扩展卡尔曼滤波(MRPT)
扩展卡尔曼滤波的状态方程和观测方程可以是非线性的。在一般情况下,无法确定过程噪声、测量噪声与方程的函数关系,因此可以简化为加性噪声: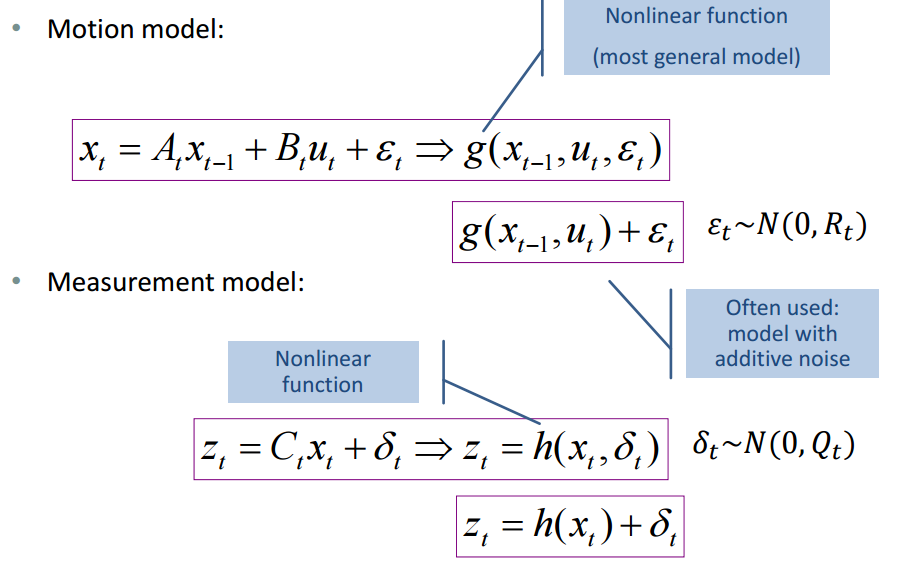
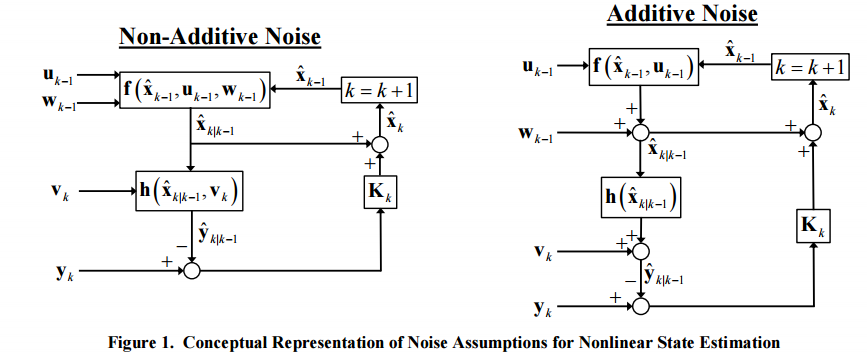
EKF relies on a linearisation of the evolution and observation functions which are good approximations of the original functions if these functions are close to linear. The state-space formulation of EKF reads :
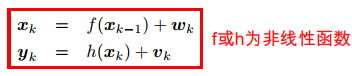
Non-linear evolution and observation functions are handled within EKF by linearising these functions around some estimates of the state; for example for the evolution function is linearized around the previous estimate of the state $\hat{x}_k$:
$$f\left(x_k\right)\approx f\left(\hat{x}_k\right)+\frac{\partial f}{\text{dx}}\left(\hat{x}_k\right)\left(x_k-\hat{x}_k\right)$$
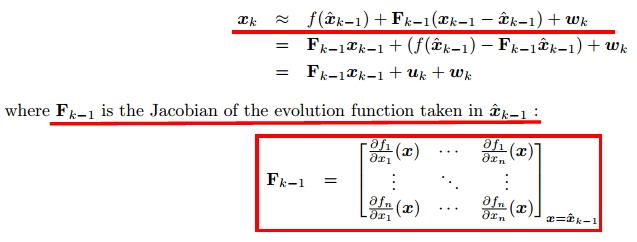
The first step in applying EKF is to linearize the evolution function around the previous estimate of the state $\hat{x}_{k-1}$
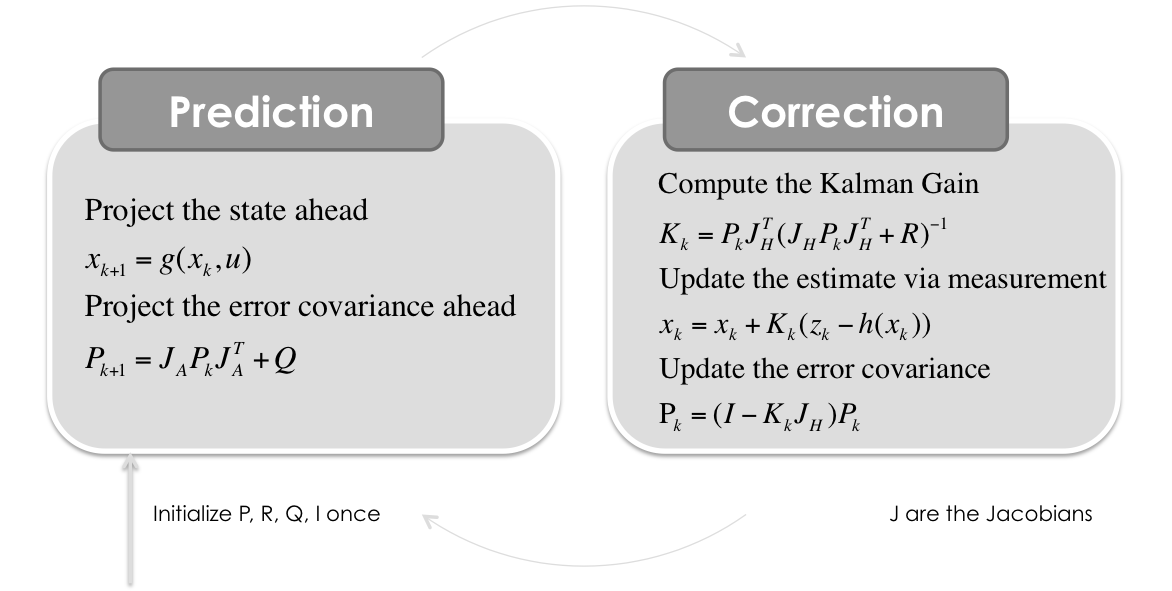
扩展卡尔曼滤波流程如下图所示:
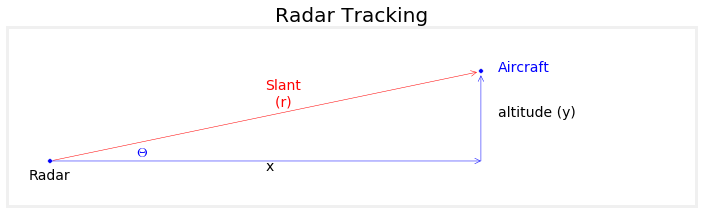
一个简单的例子:假设一架飞机以恒定水平速度飞行(高度不变),地面上有一个雷达可以发射电磁波测量飞机到雷达的距离$r$。则有如下关系:
$$\theta=arctan(\frac{y}{x})$$
$$r^2=x^2+y^2$$
我们想知道某一时刻飞机的水平位置和垂直高度,以水平位置、水平速度、垂直高度作为状态变量:
$$\mathbf{\textbf{x}}=\left(\begin{array}{c}\text{distance} \\\text{velocity} \\\text{altitude}\end{array}\right)=\left(\begin{array}{c}x \\\dot{x} \\y\end{array}\right)$$
则观测值与状态变量之间的关系为:$h\left(\hat{x}\right)=\sqrt{x^2+y^2}$,可以看出这是一个非线性的表达式。对于这个问题来说,观测方程的雅克比矩阵为:$J_H=\left[\frac{\partial h}{\partial x}\quad\frac{\partial h}{\partial \dot{x}}\quad\frac{\partial h}{\partial y}\text{ }\right]$,即
$$J_H=\left[\frac{x}{\sqrt{x^2+y^2}} \quad 0 \quad \frac{y}{\sqrt{x^2+y^2}}\right]$$
状态转移方程的雅克比矩阵为:

得到上述矩阵后我们就可以设定初值和噪声,然后根据流程图中的步骤进行迭代计算。
- MRPT中的卡尔曼滤波器
卡尔曼滤波算法都集中在 mrpt::bayes::CKalmanFilterCapable这个虚类中。 这个类中包括系统状态向量和系统协方差矩阵,以及根据选择的算法执行一个完整迭代的通用方法。在解决一个特定问题时需要从这个虚类派生一个新的类,并实现状态转移函数、观测函数以及它们的雅克比矩阵(采用EKF时)。内部的mrpt::bayes::CKalmanFilterCapable::runOneKalmanIteration()函数会依次调用用户改写的虚函数,每调用一次该函数执行一步预测+校正操作(runOneKalmanIteration():The main entry point, executes one complete step: prediction + update)
使用MRPT解决上述问题的C++代码如下:
#include <mrpt/bayes/CKalmanFilterCapable.h>
#include <mrpt/random.h>
#include <mrpt/system/os.h>
#include <mrpt/system/threads.h> #include <iostream> using namespace mrpt;
using namespace mrpt::bayes;
using namespace mrpt::math;
using namespace mrpt::utils;
using namespace mrpt::random;
using namespace std; #define DELTA_TIME 0.05f // Time Step between Filter Steps // 系统状态变量初始值(猜测值)
#define VEHICLE_INITIAL_X 10.0f
#define VEHICLE_INITIAL_Y 2000.0f
#define VEHICLE_INITIAL_V 200.0f #define TRANSITION_MODEL_STD 1.0f // 模型噪声
#define RANGE_SENSOR_NOISE_STD 5.0f // 传感器噪声 /* --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Virtual base for Kalman Filter (EKF,IEKF,UKF) implementations.
template<size_t VEH_SIZE, size_t OBS_SIZE, size_t FEAT_SIZE, size_t ACT_SIZE, typename KFTYPE>
class mrpt::bayes::CKalmanFilterCapable< VEH_SIZE, OBS_SIZE, FEAT_SIZE, ACT_SIZE, KFTYPE > The meaning of the template parameters is:
VEH_SIZE: The dimension of the "vehicle state"(系统状态变量数目)
OBS_SIZE: The dimension of each observation (eg, 2 for pixel coordinates, 3 for 3D coordinates,etc).(观测量维数)
FEAT_SIZE: The dimension of the features in the system state (the "map"), or 0 if not applicable (the default if not implemented).
ACT_SIZE: The dimension of each "action" u_k (or 0 if not applicable).(控制量的维数)
KFTYPE: The numeric type of the matrices (default: double) This base class stores the state vector and covariance matrix of the system. It has virtual methods
that must be completed by derived classes to address a given filtering problem.
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- */
// Implementation of the system models as a EKF
class CRange: public CKalmanFilterCapable<, , , >
{
public:
CRange( );
virtual ~CRange(); void Process( double DeltaTime, double observationRange); void getState( KFVector &xkk, KFMatrix &pkk)
{
xkk = m_xkk; //The system state vector.
pkk = m_pkk; //The system full covariance matrix
} protected:
float m_obsRange; // 观测值
float m_deltaTime; // Time Step between Filter Steps // return the action vector u
void OnGetAction( KFArray_ACT &out_u ) const; // Implements the transition model
void OnTransitionModel(const KFArray_ACT &in_u,KFArray_VEH &inout_x,bool &out_skipPrediction) const; // Implements the transition Jacobian
void OnTransitionJacobian(KFMatrix_VxV &out_F ) const; // Implements the transition noise covariance
void OnTransitionNoise(KFMatrix_VxV &out_Q ) const; // Return the observation NOISE covariance matrix, that is, the model of the Gaussian additive noise of the sensor.
void OnGetObservationNoise(KFMatrix_OxO &out_R) const; /** This is called between the KF prediction step and the update step
* This method will be called just once for each complete KF iteration.
* \note It is assumed that the observations are independent, i.e. there are NO cross-covariances between them.
*/
void OnGetObservationsAndDataAssociation(
vector_KFArray_OBS &out_z,
mrpt::vector_int &out_data_association,
const vector_KFArray_OBS &in_all_predictions,
const KFMatrix &in_S,
const vector_size_t &in_lm_indices_in_S,
const KFMatrix_OxO &in_R
); // Implements the observation prediction
void OnObservationModel(const vector_size_t &idx_landmarks_to_predict,vector_KFArray_OBS &out_predictions) const; // Implements the observation Jacobians
void OnObservationJacobians(const size_t &idx_landmark_to_predict,KFMatrix_OxV &Hx,KFMatrix_OxF &Hy) const;
}; CRange::CRange()
{
KF_options.method = kfEKFNaive; // 状态变量初始值 State: (x,vx,y)
m_xkk.resize(); //对于动态矩阵可以通过resize()函数来动态修改矩阵的大小
m_xkk[]= VEHICLE_INITIAL_X;
m_xkk[]= VEHICLE_INITIAL_V;
m_xkk[]= VEHICLE_INITIAL_Y; // Initial cov: Large uncertainty
m_pkk.setSize(,);
m_pkk.unit();
m_pkk = * m_pkk;
} CRange::~CRange()
{ } void CRange::Process( double DeltaTime, double observationRange)
{
m_deltaTime = (float)DeltaTime;
m_obsRange = (float)observationRange; runOneKalmanIteration(); // executes one complete step: prediction + update
} // Must return the action vector u.
// param out_u: The action vector which will be passed to OnTransitionModel
void CRange::OnGetAction( KFArray_ACT &out_u ) const
{ } /** Implements the transition model(Project the state ahead)
param in_u : The vector returned by OnGetAction.
param inout_x: prediction value
param out_skip: Set this to true if for some reason you want to skip the prediction step. Default:false
*/
void CRange::OnTransitionModel(const KFArray_ACT &in_u, KFArray_VEH &inout_x, bool &out_skipPrediction) const
{
// The constant-velocities model is implemented simply as:
inout_x[] += m_deltaTime * inout_x[];
inout_x[] = inout_x[];
inout_x[] = inout_x[];
} /** Implements the transition Jacobian
param out_F Must return the Jacobian.
The returned matrix must be N*N with N being the size of the whole state vector.
*/
void CRange::OnTransitionJacobian(KFMatrix_VxV &F) const
{
F.unit();
F(,) = m_deltaTime;
} /** Implements the transition noise covariance
param out_Q Must return the covariance matrix.
The returned matrix must be of the same size than the jacobian from OnTransitionJacobian
*/
void CRange::OnTransitionNoise(KFMatrix_VxV &Q) const
{
Q.unit();
Q *= square(TRANSITION_MODEL_STD);
} /** Return the observation NOISE covariance matrix, that is, the model of the Gaussian additive noise of the sensor.
param out_R : The noise covariance matrix. It might be non diagonal, but it'll usually be.
*/
void CRange::OnGetObservationNoise(KFMatrix_OxO &R) const
{
R.unit();
R *= square(RANGE_SENSOR_NOISE_STD);
} // This is called between the KF prediction step and the update step
void CRange::OnGetObservationsAndDataAssociation(
vector_KFArray_OBS &out_z,
mrpt::vector_int &out_data_association,
const vector_KFArray_OBS &in_all_predictions,
const KFMatrix &in_S,
const vector_size_t &in_lm_indices_in_S,
const KFMatrix_OxO &in_R
)
{
//out_z: N vectors, N being the number of "observations"
out_z.resize();
out_z[][] = m_obsRange;
} /** Implements the observation prediction
param idx_landmark_to_predict: The indices of the landmarks in the map whose predictions are expected as output. For non SLAM-like problems, this input value is undefined and the application should just generate one observation for the given problem.
param out_predictions: The predicted observations.
*/
void CRange::OnObservationModel(const vector_size_t &idx_landmarks_to_predict,vector_KFArray_OBS &out_predictions) const
{
// idx_landmarks_to_predict is ignored in NON-SLAM problems
out_predictions.resize();
out_predictions[][] = sqrt( square(m_xkk[]) + square(m_xkk[]) );
} // Implements the observation Jacobians
void CRange::OnObservationJacobians(const size_t &idx_landmark_to_predict,KFMatrix_OxV &Hx,KFMatrix_OxF &Hy) const
{
Hx.zeros();
Hx(,) = m_xkk[] / sqrt(square(m_xkk[])+square(m_xkk[]));
Hx(,) = m_xkk[] / sqrt(square(m_xkk[])+square(m_xkk[]));
} int main ()
{
// Create class instance
CRange EKF;
EKF.KF_options.method = kfEKFNaive; //select the KF algorithm // Initiate simulation
float x=, y=, v=; //状态变量真实值
float t=; while (!mrpt::system::os::kbhit())
{
// Simulate noisy observation:
x += v * DELTA_TIME;
float realRange = sqrt(square(x)+square(y)); // double mrpt::random::CRandomGenerator::drawGaussian1D_normalized(double * likelihood = NULL)
// Generate a normalized (mean=0, std=1) normally distributed sample
float obsRange = max(0.0, realRange + RANGE_SENSOR_NOISE_STD * randomGenerator.drawGaussian1D_normalized() ); printf("Real/Simulated range: %.03f / %.03f \n", realRange, obsRange ); // Process with EKF
EKF.Process(DELTA_TIME, obsRange); // Show EKF state:
CRange::KFVector EKF_xkk;
CRange::KFMatrix EKF_pkk;
EKF.getState( EKF_xkk, EKF_pkk ); printf("Real state: x:%.03f v=%.03f y=%.03f \n",x,v,y);
cout << "EKF estimation:" <<endl<< EKF_xkk << endl;
cout <<"-------------------------------------------"<<endl; // Delay(An OS-independent method for sending the current thread to "sleep" for a given period of time)
mrpt::system::sleep((int)(DELTA_TIME*));
t += DELTA_TIME;
} return ;
}
运行一段时间后结果如下图所示,可以看出状态变量基本收敛到真实值(由于传感器和模型噪声不可消除,因此只能是对真实状态的最优估计)。

参考:
Eigen: C++开源矩阵计算工具——Eigen的简单用法
KFilter - Free C++ Extended Kalman Filter Library
How to Use this Extended Kalman Filter Library?
http://www.mrpt.org/Kalman_Filters
http://reference.mrpt.org/devel/classmrpt_1_1bayes_1_1_c_kalman_filter_capable.html
https://github.com/MRPT/mrpt/blob/master/samples/bayesianTracking/test.cpp
扩展卡尔曼滤波(MRPT)的更多相关文章
- Google Cardboard的九轴融合算法——基于李群的扩展卡尔曼滤波
Google Cardboard的九轴融合算法 --基于李群的扩展卡尔曼滤波 极品巧克力 前言 九轴融合算法是指通过融合IMU中的加速度计(三轴).陀螺仪(三轴).磁场计(三轴),来获取物体姿态的方法 ...
- 扩展卡尔曼滤波EKF与多传感器融合
参考:https://blog.csdn.net/young_gy/article/details/78468153 Extended Kalman Filter(扩展卡尔曼滤波)是卡尔曼滤波的非线性 ...
- 卡尔曼滤波—Simple Kalman Filter for 2D tracking with OpenCV
之前有关卡尔曼滤波的例子都比较简单,只能用于简单的理解卡尔曼滤波的基本步骤.现在让我们来看看卡尔曼滤波在实际中到底能做些什么吧.这里有一个使用卡尔曼滤波在窗口内跟踪鼠标移动的例子,原作者主页:http ...
- 卡尔曼滤波(kalman)相关理论以及与HMM、最小二乘法关系
一.什么是卡尔曼滤波 在雷达目标跟踪中,通常会用到Kalman滤波来形成航迹,以前没有学过机器学习相关知识,学习Kalman时,总感觉公式看完就忘,而且很多东西云里雾里并不能深入理解,最后也就直接套那 ...
- 卡尔曼滤波——基本假设(1)线性系统(2)高斯分布 根据x(t) 求解x(t+1)
from:https://blog.csdn.net/u010720661/article/details/63253509 原文链接:http://www.bzarg.com/p/how-a-kal ...
- Gmapping笔记
2D-slam 激光slam: 开源代码的比较HectorSLAM Gmapping KartoSLAM CoreSLAM LagoSLAM 作者:kint_zhao 原文:https://blog. ...
- 【深度学习Deep Learning】资料大全
最近在学深度学习相关的东西,在网上搜集到了一些不错的资料,现在汇总一下: Free Online Books by Yoshua Bengio, Ian Goodfellow and Aaron C ...
- EKF的理解
若已知参考点(landmarks)的坐标,则状态向量中不必含有xL, 从而实现的仅为机器人在已知环境中的定位,求解大大减少(状态向量维度仅为运动状态).若想实现完整SLAM,必须将xL加入状态向量中. ...
- SLAM学习笔记(1)基本概念
SLAM (simultaneous localization and mapping),也称为CML (Concurrent Mapping and Localization), 即时定位与地图构建 ...
随机推荐
- javascript中的闭包、模块与模块加载
一.前言 闭包是基于词法作用域( 和动态作用域对应,词法作用域是由你写代码时,将变量写在哪里来决定的,因此当词法分析器处理代码时,会保持作用)书写代码时所产生的自然结果,甚至不需要为了利用闭包而有意 ...
- Spark on Yarn:任务提交参数配置
当在YARN上运行Spark作业,每个Spark executor作为一个YARN容器运行.Spark可以使得多个Tasks在同一个容器里面运行. 以下参数配置为例子: spark-submit -- ...
- IIS无法加载字体文件(*.woff,*.svg)的解决办法
在编写前端代码的过程中经常会遇到使用特定的字体(*.woff,*.svg),此时在加载字体时请求会被返回 Failed to load resource: the server responded w ...
- Python常见的运行错误
(1)忘记在 if , elif , else , for , while , class ,def 声明末尾添加 :(导致 "SyntaxError :invalid syntax&quo ...
- Timusoj 1982. Electrification Plan
http://acm.timus.ru/problem.aspx?space=1&num=1982 1982. Electrification Plan Time limit: 0.5 sec ...
- 【C# 进阶】事件!直接上事件!
http://www.tracefact.net/csharp-programming/delegates-and-events-in-csharp.aspx ZiYang 张,何许人也?看了他写的博 ...
- WebApi 通过类名获取类并实例化
环境:Web Api 返回值类型为DTO实体,继承基类DTO---BaseResultDto public class BaseResultDto { /// <summary> /// ...
- Ubuntu14.04安装OpenCV2.4.9
1.安装依赖 sudo apt-get install build-essential libgtk2.0-dev libjpeg-dev libtiff4-dev libjasper-dev lib ...
- 数据绑定控件之Repeater
引言 前几篇的文章在说AJAX的内容,利用AJAX技术能够开发出高效运行的网站应用程序,不过在进行B/S项目开发时只拥有AJAX技术是远远不够的,踏入到B/S要学的东西会更多,但相较C/S的复杂逻辑结 ...
- Ideas about the future of management
1. Business markets a. greater competition among companies b. increase in power of global companies ...
