MapReduce对交易日志进行排序的Demo(MR的二次排序)
1.日志源文件 (各个列分别是: 账户,营业额,花费,日期)
zhangsan@163.com 6000 0 2014-02-20
lisi@163.com 2000 0 2014-02-20
lisi@163.com 0 100 2014-02-20
zhangsan@163.com 3000 0 2014-02-20
wangwu@126.com 9000 0 2014-02-20
wangwu@126.com 0 200 2014-02-20
想要的结果: (计算出每个账户的总营业额和总花费,要求营业额排序降序,如果营业额相同则花费少的在上面)
zhangsan@163.com 9000 0 9000
wangwu@126.com 9000 200 8800
lisi@163.com 2000 100 1900
2.写代码:
InfoBean.java 对账户的后三个字段封装成一个Bean对象
import java.io.DataInput;
import java.io.DataOutput;
import java.io.IOException; import org.apache.hadoop.io.WritableComparable; //要和其他的InfoBean类型进行比较,所以此处泛型T为InfoBean
public class InfoBean implements WritableComparable<InfoBean> { private String account;
private double income;
private double expenses;
private double surplus; /*
*如果不写这个方法,封装InfoBean对象的时候就要分别set这个对象的各个属性.
*/
public void set(String account,double income,double expenses){
this.account = account;
this.income = income;
this.expenses = expenses;
this.surplus = income -expenses;
}
@Override
public void write(DataOutput out) throws IOException {
out.writeUTF(account);
out.writeDouble(income);
out.writeDouble(expenses);
out.writeDouble(surplus);
} @Override
public void readFields(DataInput in) throws IOException {
this.account = in.readUTF();
this.income = in.readDouble();
this.expenses = in.readDouble();
this.surplus = in.readDouble();
} @Override
public int compareTo(InfoBean o) {
if(this.income == o.getIncome()){
return this.expenses > o.getExpenses() ? 1 : -1;
} else {
return this.income > o.getIncome() ? -1 : 1;
}
} @Override
//toString()方法输出的格式最好和源文件trade_info.txt中的格式一样, 字段通过Tab键分隔.
//而且在SumReducer类输出k3,v3的时候会输出k3(context.write(key, v);) 所以这个地方没有必要再输出k3(account)
public String toString() {
// return "InfoBean [account=" + account + ", income=" + income
// + ", expenses=" + expenses + ", surplus=" + surplus + "]";
return this.income + "\t" + this.expenses+"\t" + this.surplus;
}
public double getIncome() {
return income;
} public void setIncome(double income) {
this.income = income;
} public double getExpenses() {
return expenses;
} public void setExpenses(double expenses) {
this.expenses = expenses;
} public double getSurplus() {
return surplus;
} public void setSurplus(double surplus) {
this.surplus = surplus;
} public String getAccount() {
return account;
} public void setAccount(String account) {
this.account = account;
} }
SumStep.java
import java.io.IOException; import org.apache.hadoop.conf.Configuration;
import org.apache.hadoop.fs.Path;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.LongWritable;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Job;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Mapper;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Reducer;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.input.FileInputFormat;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.output.FileOutputFormat; public class SumStep { public static class SumMapper extends Mapper<LongWritable, Text, Text, InfoBean>{
private Text k = new Text();
private InfoBean bean = new InfoBean(); @Override
protected void map(LongWritable key, Text value,Mapper<LongWritable, Text, Text, InfoBean>.Context context)
throws IOException, InterruptedException { String line = value.toString();
String [] fields = line.split("\t");
String account = fields[0];
double income = Double.parseDouble(fields[1]);
double expenses = Double.parseDouble(fields[2]);
k.set(account);
bean.set(account, income, expenses);
context.write(k, bean);
}
}
public static class SumReducer extends Reducer<Text, InfoBean, Text, InfoBean>{
private InfoBean v = new InfoBean();
@Override
protected void reduce(Text key, Iterable<InfoBean> values,Reducer<Text, InfoBean, Text, InfoBean>.Context context)
throws IOException, InterruptedException {
double sum_in = 0;
double sum_out = 0;
for(InfoBean bean : values){
sum_in += bean.getIncome();
sum_out += bean.getExpenses();
}
/*
* 在crxy的流量统计的案例中 是如下的方式写出k3和v3的 在reduce方法中new这个封装好的对象.
* 但是如果数据量比较大的情况下 是可能会造成内存溢出的.
* TrafficWritable v3 = new TrafficWritable(t1, t2, t3, t4);
* context.write(k2, v3);
*
* 所以建议把这个封装的对象写在"脑袋顶上" 如上所示....private InfoBean v = new InfoBean();
* 但是如果你Java基础比较好的话可能会说 在Java中是引用传递...所以后面的v会覆盖前面的v,造成最后只有最有一个v
* 其实这里是不会产生问题的,因为context.write()方法会直接把v3对应的InfoBean对象序列化.
* 虽然之前对象的引用确实覆盖了,但是之前对象的值等都保存了下来.是可以放在这个类的"脑袋顶上"的.
* 让这个类公用这个InfoBean对象.
*/ v.set(key.toString(),sum_in,sum_out);
context.write(key, v);
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
Configuration conf = new Configuration();
Job job = Job.getInstance(conf);
job.setJarByClass(SumStep.class); job.setMapperClass(SumMapper.class);
//以下两行可以在满足一定条件的时候省略掉.
//在满足k2和k3,v2和v3一一对应的时候就可以省略掉. 看SumReducer类所在行的泛型.
job.setMapOutputKeyClass(Text.class);
job.setMapOutputValueClass(InfoBean.class); FileInputFormat.setInputPaths(job, new Path(args[0])); job.setReducerClass(SumReducer.class);
job.setOutputKeyClass(Text.class);
job.setOutputValueClass(InfoBean.class);
FileOutputFormat.setOutputPath(job, new Path(args[1]));
job.waitForCompletion(true);
}
}
项目打成jar包放到Linux中,日志源文件上传到HDFS上.运行结果如下:
hadoop jar /root/itcastmr.jar itcastmr.SumStep /user/root/trade_info.txt /tradeout

但是这个结果并没有排序.还是按照账号的字典排序.
以这个MR的输出当做输入对其根据InfoBean对象进行排序.....
上代码SortStep.java:
import java.io.IOException; import org.apache.hadoop.conf.Configuration;
import org.apache.hadoop.fs.Path;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.LongWritable;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.NullWritable;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Job;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Mapper;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Reducer;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.input.FileInputFormat;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.output.FileOutputFormat; public class SortStep {
//这个Mapper读取的HDFS文件是SumStep Reduce计算输出的文件.
public static class SortMapper extends Mapper<LongWritable, Text, InfoBean, NullWritable>{
private InfoBean k = new InfoBean();
@Override
protected void map(LongWritable key,Text value,Mapper<LongWritable, Text, InfoBean, NullWritable>.Context context)
throws IOException, InterruptedException {
String line = value.toString();
String [] fields = line.split("\t");
String account = fields[0];
double income = Double.parseDouble(fields[1]);
double expenses = Double.parseDouble(fields[2]);
k.set(account, income, expenses);
//现在是要求按照InfoBean对象中的规则排序(InfoBean中有compareTo方法)...所以InfoBean对象当做k2...
context.write(k,NullWritable.get());//不能传null,NullWritable.get() 是获得的this对象.
}
}
public static class SortReducer extends Reducer<InfoBean, NullWritable, Text, InfoBean>{
private Text k = new Text();
@Override
protected void reduce(InfoBean bean, Iterable<NullWritable> values,Reducer<InfoBean, NullWritable, Text, InfoBean>.Context context)
throws IOException, InterruptedException {
String account = bean.getAccount();
k.set(account);
context.write(k, bean);
}
} public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
Configuration conf = new Configuration();
Job job = Job.getInstance(conf);
job.setJarByClass(SortStep.class); job.setMapperClass(SortMapper.class);
//以下两行可以在满足一定条件的时候省略掉.
//在满足k2和k3,v2和v3一一对应的时候就可以省略掉. 看SumReducer类所在行的泛型.
job.setMapOutputKeyClass(InfoBean.class);
job.setMapOutputValueClass(NullWritable.class); FileInputFormat.setInputPaths(job, new Path(args[0])); job.setReducerClass(SortReducer.class);
job.setOutputKeyClass(Text.class);
job.setOutputValueClass(InfoBean.class);
FileOutputFormat.setOutputPath(job, new Path(args[1]));
job.waitForCompletion(true);
}
}
打成jar包,然后运行命令....输入为上面SumStep.java的输出
hadoop jar /root/itcastmr.jar itcastmr.SortStep /tradeout /trade_sort_out
排序之后的结果:
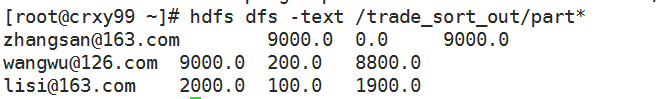
在MapReduce读取输入数据的时候,如果这个文件是以下划线开始的话,那么会不会读取这个文件中的内容...."_SUCCESS"文件就不会读取....
如果想对某个类进行排序,
1.这个类要实现WritableComparable接口,
2.还要重写compareTo方法. 根据自己的业务逻辑自定义排序.
只需要把要排序的类当做k2 就可以了...框架自动排序.
要排序对象的compareTo方法是框架调用的,框架在shuffle这个阶段会调用排序.
shuffle后面会讲,shuffle由很多很多的阶段组成,分区,排序,分组,combiner等等...把这些小的细节都讲完了之后再讲shuffle.
MapReduce对交易日志进行排序的Demo(MR的二次排序)的更多相关文章
- (转)MapReduce二次排序
一.概述 MapReduce框架对处理结果的输出会根据key值进行默认的排序,这个默认排序可以满足一部分需求,但是也是十分有限的.在我们实际的需求当中,往往有要对reduce输出结果进行二次排序的需求 ...
- Hadoop Mapreduce分区、分组、二次排序过程详解[转]
原文地址:Hadoop Mapreduce分区.分组.二次排序过程详解[转]作者: 徐海蛟 教学用途 1.MapReduce中数据流动 (1)最简单的过程: map - reduce (2) ...
- MapReduce自定义二次排序流程
每一条记录开始是进入到map函数进行处理,处理完了之后立马就入自定义分区函数中对其进行分区,当所有输入数据经过map函数和分区函数处理完之后,就调用自定义二次排序函数对其进行排序. MapReduce ...
- Hadoop Mapreduce分区、分组、二次排序
1.MapReduce中数据流动 (1)最简单的过程: map - reduce (2)定制了partitioner以将map的结果送往指定reducer的过程: map - partiti ...
- MapReduce的二次排序
附录之前总结的一个例子: http://www.cnblogs.com/DreamDrive/p/7398455.html 另外两个有价值的博文: http://www.cnblogs.com/xux ...
- 详细讲解MapReduce二次排序过程
我在15年处理大数据的时候还都是使用MapReduce, 随着时间的推移, 计算工具的发展, 内存越来越便宜, 计算方式也有了极大的改变. 到现在再做大数据开发的好多同学都是直接使用spark, hi ...
- Hadoop Mapreduce分区、分组、二次排序过程详解
转载:http://blog.tianya.cn/m/post.jsp?postId=53271442 1.MapReduce中数据流动 (1)最简单的过程: map - reduce (2)定制了 ...
- Hadoop学习之自定义二次排序
一.概述 MapReduce框架对处理结果的输出会根据key值进行默认的排序,这个默认排序可以满足一部分需求,但是也是十分有限的.在我们实际的需求当中,往 往有要对reduce输出结果进行二次排 ...
- hadoop 二次排序的一些思考
先说一下mr的二次排序需求: 假如文件有两列分别为name.score,需求是先按照name排序,name相同按照score排序 数据如下: jx 20 gj 30 jx 10 gj 15 输出结果要 ...
随机推荐
- JavaSE基础知识(5)—面向对象(5.1类和对象概念、创建及内存分配)
一.类和对象的相关概念 1.面向对象和面向过程的理解 面向对象和面向过程都属于解决问题的思考方式.面向过程:以执行者的角度思考问题,侧重于“怎么做”,比较适合解决小型项目面向对象:以指挥者的角度思考问 ...
- ABP框架提示框
abp.message.info('some info message', 'some optional title');abp.message.success('some success messa ...
- Idea创建简单Java Web项目并部署Servlet
1.打开Idea,创建JAVA Web项目 在WEB-INF目录下创建classes和lib文件夹 配置编译输出路径为刚才新建的classes文件夹 配置依赖jar包加载路径 添加tomcat ser ...
- FastFDS基础
1. FastDFS介绍 FastDFS( Fast Distributed file system)是一款轻量级的.高性能的.阿里巴巴开源的分布式文件系统.该系统的作者是余庆 (happyfish1 ...
- AC自动机——1 Trie树(字典树)介绍
AC自动机——1 Trie树(字典树)介绍 2013年10月15日 23:56:45 阅读数:2375 之前,我们介绍了Kmp算法,其实,他就是一种单模式匹配.当要检查一篇文章中是否有某些敏感词,这其 ...
- CentOS_mini下安装docker 之 yum mount
--->linux 终端输出太多前面看不到的解决办法:shift+page up --->mount命令[-参数] [设备名称] [挂载点] mkdir /mnt/CentOS mount ...
- 真·浅谈treap树
treap树是一种平衡树,它有平衡树的性质,满足堆的性质,是二叉搜索树,但是我们需要维护他 为什么满足堆的性质?因为每个节点还有一个随机权值,按照随机权值维持这个堆(树),可以用O(logn)的复杂度 ...
- maven pom.xml文件 仓库搜索服务
POM(Project Object Model),即项目对象模型,是 Maven 工程的基本工作单元,是一个 XML 文件,包含了项目的基本信息,用于描述项目如何构建.声明项目依赖 等等 Maven ...
- web集成高德地图
1.使用高德地图API需到官网添加一个Key,http://lbs.amap.com/dev/key/app 2.页面头引入 <div id="addressMap"> ...
- Java 浮点数相加
刚刚遇到个需求,需要对金额求和,上线的时候才知道这时个,这个字段是个小数. 随手就改了个Double ,然后,跑下,没啥问题,直接上线了 然后,就fuck 了 加出一大堆的小数,大概是这样的 pack ...
