codeforces 447E or 446C 线段树 + fib性质或二次剩余性质
CF446C题意:
给你一个数列\(a_i\),有两种操作:区间求和;\(\sum_{i=l}^{r}(a[i]+=fib[i-l+1])\)。\(fib\)是斐波那契数列。
思路
(一)
codeforces 447E or 446C
\(fib[n] = \frac{\sqrt5}{5}\times [(\frac{1+\sqrt5}{2})^n-(\frac{1-\sqrt5}{2})^n]\)
有关取模、同余、逆元的一些东西:
\(p = 1e9 + 9\)
\(383008016^2 ≡ 5 (mod\;p)\)
\(383008016 ≡ \sqrt5 (mod\;p)\)
\(\frac{1}{\sqrt5}≡276601605(mod\;p)\)
\(383008016的逆元 = 276601605\)
\((1+\sqrt5)/2≡691504013(mod\;p)\)
\(383008017\times 2的逆元 = 691504013\)
\((1-\sqrt5)/2≡308495997(mod\;p)\)
\((p-383008016+1)\times 2的逆元 = 308495997\)
\(fib[n] = 276601605\times [(691504013)^n-(308495997)^n] (mod\;\;p)\)
等比数列求和:\(sum = \frac{a}{a-1} \times (a^n - 1) (mod\;\;p) = a^2(a^n-1)(mod\;\;p)=a^{n+2}-a^2(mod\;\;p)\)
当\(p=1e9+9, a = 691504013或308495997时成立\)。
所以本题我们只需要用线段树lazy标记维护两个等比数列第一项为一次项的系数即可。代码如下。
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
#define lson rt<<1
#define rson rt<<1|1
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL;
const int MXN = 5e5 + 6;
const int INF = 0x3f3f3f3f;
const LL mod = 1000000009;
const LL p1 = 691504013;
const LL p2 = 308495997;
const LL p3 = 276601605;
int n, m;
LL ar[MXN], pre[MXN], mul1[MXN], mul2[MXN];
LL sum[MXN<<2], lazy1[MXN<<2], lazy2[MXN<<2];
LL ksm(LL a, LL b) {
LL res = 1;
for(;b;b>>=1,a=a*a%mod) {
if(b&1) res = res * a %mod;
}
return res;
}
void check(LL &a) {
if(a >= mod) a %= mod;
}
void push_up(int rt) {
sum[rt] = sum[lson] + sum[rson]; check(sum[rt]);
}
void push_down(int l,int r,int rt) {
if(lazy1[rt] == 0 && lazy2[rt] == 0) return;
LL a = lazy1[rt], b = lazy2[rt];
int mid = (l + r) >> 1;
int len1 = mid-l+1, len2 = r - mid;
lazy1[lson] += a; lazy2[lson] += b;
sum[lson] = sum[lson] + a*((mul1[len1+2]-mul1[2])%mod+mod); check(sum[lson]);
sum[lson] = (sum[lson] - b*((mul2[len1+2]-mul2[2])%mod+mod))%mod + mod; check(sum[lson]);
lazy1[rson] += a*mul1[len1]%mod; lazy2[rson] += b*mul2[len1]%mod;
sum[rson] = sum[rson] + a*mul1[len1]%mod*((mul1[len2+2]-mul1[2])%mod+mod); check(sum[rson]);
sum[rson] = (sum[rson] - b*mul2[len1]%mod*((mul2[len2+2]-mul2[2])%mod+mod))%mod + mod; check(sum[rson]);
lazy1[rt] = lazy2[rt] = 0;
check(lazy1[lson]);check(lazy1[rson]);check(lazy2[lson]);check(lazy2[rson]);
}
void update(int L,int R,int l,int r,int rt,LL x,LL y) {
if(L <= l && r <= R) {
lazy1[rt] += x; lazy2[rt] += y;
check(lazy1[rt]); check(lazy2[rt]);
sum[rt] = sum[rt] + x*((mul1[r-l+3]-mul1[2])%mod+mod); check(sum[rt]);
sum[rt] = (sum[rt] - y*((mul2[r-l+3]-mul2[2])%mod+mod))%mod + mod; check(sum[rt]);
return;
}
push_down(l, r, rt);
int mid = (l + r) >> 1;
if(L > mid) update(L,R,mid+1,r,rson,x,y);
else if(R <= mid) update(L,R,l,mid,lson,x,y);
else {
update(L,mid,l,mid,lson,x,y);
update(mid+1,R,mid+1,r,rson,mul1[mid-L+1]*x%mod,mul2[mid-L+1]*y%mod);
}
push_up(rt);
}
LL query(int L,int R,int l,int r,int rt) {
if(L <= l && r <= R) {
return sum[rt];
}
push_down(l,r,rt);
int mid = (l+r) >> 1;
if(L > mid) return query(L,R,mid+1,r,rson);
else if(R <= mid) return query(L,R,l,mid,lson);
else {
LL ans = query(L,mid,l,mid,lson);
ans += query(mid+1,R,mid+1,r,rson);
check(ans);
return ans;
}
}
int main() {
//printf("%d\n", ksm(691504013-1,mod-2));
//printf("%d\n", ksm(308495997-1,mod-2));
//F(n) = √5/5[((1+√5)/2)^n-((1-√5)/2)^n]
//383008016^2 ≡ 5 (mod 1e9 + 9)
//383008016 ≡ sqrt(5) (mod 1e9 + 9)
//printf("%lld\n", ksm(383008016,mod-2));//1/sqrt(5)≡276601605(mod)
//printf("%lld\n", 383008017*ksm(2,mod-2)%mod);//(1+sqrt(5))/2≡691504013(mod)
//printf("%lld\n", (mod-383008016+1)*ksm(2,mod-2)%mod);//(1-sqrt(5))/2≡308495997(mod)
scanf("%d%d", &n, &m);
mul1[0] = mul2[0] = 1;
for(int i = 1; i < 301000; ++i) {
mul1[i] = mul1[i-1] * p1;
mul2[i] = mul2[i-1] * p2;
check(mul1[i]); check(mul2[i]);
}
for(int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) scanf("%lld", &ar[i]), pre[i] = (pre[i-1] + ar[i])%mod;
while(m --) {
int opt, l, r;
scanf("%d%d%d", &opt, &l, &r);
if(opt == 1) {
update(l, r, 1, n, 1, 1, 1);
}else {
printf("%lld\n", ((p3*query(l,r,1,n,1)%mod+pre[r]-pre[l-1])%mod+mod)%mod);
}
}
return 0;
}
(二)
斐波纳契数列的一些性质:
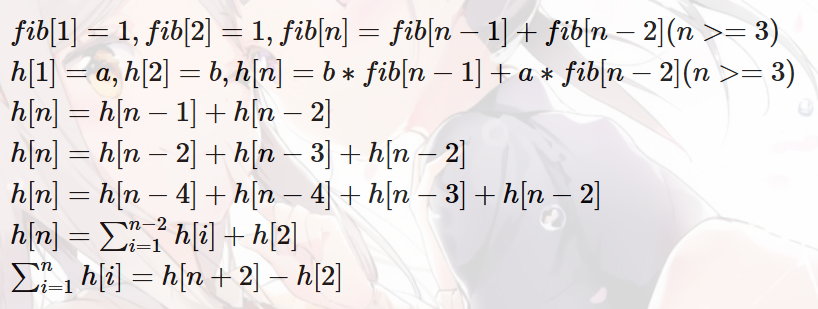
性质1:对于一个满足斐波那契性质的数列,如果我们已知它的前两项,我们可以O(1)的得到它的任意一项和任意前缀和!
性质2:两个满足斐波那契性质的数列相加后,依然是斐波那契数列。前两项的值分别为两个的和。
所以本题我们用线段树的\(lazy\)标记维护给这个区间各项加上的\(fib\)数列的前两项的值。通过这个\(lazy\)标记我们可以\(O(1)\)更新区间和,因为斐波纳契数列满足可加性,所以我们\(lazy\)标记也可以很轻松的\(push\_down\)操作。代码如下。
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
#define lson rt<<1
#define rson rt<<1|1
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL;
const int MXN = 5e5 + 6;
const int INF = 0x3f3f3f3f;
const LL mod = 1000000009;
const LL p1 = 691504013;
const LL p2 = 308495997;
const LL p3 = 276601605;
int n, m;
LL ar[MXN], fib[MXN];
LL sum[MXN<<2], lazy1[MXN<<2], lazy2[MXN<<2];
LL ksm(LL a, LL b) {
LL res = 1;
for(;b;b>>=1,a=a*a%mod) {
if(b&1) res = res * a %mod;
}
return res;
}
LL hn(int n,LL a,LL b) {
if(n == 1) return (a%mod+mod)%mod;
if(n == 2) return (b%mod+mod)%mod;
return ((a*fib[n-2] + b*fib[n-1])%mod+mod)%mod;
}
void check(LL &a) {
if(a >= mod) a %= mod;
}
void push_up(int rt) {
sum[rt] = sum[lson] + sum[rson]; check(sum[rt]);
}
void build(int l,int r,int rt) {
if(l == r) {
sum[rt] = ar[l];
return;
}
int mid = (l + r) >> 1;
build(l, mid, lson); build(mid+1, r, rson);
push_up(rt);
}
void push_down(int l,int r,int rt) {
if(lazy1[rt] == 0 && lazy2[rt] == 0) return;
LL a = lazy1[rt], b = lazy2[rt];
int mid = (l + r) >> 1;
int len1 = mid-l+1, len2 = r - mid;
lazy1[lson] += a; lazy2[lson] += b;
sum[lson] = (sum[lson] + hn(len1+2,a,b) - b)%mod+mod;
lazy1[rson] += hn(len1+1,a,b); lazy2[rson] += hn(len1+2,a,b);
sum[rson] = (sum[rson] + hn(len2+2,hn(len1+1,a,b),hn(len1+2,a,b))-hn(len1+2,a,b))%mod+mod;
check(sum[lson]); check(sum[rson]);
check(lazy1[lson]);check(lazy1[rson]);check(lazy2[lson]);check(lazy2[rson]);
lazy1[rt] = lazy2[rt] = 0;
}
void update(int L,int R,int l,int r,int rt,LL x, LL y) {
if(L <= l && r <= R) {
lazy1[rt] += x; lazy2[rt] += y;
check(lazy1[rt]); check(lazy2[rt]);
sum[rt] = (sum[rt] + hn(r-l+1+2,x,y) - y)%mod+mod; check(sum[rt]);
return;
}
push_down(l, r, rt);
int mid = (l + r) >> 1;
if(L > mid) update(L,R,mid+1,r,rson,x,y);
else if(R <= mid) update(L,R,l,mid,lson,x,y);
else {
update(L,mid,l,mid,lson,x,y);
update(mid+1,R,mid+1,r,rson,hn(mid-L+1+1,x,y), hn(mid-L+1+2,x,y));
}
push_up(rt);
}
LL query(int L,int R,int l,int r,int rt) {
if(L <= l && r <= R) {
return sum[rt];
}
push_down(l,r,rt);
int mid = (l+r) >> 1;
if(L > mid) return query(L,R,mid+1,r,rson);
else if(R <= mid) return query(L,R,l,mid,lson);
else {
LL ans = query(L,mid,l,mid,lson);
ans += query(mid+1,R,mid+1,r,rson);
check(ans);
return ans;
}
}
int main() {
scanf("%d%d", &n, &m);
fib[1] = fib[2] = 1;
for(int i = 3; i < 301000; ++i) {
fib[i] = fib[i-1] + fib[i-2];
check(fib[i]);
}
for(int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) scanf("%lld", &ar[i]);
build(1, n, 1);
while(m --) {
int opt, l, r;
scanf("%d%d%d", &opt, &l, &r);
if(opt == 1) {
update(l, r, 1, n, 1, 1, 1);
}else {
printf("%lld\n", query(l,r,1,n,1));
}
}
return 0;
}
codeforces 447E or 446C 线段树 + fib性质或二次剩余性质的更多相关文章
- [Codeforces 316E3]Summer Homework(线段树+斐波那契数列)
[Codeforces 316E3]Summer Homework(线段树+斐波那契数列) 顺便安利一下这个博客,给了我很大启发(https://gaisaiyuno.github.io/) 题面 有 ...
- Buses and People CodeForces 160E 三维偏序+线段树
Buses and People CodeForces 160E 三维偏序+线段树 题意 给定 N 个三元组 (a,b,c),现有 M 个询问,每个询问给定一个三元组 (a',b',c'),求满足 a ...
- CodeForces 877E DFS序+线段树
CodeForces 877E DFS序+线段树 题意 就是树上有n个点,然后每个点都有一盏灯,给出初始的状态,1表示亮,0表示不亮,然后有两种操作,第一种是get x,表示你需要输出x的子树和x本身 ...
- [Codeforces 1197E]Culture Code(线段树优化建图+DAG上最短路)
[Codeforces 1197E]Culture Code(线段树优化建图+DAG上最短路) 题面 有n个空心物品,每个物品有外部体积\(out_i\)和内部体积\(in_i\),如果\(in_i& ...
- [Codeforces 1199D]Welfare State(线段树)
[Codeforces 1199D]Welfare State(线段树) 题面 给出一个长度为n的序列,有q次操作,操作有2种 1.单点修改,把\(a_x\)修改成y 2.区间修改,把序列中值< ...
- Codeforces 482B Interesting Array(线段树)
题目链接:Codeforces 482B Interesting Array 题目大意:给定一个长度为N的数组,如今有M个限制,每一个限制有l,r,q,表示从a[l]~a[r]取且后的数一定为q,问是 ...
- Codeforces 1083C Max Mex [线段树]
洛谷 Codeforces 思路 很容易发现答案满足单调性,可以二分答案. 接下来询问就转换成判断前缀点集是否能组成一条链. 我最初的想法:找到点集的直径,判断直径是否覆盖了所有点,需要用到树套树,复 ...
- Codeforces 1132G Greedy Subsequences [线段树]
洛谷 Codeforces 看到题解那么少就来发一篇吧-- 思路 看完题目一脸懵逼,感觉无从下手. 莫名其妙地想到笛卡尔树,但笛卡尔树好像并没有太大作用. 考虑把笛卡尔树改一下:每个点的父亲设为它的右 ...
- Codeforces Gym 100231B Intervals 线段树+二分+贪心
Intervals 题目连接: http://codeforces.com/gym/100231/attachments Description 给你n个区间,告诉你每个区间内都有ci个数 然后你需要 ...
随机推荐
- 【Flutter学习】组件学习之目录
01. Flutter组件-Layout-Container-容器 02. Flutter组件-Text-Text-文本 03. Flutter组件-Text-RichText-富文本 04. ...
- Jetson Nano系列教程0:初识Jetson Nano
关于Jetson Nano Developer Kit Jetson nano搭载四核Cortex-A57 MPCore 处理器,采用128 核 Maxwell™ GPU.支持JetPack SDK ...
- php开发面试题---Apache 运行PHP原理(整理)
php开发面试题---Apache 运行PHP原理(整理) 一.总结 一句话总结: 不要忘记 php引擎将页面静态化 和 php引擎和apache之间通讯 反思的回顾非常有用,因为决定了我的方向和技巧 ...
- spss-数据清洗-处理重复数据
spss-数据清洗-处理重复数据 数据导入之后就需要对数据进行清洗.数据清洗主要是对多余重复的数据筛选清除,将缺失的数据补充完整,将错误的数据纠正或者删除.接下来操作如何将重复数据处理操作. 步骤一: ...
- Windows环境下Oracle数据库的自动备份脚本自动删除30天前的备份
@echo off echo ================================================ echo Windows环境下Oracle数据库的自动备份脚本 echo ...
- linux中errno及perror的应用
1 perror 定义在头文件<stdlib.h>中 void perror(const char *s);函数说明 perror ( )用 来 将 上 一 个 函 数 发 生 错 误 的 ...
- 导出CSV格式
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;import org.springframework.stereotype. ...
- 开启linux下面vsftp自身的服务
最近业务需求搞了一下sftp,配合samba感觉还是不错的. 上干货:笔者的环境是centos7.4 1.建立一个名为sftpusers的sftp用户组 groupadd sftpusers 2.建立 ...
- ollvm 使用——“Cannot open /dev/random”错误的解决方法
找到 \obfuscator-llvm-4.0\lib\Transforms\Obfuscation\CryptoUtils.cpp 这个文件, 新增两个头文件 #include <window ...
- 《代码大全2》读书笔记 Week8
这一周博主阅读了<代码大全2>第11章至第13章,第三部分——"变量"就结束了,第四部分作者将转入语句的讨论. 第十一章作者详细阐述了变量名的有效命名规则,第十二和十三 ...
