C# 序列化与反序列化之xml对属性或者字段的子类化的子对象进行序列化的解决方案
C# 序列化与反序列化之xml对属性或者字段的子类化的子对象进行序列化的解决方案
xml序列化涉及到XmlRoot,XmlInclude,XmlElement,XmlAttribute,XmlType(用于继承的子类),XmlArray,XmlArrayItem(集合和集合项)等
新建控制台console项目,添加类XmlPerson以及XmlPerson的子类XmlStudent,XmlTeacher,添加Address类以及Address的的子类USAddress,AUAddress
1、运行的主方法代码如下:
using log4net;
using System;
using System.Data;
using System.Data.SQLite;
using System.Diagnostics;
using System.IO;
using System.IO.Compression;
using System.IO.MemoryMappedFiles;
using System.IO.Pipes;
using System.Linq;
using System.Net;
using System.Security.AccessControl;
using System.Security.Principal;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using System.Xml;
using System.Xml.Serialization;
using System.Reflection;
using System.ServiceModel;
using System.ServiceModel.Channels;
using System.Runtime.Serialization; namespace SupremeConsole
{
class Program
{ static void Main(string[] args)
{ TestSeri();
Console.ReadLine();
} public static void TestSeri()
{
//Team team = new Team { TName="123",PlayerList = { new Person { Name="1",Age=1},new Person { Name = "2", Age = 2 } } };
#region BinarySerialize 必须添可序列化属性,即要序列化的对象必须添加SerializableAttribute属性,[Serializable]
//string s = SerializeManager.Instance.BinarySerialize<Team>(team);//序列化
//Console.ForegroundColor = ConsoleColor.Green;
//Console.WriteLine("测试序列化成功。。。");
//Console.WriteLine($"测试序列化结果:\r\n{s}"); //string path = Path.Combine(AppDomain.CurrentDomain.BaseDirectory, "序列化11111.bin");//序列化
//SerializeManager.Instance.BinarySerialize<Team>(team, path); //string path = Path.Combine(AppDomain.CurrentDomain.BaseDirectory, "序列化11111.bin");
//Team test = SerializeManager.Instance.BinaryDeserialize<Team>(path);//反序列化
//if (test != null)
//{
// Console.WriteLine($"测试序列化结果:{test.ToString()}");
//}
#endregion #region SoapSerialize 必须添可序列化属性,即要序列化的对象必须添加SerializableAttribute属性,[Serializable]
//string s = SerializeManager.Instance.SoapSerialize<Team>(team);//序列化
//Console.ForegroundColor = ConsoleColor.Green;
//Console.WriteLine("测试序列化成功。。。");
//Console.WriteLine($"测试序列化结果:\r\n{s}"); //string path = Path.Combine(AppDomain.CurrentDomain.BaseDirectory, "Soap序列化.xml");//序列化
//SerializeManager.Instance.SoapSerialize<Team>(team, path); //string path = Path.Combine(AppDomain.CurrentDomain.BaseDirectory, "Soap序列化.xml");
//Team test = SerializeManager.Instance.SoapDeserialize<Team>(path);//反序列化
//if (test != null)
//{
// Console.WriteLine($"测试序列化结果:{test.ToString()}");
//}
#endregion #region XmlSerialize 要序列化的对象可以不添加SerializableAttribute属性,[Serializable]
//XmlPerson xmlPerson = new XmlPerson { Name = "1111", Age = 12,Address="住址。。。。" };
XmlPerson xmlPerson = new XmlPerson { Name = "", Age = , HomeAddress = new Address { Street = "默默大街三号", PostCode = "" } };
//XmlPerson xmlPerson = new XmlPerson { Name = "1111", Age = 12, HomeAddress = new USAddress { Street = "默默大街三号", PostCode = "233664", Neighbor="邻居666" } };
string s = SerializeManager.Instance.XmlSerialize<XmlPerson>(xmlPerson);//序列化
Console.ForegroundColor = ConsoleColor.Green;
Console.WriteLine("测试序列化成功。。。");
Console.WriteLine($"测试序列化结果:\r\n{s}"); //string path = Path.Combine(AppDomain.CurrentDomain.BaseDirectory, "序列化.txt");//序列化
//SerializeManager.Instance.XmlSerialize<TestClass>(testClass, path); //备用
//string json = "{\"Address\":\"中国南京\",\"Age\":10,\"Id\":1,\"Name\":\"张三\",\"Sex\":\"男\"}";
//TestClass test = SerializeManager.Instance.DataContractJsonDeserializeJson<TestClass>(json);//反序列化
//if (test != null)
//{
// Console.WriteLine($"测试序列化结果:{test.ToString()}");
//} //string path = Path.Combine(AppDomain.CurrentDomain.BaseDirectory, "序列化.txt");
//TestClass test = SerializeManager.Instance.XmlDeserialize<TestClass>(path);//反序列化
//if (test != null)
//{
// Console.WriteLine($"测试序列化结果:{test.ToString()}");
//}
#endregion
}
}
}
2、xml对属性或者字段的子类化的子对象进行序列化,首先添加类XmlPerson以及XmlPerson的子类XmlStudent,XmlTeacher,添加Address类以及Address的的子类USAddress,AUAddress
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using System.Xml.Serialization; namespace SupremeConsole
{
#region 继承XmlPerson以及继承的子类
/// <summary>
/// xml序列化测试类
/// </summary>
//继承XmlPerson的子类XmlStudent,XmlTeacher的序列化
//[XmlInclude(typeof(继承的子类1))]//XmlInclude指明了,继承子类的序列化的类型,如 XmlInclude(typeof(XmlStudent)),或者再序列化的时候添加子类类型XmlSerializer xs = new XmlSerializer (typeof (XmlPerson),new Type[] { typeof (继承的子类1), typeof (继承的子类2)} );,如:new Type[] { typeof (XmlStudent), typeof (XmlTeacher)};
[XmlRoot("haha")]
//[XmlInclude(typeof(XmlStudent))]
//[XmlInclude(typeof(XmlTeacher))]
public class XmlPerson
{
/// <summary>
/// 姓名
/// </summary>
[XmlElement("MyName", Order = )]
public string Name { get; set; } /// <summary>
/// 年龄
/// </summary>
[XmlAttribute("MyAge")]
public int Age { get; set; } ///// <summary>
///// 住址
///// </summary>
//[XmlElement("Residence", Order = 1)]
//public string Address { get; set; } /// <summary>
/// 住址
/// </summary>
[XmlElement("Residence", Order = )]
public Address HomeAddress = new Address();//常规序列化
} [XmlType("SubXmlPersonIsXmlStudent")]//XmlStudent序列化后的名称
public class XmlStudent : XmlPerson
{
/// <summary>
/// 学号
/// </summary>
public string StuNumber { get; set; }
} [XmlType("SubXmlPersonIsXmlTeacher")]//XmlTeacher序列化后的名称
public class XmlTeacher : XmlPerson
{
/// <summary>
/// 工号
/// </summary>
public string TeachNumber { get; set; } }
#endregion #region Address以及继承的子类 public class Address //常规序列化
{
public string Street, PostCode;
} [XmlType("USAddressISSubAddress")]
public class USAddress : Address //子类的序列化
{
public string Neighbor; //邻居
} [XmlType("AUAddressISSubAddress")]
public class AUAddress : Address //子类的序列化
{
public string OldNeighbor; //邻居
}
#endregion
}
运行效果:
测试序列化成功。。。
测试序列化结果:
<?xml version="1.0"?>
<haha xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:xsd="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema" MyAge="12">
<Residence>
<Street>默默大街三号</Street>
<PostCode>233664</PostCode>
</Residence>
<MyName>1111</MyName>
</haha>

运行结果中的红色标记就是XmlPerson中的HomeAddress 设置的别名Residence
/// <summary>
/// 住址
/// </summary>
[XmlElement("Residence", Order = 1)]
public Address HomeAddress = new Address();//常规序列化
修改XmlPerson中的
[XmlElement("Residence", Order = 1)]
public Address HomeAddress = new Address();//常规序列化
改成
[XmlElement("Residence", Order = 1)]
public Address HomeAddress = new USAddress();//子类的序列化
同时修改 Address,在Address类上添加特性[XmlInclude(typeof(USAddress))],[XmlInclude(typeof(AUAddress))]
[XmlInclude(typeof(USAddress))]
[XmlInclude(typeof(AUAddress))]
public class Address //常规序列化
{
public string Street, PostCode;
}
把TestSeri法中的
XmlPerson xmlPerson = new XmlPerson { Name = "1111", Age = 12, HomeAddress = new Address { Street = "默默大街三号", PostCode = "233664" } };
改成
XmlPerson xmlPerson = new XmlPerson { Name = "1111", Age = 12, HomeAddress = new USAddress { Street = "默默大街三号", PostCode = "233664", Neighbor="邻居666" } };
运行结果:
测试序列化成功。。。
测试序列化结果:
<?xml version="1.0"?>
<haha xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:xsd="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema" MyAge="12">
<Residence xsi:type="USAddressISSubAddress">
<Street>默默大街三号</Street>
<PostCode>233664</PostCode>
<Neighbor>邻居666</Neighbor>
</Residence>
<MyName>1111</MyName>
</haha>
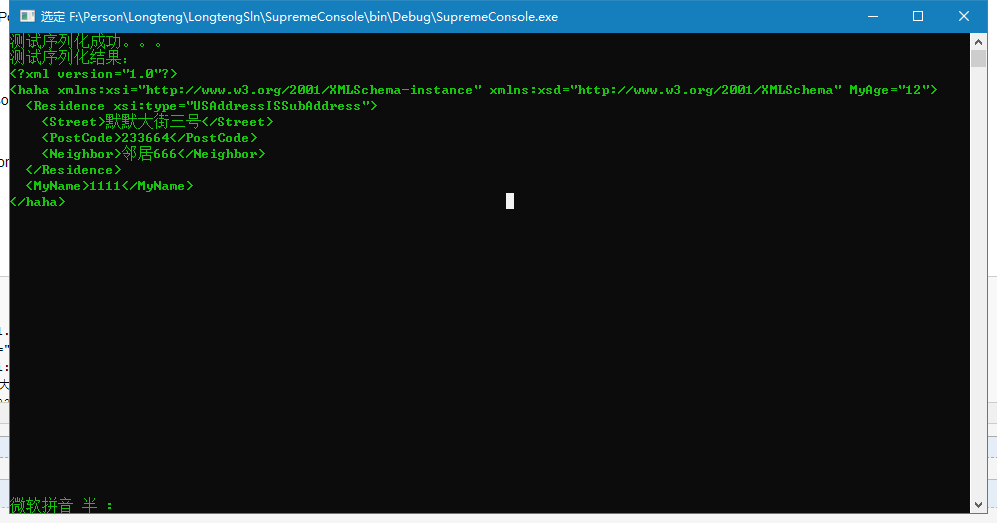
运行的结果来看出现了 Residence xsi:type="USAddressISSubAddress",出现的原因是在Address类上添加特性[XmlInclude(typeof(USAddress))],这就是xml对属性或者字段的子类化的子对象进行序列化的结果
要想出现下面的效果
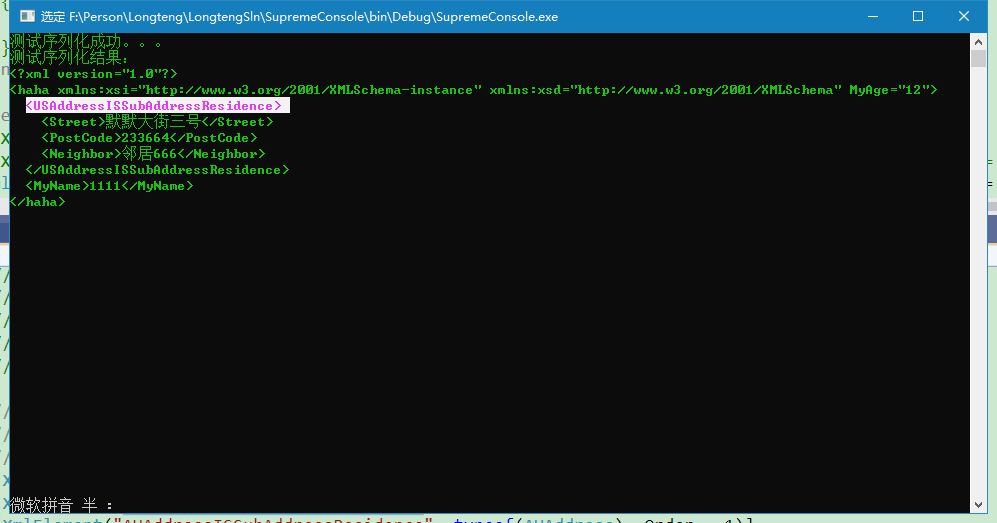
修改
[XmlElement("Residence", Order = 1)]
//public Address HomeAddress = new USAddress();//子类的序列化
改为
[XmlElement("Residence", typeof(Address), Order = 1)]
[XmlElement("USAddressISSubAddressResidence", typeof(USAddress), Order = 1)]
[XmlElement("AUAddressISSubAddressResidence", typeof(AUAddress), Order = 1)]
public Address HomeAddress = new USAddress();//子类的序列化
这时候就可以达到上述效果,但是Address类上添加特性[XmlInclude(typeof(USAddress))]对结果没有影响,可以去掉。
3、xml对属性或者字段是泛型集合的序列化处理方式如下
首先把XmlPerson类中的
public Address HomeAddress = new USAddress();//子类的序列化
改成
[XmlArray("集合列表的名称", Order = 1)]//默认序列化以后的名称是Addresses ,现在通过XmlArray来修改为指定的名称,如:[XmlArray("集合列表的名称", Order = 1)]
[XmlArrayItem("集合列表中的项的名称")]//默认序列化以后的名称是Address,现在通过XmlArrayItem来修改为指定的名称,如:[XmlArrayItem("集合列表中的项的名称")]
public List<Address> Addresses = new List<Address>();
注意:XmlElement、XmlText 和 XmlAnyElement 不能与 XmlAttribute、XmlAnyAttribute、XmlArray 或 XmlArrayItem 一起使用,否则会报错。
把TestSeri方法中的
XmlPerson xmlPerson = new XmlPerson { Name = "1111", Age = 12, HomeAddress = new USAddress { Street = "默默大街三号", PostCode = "233664", Neighbor="邻居666" } };
改成
XmlPerson xmlPerson = new XmlPerson { Name = "1111", Age = 12, Addresses = new List<Address> { new Address { Street = "大街三三号", PostCode = "123"}, new USAddress { Street = "大街六六号", PostCode = "456", Neighbor = "邻居666" } } };
运行效果

把 public List<Address> Addresses = new List<Address>();上的特性改成
[XmlElement("Address", typeof(Address), Order = 1)]
[XmlElement("AUAddress", typeof(AUAddress))]
[XmlElement("USAddress", typeof(USAddress))]
public List<Address> Addresses = new List<Address>();
把TestSeri方法中的
XmlPerson xmlPerson = new XmlPerson { Name = "1111", Age = 12, Addresses = new List<Address> { new Address { Street = "大街三三号", PostCode = "123"}, new USAddress { Street = "大街六六号", PostCode = "456", Neighbor = "邻居666" } } };
改成
XmlPerson xmlPerson = new XmlPerson { Name = "1111", Age = 12, Addresses = new List<Address> { new Address { Street = "大街三三号", PostCode = "123"}, new USAddress { Street = "大街六六号", PostCode = "456", Neighbor = "邻居666" }, new AUAddress { Street = "大街八八号", PostCode = "789", OldNeighbor = "旧朋友邻居8888" } } };
运行效果

把
[XmlElement("Address", typeof(Address), Order = 1)]
[XmlElement("AUAddress", typeof(AUAddress))]
[XmlElement("USAddress", typeof(USAddress))]
public List<Address> Addresses = new List<Address>();
上的特性
改成
[XmlArray(Order = 1)]
[XmlArrayItem("Address", typeof(Address))]
[XmlArrayItem("AUAddress", typeof(AUAddress))]
[XmlArrayItem("USAddress", typeof(USAddress))]
public List<Address> Addresses = new List<Address>();
运行效果

上述测试的全部代码如下:
Main主方法代码:
using log4net;
using System;
using System.Data;
using System.Data.SQLite;
using System.Diagnostics;
using System.IO;
using System.IO.Compression;
using System.IO.MemoryMappedFiles;
using System.IO.Pipes;
using System.Linq;
using System.Net;
using System.Security.AccessControl;
using System.Security.Principal;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using System.Xml;
using System.Xml.Serialization;
using System.Reflection;
using System.ServiceModel;
using System.ServiceModel.Channels;
using System.Runtime.Serialization;
using System.Collections.Generic; namespace SupremeConsole
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
TestSeri();
Console.ReadLine();
} public static void TestSeri()
{
//Team team = new Team { TName="123",PlayerList = { new Person { Name="1",Age=1},new Person { Name = "2", Age = 2 } } };
#region BinarySerialize 必须添可序列化属性,即要序列化的对象必须添加SerializableAttribute属性,[Serializable]
//string s = SerializeManager.Instance.BinarySerialize<Team>(team);//序列化
//Console.ForegroundColor = ConsoleColor.Green;
//Console.WriteLine("测试序列化成功。。。");
//Console.WriteLine($"测试序列化结果:\r\n{s}"); //string path = Path.Combine(AppDomain.CurrentDomain.BaseDirectory, "序列化11111.bin");//序列化
//SerializeManager.Instance.BinarySerialize<Team>(team, path); //string path = Path.Combine(AppDomain.CurrentDomain.BaseDirectory, "序列化11111.bin");
//Team test = SerializeManager.Instance.BinaryDeserialize<Team>(path);//反序列化
//if (test != null)
//{
// Console.WriteLine($"测试序列化结果:{test.ToString()}");
//}
#endregion #region SoapSerialize 必须添可序列化属性,即要序列化的对象必须添加SerializableAttribute属性,[Serializable]
//string s = SerializeManager.Instance.SoapSerialize<Team>(team);//序列化
//Console.ForegroundColor = ConsoleColor.Green;
//Console.WriteLine("测试序列化成功。。。");
//Console.WriteLine($"测试序列化结果:\r\n{s}"); //string path = Path.Combine(AppDomain.CurrentDomain.BaseDirectory, "Soap序列化.xml");//序列化
//SerializeManager.Instance.SoapSerialize<Team>(team, path); //string path = Path.Combine(AppDomain.CurrentDomain.BaseDirectory, "Soap序列化.xml");
//Team test = SerializeManager.Instance.SoapDeserialize<Team>(path);//反序列化
//if (test != null)
//{
// Console.WriteLine($"测试序列化结果:{test.ToString()}");
//}
#endregion #region XmlSerialize 要序列化的对象可以不添加SerializableAttribute属性,[Serializable]
//XmlPerson xmlPerson = new XmlPerson { Name = "1111", Age = 12,Address="住址。。。。" };
//XmlPerson xmlPerson = new XmlPerson { Name = "1111", Age = 12, HomeAddress = new Address { Street = "默默大街三号", PostCode = "233664" } };
//XmlPerson xmlPerson = new XmlPerson { Name = "1111", Age = 12, HomeAddress = new USAddress { Street = "默默大街三号", PostCode = "233664", Neighbor="邻居666" } };
XmlPerson xmlPerson = new XmlPerson { Name = "", Age = , Addresses = new List<Address> { new Address { Street = "大街三三号", PostCode = ""}, new USAddress { Street = "大街六六号", PostCode = "", Neighbor = "邻居666" }, new AUAddress { Street = "大街八八号", PostCode = "", OldNeighbor = "旧朋友邻居8888" } } };
string s = SerializeManager.Instance.XmlSerialize<XmlPerson>(xmlPerson);//序列化
Console.ForegroundColor = ConsoleColor.Green;
Console.WriteLine("测试序列化成功。。。");
Console.WriteLine($"测试序列化结果:\r\n{s}"); //string path = Path.Combine(AppDomain.CurrentDomain.BaseDirectory, "Addresses序列化.txt");//序列化
//SerializeManager.Instance.XmlSerialize<XmlPerson>(xmlPerson, path); //string path = Path.Combine(AppDomain.CurrentDomain.BaseDirectory, "Addresses序列化.txt");
//XmlPerson test = SerializeManager.Instance.XmlDeserialize<XmlPerson>(path);//反序列化
//if (test != null)
//{
// Console.WriteLine($"测试序列化结果:{test.ToString()}");
//}
#endregion
}
}
}
xmlPerson类
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using System.Xml.Serialization; namespace SupremeConsole
{
#region 继承XmlPerson以及继承的子类
/// <summary>
/// xml序列化测试类
/// </summary>
//继承XmlPerson的子类XmlStudent,XmlTeacher的序列化
//[XmlInclude(typeof(继承的子类1))]//XmlInclude指明了,继承子类的序列化的类型,如 XmlInclude(typeof(XmlStudent)),或者再序列化的时候添加子类类型XmlSerializer xs = new XmlSerializer (typeof (XmlPerson),new Type[] { typeof (继承的子类1), typeof (继承的子类2)} );,如:new Type[] { typeof (XmlStudent), typeof (XmlTeacher)};
[XmlRoot("haha")]
//[XmlInclude(typeof(XmlStudent))]
//[XmlInclude(typeof(XmlTeacher))]
public class XmlPerson
{
/// <summary>
/// 姓名
/// </summary>
[XmlElement("MyName", Order = )]
public string Name { get; set; } /// <summary>
/// 年龄
/// </summary>
[XmlAttribute("MyAge")]
public int Age { get; set; } ///// <summary>
///// 住址
///// </summary>
//[XmlElement("Residence", Order = 1)]
//public string Address { get; set; } ///// <summary>
///// 住址
///// </summary>
//[XmlElement("Residence", Order = 1)]
//public Address HomeAddress = new Address();//常规序列化 ///// <summary>
///// 住址
///// </summary>
//[XmlElement("Residence", Order = 1)]
//public Address HomeAddress = new USAddress();//子类的序列化 ///// <summary>
///// 住址
///// </summary>
//[XmlElement("Residence", typeof(Address), Order = 1)]
//[XmlElement("USAddressISSubAddressResidence", typeof(USAddress), Order = 1)]
//[XmlElement("AUAddressISSubAddressResidence", typeof(AUAddress), Order = 1)]
//public Address HomeAddress = new USAddress();//子类的序列化 ///// <summary>
///// 地址集合
///// </summary>
//[XmlArray("集合列表的名称", Order = 1)]
//[XmlArrayItem("集合列表中的项的名称")]
//public List<Address> Addresses = new List<Address>();
[XmlArray(Order = )]
[XmlArrayItem("Address", typeof(Address))]
[XmlArrayItem("AUAddress", typeof(AUAddress))]
[XmlArrayItem("USAddress", typeof(USAddress))]
public List<Address> Addresses = new List<Address>(); //[XmlElement("Address", typeof(Address), Order = 1)]
//[XmlElement("AUAddress", typeof(AUAddress))]
//[XmlElement("USAddress", typeof(USAddress))]
//public List<Address> Addresses = new List<Address>();
} [XmlType("SubXmlPersonIsXmlStudent")]//XmlStudent序列化后的名称
public class XmlStudent : XmlPerson
{
/// <summary>
/// 学号
/// </summary>
public string StuNumber { get; set; }
} [XmlType("SubXmlPersonIsXmlTeacher")]//XmlTeacher序列化后的名称
public class XmlTeacher : XmlPerson
{
/// <summary>
/// 工号
/// </summary>
public string TeachNumber { get; set; } }
#endregion #region Address以及继承的子类 [XmlInclude(typeof(USAddress))]
[XmlInclude(typeof(AUAddress))]
public class Address //常规序列化
{
public string Street, PostCode;
} [XmlType("USAddressISSubAddress")]
public class USAddress : Address //子类的序列化
{
public string Neighbor; //邻居
} [XmlType("AUAddressISSubAddress")]
public class AUAddress : Address //子类的序列化
{
public string OldNeighbor; //邻居
}
#endregion
}
C# 序列化与反序列化之xml对属性或者字段的子类化的子对象进行序列化的解决方案的更多相关文章
- JSON 序列化与反序列化, 与XML相互转换.
方式一: 使用于 JavaScriptSerializer类 适用于普通场景, Excel导入导出, 前台传输查询参数直接处理等. JavaScriptSerializer serializer = ...
- C# XML序列化与反序列化与XML格式详解
1.https://www.cnblogs.com/sandyliu1999/p/4844664.html XML是有层次结构的,序列化实际就是内存化,用连续的结构化的内存来存储表示一个对象,那么这两 ...
- C#学习日志 day8 -------------- async await 异步方法入门(引用博客)以及序列化和反序列化的XML及json实现
首先是异步方法的介绍,这里引用自http://www.cnblogs.com/LoveJenny/archive/2011/11/01/2230933.html async and await 简单的 ...
- C# 序列化与反序列化之xml通过实现IXmlSerializable进行序列化的解决方案
新建控制台console项目,添加XmlPersonIXmlSerializable类,和AddressIXmlSerializable类(实现IXmlSerializable)以及AddressIX ...
- go语言学习 ---struct 对象的序列化和反序列化(xml)
实例1: //main package main import ( "encoding/xml" "fmt" ) type person struct { Na ...
- 将对象序列化,反序列化到XML
using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.IO; using System.Linq; using System.Tex ...
- .NET中XML序列化和反序列化常用类和用来控制XML序列化的属性总结(XmlSerializer,XmlTypeAttribute,XmlElementAttribute,XmlAttributeAttribute,XmlArrayAttribute...)
序列化和反序列化是指什么? 序列化(seriallization): 将对象转化为便于传输的数据格式, 常见的序列化格式:二进制格式,字节数组,json字符串,xml字符串.反序列化(deserial ...
- C#: .net序列化及反序列化 [XmlElement(“节点名称”)] [XmlAttribute(“节点属性”)] (下篇)
介绍 XML 序列化 .NET Framework 开发员指南 序列化是将对象转换为容易传输的格式的过程.例如,可以序列化一个对象,然后使用 HTTP 通过 Internet 在客户端和服务器之间 ...
- PHP中的抽象类与抽象方法/静态属性和静态方法/PHP中的单利模式(单态模式)/串行化与反串行化(序列化与反序列化)/约束类型/魔术方法小结
前 言 OOP 学习了好久的PHP,今天来总结一下PHP中的抽象类与抽象方法/静态属性和静态方法/PHP中的单利模式(单态模式)/串行化与反串行化(序列化与反序列化). 1 PHP中的抽象 ...
随机推荐
- html5直接调用手机相机照相/录像
现在的h5功能越来越强大.之前做项目时上传功能input type=file时,在IOS下居然可以直接照相...但是在安卓上是不能.后面研究 了下,其实安卓下也可以的. 就是在input上加上capt ...
- .Net core 如何生成Nuget包
以前引用了很多neget包,觉得nuget包方便了很多,是不是有些通用的代码可以封装到nuget中,想要用的时候引用就可以了, 这样其实有两个好处: 1. 首先不用重复的coding,节约了时间. 2 ...
- 大数据:Hadoop(JDK安装、HDFS伪分布式环境搭建、HDFS 的shell操作)
所有的内容都来源与 Hadoop 官方文档 一.Hadoop 伪分布式安装步骤 1)JDK安装 解压:tar -zxvf jdk-7u79-linux-x64.tar.gz -C ~/app 添加到系 ...
- 为Linux操作系统配置SSH互信
Linux 互信,免登陆 1.切换到要建立互信的用户(以root为例): su - root cd ~ 2.制作密钥并赋权: # ssh-keygen -t dsa #出现 ...
- No root/virtual joint specified in SRDF. Assuming fixed joint
在用MoveIt!配置文件时,加载urdf模型时,显示Success......但没有显示模型,终端显示错误如下: 增加虚拟关节就好.
- Docker 中 MySQL 数据的导入导出
Creating database dumps Most of the normal tools will work, although their usage might be a little c ...
- Gradle 知识点
mac 系统中,下载的 Gradle 压缩包解压后存储的文件夹:/Users//.gradle/wrapper/dists 当Gradle运行时,会根据settings.gradle的配置情况,构建一 ...
- 【IIS】跨域(转)
Access to XMLHttpRequest at 'http://*****/.dae' from origin 'http://192.168.198.21:22222' has been b ...
- Cookies and Custom Protocols
https://developer.apple.com/library/content/documentation/Cocoa/Conceptual/URLLoadingSystem/Cookiesa ...
- Mac 上 brew 安装Tomcat
首先保证brew命令能够正常使用: 搜索tomcat是否存在:brew search tomcat 安装tomcat:brew install tomcat 检查是否安装成功:catalina -h ...
