步进电机的Arduino库函数
This library allows you to control unipolar or bipolar stepper motors. To use it you will need a stepper motor, and the appropriate hardware to control it. For more on that, see Tom Igoe's notes on steppers.
函数
Stepper(steps, pin1, pin2) 步进电机定义
Stepper(steps, pin1, pin2, pin3, pin4) 步进电机定义
Description 解释
This function creates a new instance of the Stepper class that represents a particular stepper motor attached to your Arduino board. Use it at the top of your sketch, above setup() and loop(). The number of parameters depends on how you've wired your motor - either using two or four pins of the Arduino board.
Parameters 参数
steps: the number of steps in one revolution of your motor. If your motor gives the number of degrees per step, divide that number into 360 to get the number of steps (e.g. 360 / 3.6 gives 100 steps). (int) 一圈对应的步数
pin1, pin2: two pins that are attached to the motor (int)
pin3, pin4: optional the last two pins attached to the motor, if it's connected to four pins (int)
Returns A new instance of the Stepper motor class.
setSpeed(rpm) 速度设定
Description 解释
Sets the motor speed in rotations per minute (RPMs). This function doesn't make the motor turn, just sets the speed at which it will when you call step().
Parameters 参数
rpms: the speed at which the motor should turn in rotations per minute - a positive number (long)
Returns None 无返回值
step(steps) 步数执行
Description
Turns the motor a specific number of steps, at a speed determined by the most recent call to setSpeed(). This function is blocking; that is, it will wait until the motor has finished moving to pass control to the next line in your sketch. For example, if you set the speed to, say, 1 RPM and called step(100) on a 100-step motor, this function would take a full minute to run. For better control, keep the speed high and only go a few steps with each call to step().
Parameters
steps: the number of steps to turn the motor - positive to turn one direction, negative to turn the other (int)
Returns None
举例
例1 Stepper Motor Knob 用电位器控制步进电机步数
Control a highly accurate stepper motor using a potentiometer
Stepper motors, due to their unique design, can be controlled to a high degree of accuracy without any feedback mechanisms. The shaft of a stepper, mounted with a series of magnets, is controlled by a series of electromagnetic coils that are charged positively and negatively in a specific sequence, precisely moving it forward or backward in small "steps".
There are two types of steppers, Unipolars and Bipolars, and it is very important to know which type you are working with. For each of the motors, there is a different circuit. The example code will control both kinds of motors. See the unipolar and bipolar motor schematics for information on how to wire up your motor.
In this example, a potentiometer (or other sensor) on analog input 0 is used to control the movement of a stepper motor using the Arduino Stepper Library. The stepper is controlled by with digital pins 8, 9, 10, and 11 for either unipolar or bipolar motors.
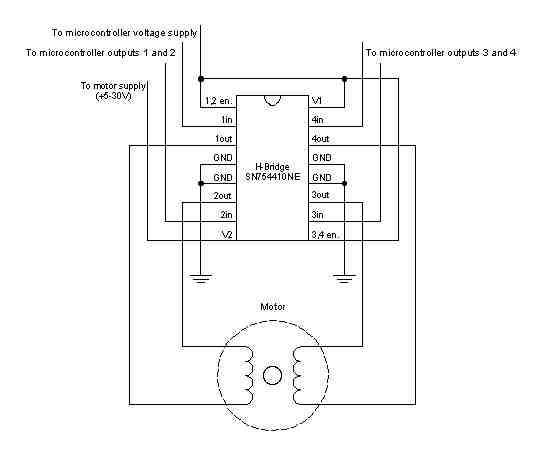
The Arduino or Genuino board will connect to a U2004 Darlington Array if you're using a unipolar stepper or a SN754410NE H-Bridge if you have a bipolar motor.
For more information about the differences of the two types, please take a look at Tom Igoe's page on stepper motors.
Hardware Required 硬件
Arduino or Genuino Board
10k ohm potentiometer
stepper motor
U2004 Darlington Array (if using a unipolar stepper)
SN754410ne H-Bridge (if using a bipolar stepper)
power supply appropriate for your particular stepper
hook-up wires
breadboard
Circuits 电路
Below you'll find circuits for both unipolar and bipolar steppers. In either case, it is best to power your stepper motors from an external supply, as they draw too much to be powered directly from your Arduino board.
In both circuits, connect a 10k pot to power and ground, with it's wiper outputting to analog pin 0.
Note: Both circuits below are four wire configurations. Two wire configurations will not work with the code provided.
Unipolar Stepper Circuit and schematic:
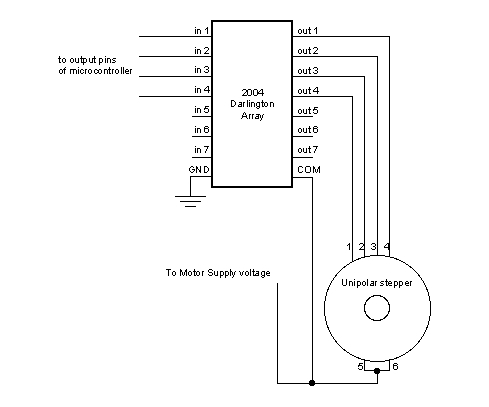
Bipolar Stepper Circuit and schematic:
Code 程序
For both unipolar and bipolar steppers
1 /*
2 * MotorKnob
3 ** A stepper motor follows the turns of a potentiometer (or other sensor) on analog input 0.
4 ** http://www.arduino.cc/en/Reference/Stepper
5 * This example code is in the public domain.
6 */
7
8 #include <Stepper.h>
9 #define STEPS 100 // change this to the number of steps on your motor
10 // create an instance of the stepper class, specifying
11 // the number of steps of the motor and the pins it's attached to
12 Stepper stepper(STEPS, 8, 9, 10, 11);
13 int previous = 0; // the previous reading from the analog input
14
15 void setup()
16 {
17 stepper.setSpeed(30); // set the speed of the motor to 30 RPMs
18 }
19
20 void loop()
21 {
22 int val = analogRead(0); // get the sensor value
23 // move a number of steps equal to the change in the sensor reading
24 stepper.step(val - previous); // remember the previous value of the sensor
25 previous = val;
26 }
例2 Stepper Speed Control 用电位器控制步进电机速度
Control the stepping speed with a potentiometer
硬件与电路部分,与上例同
Code 程序
For both unipolar and bipolar steppers
1 /*
2 Stepper Motor Control - speed control
3 This program drives a unipolar or bipolar stepper motor.
4 The motor is attached to digital pins 8 - 11 of the Arduino.
5 A potentiometer is connected to analog input 0.
6 The motor will rotate in a clockwise direction. The higher the potentiometer value,the faster the motor speed. Because setSpeed() sets the delay between steps,you may notice the motor is less responsive to changes in the sensor value at low speeds.
7
8 Created 30 Nov. 2009,Modified 28 Oct 2010,by Tom Igoe
9 */
10
11 #include <Stepper.h>
12 const int stepsPerRevolution = 200;
13 // change this to fit the number of steps per revolution
14 // for your motor initialize the stepper library on pins 8 through 11:
15 Stepper myStepper(stepsPerRevolution, 8, 9, 10, 11);
16 int stepCount = 0; // number of steps the motor has taken
17
18 void setup()
19 {
20 // nothing to do inside the setup
21 }
22
23 void loop()
24 {
25 int sensorReading = analogRead(A0); // read the sensor value:
26 int motorSpeed = map(sensorReading, 0, 1023, 0, 100);
27 // map it to a range from 0 to 100
28 if (motorSpeed > 0) // set the motor speed:
29 {
30 myStepper.setSpeed(motorSpeed);
31 myStepper.step(stepsPerRevolution / 100); // step 1/100 of a revolution:
32 }
33 }
例3 Stepper One Revolution 正转一圈反转一圈
Turn the shaft one revolution clockwise and one counterclockwise.
硬件与电路部分,与上例同
Code 程序
For both unipolar and bipolar steppers
1 /*
2 Stepper Motor Control - one revolution
3 This program drives a unipolar or bipolar stepper motor.
4 The motor is attached to digital pins 8 - 11 of the Arduino.
5 The motor should revolve one revolution in one direction, then one revolution in the other direction.
6
7 Created 11 Mar. 2007,Modified 30 Nov. 2009,by Tom Igoe
8 */
9 #include <Stepper.h>
10 const int stepsPerRevolution = 200;
11 // change this to fit the number of steps per revolution
12 // for your motor initialize the stepper library on pins 8 through 11:
13 Stepper myStepper(stepsPerRevolution, 8, 9, 10, 11);
14
15 void setup()
16 {
17 myStepper.setSpeed(60); // set the speed at 60 rpm:
18 Serial.begin(9600); // initialize the serial port:
19 }
20
21 void loop()
22 {
23 Serial.println("clockwise"); // step one revolution in one direction:
24 myStepper.step(stepsPerRevolution);
25 delay(500);
26 Serial.println("counterclockwise"); // step one revolution in the other direction:
27 myStepper.step(-stepsPerRevolution);
28 delay(500);
29 }
例4 One step at a time 一次只走一步
Turn the shaft step by step to check the proper wiring of the motor.
硬件与电路部分,与上例同
Code 程序
For both unipolar and bipolar steppers
1 /*
2 Stepper Motor Control - one step at a time
3 This program drives a unipolar or bipolar stepper motor.
4 The motor is attached to digital pins 8 - 11 of the Arduino.
5 The motor will step one step at a time, very slowly. You can use this to test that you've got the four wires of your stepper wired to the correct pins. If wired correctly, all steps should be in the same direction.
6 Use this also to count the number of steps per revolution of your motor,if you don't know it. Then plug that number into the one Revolution example to see if you got it right.
7
8 Created 30 Nov. 2009,by Tom Igoe
9 */
10
11 #include <Stepper.h>
12 const int stepsPerRevolution = 200; // change this to fit the number of steps per revolution
13 // for your motor initialize the stepper library on pins 8 through 11:
14 Stepper myStepper(stepsPerRevolution, 8, 9, 10, 11);
15 int stepCount = 0; // number of steps the motor has taken
16
17 void setup()
18 {
19 Serial.begin(9600); // initialize the serial port:
20 }
21
22 void loop()
23 {
24 myStepper.step(1); // step one step:
25 Serial.print("steps:");
26 Serial.println(stepCount);
27 stepCount++;
28 delay(500);
29 }
步进电机的Arduino库函数的更多相关文章
- 总线SPI的Arduino库函数
来源参考:https://www.cnblogs.com/MyAutomation/p/9348480.html 总线SPI的Arduino库函数 SPI基本知识 SPI:高速同步串行口.是一种标准的 ...
- OneWire总线的Arduino库函数
OneWire总线基本点 One-wire总线是DALLAS公司研制开发的一种协议,采用单根信号线,既传输时钟,又传输数据而且数据传输是双向的.它具有节省I/O 口线资源.结构简单.成本低廉.便于总线 ...
- I2C总线的Arduino库函数
I2C总线的Arduino库函数 I2C即Inter-Integrated Circuit串行总线的缩写,是PHILIPS公司推出的芯片间串行传输总线.它以1根串行数据线(SDA)和1根串行时钟线(S ...
- Arduino库函数中文说明
#define 常量名 常量值 % 取模运算符 String abc / char abc[n] 定义字符串 pinMode(pin,mode); 用于引脚的初始化 mode包括 INPUT ...
- arduino库函数1
https://wenku.baidu.com/view/e657b1f0bcd126fff6050baf.html 的阅读笔记.现在到了 第四十页. setup应该是 在开始 执行一次. 然后 lo ...
- 伺服电机的Arduino库函数
servo.attach(pin) //连接伺服电机的信号线于控制板的引脚,9或10号引脚servo.attach(pin, min, max) servo: a variable of type ...
- Arduino小车学习与研究
信安系统设计基础实践模块 Arduino小车学习与研究 ================== 陈都(20135328) 余佳源(20135321) 莫凡(20135225) ---------- 索引 ...
- Arduino小车学习与研究博客
Arduino小车学习与研究博客 信安系统设计基础实践模块 Arduino小车学习与研究 ================== 陈都(20135328) 余佳源(20135321) 莫凡(201352 ...
- AVR开发 Arduino方法(一) 端口子系统
Arduino UNO R3使用的主处理器ATMega328P上有3个8位的输入/输出端口,它们分别是PB,PC和PD.Arduino IDE提供的Blink示例可以帮助我们了解端口的数字输出功能: ...
随机推荐
- Python 爬虫+tkinter界面 实现历史天气查询
文章目录 一.实现效果 1. python代码 2. 运行效果 二.基本思路 1. 爬虫部分 2. tkinter界面 一.实现效果 很多人学习python,不知道从何学起.很多人学习python,掌 ...
- lidar激光雷达领域的分类
lidar领域可以按分为以下五方面: 激光雷达系统与装备 激光雷达系统与开发 激光雷达光源 激光雷达探测 多光谱激光雷达系统 单光子激光雷达系统 低成本RGB-D距离传感器 激光雷达元器件及装备等 激 ...
- 【Maven】maven脚本中的maven.test.skip和skipTests的区别
命令 两种方式跳过编译 test mvn clean install -DskipTests mvn clean install -Dmaven.test.skip=true -DskipTests, ...
- 01vue.config.js
const path = require('path'); module.exports = { // 基本路径 publicPath: process.env.NODE_ENV === 'pro ...
- C005:计算多项式的值
程序: #include "stdafx.h" int _tmain(int argc, _TCHAR* argv[]) { float x; do{ printf("E ...
- 使用SVG symbols建立图标系统
在实现Web项目的图标系统时,SVG是一个不错的选择.虽然使用SVG创建图标系统有多种方式.在这篇文章中,我们只看其中一种:SVG symbols.这项技术基于两个元素的使用:<symbol&g ...
- RabbitMQ和Kafka的高可用集群原理
前言 小伙伴们,通过前边文章的阅读,相信大家已经对RocketMQ的基本原理有了一个比较深入的了解,那么大家对当前比较常用的RabbitMQ和Kafka是不是也有兴趣了解一些呢,了解的多一些也不是坏事 ...
- flutter dio网络请求封装实现
flutter dio网络请求封装实现 文章友情链接: https://juejin.im/post/6844904098643312648 在Flutter项目中使用网络请求的方式大致可分为两种 ...
- 漏桶、令牌桶限流的Go语言实现
限流 限流又称为流量控制(流控),通常是指限制到达系统的并发请求数. 我们生活中也会经常遇到限流的场景,比如:某景区限制每日进入景区的游客数量为8万人:沙河地铁站早高峰通过站外排队逐一放行的方式限制同 ...
- [LeetCode]394. 字符串解码(栈)
题目 给定一个经过编码的字符串,返回它解码后的字符串. 编码规则为: k[encoded_string],表示其中方括号内部的 encoded_string 正好重复 k 次.注意 k 保证为正整数. ...
