们要怎么进行备份呢? 首先,我们得了解下面4个命 ...
- Redis命令拾遗一(字符串类型)
文章归博客园和作者“蜗牛”共同所有 .转载和爬虫请注明原文Redis系列链接 http://www.cnblogs.com/tdws/tag/NoSql/ Redis有五种基本数据类型.他们分别是字符 ...
