Matplotlib绘图设置---图形颜色和风格调整
绘图函数
plt.plot()函数可以通过相应的参数设置绘图风格。
plt.plot(*args, scalex=True, scaley=True, data=None, **kwargs)
Docstring:
Plot y versus x as lines and/or markers.
Call signatures::
plot([x], y, [fmt], *, data=None, **kwargs)
plot([x], y, [fmt], [x2], y2, [fmt2], ..., **kwargs)
The coordinates of the points or line nodes are given by *x*, *y*.
The optional parameter *fmt* is a convenient way for defining basic
formatting like color, marker and linestyle. It's a shortcut string
notation described in the *Notes* section below.
>>> plot(x, y) # plot x and y using default line style and color
>>> plot(x, y, 'bo') # plot x and y using blue circle markers
>>> plot(y) # plot y using x as index array 0..N-1
>>> plot(y, 'r+') # ditto, but with red plusses
You can use `.Line2D` properties as keyword arguments for more
control on the appearance. Line properties and *fmt* can be mixed.
The following two calls yield identical results:
>>> plot(x, y, 'go--', linewidth=2, markersize=12)
>>> plot(x, y, color='green', marker='o', linestyle='dashed',
... linewidth=2, markersize=12)
When conflicting with *fmt*, keyword arguments take precedence.
**Plotting labelled data**
There's a convenient way for plotting objects with labelled data (i.e.
data that can be accessed by index ``obj['y']``). Instead of giving
the data in *x* and *y*, you can provide the object in the *data*
parameter and just give the labels for *x* and *y*::
>>> plot('xlabel', 'ylabel', data=obj)
All indexable objects are supported. This could e.g. be a `dict`, a
`pandas.DataFame` or a structured numpy array.
**Plotting multiple sets of data**
There are various ways to plot multiple sets of data.
- The most straight forward way is just to call `plot` multiple times.
Example:
>>> plot(x1, y1, 'bo')
>>> plot(x2, y2, 'go')
- Alternatively, if your data is already a 2d array, you can pass it
directly to *x*, *y*. A separate data set will be drawn for every
column.
Example: an array ``a`` where the first column represents the *x*
values and the other columns are the *y* columns::
>>> plot(a[0], a[1:])
- The third way is to specify multiple sets of *[x]*, *y*, *[fmt]*
groups::
>>> plot(x1, y1, 'g^', x2, y2, 'g-')
In this case, any additional keyword argument applies to all
datasets. Also this syntax cannot be combined with the *data*
parameter.
By default, each line is assigned a different style specified by a
'style cycle'. The *fmt* and line property parameters are only
necessary if you want explicit deviations from these defaults.
Alternatively, you can also change the style cycle using the
'axes.prop_cycle' rcParam.
Parameters
----------
x, y : array-like or scalar
The horizontal / vertical coordinates of the data points.
*x* values are optional and default to `range(len(y))`.
Commonly, these parameters are 1D arrays.
They can also be scalars, or two-dimensional (in that case, the
columns represent separate data sets).
These arguments cannot be passed as keywords.
fmt : str, optional
A format string, e.g. 'ro' for red circles. See the *Notes*
section for a full description of the format strings.
Format strings are just an abbreviation for quickly setting
basic line properties. All of these and more can also be
controlled by keyword arguments.
This argument cannot be passed as keyword.
data : indexable object, optional
An object with labelled data. If given, provide the label names to
plot in *x* and *y*.
.. note::
Technically there's a slight ambiguity in calls where the
second label is a valid *fmt*. `plot('n', 'o', data=obj)`
could be `plt(x, y)` or `plt(y, fmt)`. In such cases,
the former interpretation is chosen, but a warning is issued.
You may suppress the warning by adding an empty format string
`plot('n', 'o', '', data=obj)`.
Other Parameters
----------------
scalex, scaley : bool, optional, default: True
These parameters determined if the view limits are adapted to
the data limits. The values are passed on to `autoscale_view`.
**kwargs : `.Line2D` properties, optional
*kwargs* are used to specify properties like a line label (for
auto legends), linewidth, antialiasing, marker face color.
Example::
>>> plot([1,2,3], [1,2,3], 'go-', label='line 1', linewidth=2)
>>> plot([1,2,3], [1,4,9], 'rs', label='line 2')
If you make multiple lines with one plot command, the kwargs
apply to all those lines.
Here is a list of available `.Line2D` properties:
agg_filter: a filter function, which takes a (m, n, 3) float array and a dpi value, and returns a (m, n, 3) array
alpha: float
animated: bool
antialiased or aa: bool
clip_box: `.Bbox`
clip_on: bool
clip_path: [(`~matplotlib.path.Path`, `.Transform`) | `.Patch` | None]
color or c: color
contains: callable
dash_capstyle: {'butt', 'round', 'projecting'}
dash_joinstyle: {'miter', 'round', 'bevel'}
dashes: sequence of floats (on/off ink in points) or (None, None)
drawstyle or ds: {'default', 'steps', 'steps-pre', 'steps-mid', 'steps-post'}, default: 'default'
figure: `.Figure`
fillstyle: {'full', 'left', 'right', 'bottom', 'top', 'none'}
gid: str
in_layout: bool
label: object
linestyle or ls: {'-', '--', '-.', ':', '', (offset, on-off-seq), ...}
linewidth or lw: float
marker: marker style
markeredgecolor or mec: color
markeredgewidth or mew: float
markerfacecolor or mfc: color
markerfacecoloralt or mfcalt: color
markersize or ms: float
markevery: None or int or (int, int) or slice or List[int] or float or (float, float)
path_effects: `.AbstractPathEffect`
picker: float or callable[[Artist, Event], Tuple[bool, dict]]
pickradius: float
rasterized: bool or None
sketch_params: (scale: float, length: float, randomness: float)
snap: bool or None
solid_capstyle: {'butt', 'round', 'projecting'}
solid_joinstyle: {'miter', 'round', 'bevel'}
transform: `matplotlib.transforms.Transform`
url: str
visible: bool
xdata: 1D array
ydata: 1D array
zorder: float
Returns
-------
lines
A list of `.Line2D` objects representing the plotted data.
颜色设置
通过color参数设置。
#标准颜色名称
plt.plot(x, np.sin(x-0), color='blue')
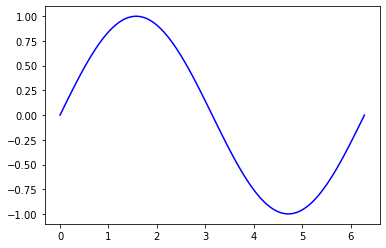
#缩写颜色代码(rgbcmyk)
plt.plot(x, np.sin(x-1), color='g')
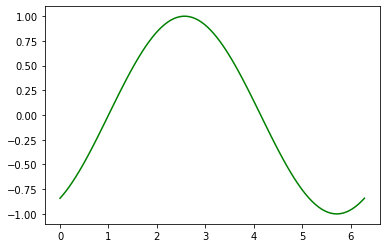
#范围在0~1的灰度值
plt.plot(x, np.sin(x-2), color='0.75')
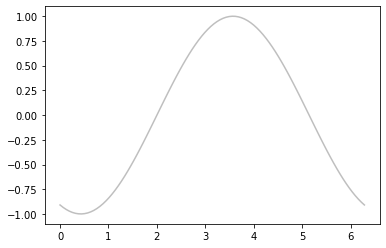
#十六进制(RRGGBB, 00~FF)
plt.plot(x, np.sin(x-3), color='#FFDD44')
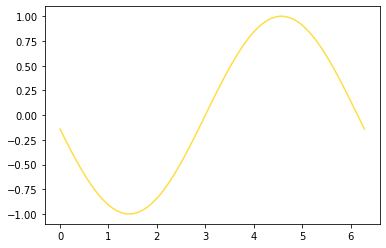
#RGB元组,范围在0~1
plt.plot(x, np.sin(x-4), color=(1.0, 0.2, 0.3))
#HTML颜色名称
plt.plot(x, np.sin(x-5), color='chartreuse')
线条风格设置
通过linesyle设置线条风格。
#实线
plt.plot(x, np.sin(x-0), linestyle='solid')
# plt.plot(x, np.sin(x-0), linestyle='-')
#虚线
plt.plot(x, np.sin(x-1), linestyle='dashed')
# plt.plot(x, np.sin(x-0), linestyle='--')
#点划线
plt.plot(x, np.sin(x-2), linestyle='dashdot')
# plt.plot(x, np.sin(x-0), linestyle='-.')
#实点线
plt.plot(x, np.sin(x-3), linestyle='dotted')
# plt.plot(x, np.sin(x-0), linestyle=':')
组合设置
将linestyle和color编码组合起来。
#绿色实线
plt.plot(x, x + 0, '-g')
#青色虚线
plt.plot(x, x + 1, '--c')
#黑色点划线
plt.plot(x, x + 2, '-.k')
#红色实点线
plt.plot(x, x + 3, ':r')
Matplotlib绘图设置---图形颜色和风格调整的更多相关文章
- matplotlib学习——设置线条颜色及形状
在图形表示中,不同的画布或画布中不同的函数,我们常常要用不同的形状或颜色来区分开,这里小编向大家介绍这些参数的表示方法: 一.控制颜色 b--blue c--cyan(青色) ...
- Python matplotlib绘图设置图例
一.语法简介 plt.legend(loc=2,edgecolor='red',facecolor='green',shadow='True',fontsize=10) #edgecolor 图例边框 ...
- Python matplotlib绘图设置坐标轴的标题
一.语法简介 plt.xlabel("销售月份",fontsize=16,color='red',fontweight='bold',loc='center',background ...
- 【划重点】Python matplotlib绘图设置坐标轴的刻度
一.语法简介 plt.xticks(ticks,labels,rotation=30,fontsize=10,color='red',fontweight='bold',backgroundcolor ...
- 【原】在Matplotlib绘图中添加Latex风格公式
Matplotlib绘图的过程中,可以为各个轴的Label,图像的Title.Legend等元素添加Latex风格的公式. 只需要在Latex公式的文本前后各增加一个$符号,Matplotlib就可以 ...
- matplotlib 设置图形大小时 figsize 与 dpi 的关系
matplotlib 中设置图形大小的语句如下: fig = plt.figure(figsize=(a, b), dpi=dpi) 其中: figsize 设置图形的大小,a 为图形的宽, b 为图 ...
- matplotlib绘图教程,设置标签与图例
大家好,欢迎大家阅读周四数据处理专题,我们继续介绍matplotlib作图工具. 在上一篇文章当中我们介绍了matplotlib这个包当中颜色.标记和线条这三种画图的设置,今天我们同样也介绍三种新的设 ...
- UI设计篇·入门篇·绘制简单自定义矩形图/设置按钮按下弹起颜色变化/设置图形旋转
Android的基本控件和图形有限,难以满足所有的实际需要和设计需求,好在Android给出了相对完善的图形绘制和自定义控件的API,利用这些API,可以基本满足设计的需求. 自定义图像和控件的方法: ...
- Matplotlib绘图双纵坐标轴设置及控制设置时间格式
双y轴坐标轴图 今天利用matplotlib绘图,想要完成一个双坐标格式的图. fig=plt.figure(figsize=(20,15)) ax1=fig.add_subplot(111) ax1 ...
- 使用ECharts制作图形时,如何设置指定图形颜色?
使用ECharts制作图形时,图形颜色是默认的颜色,有时需求需要指定图形颜色,这就需要自己去设置. 在option下的series属性中设置itemStyle,如下所示: itemStyle: { n ...
随机推荐
- 【Azure K8S | AKS】在中国区AKS上遇见ImagePullBackOff时的替代方案
问题描述 在AKS集群中部署calico时候,遇见 ImagePullBackOff 问题. 在创建POD calico-typha-horizontal-autoscale 时候遇见拉取镜像失败问题 ...
- 【Azure 应用服务】App Service 通过门户配置数据库连接字符串不生效
应用设置 Application Setting 在应用服务中,应用设置是作为环境变量传递给应用程序代码的变量. 对于 Linux 应用和自定义容器,应用服务使用 --env 标志将应用设置传递到容器 ...
- 简单配置Sql专家云
一.实例配置 1.添加实例 点击全面诊断实例配置,右上角点击添加. 2.填写实例信息 根据下图填写对应的信息,连接测试成功后点击保存. 3.添加完成 4.修改实例 找到对应的实例,点击下图蓝色框修改即 ...
- 掌握pandas cut函数,一键实现数据分类
pandas中的cut函数可将一维数据按照给定的区间进行分组,并为每个值分配对应的标签.其主要功能是将连续的数值数据转化为离散的分组数据,方便进行分析和统计. 1. 数据准备 下面的示例中使用的数据采 ...
- [笔记]git pull vs git pull --rebase
git pull vs git pull -rebase 背景 最近在实际开发过程,之前一直使用git pull 去更新该分支的代码,之前认为一旦pull 操作产生新的节点是对合并操作的一个记录,但是 ...
- aardio调用c语言dll动态库传结构体详细教程
开发日记3.11 此篇用于记录发那科数控机床(Fanuc CNC)采集程序开发中,C语言写底层然后用aardio写窗口调用dll的摸索出来的类型对应和踩坑整理. 由于发那科提供的开发套件是C语言的,所 ...
- InputNumber 不能输入点 viewDesign 需求是 只能是整数
<InputNumber ref="xxxRef" v-model="xxx" :disabled="xxx" style=" ...
- ReACT介绍与llama_index ReActAgent实践
Agent是大模型的重要应用方向,而ReACT是学术界提出的重要方法,本文介绍ReACT论文,然后通过llama_index ReActAgent来分析ReACT的执行过程. ReACT <RE ...
- HISI3520DV300 折腾记录(二)之《内存映射、存储(DDRC,FMC)、启动模式分析》
PS:要转载请注明出处,本人版权所有. PS: 这个只是基于<我自己>的理解, 如果和你的原则及想法相冲突,请谅解,勿喷. 前置说明 本文作为本人csdn blog的主站的备份.(Bl ...
- 游戏引擎中的实时渲染和在V-Ray中渲染有什么区别 2022-11-25
游戏引擎中的实时渲染和在V-Ray中渲染有什么区别,下面我们一起来分析一下,从2个方面来具体分析实时渲染和在V-Ray中渲染种的不一样的区别. 原理区别 VRay等渲染器原理上叫做离线渲染(Offli ...
