UVA1589 Xiangqi
Xiangqi is one of the most popular two-player board games in China. The game represents a battle between two armies with the goal of capturing the enemy's ``general" piece. In this problem, you are given a situation of later stage in the game. Besides, the red side has already ``delivered a check". Your work is to check whether the situation is ``checkmate".
Now we introduce some basic rules of Xiangqi. Xiangqi is played on a 10 x 9 board and the pieces are placed on the intersections (points). The top left point is (1,1) and the bottom right point is (10,9). There are two groups of pieces marked by black or red Chinese characters, belonging to the two players separately. During the game, each player in turn moves one piece from the point it occupies to another point. No two pieces can occupy the same point at the same time. A piece can be moved onto a point occupied by an enemy piece, in which case the enemy piece is``captured" and removed from the board. When the general is in danger of being captured by the enemy player on the enemy player's next move, the enemy player is said to have ``delivered a check". If the general's player can make no move to prevent the general's capture by next enemy move, the situation is called ``checkmate".
We only use 4 kinds of pieces introducing as follows:

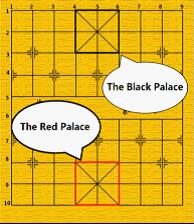
- General: the generals can move and capture one point either vertically or horizontally and cannot leave the `` palace" unless the situation called `` flying general" (see the figure above). ``Flying general" means that one general can ``fly" across the board to capture the enemy general if they stand on the same line without intervening pieces.

- Chariot: the chariots can move and capture vertically and horizontally by any distance, but may not jump over intervening pieces

- Cannon: the cannons move like the chariots, horizontally and vertically, but capture by jumping exactly one piece (whether it is friendly or enemy) over to its target.

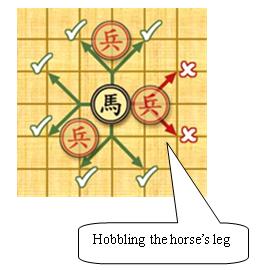
- Horse: the horses have 8 kinds of jumps to move and capture shown in the left figure. However, if there is any pieces lying on a point away from the horse horizontally or vertically it cannot move or capture in that direction (see the figure below), which is called `` hobbling the horse's leg".
Now you are given a situation only containing a black general, a red general and several red chariots, cannons and horses, and the red side has delivered a check. Now it turns to black side's move. Your job is to determine that whether this situation is ``checkmate".
Input
The input contains no more than 40 test cases. For each test case, the first line contains three integers representing the number of red pieces N ( 2 N
N 7) and the position of the black general. The following N lines contain details of N red pieces. For each line, there are a char and two integers representing the type and position of the piece (type char `G' for general, `R' for chariot, `H' for horse and `C' for cannon). We guarantee that the situation is legal and the red side has delivered the check.
7) and the position of the black general. The following N lines contain details of N red pieces. For each line, there are a char and two integers representing the type and position of the piece (type char `G' for general, `R' for chariot, `H' for horse and `C' for cannon). We guarantee that the situation is legal and the red side has delivered the check.
There is a blank line between two test cases. The input ends by `0 0 0'.
Output
For each test case, if the situation is checkmate, output a single word ` YES', otherwise output the word ` NO'.
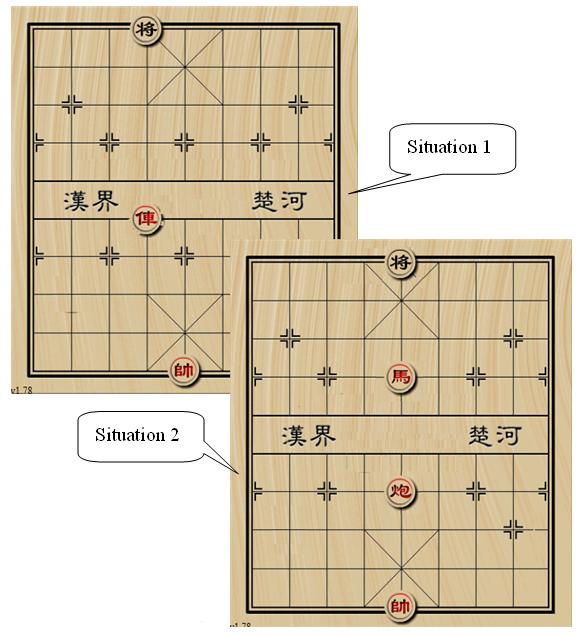
Hint: In the first situation, the black general is checked by chariot and ``flying general''. In the second situation, the black general can move to (1, 4) or (1, 6) to stop check. See the figure below.
Sample Input
2 1 4
G 10 5
R 6 4 3 1 5
H 4 5
G 10 5
C 7 5 0 0 0
Sample Output
YES
NO
看到这么个问题确实有点头疼,但是仔细想过之后不难用模拟来解决问题,附上代码(略长);
#include<stdio.h>
#include<string.h>
struct L
{
int a,b;
};
struct L General;
struct L Chariot[];
struct L Horse[];
struct L Cannon[];
int Qipan[][];
int n,x,y;
int tempx,tempy;
char type[];
int i1,i2,i3;
int mainflag;
int checkGenerals(int,int);
int checkChariot(int,int,int,int);
int checkHorse(int,int,int,int);
int checkCannon(int,int,int,int);
int checkPoint(int,int);
int main()
{
while(scanf("%d%d%d",&n,&x,&y)==&&n)
//Pay attention to the point (x,y),which is the black general located.
{
memset(Qipan,,sizeof(Qipan));
//Create a Qipan and define all of it are 0.
Qipan[x][y]=;
// When put some point on the broad,transfer it into 1.
//input the date,and store it into struct General,Chariot,Horse,Cannon.
i1=i2=i3=;
for(int i=;i<n;i++)
{
scanf("%s%d%d",type,&tempx,&tempy);
Qipan[tempx][tempy]=;
if(type[]=='G')
{
General.a=tempx;
General.b=tempy;
}
else if(type[]=='R')
{
Chariot[i1].a=tempx;
Chariot[i1++].b=tempy;
}
else if(type[]=='H')
{
Horse[i2].a=tempx;
Horse[i2++].b=tempy;
}
else if(type[]=='C')
{
Cannon[i3].a=tempx;
Cannon[i3++].b=tempy;
}
}
// Now it's high time to deal with the problem,with all of the dates are stored in order.
// The first we must check whether the two generals face to face directly.
if(checkGenerals(x,y))
{
printf("NO\n");
continue;
}
mainflag=;
if(x+<)
{
Qipan[x][y]=;
Qipan[x+][y]++;
if(checkPoint(x+,y))
mainflag=;
Qipan[x][y]=;
Qipan[x+][y]--;
}
if(mainflag)
{
printf("NO\n");
continue;
}
if(x->)
{
Qipan[x][y]=;
Qipan[x-][y]++;
if(checkPoint(x-,y))
mainflag=;
Qipan[x][y]=;
Qipan[x-][y]--;
}
if(mainflag)
{
printf("NO\n");
continue;
}
if(y+<)
{
Qipan[x][y]=;
Qipan[x][y+]++;
if(checkPoint(x,y+))
mainflag=;
Qipan[x][y]=;
Qipan[x][y+]--;
}
if(mainflag)
{
printf("NO\n");
continue;
}
if(y->)
{
Qipan[x][y]=;
Qipan[x][y-]++;
if(checkPoint(x,y-))
mainflag=;
Qipan[x][y]=;
Qipan[x][y-]++;
}
if(mainflag)
{
printf("NO\n");
continue;
}
printf("YES\n");
}
}
int checkGenerals(int x,int y)
{
if(General.b==y)
{
int Flag=;
for(int i=x+;i<General.a;i++)
if(Qipan[i][y])
Flag++;
if(Flag==)
return ;
}
return ;
}
int checkChariot(int x1,int y1,int x2,int y2)
{
int Flag;
int xj1,yj1,xj2,yj2;
xj1=x1<x2?x1:x2;
xj2=x1>x2?x1:x2;
yj1=y1<y2?y1:y2;
yj2=y1>y2?y1:y2;
if(x1==x2&&y1==y2)
return ;
if(x1==x2)
{
Flag=;
for(int j=yj1+;j<yj2;j++)
if(Qipan[x1][j])
Flag=;
if(Flag==) return ;
}
if(y1==y2)
{
Flag=;
for(int i=xj1+;i<xj2;i++)
if(Qipan[i][y1])
Flag=;
if(Flag==) return ;
}
return ;
}
int checkHorse(int x1,int y1,int x2,int y2)
{
if(x1+==x2&&y1+==y2)
if(Qipan[x1][y1+]==)
return ;
if(x1+==x2&&y1-==y2)
if(Qipan[x1][y1-]==)
return ;
if(x1-==x2&&y1+==y2)
if(Qipan[x1][y1+]==)
return ;
if(x1-==x2&&y1-==y2)
if(Qipan[x1][y1-]==)
return ;
if(x1+==x2&&y1+==y2)
if(Qipan[x1+][y1]==)
return ;
if(x1+==x2&&y1-==y2)
if(Qipan[x1+][y1]==)
return ;
if(x1-==x2&&y1+==y2)
if(Qipan[x1-][y1]==)
return ;
if(x1-==x2&&y1-==y2)
if(Qipan[x1-][y1]==)
return ;
return ;
}
int checkCannon(int x1,int y1,int x2,int y2)
{
int Flag=;
int xj1,yj1,xj2,yj2;
xj1=x1<x2?x1:x2;
xj2=x1>x2?x1:x2;
yj1=y1<y2?y1:y2;
yj2=y1>y2?y1:y2;
if(x1==x2&&y1==y2) return ;
if(x1==x2)
{
for(int j=yj1+;j<yj2;j++)
if(Qipan[x1][j]) Flag++;
if(Flag==) return ;
}
if(y1==y2)
{
for(int i=xj1+;i<xj2;i++)
if(Qipan[i][y1]) Flag++;
if(Flag==) return ;
}
return ;
}
int checkPoint(int x,int y)
{
if(checkGenerals(x,y))
return ;
for(int i=;i<i1;i++)
if(checkChariot(Chariot[i].a,Chariot[i].b,x,y))
return ;
for(int i=;i<i2;i++)
if(checkHorse(Horse[i].a,Horse[i].b,x,y))
return ;
for(int i=;i<i3;i++)
{
if(checkCannon(Cannon[i].a,Cannon[i].b,x,y))
return ;
}
return ;
}
UVA1589 Xiangqi的更多相关文章
- [刷题]算法竞赛入门经典(第2版) 4-1/UVa1589 - Xiangqi
书上具体所有题目:http://pan.baidu.com/s/1hssH0KO 代码:(Accepted,0 ms) //UVa1589 #include<iostream> #incl ...
- UVA1589——xiangqi
开始碰到这个题时觉得太麻烦了直接跳过没做,现在放假了再次看这个题发现没有想象中那么麻烦,主要是题目理解要透彻,基本思路就是用结构体数组存下红方棋子,让黑将军每次移动一下,看移动后是否有一个红方棋子可以 ...
- 【习题4-1 Uva1589】Xiangqi
[链接] 我是链接,点我呀:) [题意] 在这里输入题意 [题解] 车是可以被吃掉的... 注意这个情况. 其他的模拟即可. [代码] #include <bits/stdc++.h> u ...
- HDU 4121 Xiangqi 我老了?
Xiangqi Time Limit: 2000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 32768/32768 K (Java/Others)Total Sub ...
- HDU 4121 Xiangqi 模拟题
Xiangqi Time Limit: 20 Sec Memory Limit: 256 MB 题目连接 http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=4121 ...
- Uva - 1589 - Xiangqi
Xiangqi is one of the most popular two-player board games in China. The game represents a battle bet ...
- [算法竞赛入门经典] 象棋 ACM/ICPC Fuzhou 2011, UVa1589 较详细注释
Description: Xiangqi is one of the most popular two-player board games in China. The game represents ...
- Xiangqi(简单模拟)
4746: Xiangqi 时间限制(普通/Java):1000MS/3000MS 内存限制:65536KByte 总提交: 15 测试通过:2 描述 Xiangqi i ...
- TZOJ 4746 Xiangqi(模拟棋盘数组)
描述 Xiangqi is one of the most popular two-player board games in China. The game represents a battle ...
随机推荐
- Swift学习之常用UI的使用
Swift学习之常用UI的使用 最近笔者在开始学习苹果最新的编程语言,因为笔者认为,苹果既然出了这门语言就绝对不会放弃,除非苹果倒闭了(当然这里知识一个玩笑). 所以在不久的将来,swift绝对是iO ...
- 关于Linux平台malloc的写时拷贝(延迟分配)【转】
Linux内核定义了“零页面”(内容全为0的一个物理页,且物理地址固定),应用层的内存分配请求,如栈扩展.堆分配.静态分配等,分配线性地址后,就将页表项条目指向“零页面”(指定初始值的情况除外),这样 ...
- Scala学习笔记--文件IO
补充: http://blog.csdn.net/lyrebing/article/details/20369445 http://developer.51cto.com/art/200907/134 ...
- iOS应用崩溃日志分析-备用
作为一名应用开发者,你是否有过如下经历? 为确保你的应用正确无误,在将其提交到应用商店之前,你必定进行了大量的测试工作.它在你的设备上也运行得很好,但是,上了应用商店后,还是有用户抱怨会闪退 ! ...
- (转)Oracle Data Guard配置
data guard配置的条件1.在主库和从库的所有机器上必须安装同一个版本的Oracle企业版.2.主库必须运行在归档模式下.3.主库和从库的操作系统必须一样(允许版本不同),从库可以使用与主库不同 ...
- cf E. Valera and Queries
http://codeforces.com/contest/369/problem/E 题意:输入n,m; n 代表有多少个线段,m代表有多少个询问点集.每一个询问输出这些点的集合所占的线段的个数. ...
- 11G在线重建索引
SQL> select count(*) from test_idx; COUNT(*) ---------- 19087751 SQL> select segment_name,segm ...
- BHO多线程中实现右键菜单
在BHO中实现右键菜单网上相关文章很多,可以通过实现IDocHostUIHandler接口的ShowContextMenu.截获HTMLDocumentEvents2的OnContextMenu消息等 ...
- 使用layer显示弹出框笔记
$.layer({ area : ['200px','auto'], //控制层宽高.当设置为auto时,意味着采用自适应, 当然,对于宽度,并不推荐这样做.例如:area : ['310px ...
- Django之验证码 + session 认证
验证码 + session认证 目录结构 . └── project ├── app01 │ ├── admin.py │ ├── apps.py │ ├── __init__.py │ ...
