day16-Python运维开发基础(os / os.path / shutil模块)
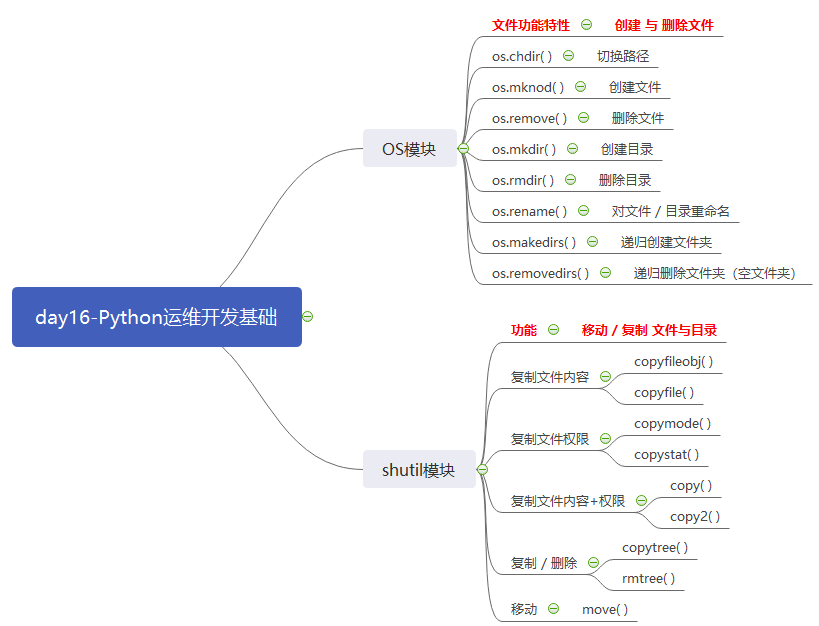
1. OS模块与shutil模块
os :新建/删除
shutil: 复制/移动
# ### os模块 与 shutil模块
"""
os 新建/删除
shutil 复制/移动
"""
import os
os.chdir("/home/wangwen/mywork") #os.mknod 创建文件
# os.mknod("ceshi111.txt") #os.remove 删除文件
# os.remove("ceshi111.txt") #os.mkdir 创建目录(文件夹)
# os.mkdir("ceshi200") #os.rmdir 删除目录(文件夹)
# os.rmdir("ceshi200") #os.rename 对文件,目录重命名
# os.rename("ceshi100","ceshi1001") #os.makedirs 递归创建文件夹
# os.makedirs("a/b/c/d/e/f") #os.removedirs 递归删除文件夹(空文件夹)
# os.removedirs("a/b/c/d/e/f") # ### shutil
import shutil # 1. 单纯仅仅复制文件内容
#copyfileobj(fsrc, fdst[, length=16*1024]) 复制文件 (length的单位是字符(在r模式下,read单位是字符个数,在rb模式read单位是字节个数))
# fp1 = open("ceshi100.py",mode="r",encoding="utf-8")
# fp2 = open("ceshi101.py",mode="w",encoding="utf-8")
# shutil.copyfileobj(fp1,fp2) #copyfile(src,dst) #单纯的仅复制文件内容 , 底层调用了 copyfileobj
# shutil.copyfile("ceshi101.py","ceshi102.py") # 2. 单纯仅仅复制文件权限
#copymode(src,dst) #单纯的仅复制文件权限 , 不包括内容 (虚拟机共享目录都是默认777)
# shutil.copymode("ceshi102.py","103.py") #copystat(src,dst) #复制所有状态信息,包括权限,修改时间等,不包括内容
# shutil.copystat("ceshi102.py","104.py") # 3. 文件内容 + 文件权限
#copy(src,dst) #复制文件权限和内容
# shutil.copy("ceshi102.py","105.py")
#copy2(src,dst) #复制文件权限和内容,还包括权限,时间等
# shutil.copy2("ceshi102.py","106.py") # 4.复制 / 删除
#copytree(src,dst) #拷贝文件夹里所有内容(递归拷贝)
# shutil.copytree("ceshi1001","ceshi1002") #rmtree(path) #删除当前文件夹及其中所有内容(递归删除)
# shutil.rmtree("ceshi1002") # 5.移动 move(path1,paht2) #移动文件或者文件夹
# 移动文件夹
# shutil.move("ceshi1001","../ceshi1003")
# 移动文件
shutil.move("104.py","../111.py")
os模块 与 shutil模块 示例代码
2. os.path 模块

# ### os.path
import os
strvar = "/home/wangwen/mywork/ceshi1.py"
#basename() 返回文件名部分
res = os.path.basename(strvar)
print(res) #dirname() 返回路径部分
res = os.path.dirname(strvar)
print(res) #split() 将路径拆分成单独的文件部分和路径部分 组合成一个元组
res = os.path.split(strvar)
print(res) #join() 将多个路径和文件组成新的路径 可以自动通过不同的系统加不同的斜杠 linux / windows\
path1 = "home"
path2 = "wangwen"
path3 = "mywork"
# 方法一
pathvar = path1 + os.sep + path2 + os.sep + path3
print(pathvar)
# 方法二
pathvar = os.path.join(path1,path2,path3)
print(pathvar)
# d:\home\wangwen\mywork
# D:\gongxiang8\day16
# /home/wangwen/mywork/ #splitext() 将路径分割为后缀和其他部分 (了解)
strvar = "/home/wangwen/mywork/ceshi1.py"
res = os.path.splitext(strvar)
print(res)
# 用字符串中的split也可以分割出后缀部分
a,b = strvar.split(".")
print(a,b) #getsize() 获取文件的大小
res = os.path.getsize("1.py")
print(res) # ### isdir / isfile / islink
#isdir() 检测路径是否是一个文件夹
res = os.path.isdir("ceshi100")
print(res) #isfile() 检测路径是否是一个文件
res = os.path.isfile("1.py")
print(res) #islink() 检测路径数否是一个链接
res = os.path.islink("/home/wangwen/ceshi200/ceshi100")
print(res) # ### getctime / getmtime / getatime
#getctime() [windows]文件的创建时间,[linux]权限的改动时间(返回时间戳)
pathvar = "/home/wangwen/mywork/103.py"
res = os.path.getctime(pathvar)
print(res) import time
str_time = time.ctime(res)
print(str_time) #getmtime() 获取文件最后一次修改时间(返回时间戳)
res = os.path.getmtime(pathvar)
print(res) import time
str_time = time.ctime(res)
print(str_time) #getatime() 获取文件最后一次访问时间(返回时间戳)
res = os.path.getatime(pathvar)
print(res) import time
str_time = time.ctime(res)
print(str_time) #exists() 检测指定的路径是否存在
pathvar = "/home/wangwen/mywork/10323223.py"
res = os.path.exists(pathvar)
print(res) #isabs() 检测一个路径是否是绝对路径
pathvar = "."
res = os.path.isabs(pathvar)
print(res) #abspath() 将相对路径转化为绝对路径
res = os.path.abspath(pathvar)
print(res) # 结合使用
if not os.path.isabs(pathvar):
pathnew = os.path.abspath(pathvar)
print(pathnew)
os.path 模块 示例代码
# ### 如何计算一个文件夹中所有文件的大小
import os
pathvar = "/mnt/hgfs/gongxiang8/day16/ceshi100"
# (1)获取文件夹中所有的文件名称
lst = os.listdir(pathvar)
print(lst)
"""
拼接路径,计算文件大小
res = os.path.join(pathvar,"1.txt")
print(res) # "/mnt/hgfs/gongxiang8/day16/ceshi100/1.txt"
res2 = os.path.getsize(res)
print(res2)
""" # (2)计算所有文件的大小 [缺陷:不能计算文件夹中的内容]
size = 0
for i in lst:
pathnew = os.path.join(pathvar,i)
# 判断是否是文件
if os.path.isfile(pathnew):
print(i,"[是文件]")
size += os.path.getsize(pathnew)
# 判断是否是文件夹
elif os.path.isdir(pathnew):
print(i,"[是文件夹]") # (3)使用递归计算文件夹中所有文件大小
def getallsize(pathvar):
size = 0
lst = os.listdir(pathvar)
for i in lst:
# 路径 + 文件名 => 绝对路径
pathnew = os.path.join(pathvar,i)
if os.path.isfile(pathnew):
# 计算文件大小
size += os.path.getsize(pathnew)
elif os.path.isdir(pathnew):
size += getallsize(pathnew) return size
res = getallsize(pathvar)
print(res)
如何计算一个文件夹中所有文件的大小 示例代码
3. tarfile 压缩模块

# ### tarfile 压缩模块 后缀为.tar | .tar.gz | .tar.bz2
import tarfile # ### 1.创建tar压缩包 [官方: 理论上可以压缩到最小的模式是bz2]
# (1) 创建压缩包
""".tar的压缩包,只打包不压缩 276480"""
tf = tarfile.open("ceshi1029.tar","w",encoding="utf-8")
# (2) 写入文件到压缩包中
tf.add("/bin/ntfscmp","ntfscmp")
tf.add("/bin/openvt","openvt")
tf.add("/bin/grep","tmp/grep")
# (3) 关闭压缩包
tf.close() # 2.创建.tar.gz压缩包 120462
tf = tarfile.open("ceshi1030.tar.gz","w:gz",encoding="utf-8")
tf.add("/bin/ntfscmp","ntfscmp")
tf.add("/bin/openvt","openvt")
tf.add("/bin/grep","tmp/grep")
tf.close() # 3.创建.tar.bz2压缩包 115728
tf = tarfile.open("ceshi1031.tar.bz2","w:bz2",encoding="utf-8")
tf.add("/bin/ntfscmp","ntfscmp")
tf.add("/bin/openvt","openvt")
tf.add("/bin/grep","tmp/grep")
tf.close() # ### 2.解压压缩包
tf = tarfile.open("ceshi1030.tar.gz","r",encoding="utf-8")
# extract(文件,路径)
# tf.extract("ntfscmp","ceshi1030")
# extractall(路径)
tf.extractall("ceshi1030")
tf.close() # ### 3.追加文件 支持with语法
with tarfile.open("ceshi1029.tar","a",encoding="utf-8") as tf :
tf.add("/bin/gzip","gzip") # error tarfile中的追加,只能是对只打包不压缩的包进行追加,其他的模式不可以;
"""
with tarfile.open("ceshi1031.tar.bz2","a",encoding="utf-8") as tf:
tf.add("/bin/gzip","gzip")
""" # ### 4.查看压缩包中的内容
with tarfile.open("ceshi1029.tar","r",encoding="utf-8") as tf :
lst = tf.getnames()
print(lst) # ### 如何解决tarfile中存在的缺陷?(不能追加文件到已经压缩的包)
"""
(1) 先解压所有文件到文件夹
(2) 把想要追加的内容复制到文件夹中
(3) 经过过滤筛选,重新打包压缩
"""
import os
# 获取当前脚本所在的路径
pathvar = os.getcwd()
# print(res) # /mnt/hgfs/gongxiang8/day16 # 压缩包路径
path1 = os.path.join(pathvar,"ceshi1031.tar.bz2")
print(path1)
# 解压的路径
path2 = os.path.join(pathvar,"ceshi1031") # (1) 先解压所有文件到文件夹
with tarfile.open( path1 , "r",encoding="utf-8") as tf:
tf.extractall(path2) # (2) 把想要追加的内容复制到文件夹中
mybin = "cp -a /bin/ip " + path2 # cp -a /bin/ip /mnt/hgfs/gongxiang8/day16/ceshi1031
os.system(mybin) # (3) 经过过滤筛选,重新打包压缩
lst = os.listdir(path2)
print(lst) with tarfile.open(path1,"w:bz2",encoding="utf-8") as tf:
for i in lst:
if i != "openvt":
# 拼接绝对路径
pathnew = os.path.join(path2,i)
# add(路径,别名)
tf.add(pathnew,i)
tarfile 压缩模块 示例代码
day16
day16-Python运维开发基础(os / os.path / shutil模块)的更多相关文章
- Python运维开发基础09-函数基础【转】
上节作业回顾 #!/usr/bin/env python3 # -*- coding:utf-8 -*- # author:Mr.chen # 实现简单的shell命令sed的替换功能 import ...
- Python运维开发基础08-文件基础【转】
一,文件的其他打开模式 "+"表示可以同时读写某个文件: r+,可读写文件(可读:可写:可追加) w+,写读(不常用) a+,同a(不常用 "U"表示在读取时, ...
- Python运维开发基础06-语法基础【转】
上节作业回顾 (讲解+温习120分钟) #!/usr/bin/env python3 # -*- coding:utf-8 -*- # author:Mr.chen # 添加商家入口和用户入口并实现物 ...
- Python运维开发基础05-语法基础【转】
上节作业回顾(讲解+温习90分钟) #!/usr/bin/env python # -*- coding:utf-8 -*- # author:Mr.chen import os,time Tag = ...
- Python运维开发基础04-语法基础【转】
上节作业回顾(讲解+温习90分钟) #!/usr/bin/env python3 # -*- coding:utf-8 -*- # author:Mr.chen # 仅用列表+循环实现“简单的购物车程 ...
- Python运维开发基础03-语法基础 【转】
上节作业回顾(讲解+温习60分钟) #!/usr/bin/env python3 # -*- coding:utf-8 -*- # author:Mr.chen #只用变量和字符串+循环实现“用户登陆 ...
- Python运维开发基础10-函数基础【转】
一,函数的非固定参数 1.1 默认参数 在定义形参的时候,提前给形参赋一个固定的值. #代码演示: def test(x,y=2): #形参里有一个默认参数 print (x) print (y) t ...
- Python运维开发基础07-文件基础【转】
一,文件的基础操作 对文件操作的流程 [x] :打开文件,得到文件句柄并赋值给一个变量 [x] :通过句柄对文件进行操作 [x] :关闭文件 创建初始操作模板文件 [root@localhost sc ...
- Python运维开发基础02-语法基础【转】
上节作业回顾(讲解+温习60分钟) #!/bin/bash #user login User="yunjisuan" Passwd="666666" User2 ...
- Python运维开发基础01-语法基础【转】
开篇导语 整个Python运维开发教学采用的是最新的3.5.2版,当遇到2.x和3.x版本的不同点时,会采取演示的方式,让同学们了解. 教学预计分为四大部分,Python开发基础,Python开发进阶 ...
随机推荐
- laravel npm安装yarn
npm install -g yarn yarn install --no-bin-links yarn add cross-env npm run dev Laravel 默认集成了一些 NPM 扩 ...
- jmh 微基准测试
选择依据:对某段代码的性能测试. 1.运行方法 mvn clean install java -jar target/benchmarks.jar JMHSample_02 -f 1 2.maven ...
- Linux 的三种软件安装包介绍
通过RPM软件包来安装 说起RPM(RedHat Package Management)标准的软件包,大家可能都会想起大名鼎鼎的REDHAT公司,正是RPM软件包发行方式的出现,使Linux中的应用软 ...
- Spring学习(十)
需要的jar包 1.Spring核心必须依赖的库:commons-logging-1.1.1.jar2.Spring IoC部分核心库: spring-beans-4.3.9.RELEASE.jar ...
- 【原】tcp三次握手和四次挥手
- ipfs 资料汇集
目录 js ipfs u can use wikipeida here js ipfs https://github.com/ipfs/js-ipfs u can use wikipeida here ...
- Python学习第二十四课——Mysql 外键约束
外键:主要是关联两个表的 举个栗子:在建表中创建外键 -- 添加外键例子 CREATE TABLE teacher( id TINYINT PRIMARY KEY auto_increment, na ...
- Python学习第二十一课——Mysql 对数据库的基本操作
数据库操作(DDL) 在数据库下创建表(create_table) 创建表代码块: CREATE TABLE employee( id TINYINT PRIMARY KEY auto_increme ...
- 如何用 pycharm 调试 airflow
airflow 和 pycharm 相关基础知识请看其他博客 我们在使用 airflow的 dag时. 每次写完不知道对不对的,总不能到页面环境中跑一下,等到报错再调试吧.这是很让人恼火的事情 这里我 ...
- SpringMVC笔记三
课程安排: 第一天:springmvc的基础知识 什么是springmvc? springmvc框架原理(掌握) 前端控制器.处理器映射器.处理器适配器.视图解析器 springmvc入门程序 目的: ...
