实验1:c++简单程序设计(1)
//文中有格式错误请无视
//这个编辑器一言难尽
实验目的
1. 掌握c++中类c部分的编程知识: 数据类型,常量,变量,运算符,表达式,分支结构,循环结构
2. 掌握C++中数据输入和输出的基本方法
3. 熟练使用c++程序开发环境,掌握c++程序编写、编译、运行、调试的方法
实验准备
1. 简单的c++程序结构 学习/复习教材「2.1.3 C++程序实例」
2. c++中数据输入输出的基本方法 学习/复习教材2.3节,学习C++中I/O流、预定义的插入符<<和提取符>>的基本用法。
3. if语句、switch语句、while语句、do…while语句的用法 学习/复习教材2.4节,通过示例理解背后简单算法及c++分支语句、循环语句的用法
4. 自定义数据类型: typedef,枚举类型用法 学习/复习教材2.5节,结合示例理解枚举类型和int型在类型转换时的注意事项
实验内容
Part2: 编程练习
教材第2章习题2-28 简单的菜单程序
教材第2章习题2-29 穷举法求质数
教材第2章习题2-32 猜数
教材第2章习题2-34排列组合
实验结论
2-28简单的菜单程序(if-else
Code:
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
cout<<"Menu:A(dd) D(elete) S(ort) Q(uit)";
cout<<"Select one:";
char k;
while(cin>>k)
{
if(k=='A')
cout<<"Data has added.\n"<<"Menu:A(dd) D(elete) S(ort) Q(uit)"<<"Select one:";
else if(k=='D')
cout<<"Data has deleted.\n"<<"Menu:A(dd) D(elete) S(ort) Q(uit)"<<"Select one:";
else if(k=='S')
cout<<"Data has sorted.\n"<<"Menu:A(dd) D(elete) S(ort) Q(uit)"<<"Select one:";
else if(k=='Q')
break;
else
cout<<"No such choice,please select again.\n"<<"Menu:A(dd) D(elete) S(ort) Q(uit)"<<"Select one:";
}
return ;
}
Screenshot:

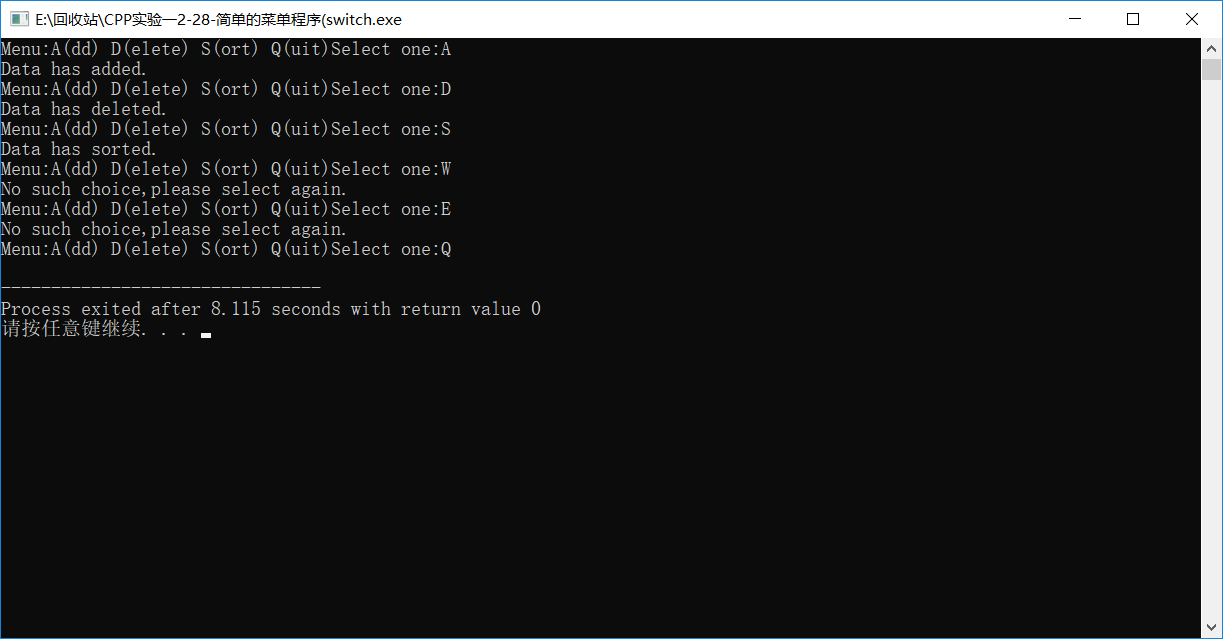
(switch
Code:
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
cout<<"Menu:A(dd) D(elete) S(ort) Q(uit)";
cout<<"Select one:";
char k;
while(cin>>k&&k!='Q')
{
switch(k)
{
case 'A':
cout<<"Data has added.\n"<<"Menu:A(dd) D(elete) S(ort) Q(uit)"<<"Select one:";
continue;
case 'D':
cout<<"Data has deleted.\n"<<"Menu:A(dd) D(elete) S(ort) Q(uit)"<<"Select one:";
continue;
case 'S':
cout<<"Data has sorted.\n"<<"Menu:A(dd) D(elete) S(ort) Q(uit)"<<"Select one:";
continue;
default:cout<<"No such choice,please select again.\n"<<"Menu:A(dd) D(elete) S(ort) Q(uit)"<<"Select one:";
}
}
return ;
}
Screenshop:
2-29 穷举法求质数(while
Code:
#include<iostream>
#include<cmath>
#include<iomanip>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
cout<<"1~100间的质数为:"<<endl;
int x=;
int a,b,c=;
while(x<=)
{
a=sqrt(x);
if(x!=)
{
b=;
while(x%b!=&&b<=a)
b++;
if(b>a)
{
c++;
cout<<setw()<<x;
if(c%==)
cout<<"\n";
}
}
x++;
}
return ;
}
Screenshop:

(for
Code:
#include<iostream>
#include<cmath>
#include<iomanip>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
cout<<"1~100间的质数为:"<<endl;
int x;
int a,b,c=;
for(x=;x<=;x++)
{
a=sqrt(x);
if(x==)
continue;
else
{
for(b=;b<=a;b++)
if(x%b==)
break;
if(b>a)
{
c++;
cout<<setw()<<x;
if(c%==)
cout<<"\n";
}
}
}
return ;
}
Screenshop:

(do-while
Code:
#include<iostream>
#include<cmath>
#include<iomanip>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
cout<<"1~100间的质数为:"<<endl;
int x=;
int a,b,c=;
do
{
x++;
a=sqrt(x);
if(x!=)
{
b=;
do
{
b++;
}while(x%b!=&&b<=a);
if(b>a)
{
c++;
cout<<setw()<<x;
if(c%==)
cout<<"\n";
}
}
}while(x<);
return ;
}
Screenshop:

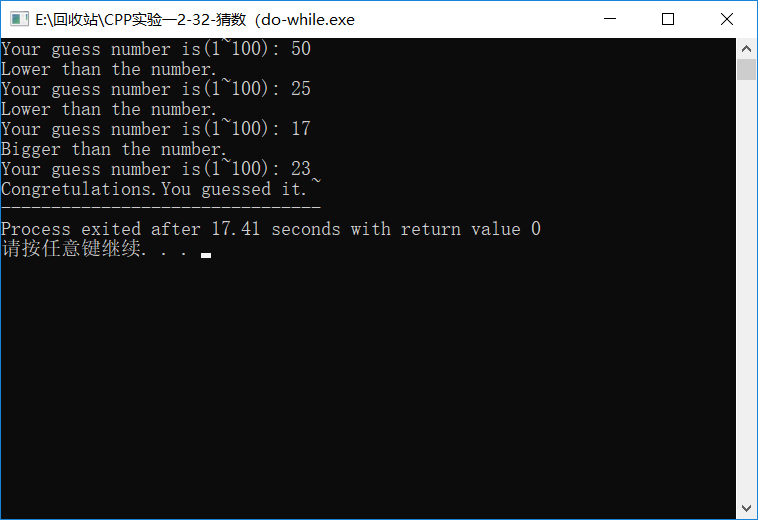
2-32 猜数(while
Code:
#include<iostream>
#include<ctime>
#include<cstdlib>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int x;
int a;
srand(time(NULL));
x=+rand()%(-+);
cout<<"Your guess number is(1~100): ";
cin>>a;
while(a!=x)
{
if(a<x)
{
cout<<"Bigger than the number."<<endl;
cout<<"Your guess number is(1~100): ";
cin>>a;
}
else
{
cout<<"Lower than the number. "<<endl;
cout<<"Your guess number is(1~100): ";
cin>>a;
}
}
cout<<"Congretulations.You guessed it.~";
return ;
}
Screenshop:
(do-while
Code:
#include<iostream>
#include<ctime>
#include<cstdlib>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int x;
int a;
srand(time(NULL));
x=+rand()%(-+);
cout<<"Your guess number is(1~100): ";
do
{
cin>>a;
if(a<x)
{
cout<<"Bigger than the number."<<endl;
cout<<"Your guess number is(1~100): ";
}
else if(a>x)
{
cout<<"Lower than the number. "<<endl;
cout<<"Your guess number is(1~100): ";
}
}while(a!=x);
cout<<"Congretulations.You guessed it.~";
return ;
}
Screenshop:
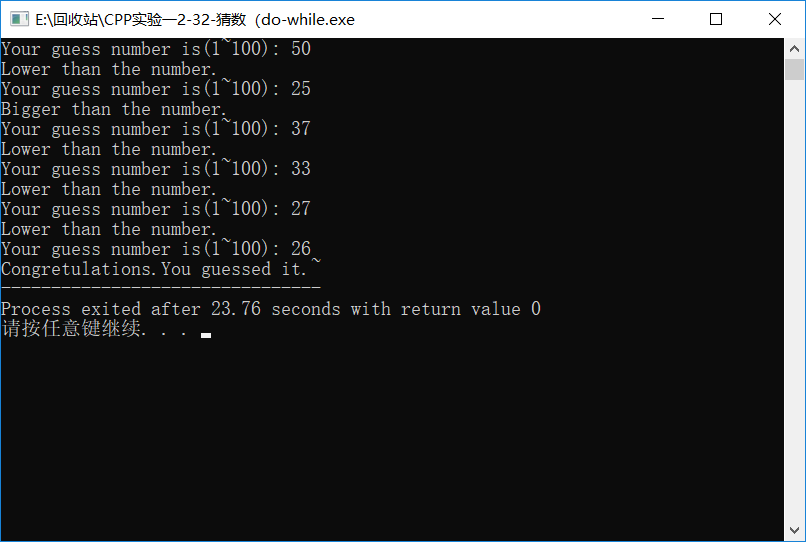
//暴力循环
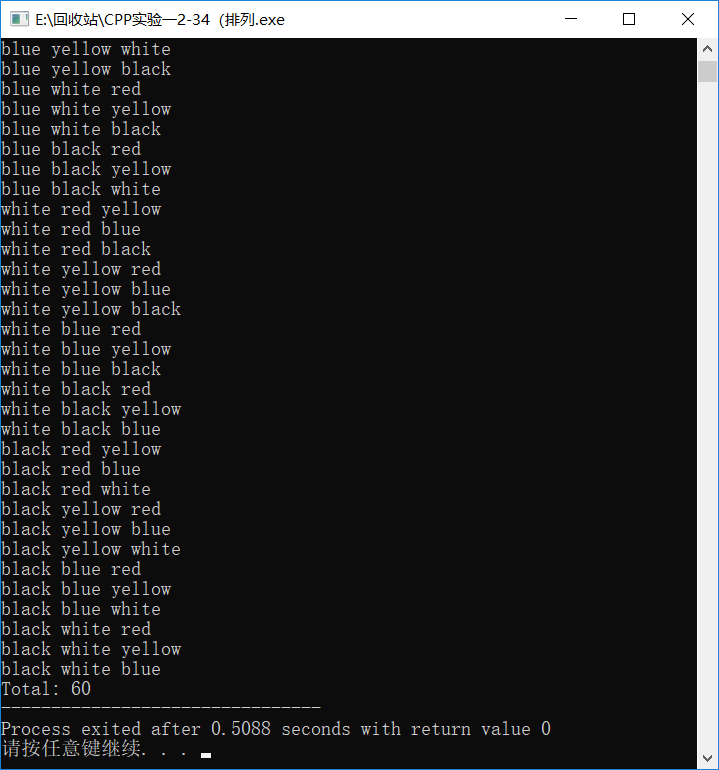
2-34排列组合(排列
Code:
#include<iostream>
#include<iomanip>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int x[],k=,i;
for(x[]=;x[]<=;x[]++)
{
for(x[]=;x[]<=;x[]++)
{
if(x[]==x[])
continue;
else
{
for(x[]=;x[]<=;x[]++)
{
if(x[]==x[]||x[]==x[])
continue;
else
{
k++;
for(i=;i<=;i++)
{
if(i!=)
{
switch(x[i])
{
case :
cout<<"red ";
continue;
case :
cout<<"yellow ";
continue;
case :
cout<<"blue ";
continue;
case :
cout<<"white ";
continue;
case :
cout<<"black ";
}
}
else
{
switch(x[i])
{
case :
cout<<"red\n";
continue;
case :
cout<<"yellow\n";
continue;
case :
cout<<"blue\n";
continue;
case :
cout<<"white\n";
continue;
case :
cout<<"black\n";
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
cout<<"Total: "<<k;
return ;
}
Screenshop:
(组合
Code:
#include<iostream>
#include<iomanip>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int x[],k=,i;
for(x[]=;x[]<=;x[]++)
for(x[]=x[]+;x[]<=;x[]++)
for(x[]=x[]+;x[]<=;x[]++)
{
k++;
for(i=;i<=;i++)
{
if(i!=)
{
switch(x[i])
{
case :
cout<<"red ";
continue;
case :
cout<<"yellow ";
continue;
case :
cout<<"blue ";
continue;
case :
cout<<"white ";
continue;
case :
cout<<"black ";
}
}
else
{
switch(x[i])
{
case :
cout<<"red\n";
continue;
case :
cout<<"yellow\n";
continue;
case :
cout<<"blue\n";
continue;
case :
cout<<"white\n";
continue;
case :
cout<<"black\n";
}
}
}
}
cout<<"Total: "<<k;
return ;
}
Screenshop:
实验总结
这次试验主要是类C的部分,CPP的特性我还没有完全体会到(从I/O流已经可以看出些特点的程度)。
在进行多次判断时还是用switch更方便。
多数时候for循环较为好用。
写程序时尽量避免嵌套过多层循环,严重拖慢编译和运行速度。
srand(time(NULL));
x=1+rand()%(100-1+1);
以此来取一定范围内的随机数。
枚举数据类型不同于整型或字符型。
实验1:c++简单程序设计(1)的更多相关文章
- 实验一 c++简单程序设计
一.实验内容 1.ex 2_28 (1) 用if...else判断 #include<iostream> using namespace std; int main() { char i; ...
- 实验二 Java面向对象程序设计
实验二 Java面向对象程序设计 实验内容 1. 初步掌握单元测试和TDD 2. 理解并掌握面向对象三要素:封装.继承.多态 3. 初步掌握UML建模 4. 熟悉S.O.L.I.D原则 5. 了解设计 ...
- 160809209_李梦鑫_C语言程序设计实验3 循环结构程序设计
<C语言程序设计>实验报告 学 号 160809209 姓 名 李梦鑫 专业.班 计科16-2班 学 期 2016-2017 第1学期 指导教师 黄俊莲 吉吉老师 实验地点 C05 ...
- 20145206《Java程序设计》实验二Java面向对象程序设计实验报告
20145206<Java程序设计>实验二Java面向对象程序设计实验报告 实验内容 初步掌握单元测试和TDD 理解并掌握面向对象三要素:封装.继承.多态 初步掌握UML建模 熟悉S.O. ...
- 20145208 实验三 Java面向对象程序设计
20145208 实验三 Java面向对象程序设计 实验内容 初步掌握单元测试和TDD 理解并掌握面向对象三要素:封装.继承.多态 初步掌握UML建模 熟悉S.O.L.I.D原则 了解设计模式 实验步 ...
- 20162330 实验四 《Android程序设计》 实验报告
2016-2017-2 实验报告目录: 1 2 3 4 5 20162330 实验四 <Android程序设计> 实验报告 课程名称:<程序设计与数据结构> 学生班级:1623 ...
- 20162302 实验四《Android程序设计》实验报告
实 验 报 告 课程:程序设计与数据结构 姓名:杨京典 班级:1623 学号:20162302 实验名称:Android程序设计 实验器材:装有Android Studio的联想拯救者80RQ 实验目 ...
- java实验四《Android程序设计》实验报告
一.实验报告封面 课程:Java程序设计 班级:1653班 姓名:张士洋 学号:20165308 指导教师:娄嘉鹏 实验日期:2018年5月14日 实验时间:13:45 - 15:25 实验序号:08 ...
- 2017-2018-2 20165312 实验四《Android程序设计》实验报告
2017-2018-2 20165312 实验四<Android程序设计>实验报告 一.安装Android Studio并进行Hello world测试和调试程序 安装Android St ...
随机推荐
- [UE4]Selector和Sequence的区别
Selector和Sequence子节点都是返回true才会执行下一个子节点. Sequence是从左到右依次执行,左边节点如果返回false,则不会执行右边的节点 Selector会同步执行所有子节 ...
- javascript控制滚动条的位置,获取控件的位置
一.如下是定位鼠标在视窗中的位置,先定位视窗和页面直接的距离. function getMousePoint() { var point = {x:0,y:0}; // 如果浏览器支持 pageYOf ...
- Storm存储结果至Redis
原有的事务支持使用MemcachedState来进行,现在需要将其迁移至Redis,并且需要记录所有key值列表,因为在redis中虽然可以使用keys *操作,但不是被推荐的方式,所以把所有结果 ...
- keras中调用tensorboard:from keras.callbacks import TensorBoard
from keras.models import Sequential from keras.layers import Dense from keras.wrappers.scikit_learn ...
- web.py模版系统
介绍: 调用的web.py模版语言Templetor旨在将python的强大功能带入模版.它不是为模板创建新语法,而是重用python语法. Templetor故意限制模版中的变量访问.用户可以访问传 ...
- Spring AOP的总结
- jenkins 构建一个maven项目
1.首先在 全局工具配置 里配置maven的路径信息 这里因为之前已经下载了maven并放在了E盘,因此只需要在 MAVEN_HOME 添加maven文件夹的路径 如若本地还没maven,勾选 “自动 ...
- OpenACC 梯度下降法求解线性方程的优化
▶ 书上第二章,用一系列步骤优化梯度下降法解线性方程组.才发现 PGI community 编译器不支持 Windows 下的 C++ 编译(有 pgCC 命令但是不支持 .cpp 文件,要专业版才支 ...
- MySQL中使用BIT属性
如果是组合类型,用bit比较好,有那个类型,就将那以为设为1即可.不然还有将所有类型的组合求出来用map来存对应数字. 用bit,即省空间又方便. 注意用bit不能直接在记录里面直接填数据,要通过sq ...
- cmd查看电脑是32位还是64位
代码如下 @echo off if "%PROCESSOR_ARCHITECTURE%" == "AMD64" ( echo OS is 64bit) EL ...
