Java集合源码分析(三)——LinkedList
简介
LinkedList是一个链表结构的列表,也可以被作为堆栈、队列或双端队列使用。它继承于AbstractSequentialList双向链表,实现了List、Deque、Cloneable、java.io.Serializable接口。
源码分析
public class LinkedList<E>
extends AbstractSequentialList<E>
implements List<E>, Deque<E>, Cloneable, Serializable {}
下面分析几个我认为比较重要的,能够体现其设计精髓的API源码。
实现接口
- List
- Deque
- Cloneable
- java.io.Serializable
父类
- AbstractSequentialList
字段
- first:双向链表的头节点。
- last:双向链表的尾节点。
- size:表中元素的个数。
- serialVersionUID:版本号。
transient int size = 0;
transient Node<E> first;
transient Node<E> last;
private static final long serialVersionUID = 876323262645176354L;
内部类
1.节点数据结构
private static class Node<E> {
E item;
Node<E> next;
Node<E> prev;
Node(Node<E> prev, E element, Node<E> next) {
this.item = element;
this.next = next;
this.prev = prev;
}
}
这个是LinkedList中节点基本的数据结构,从这里就可以看出,LinkedList是一个双向链表,每个节点包含节点元素值,和指前、指后的引用。
2.迭代器
// List迭代器
public ListIterator<E> listIterator(int index) {
checkPositionIndex(index);
return new ListItr(index);
}
private class ListItr implements ListIterator<E> {
// 之前最新返回的节点
private Node<E> lastReturned;
// 装下一个元素的节点
private Node<E> next;
// 存储下一个元素的索引号
private int nextIndex;
// 存储构造器生成时的修改版本号
private int expectedModCount = modCount;
ListItr(int index) {
// assert isPositionIndex(index);
next = (index == size) ? null : node(index);
nextIndex = index;
}
public boolean hasNext() {
return nextIndex < size;
}
public E next() {
checkForComodification();
if (!hasNext())
throw new NoSuchElementException();
lastReturned = next;
next = next.next;
nextIndex++;
return lastReturned.item;
}
public boolean hasPrevious() {
return nextIndex > 0;
}
public E previous() {
checkForComodification();
if (!hasPrevious())
throw new NoSuchElementException();
lastReturned = next = (next == null) ? last : next.prev;
nextIndex--;
return lastReturned.item;
}
public int nextIndex() {
return nextIndex;
}
public int previousIndex() {
return nextIndex - 1;
}
public void remove() {
checkForComodification();
if (lastReturned == null)
throw new IllegalStateException();
Node<E> lastNext = lastReturned.next;
unlink(lastReturned);
if (next == lastReturned)
next = lastNext;
else
nextIndex--;
lastReturned = null;
expectedModCount++;
}
public void set(E e) {
if (lastReturned == null)
throw new IllegalStateException();
checkForComodification();
lastReturned.item = e;
}
public void add(E e) {
checkForComodification();
lastReturned = null;
if (next == null)
linkLast(e);
else
linkBefore(e, next);
nextIndex++;
expectedModCount++;
}
public void forEachRemaining(Consumer<? super E> action) {
Objects.requireNonNull(action);
while (modCount == expectedModCount && nextIndex < size) {
action.accept(next.item);
lastReturned = next;
next = next.next;
nextIndex++;
}
checkForComodification();
}
final void checkForComodification() {
if (modCount != expectedModCount)
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
}
}
private static class Node<E> {
E item;
Node<E> next;
Node<E> prev;
Node(Node<E> prev, E element, Node<E> next) {
this.item = element;
this.next = next;
this.prev = prev;
}
}
这里通过实现ListIterator接口,给外部提供迭代器的接口。
不同于直接对List的操作API,这里的迭代器中每次操作都会通过checkForComodification()语句判断线程是否安全,可以看出LinkedList是没有线程安全的,迭代器通过修改版本号的比较,实现线程不安全的检测。用来实现fail-fast机制。其实还有一个作用就是在防止在迭代器遍历的中,当前线程对列表进行修改。
其实这样做还是不安全的,如果在执行checkForComodification()之后,数据被其他线程修改了,而迭代器的线程继续执行下面的语句,就会出现问题。
方法
从基本的节点操作方法开始举例分析。
1.添加节点
// 将节点(节点数据是e)添加到succ节点之前。
void linkBefore(E e, Node<E> succ) {
// assert succ != null;
final Node<E> pred = succ.prev;
final Node<E> newNode = new Node<>(pred, e, succ);
succ.prev = newNode;
// 如果前驱节点是空的,说明succ是原来的头节点,所以需要更新头节点
if (pred == null)
first = newNode;
else
pred.next = newNode;
size++;
modCount++;
}
// 将节点添加到末尾
void linkLast(E e) {
final Node<E> l = last;
final Node<E> newNode = new Node<>(l, e, null);
last = newNode;
// 如果末尾节点是空的,说明链表还是空的,需要更新头节点,这时候末尾节点和头节点指向同一个节点
if (l == null)
first = newNode;
else
l.next = newNode;
size++;
modCount++;
}
这是LinkedList添加节点最底层的操作,其他的API的添加操作都是基于这些函数实现的。
2.删除节点
// 将节点从链表中删除
E unlink(Node<E> x) {
// assert x != null;
final E element = x.item;
final Node<E> next = x.next;
final Node<E> prev = x.prev;
// 判断是否为头节点
if (prev == null) {
first = next;
} else {
prev.next = next;
x.prev = null;
}
// 判断是否为末尾节点
if (next == null) {
last = prev;
} else {
next.prev = prev;
x.next = null;
}
x.item = null;
size--;
modCount++;
return element;
}
实现原理: 如果删除节点是头节点,那么就需要更新头节点,如果是尾节点,同样更新。不是头尾节点的话,就只需要将节点前后相连,然后将这个节点的引用置空,从而回收原有对象。
3.添加元素
// 将元素(E)添加到LinkedList中
public boolean add(E e) {
linkLast(e);
return true;
}
这里就是调用了上面的linkLast,将元素添加到last节点后面,也就时链表末尾。
4.获取对应位置的节点
// 获取双向链表中指定位置的节点
Node<E> node(int index) {
// assert isElementIndex(index);
// 判断索引的位置
if (index < (size >> 1)) {
Node<E> x = first;
for (int i = 0; i < index; i++)
x = x.next;
return x;
} else {
Node<E> x = last;
for (int i = size - 1; i > index; i--)
x = x.prev;
return x;
}
}
LinkedList的随机访问都是需要通过这个函数来实现的。
实现原理:本质就是通过链表的不断遍历,查找获取到对应下标的节点。首先判断下标是否越界,然后进行遍历,为了提高查找的效率,会对需求的下标进行判断,从而确定从前还是从后开始遍历。
所以可以从这里看出来,LinkedList的随机访问效率很低,而且不稳定,访问时间和列表内数据量成正比。
5.删除对应位置的元素
// 删除index位置的节点
public E remove(int index) {
checkElementIndex(index);
return unlink(node(index));
}
**实现原理:**先调用上面的函数,找到对应位置的节点,然后再删除该节点。
删除利用查找方法,所以,开销和上面也是一样的。
6.转化为数组
// 返回LinkedList的Object[]数组
public Object[] toArray() {
Object[] result = new Object[size];
int i = 0;
for (Node<E> x = first; x != null; x = x.next)
result[i++] = x.item;
return result;
}
// 返回LinkedList的模板数组。所谓模板数组,即可以将T设为任意的数据类型
public <T> T[] toArray(T[] a) {
if (a.length < size)
a = (T[])java.lang.reflect.Array.newInstance(
a.getClass().getComponentType(), size);
int i = 0;
// 创建一个新的数组
Object[] result = a;
// 遍历链表,把数据填进数组
for (Node<E> x = first; x != null; x = x.next)
result[i++] = x.item;
if (a.length > size)
a[size] = null;
return a;
}
和ArrayList一样,转化为数组提供了两种方法,前者直接丢出Object类型,后者时根据传入的模板数组的类型,将Object类转换为所需类型,再丢出去。
实现原理:创建一个数组,通过遍历链表,将数据填到数组里面即可。
7.添加集合
// 从双向链表的index开始,将“集合(c)”添加到双向链表中。
public boolean addAll(int index, Collection<? extends E> c) {
checkPositionIndex(index);
// 先把集合转化为数组
Object[] a = c.toArray();
int numNew = a.length;
if (numNew == 0)
return false;
Node<E> pred, succ;
if (index == size) {
succ = null;
pred = last;
} else {
succ = node(index);
pred = succ.prev;
}
// 遍历数组,把元素包装了新节点中,再接到链表中去
for (Object o : a) {
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked") E e = (E) o;
Node<E> newNode = new Node<>(pred, e, null);
if (pred == null)
first = newNode;
else
pred.next = newNode;
pred = newNode;
}
if (succ == null) {
last = pred;
} else {
pred.next = succ;
succ.prev = pred;
}
size += numNew;
modCount++;
return true;
}
实现原理: 先把该集合转化为数组,然后将需要添加的位置给断开,根据数组里面的元素生成新的节点,再挨个将节点串到需要的位置,最后再把尾巴连上。
8.克隆
// 克隆函数。返回LinkedList的克隆对象。
public Object clone() {
LinkedList<E> clone = superClone();
// Put clone into "virgin" state
clone.first = clone.last = null;
clone.size = 0;
clone.modCount = 0;
// Initialize clone with our elements
for (Node<E> x = first; x != null; x = x.next)
clone.add(x.item);
return clone;
}
实现原理: 先调用父类的克隆接口函数,然后再将自己链表中的节点值挨个填入,让新链表自己创建元素。
9.构造函数
// 没有参数的构造
public LinkedList() {
}
// 包含“集合”的构造函数:创建一个包含“集合”的LinkedList
public LinkedList(Collection<? extends E> c) {
this();
addAll(c);
}
成员变量在对象分配的时候就
总结
源码总结
- LinkedList内部数据结构是双向链表。它有一个非常重要的内部类:Node,是双向链表的数据结构,其中包括节点的数据内容,上一个节点和下一个节点。
- LinkedList由于是链表,所以不存在扩容的问题。
- 克隆函数就是将该对象的所有数据值都复制到一个新的LinkedList中。
- LinkedList实现java.io.Serializable。当写入到输出流时,先写入“容量”,再依次写入“每一个节点保护的值”;当读出输入流时,先读取“容量”,再依次读取“每一个元素”。
- 由于LinkedList实现了Deque,而Deque接口定义了在双端队列两端访问元素的方法。提供插入、移除和检查元素的方法。每种方法都存在两种形式:一种形式在操作失败时抛出异常,另一种形式返回一个特殊值(null 或 false,具体取决于操作)。
- 由于Linked内部是链表,所以,中间插入和删除的操作本身开销比较小,但是找到中间元素的随机访问开销十分打,且稳定,依据元素的个数的一半。
源码相关总结
遍历方式:
- 迭代器
- 随机访问
- foreach
- pollFirst
- pollLast
- removeFirst
- removeLast
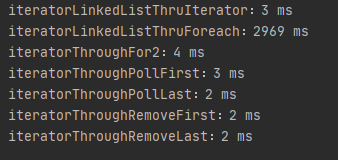
由图可见,remove的效率最高,poll的效率其次。所以,如果需要遍历LinkedList,尽量避免随机访问,而是采用迭代器或者for。
Java集合源码分析(三)——LinkedList的更多相关文章
- Java集合源码分析之LinkedList
1. LinkedList简介 public class LinkedList<E> extends AbstractSequentialList<E> implements ...
- Java集合源码分析之 LinkedList
一.简介 LinkedList是一个常用的集合类,用于顺序存储元素.LinkedList经常和ArrayList一起被提及.大部分人应该都知道ArrayList内部采用数组保存元素,适合用于随机访问比 ...
- Java集合源码分析(三)LinkedList
LinkedList简介 LinkedList是基于双向循环链表(从源码中可以很容易看出)实现的,除了可以当做链表来操作外,它还可以当做栈.队列和双端队列来使用. LinkedList同样是非线程安全 ...
- java集合源码分析(三):ArrayList
概述 在前文:java集合源码分析(二):List与AbstractList 和 java集合源码分析(一):Collection 与 AbstractCollection 中,我们大致了解了从 Co ...
- java集合源码分析(六):HashMap
概述 HashMap 是 Map 接口下一个线程不安全的,基于哈希表的实现类.由于他解决哈希冲突的方式是分离链表法,也就是拉链法,因此他的数据结构是数组+链表,在 JDK8 以后,当哈希冲突严重时,H ...
- Java 集合源码分析(一)HashMap
目录 Java 集合源码分析(一)HashMap 1. 概要 2. JDK 7 的 HashMap 3. JDK 1.8 的 HashMap 4. Hashtable 5. JDK 1.7 的 Con ...
- Java集合源码分析(二)ArrayList
ArrayList简介 ArrayList是基于数组实现的,是一个动态数组,其容量能自动增长,类似于C语言中的动态申请内存,动态增长内存. ArrayList不是线程安全的,只能用在单线程环境下,多线 ...
- Java集合源码分析(四)Vector<E>
Vector<E>简介 Vector也是基于数组实现的,是一个动态数组,其容量能自动增长. Vector是JDK1.0引入了,它的很多实现方法都加入了同步语句,因此是线程安全的(其实也只是 ...
- java集合源码分析几篇文章
java集合源码解析https://blog.csdn.net/ns_code/article/category/2362915
随机推荐
- Ubuntu12.10 设置默认命令行启动
在虚拟机当中安装ubuntu12.10的时候默认把图形界面给装上了,由于不需要使用桌面,所以为了省去每次进入到图形界面然后再用ctrl+F1的方式切换到命令行的步骤,希望能够默认进入的是命令行模式,那 ...
- day96:flask:flask-migrate&flask-session&蓝图Blueprint&蓝图的运行机制
目录 1.flask-migrate 2.flask-session 3.蓝图:Blueprint 4.蓝图的运行机制 1.数据库迁移:flask-migrate 1.Flask的数据库迁移 在开发过 ...
- ios开发中如何调用苹果自带地图导航
前段时间一直在赶项目,在外包公司工作就是命苦,天天加班不说,工作都是和工期合同挂钩的,稍微逾期就有可能被扣奖金,不谈这些伤脑筋的事情了,让我们说说iOS开发中如何调用苹果手机自带的地图. 学习如逆水行 ...
- Windows/Linux 代码共享,开发者称此举使Linux有了更差的结局
英特尔近期披露了 Linux 图形驱动程序相关的一些细节并指出,英特尔的图形驱动程序现在已在 Windows/Linux 之间共享约 60% 的代码库,90~100% 的性能. 针对此事,红帽公司的高 ...
- linux下安装python3.7.1
一.安装依赖环境 输入命令:yum -y install zlib-devel bzip2-devel openssl-devel ncurses-devel sqlite-devel readlin ...
- zuul1.x和gateway的区别
阻塞与非阻塞: 1.实际上是Spring mvc与Spring webflux的区别 转载:https://www.cnblogs.com/lixinjie/p/a-brother-of-spring ...
- 【mq读书笔记】顺序消息
注意异常情况导致整个消费无限重试 阻塞消费 mq支持局部消息顺序消费,可以确保同一个消息消费队列中的消息被顺序消费.看下针对顺序消息在整个消费过程中做的调整: 队列负载: DefaultMQPushC ...
- 【论文解读】【半监督学习】【Google教你水论文】A Simple Semi-Supervised Learning Framework for Object Detection
题记:最近在做LLL(Life Long Learning),接触到了SSL(Semi-Supervised Learning)正好读到了谷歌今年的论文,也是比较有点开创性的,浅显易懂,对比实验丰富, ...
- houdini 鱼眼相机
http://mattebb.com/weblog/houdini-fisheye-camera/ 这个网站是有提供一个相机shader的,,如图是方形的,国内的用户,比较多是做球幕的小伙伴,圆形就行 ...
- 自动化运维工具之Puppet常用资源(一)
前文我们聊到了puppet的架构,单机模型和master/agent模型的工作流程以及puppet的基础使用,回顾请参考https://www.cnblogs.com/qiuhom-1874/p/14 ...
