String类源码解析
1. String是使用char[]数组来存储的,并且String值在创建之后就不可以改变了。char[]数组的定义为:
/** The value is used for character storage. */
private final char value[];
char[]数组value使用final修饰,因此赋值之后就不可以改变了。再看一下String的hashCode()方法的实现就更能说明这一点:
/** Cache the hash code for the string */
private int hash; // Default to 0
成员变量hash,用来缓存String对象的hash code。为什么可以缓存?
因为String对象不可以改变,求hash code也不会变,因此有了缓存,不需要每次都求。代码如下:
/**
* Returns a hash code for this string. The hash code for a
* <code>String</code> object is computed as
* <blockquote><pre>
* s[0]*31^(n-1) + s[1]*31^(n-2) + ... + s[n-1]
* </pre></blockquote>
* using <code>int</code> arithmetic, where <code>s[i]</code> is the
* <i>i</i>th character of the string, <code>n</code> is the length of
* the string, and <code>^</code> indicates exponentiation.
* (The hash value of the empty string is zero.)
*
* @return a hash code value for this object.
*/
public int hashCode() {
// hash值为缓存值
int h = hash;
// 如果缓存的hash值为0,表示已经求过hash值,所以直接返回该值
// 如果是空字符串,那么hash值为0
if (h == 0 && value.length > 0) {
char val[] = value; for (int i = 0; i < value.length; i++) {
h = 31 * h + val[i];
}
hash = h;
}
return h;
}
2. String的构造函数有多个,空串的构造函数为:
/**
* Initializes a newly created {@code String} object so that it represents
* an empty character sequence. Note that use of this constructor is
* unnecessary since Strings are immutable.
*/
public String() {
this.value = new char[0];
}
从代码可以看出,该构造方法生成一个空的char序列,就如注释所说“使用该构造方法是没有任何意义的”。
最常用的构造方法莫过于new String(String original):
/**
* Initializes a newly created {@code String} object so that it represents
* the same sequence of characters as the argument; in other words, the
* newly created string is a copy of the argument string. Unless an
* explicit copy of {@code original} is needed, use of this constructor is
* unnecessary since Strings are immutable.
*
* @param original
* A {@code String}
*/
public String(String original) {
this.value = original.value;
this.hash = original.hash;
}
该构造方法其实copy了original的value值和hash值,他们还是使用的同一串char序列。但是又创建了一个新的String对象,和original是不同的对象了。
3. 接下来通过一个例子来了解String是如何存储的。了解之前先回顾下java内存分配的几个术语:
栈:由JVM分配区域,用于保存线程执行的动作和数据引用。栈是一个运行的单位,Java中一个线程就会相应有一个线程栈与之对应。
堆:由JVM分配的,用于存储对象等数据的区域。
常量池:在编译的阶段,在堆中分配出来的一块存储区域,用于存储显式(不是通过new生成的)的String,float或者integer.例如String str="abc"; abc这个字符串是显式声明,所以存储在常量池。
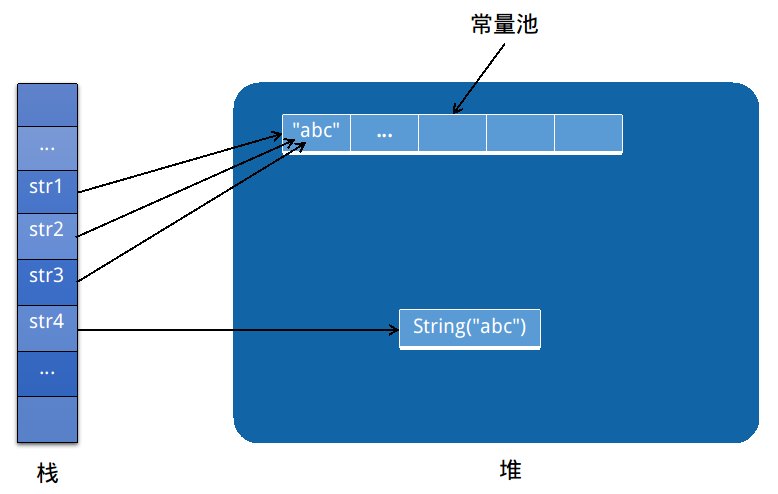
例子:
String str1 = "abc";
String str2 = "abc";
String str3 = "ab" + "c";
String str4 = new String(str2);
//str1和str2引用自常量池里的同一个string对象
System.out.println(str1 == str2); // true
//str3通过编译优化,与str1引用自同一个对象
System.out.println(str1 == str3); // true
//str4因为是在堆中重新分配的另一个对象,所以它的引用与str1不同
System.out.println(str1 == str4); // false
- 第一个“str1 == str2”很好理解,因为在编译的时候,"abc"被存储在常量池中,str1和str2的引用都是指向常量池中的"abc"。所以str1和str2引用是相同的。
- 第二个“str1 == str3”是由于编译器做了优化,编译器会先把字符串拼接,再在常量池中查找这个字符串是否存在,如果存在,则让变量直接引用该字符串。所以str1和str3引用也是相同的。
- str4的对象不是显式赋值的,编译器会在堆中重新分配一个区域来存储它的对象数据。所以str1和str4的引用是不一样的。
图形化示例如下图所示:
3. 常用的equals()方法就比较朴实了,就是依次比较字符是否相同,
public boolean equals(Object anObject) {
if (this == anObject) {
return true;
}
if (anObject instanceof String) {
String anotherString = (String) anObject;
int n = value.length;
if (n == anotherString.value.length) {
char v1[] = value;
char v2[] = anotherString.value;
int i = 0;
while (n-- != 0) {
if (v1[i] != v2[i])
return false;
i++;
}
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
4. String实现了Comparable接口,自然有其compareTo()方法
public int compareTo(String anotherString) {
int len1 = value.length;
int len2 = anotherString.value.length;
// 获取两个String串的最小长度
int lim = Math.min(len1, len2);
char v1[] = value;
char v2[] = anotherString.value;
int k = 0;
// 依次比较两个String串最小长度范围内的相同位置的字符是否相同
// 如果不同,则返回Unicode编码的差值
while (k < lim) {
char c1 = v1[k];
char c2 = v2[k];
if (c1 != c2) {
return c1 - c2;
}
k++;
}
// 如果最小长度范围内的字符完全相同,则返回两个String串的长度之差
return len1 - len2;
}
String类源码解析的更多相关文章
- Java集合---Array类源码解析
Java集合---Array类源码解析 ---转自:牛奶.不加糖 一.Arrays.sort()数组排序 Java Arrays中提供了对所有类型的排序.其中主要分为Prim ...
- java.lang.Void类源码解析_java - JAVA
文章来源:嗨学网 敏而好学论坛www.piaodoo.com 欢迎大家相互学习 在一次源码查看ThreadGroup的时候,看到一段代码,为以下: /* * @throws NullPointerEx ...
- java.lang.String 类源码解读
String类定义实现了java.io.Serializable, Comparable<String>, CharSequence 三个接口:并且为final修饰. public fin ...
- Java集合---Arrays类源码解析
一.Arrays.sort()数组排序 Java Arrays中提供了对所有类型的排序.其中主要分为Primitive(8种基本类型)和Object两大类. 基本类型:采用调优的快速排序: 对象类型: ...
- Thread类源码解析
源码版本:jdk8 其中的部分论证和示例代码:Java_Concurrency 类声明: Thread本身实现了Runnable接口 Runnable:任务,<java编程思想>中表示该命 ...
- Dom4j工具类源码解析
话不多说,上源码: package com.changeyd.utils;import java.io.File;import java.io.FileNotFoundException;import ...
- Spring-IOC MethodInvokingFactoryBean 类源码解析
MethodInvokingFactoryBean MethodInvokingFactoryBean的作用是,通过定义类和它的方法,然后生成的bean是这个方法的返回值,即可以注入方法返回值. Me ...
- Java String类源码
String类的签名(JDK 8): public final class String implements java.io.Serializable, Comparable<String&g ...
- String 类源码分析
String 源码分析 String 类代表字符序列,Java 中所有的字符串字面量都作为此类的实例. String 对象是不可变的,它们的值在创建之后就不能改变,因此 String 是线程安全的. ...
随机推荐
- JDK自带工具keytool生成ssl证书
前言: 因为公司项目客户要求使用HTTPS的方式来保证数据的安全,所以木有办法研究了下怎么生成ssl证书来使用https以保证数据安全. 百度了不少资料,看到JAVA的JDK自带生成SSL证书的工具: ...
- bufferedwriter写json文件中文乱码
需要用writer writer = new BufferedWriter(new OutputStreamWriter(new FileOutputStream(file),"utf-8& ...
- P1074 靶形数独
P1074 靶形数独正着搜80分,完全倒置95分,完全倒置后左右再倒置,就会A掉,到时候脑洞要大一些. #include<iostream> #include<cstdio> ...
- Alpha(10/10)
鐵鍋燉腯鱻 项目:小鱼记账 团队成员 项目燃尽图 冲刺情况描述 站立式会议照片 各成员情况 团队成员 学号 姓名 git地址 博客地址 031602240 许郁杨 (组长) https://githu ...
- XamarinAndroid组件教程RecylerView适配器使用动画
XamarinAndroid组件教程RecylerView适配器使用动画 为RecylerView使用RecylerViewAnimators组件中提供的适配器动画,需要使用RecyclerView类 ...
- LR逻辑回归文章
http://blog.csdn.net/suipingsp/article/details/41822313
- 通过Obfuscated ssh避免时不时ssh连接不畅的问题【转】
众所周知的原因,为了能流畅的使用google.使用某些“不存在”的网站,我们一般都是需要通过某些不方便光明正大说明使用用途的技术.比如通过ssh tunnel,这是最简单的,也是用得最多的. 不过,这 ...
- 潭州课堂25班:Ph201805201 django 项目 第七课 用户模型设计 (课堂笔记
在 user 的应用中的 models.py: 导入 dango 自带的用户模型 from django.contrib.auth.models import AbstractUser,UserMan ...
- git 撤销更改的文件
在没有git add之前: 1.撤销所有更改:git checkout . 2.撤销指定文件的更改:git checkout -- file.txt git add之后: git reset HEAD ...
- BZOJ2670 : Almost
求出前缀和$s[]$,那么区间$[l,r]$的几乎平均数$=\frac{s[r]-s[l-1]}{r-l}$. 若只有一个询问,那么可以维护$(i,s[i-1])$的凸壳,在凸壳上二分点$(i,s[i ...
