LSTM时间序列预测及网络层搭建
一、LSTM预测未来一年某航空公司的客运流量
给你一个数据集,只有一列数据,这是一个关于时间序列的数据,从这个时间序列中预测未来一年某航空公司的客运流量。数据形式:

二、实战
1)数据下载
你可以google passenger.csv文件,即可找到对应的项目数据,如果没有找到,这里提供数据的下载链接:https://pan.baidu.com/s/1a7h5ZknDyT0azW9mv5st7w 提取码:u5h3
2)jupyter notebook
桌面新建airline文件夹,passenger.csv移动进去,按住shift+右键,选择在此处新建命令窗口,输入jupyter notebook,新建名为airline_predict的脚本
3)查看数据:
import pandas as pd
df = pd.read_csv('passenger.csv', header=None)
df.columns = ['time', 'passengers']
df.head(12)
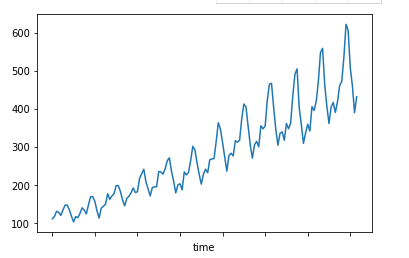
结果如下:我们发现数据以年为单位,记录了每一年中每一月份的乘客量

我们来做出趋势图,看看客运量是如何变化的:
df = df.set_index('time')#将第一列设置为行索引
df.head(12)
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
df['passengers'].plot()
plt.show()
结果如下:从图上看出,客运量还是逐年增加的

4)处理数据,划分训练集和测试集
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
from sklearn.preprocessing import MinMaxScaler class Airline_Predict:
def __init__(self, filename, sequence_length=10, split=0.8):
self.filename = filename
self.sequence_length = sequence_length
self.split = split def load_data(self):
df = pd.read_csv(self.filename, sep=',', usecols=[1], header=None) data_all = np.array(df).astype('float')
print(data_all.shape)#(144, 1) #数据归一化
MMS = MinMaxScaler()
data_all = MMS.fit_transform(data_all)
print(data_all.shape) #构造输入lstm的3D数据:(133, 11, 1)
#其中特征是10个,第11个是数值标签 data = []
for i in range( len(data_all) - self.sequence_length - 1 ):
data.append( data_all[ i: i+self.sequence_length+1 ] ) #global reshaped_data
reshaped_data = np.array(data).astype('float64')
print(reshaped_data.shape)#(133, 11, 1) #打乱第一维数据
np.random.shuffle(reshaped_data) #对133组数据处理,每组11个数据,前10个作为特征,第11个是数值标签:(133, 10,1)
x = reshaped_data[:, :-1]
print('samples shape:', x.shape, '\n')#(133, 10, 1)
y = reshaped_data[:, -1]
print('labels shape:', y.shape, '\n')#(133, 1) #构建训练集
split_boundary = int(reshaped_data.shape[0] * self.split)
train_x = x[:split_boundary]
print('train_x shape:', train_x.shape) #构建测试集
test_x = x[ split_boundary: ]
print('test_x shape:', test_x.shape) #训练集标签
train_y = y[ : split_boundary ]
print('train_y shape', train_y.shape) #测试集标签
test_y = y[ split_boundary: ]
print('test_y shape', test_y.shape) return train_x, train_y, test_x, test_y, MMS filename = 'passenger.csv'
AirLine = Airline_Predict(filename)
train_x, train_y, test_x, test_y, MMS = AirLine.load_data()
5)训练模型
#coding=gbk import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
from sklearn.preprocessing import MinMaxScaler import warnings
warnings.filterwarnings('ignore') from keras.models import Sequential
from keras.layers import LSTM, Dense, Activation import matplotlib.pyplot as plt class Airline_Predict:
def __init__(self, filename, sequence_length=10, split=0.8):
self.filename = filename
self.sequence_length = sequence_length
self.split = split def load_data(self):
df = pd.read_csv(self.filename, sep=',', usecols=[1], header=None) data_all = np.array(df).astype('float')
print(data_all.shape)#(144, 1) #数据归一化
MMS = MinMaxScaler()
data_all = MMS.fit_transform(data_all)
print(data_all.shape) #构造输入lstm的3D数据:(133, 11, 1)
#其中特征是10个,第11个是数值标签 data = []
for i in range( len(data_all) - self.sequence_length - 1 ):
data.append( data_all[ i: i+self.sequence_length+1 ] ) #global reshaped_data
reshaped_data = np.array(data).astype('float64')
print(reshaped_data.shape)#(133, 11, 1) #打乱第一维数据
np.random.shuffle(reshaped_data) #对133组数据处理,每组11个数据,前10个作为特征,第11个是数值标签:(133, 10,1)
x = reshaped_data[:, :-1]
print('samples shape:', x.shape, '\n')#(133, 10, 1)
y = reshaped_data[:, -1]
print('labels shape:', y.shape, '\n')#(133, 1) #构建训练集
split_boundary = int(reshaped_data.shape[0] * self.split)
train_x = x[:split_boundary]
print('train_x shape:', train_x.shape) #构建测试集
test_x = x[ split_boundary: ]
print('test_x shape:', test_x.shape) #训练集标签
train_y = y[ : split_boundary ]
print('train_y shape', train_y.shape) #测试集标签
test_y = y[ split_boundary: ]
print('test_y shape', test_y.shape) return train_x, train_y, test_x, test_y, MMS def build_model(self):
#LSTM函数的input_dim参数是输入的train_x的最后一个维度
#train_x的维度为(n_samples, time_sequence_steps, input_dim)
#在keras 的官方文档中,说了LSTM是整个Recurrent层实现的一个具体类,它需要的输入数据维度是:
#形如(samples,timesteps,input_dim)的3D张量
#而这个time_sequence_steps就是我们采用的时间窗口,即把一个时间序列当成一条长链,我们固定一个一定长度的窗口对这个长链进行采用
#这里使用了两个LSTM进行叠加,第二个LSTM的第一个参数指的是输入的维度,这和第一个LSTM的输出维度并不一样,这也是LSTM比较随意的地方
#最后一层采用了线性层 model = Sequential()
model.add( LSTM( input_dim=1, output_dim=50, return_sequences=True ) )
print( "model layers:",model.layers ) model.add( LSTM(100, return_sequences=False) )
model.add( Dense( output_dim=1 ) )
model.add( Activation('linear') ) model.compile( loss='mse', optimizer='rmsprop' )
return model def train_model(self, train_x, train_y, test_x, test_y):
model = self.build_model() try:
model.fit( train_x, train_y, batch_size=512, nb_epoch=100, validation_split=0.1 )
predict = model.predict(test_x)
#print(predict.size)
predict = np.reshape( predict, (predict.size, ) )#变成向量
test_y = np.reshape( test_y, (test_y.size, ) )
except KeyboardInterrupt:
print('predict:',predict)
print('test_y',test_y) print('After predict:\n',predict)
print('The right test_y:\n',test_y) try:
fig1 = plt.figure(1)
plt.plot(predict, 'r')
plt.plot(test_y, 'g-')
plt.title('This pic is drawed using Standard Data')
plt.legend(['predict', 'true']) except Exception as e:
print(e) return predict, test_y filename = 'passenger.csv'
AirLine = Airline_Predict(filename)
train_x, train_y, test_x, test_y, MMS = AirLine.load_data() predict_y, test_y = AirLine.train_model(train_x, train_y, test_x, test_y) #对标注化后的数据还原
predict_y = MMS.inverse_transform( [ [i] for i in predict_y ] )
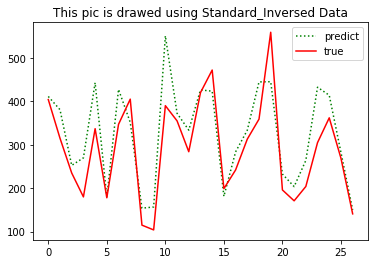
test_y = MMS.inverse_transform( [ [i] for i in test_y ] ) fig2 = plt.figure(2)
plt.plot(predict_y, 'g:', label='prediction')
plt.plot(test_y, 'r-', label='True')
plt.title('This pic is drawed using Standard_Inversed Data')
plt.legend(['predict', 'true'])
plt.show() print('predict:',np.reshape(predict_y, (predict_y.size,)) )
print('True:',np.reshape(test_y, (test_y.size,)))

三、代码结构

LSTM时间序列预测及网络层搭建的更多相关文章
- (数据科学学习手札40)tensorflow实现LSTM时间序列预测
一.简介 上一篇中我们较为详细地铺垫了关于RNN及其变种LSTM的一些基本知识,也提到了LSTM在时间序列预测上优越的性能,本篇就将对如何利用tensorflow,在实际时间序列预测任务中搭建模型来完 ...
- Kesci: Keras 实现 LSTM——时间序列预测
博主之前参与的一个科研项目是用 LSTM 结合 Attention 机制依据作物生长期内气象环境因素预测作物产量.本篇博客将介绍如何用 keras 深度学习的框架搭建 LSTM 模型对时间序列做预测. ...
- Pytorch循环神经网络LSTM时间序列预测风速
#时间序列预测分析就是利用过去一段时间内某事件时间的特征来预测未来一段时间内该事件的特征.这是一类相对比较复杂的预测建模问题,和回归分析模型的预测不同,时间序列模型是依赖于事件发生的先后顺序的,同样大 ...
- keras-anomaly-detection 代码分析——本质上就是SAE、LSTM时间序列预测
keras-anomaly-detection Anomaly detection implemented in Keras The source codes of the recurrent, co ...
- LSTM时间序列预测学习
一.文件准备工作 下载好的例程序 二.开始运行 1.在程序所在目录中(chapter_15)打开终端 输入下面的指令运行 python train_lstm.py 此时出现了报错提示没有安装mat ...
- Python中利用LSTM模型进行时间序列预测分析
时间序列模型 时间序列预测分析就是利用过去一段时间内某事件时间的特征来预测未来一段时间内该事件的特征.这是一类相对比较复杂的预测建模问题,和回归分析模型的预测不同,时间序列模型是依赖于事件发生的先后顺 ...
- 时间序列深度学习:状态 LSTM 模型预测太阳黑子
目录 时间序列深度学习:状态 LSTM 模型预测太阳黑子 教程概览 商业应用 长短期记忆(LSTM)模型 太阳黑子数据集 构建 LSTM 模型预测太阳黑子 1 若干相关包 2 数据 3 探索性数据分析 ...
- 使用tensorflow的lstm网络进行时间序列预测
https://blog.csdn.net/flying_sfeng/article/details/78852816 版权声明:本文为博主原创文章,未经博主允许不得转载. https://blog. ...
- 基于 Keras 用 LSTM 网络做时间序列预测
目录 基于 Keras 用 LSTM 网络做时间序列预测 问题描述 长短记忆网络 LSTM 网络回归 LSTM 网络回归结合窗口法 基于时间步的 LSTM 网络回归 在批量训练之间保持 LSTM 的记 ...
随机推荐
- js判断一个元素是否在数组中
js判断一个元素是否在数组中 var arr = ['a','s','d','f']; console.info(isInArray(arr,'a'));//循环的方式 function isInAr ...
- thymeleaf手动映射根路径映射
到/src/java/resources/templates/index.html下 @RequestMapping("/") public String index(){ ret ...
- 【BZOJ3625】【CF438E】小朋友和二叉树 NTT 生成函数 多项式开根 多项式求逆
题目大意 考虑一个含有\(n\)个互异正整数的序列\(c_1,c_2,\ldots ,c_n\).如果一棵带点权的有根二叉树满足其所有顶点的权值都在集合\(\{c_1,c_2,\ldots ,c_n\ ...
- IntegrityError at /admin/users/userprofile/add/ (1452, 'Cannot add or update a child row: a foreign key constraint fails (`mxonline`.`django_admin_log`, CONSTRAINT `django_admin_log_user_id_c564eba6_
报错现象 在执行 django 后台管理的时候添加数据导致 1452 错误 报错代码 IntegrityError at /admin/users/userprofile/add/ (1452, 'C ...
- U盘启动盘还原
cmd运行 diskpart list disk clean 一般都是disk 1,不过最好先list查一下 右击桌面上的计算机图标,选择管理,进入磁盘管理,能看到u盘分区是未分配的(黑色),右击,新 ...
- 正睿 2019 省选附加赛 Day10
A 核心就是一个公式 \[\sum_{i = 0}^{k} S(k, i) \tbinom{x}{i} i\] S是第二类斯特林数 递推公式 \(S_2(n,k)=S_2(n−1,k−1)+kS_2( ...
- Hdoj 1003.Max Sum 题解
Problem Description Given a sequence a[1],a[2],a[3]......a[n], your job is to calculate the max sum ...
- iis express添加虚拟目录
在调试WEB时,还是使用IIS EXPRESS比较方便, 在IIS中,选择网站,右击,添加虚拟目录或者应用程序,就能添加虚拟目录了.. 在IIS EXPRESS中,添加虚拟目录如下 1.右击IIS E ...
- python中无法被转化为set的list[list组成的list]
arr = [[a],[b]] set(arr) output: Traceback (most recent call last): File "<stdin>", ...
- cf1088C Ehab and a 2-operation task (构造)
题意:给一个数列,你可以进行至多n+1次操作,每次给一个前缀对某数取模或者加某数,使得最后数列严格单增 考虑到因为是前缀和而且还不能加负数,光靠加是不能让前面的小于后面的 所以要让他先在模某数意义下单 ...
