misc设备
WatchDog Timer驱动
混杂设备
Misc(或miscellaneous)驱动是一些拥有着共同特性的简单字符设备驱动。内核抽象出这些特性而形成一些API(在文件drivers/char/misc.c中实现),以简化这些设备驱动程序的初始化。所有的misc设备被分配同一个主设备号MISC_MAJOR(10),但是每一个可以选择一个单独的次设备号。如果一个字符设备驱动要驱动多个设备,那么它就不应该用misc设备来实现。
通常情况下,一个字符设备都不得不在初始化的过程中进行下面的步骤:
通过alloc_chrdev_region()分配主/次设备号。
使用cdev_init()和cdev_add()来以一个字符设备注册自己。
而一个misc驱动,则可以只用一个调用misc_register()来完成这所有的步骤。
所有的miscdevice设备形成一个链表,对设备访问时,内核根据次设备号查找对应的miscdevice设备,然后调用其file_operations中注册的文件操作方法进行操作。
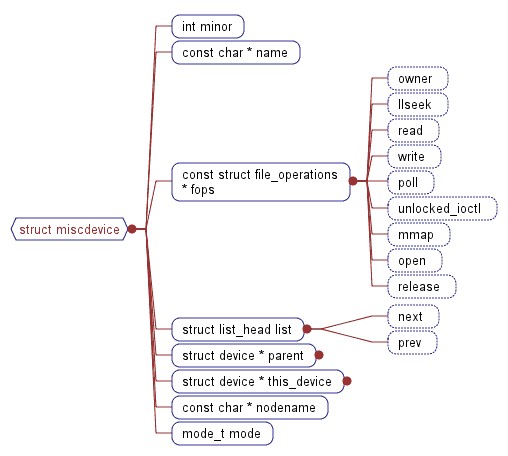
在Linux内核中,使用struct miscdevice来表示miscdevice。这个结构体的定义为:
struct miscdevice {
int minor;
const char *name;
const struct file_operations *fops;
struct list_head list;
struct device *parent;
struct device *this_device;
const char *nodename;
mode_t mode;
};
minor是这个混杂设备的次设备号,若由系统自动配置,则可以设置为MISC_DYNANIC_MINOR,name是设备名。
每一个misc驱动会自动出现在/sys/class/misc下,而不需要驱动程序作者明确的去做。Linux watchdog timer驱动被实现为misc 驱动,他们被放在drivers/char/watchdog/目录下。Watchdog 驱动也导出了一个标准设备接口到用户空间。这样就可以使符合这个接口的应用程序的实现独立于Watchdog硬件。这个API在内核树中的Documentation/watchdog/watchdog-api.txt文件中有详细的说明。
在Linux驱动中把无法归类的五花八门的设备定义为混杂设备(用miscdevice结构体表述)。miscdevice共享一个主设备号MISC_MAJOR(即10),但次设备号不同。 所有的miscdevice设备形成了一个链表,对设备访问时内核根据次设备号查找对应的miscdevice设备,然后调用其file_operations结构中注册的文件操作接口进行操作。 在内核中用struct miscdevice表示miscdevice设备,然后调用其file_operations结构中注册的文件操作接口进行操作。miscdevice的API实现在drivers/char/misc.c中。
下边是描述这个设备的结构体:
- struct miscdevice {
- int minor; //次设备号
- const char *name; //设备的名称
- const struct file_operations *fops; //文件操作
- struct list_head list; //misc_list的链表头
- struct device *parent; //父设备(Linux设备模型中的东东了,哈哈)
- struct device *this_device; //当前设备,是device_create的返回值,下边会看到
- };
然后来看看misc子系统的初始化函数:
- static int __init misc_init(void)
- {
- int err;
- #ifdef CONFIG_PROC_FS
- /*创建一个proc入口项*/
- proc_create("misc", 0, NULL, &misc_proc_fops);
- #endif
- /*在/sys/class/目录下创建一个名为misc的类*/
- misc_class = class_create(THIS_MODULE, "misc");
- err = PTR_ERR(misc_class);
- if (IS_ERR(misc_class))
- goto fail_remove;
- err = -EIO;
- /*注册设备,其中设备的主设备号为MISC_MAJOR,为10。设备名为misc,misc_fops是操作函数的集合*/
- if (register_chrdev(MISC_MAJOR,"misc",&misc_fops))
- goto fail_printk;
- return 0;
- fail_printk:
- printk("unable to get major %d for misc devices/n", MISC_MAJOR);
- class_destroy(misc_class);
- fail_remove:
- remove_proc_entry("misc", NULL);
- return err;
- }
- /*misc作为一个子系统被注册到linux内核中*/
- subsys_initcall(misc_init);
下边是register_chrdev函数的实现:
- int register_chrdev(unsigned int major, const char *name,
- const struct file_operations *fops)
- {
- struct char_device_struct *cd;
- struct cdev *cdev;
- char *s;
- int err = -ENOMEM;
- /*主设备号是10,次设备号为从0开始,分配256个设备*/
- cd = __register_chrdev_region(major, 0, 256, name);
- if (IS_ERR(cd))
- return PTR_ERR(cd);
- /*分配字符设备*/
- cdev = cdev_alloc();
- if (!cdev)
- goto out2;
- cdev->owner = fops->owner;
- cdev->ops = fops;
- /*Linux设备模型中的,设置kobject的名字*/
- kobject_set_name(&cdev->kobj, "%s", name);
- for (s = strchr(kobject_name(&cdev->kobj),'/'); s; s = strchr(s, '/'))
- *s = '!';
- /*把这个字符设备注册到系统中*/
- err = cdev_add(cdev, MKDEV(cd->major, 0), 256);
- if (err)
- goto out;
- cd->cdev = cdev;
- return major ? 0 : cd->major;
- out:
- kobject_put(&cdev->kobj);
- out2:
- kfree(__unregister_chrdev_region(cd->major, 0, 256));
- return err;
- }
来看看这个设备的操作函数的集合:
- static const struct file_operations misc_fops = {
- .owner = THIS_MODULE,
- .open = misc_open,
- };
可以看到这里只有一个打开函数,用户打开miscdevice设备是通过主设备号对应的打开函数,在这个函数中找到次设备号对应的相应的具体设备的open函数。它的实现如下:
- static int misc_open(struct inode * inode, struct file * file)
- {
- int minor = iminor(inode);
- struct miscdevice *c;
- int err = -ENODEV;
- const struct file_operations *old_fops, *new_fops = NULL;
- lock_kernel();
- mutex_lock(&misc_mtx);
- /*找到次设备号对应的操作函数集合,让new_fops指向这个具体设备的操作函数集合*/
- list_for_each_entry(c, &misc_list, list) {
- if (c->minor == minor) {
- new_fops = fops_get(c->fops);
- break;
- }
- }
- if (!new_fops) {
- mutex_unlock(&misc_mtx);
- /*如果没有找到,则请求加载这个次设备号对应的模块*/
- request_module("char-major-%d-%d", MISC_MAJOR, minor);
- mutex_lock(&misc_mtx);
- /*重新遍历misc_list链表,如果没有找到就退出,否则让new_fops指向这个具体设备的操作函数集合*/
- list_for_each_entry(c, &misc_list, list) {
- if (c->minor == minor) {
- new_fops = fops_get(c->fops);
- break;
- }
- }
- if (!new_fops)
- goto fail;
- }
- err = 0;
- /*保存旧打开函数的地址*/
- old_fops = file->f_op;
- /*让主设备号的操作函数集合指针指向具体设备的操作函数集合*/
- file->f_op = new_fops;
- if (file->f_op->open) {
- /*使用具体设备的打开函数打开设备*/
- err=file->f_op->open(inode,file);
- if (err) {
- fops_put(file->f_op);
- file->f_op = fops_get(old_fops);
- }
- }
- fops_put(old_fops);
- fail:
- mutex_unlock(&misc_mtx);
- unlock_kernel();
- return err;
- }
再来看看misc子系统对外提供的两个重要的API,misc_register,misc_deregister:
- int misc_register(struct miscdevice * misc)
- {
- struct miscdevice *c;
- dev_t dev;
- int err = 0;
- /*初始化misc_list链表*/
- INIT_LIST_HEAD(&misc->list);
- mutex_lock(&misc_mtx);
- /*遍历misc_list链表,看这个次设备号以前有没有被用过,如果次设备号已被占有则退出*/
- list_for_each_entry(c, &misc_list, list) {
- if (c->minor == misc->minor) {
- mutex_unlock(&misc_mtx);
- return -EBUSY;
- }
- }
- /*看是否是需要动态分配次设备号*/
- if (misc->minor == MISC_DYNAMIC_MINOR) {
- /*
- *#define DYNAMIC_MINORS 64 /* like dynamic majors */
- *static unsigned char misc_minors[DYNAMIC_MINORS / 8];
- *这里存在一个次设备号的位图,一共64位。下边是遍历每一位,
- *如果这位为0,表示没有被占有,可以使用,为1表示被占用。
- */
- int i = DYNAMIC_MINORS;
- while (--i >= 0)
- if ( (misc_minors[i>>3] & (1 << (i&7))) == 0)
- break;
- if (i<0) {
- mutex_unlock(&misc_mtx);
- return -EBUSY;
- }
- /*得到这个次设备号*/
- misc->minor = i;
- }
- /*设置位图中相应位为1*/
- if (misc->minor < DYNAMIC_MINORS)
- misc_minors[misc->minor >> 3] |= 1 << (misc->minor & 7);
- /*计算出设备号*/
- dev = MKDEV(MISC_MAJOR, misc->minor);
- /*在/dev下创建设备节点,这就是有些驱动程序没有显式调用device_create,却出现了设备节点的原因*/
- misc->this_device = device_create(misc_class, misc->parent, dev, NULL,
- "%s", misc->name);
- if (IS_ERR(misc->this_device)) {
- err = PTR_ERR(misc->this_device);
- goto out;
- }
- /*
- * Add it to the front, so that later devices can "override"
- * earlier defaults
- */
- /*将这个miscdevice添加到misc_list链表中*/
- list_add(&misc->list, &misc_list);
- out:
- mutex_unlock(&misc_mtx);
- return err;
- }
这个是miscdevice的卸载函数:
- int misc_deregister(struct miscdevice *misc)
- {
- int i = misc->minor;
- if (list_empty(&misc->list))
- return -EINVAL;
- mutex_lock(&misc_mtx);
- /*在misc_list链表中删除miscdevice设备*/
- list_del(&misc->list);
- /*删除设备节点*/
- device_destroy(misc_class, MKDEV(MISC_MAJOR, misc->minor));
- if (i < DYNAMIC_MINORS && i>0) {
- /*释放位图相应位*/
- misc_minors[i>>3] &= ~(1 << (misc->minor & 7));
- }
- mutex_unlock(&misc_mtx);
- return 0;
- }
misc设备的更多相关文章
- 手把手教你从零实现Linux misc设备驱动一(基于友善之臂4412开发板)
关于怎样来写一个misc设备,在前面有篇文章已经介绍了大致的流程,如今就让我们来实现一个最简单的misc设备驱动. http://blog.csdn.net/morixinguan/article/d ...
- 【linux驱动分析】misc设备驱动
misc设备驱动.又称混杂设备驱动. misc设备驱动共享一个设备驱动号MISC_MAJOR.它在include\linux\major.h中定义: #define MISC_MAJO ...
- 跟着内核学框架-从misc子系统到3+2+1设备识别驱动框架
misc子系统在Linux中是一个非常简单的子系统,但是其清晰的框架结构非常适合用来研究设备识别模型.本文从misc子系统的使用出发,通过了解其机制来总结一套的设备识别的驱动框架,即使用使用同一个驱动 ...
- Linux驱动框架之misc类设备驱动框架
1.何为misc设备 (1)misc中文名就是杂项设备\杂散设备,因为现在的硬件设备多种多样,有好些设备不好对他们进行一个单独的分类,所以就将这些设备全部归属于 杂散设备,也就是misc设备,例如像a ...
- misc类设备
何为misc (1)中文名:杂项设备\杂散设备,它是一种典型的字符设,在一般情况下在内核中,所有的misc设备的主设备号是固定的,为10,它们的次设备号不一样:(2)可以在根文件系统中看到:/sys/ ...
- linux之misc及使用misc创建字符设备
1:linux字符设备及udev 1.1字符设备 字符设备就是:一个一个字节来进行访问的,不能对字符设备进行随机读写.简单字符设备创建实例如下: #include <linux/module.h ...
- 设备驱动基础学习--misc device简单实现
在Linux驱动中把无法归类的五花八门的设备定义为混杂设备(用miscdevice结构体表述).miscdevice共享一个主设备号MISC_MAJOR(即10),但次设备号不同. 所有的miscde ...
- linux 字符设备驱动写法
字符设备,块设备书 一.register_chrdev_region, register_chrdev, misc_register misc device(杂项设备) 在 Linux 内核的incl ...
- i2c总线,设备,驱动之间的关系
------ 总线上先添加好所有具体驱动,i2c.c遍历i2c_boardinfo链表,依次建立i2c_client, 并对每一个i2c_client与所有这个线上的驱动匹配,匹配上,就调用这个驱动的 ...
随机推荐
- Python源代码目录组织结构
- POJ 3903:Stock Exchange(裸LIS + 二分优化)
http://poj.org/problem?id=3903 Stock Exchange Time Limit: 1000MS Memory Limit: 65536K Total Submis ...
- 【转载】使用barman备份PostgreSQL
什么是barman Barman (备份和恢复管理器) 是 PostgreSQL 数据库服务器中非常方便的备份和恢复工具,允许远程备份多个服务器,允许从一个备份集中一个命令就恢复数据库.同时还可以对多 ...
- Linux C socket 编程之TCP
推荐:http://www.cnblogs.com/tianshuai11/archive/2011/11/30/2477224.html
- preparedStatement和Statement 有什么不一样
1. PreparedStatement接口继承Statement, PreparedStatement 实例包含已编译的 SQL 语句,所以其执行速度要快于 Statement 对象. 2.作 ...
- MultiSelectComboBox(一)
1. MultiSelectComboBox.xaml <UserControl x:Class="MultiSelectComboBox.MultiSelectComboBox&qu ...
- 【linux命令与工具】lsmod命令
lsmod命令用来显示已被内核加载的模块的状态 描述: lsmod命令可以美观地显示/prco/module中的内容,这些内容是被已被内核加载模块的信息. 使用lsmod之后,系统会显示出目前已经存在 ...
- zend studio 12.0 怎么汉化?
网上搜索到的答案在:http://zhidao.baidu.com/link?url=OUGXDr0H28ad0UYSCUQ27BziJnymTcfWCmNAmzSRorOe3ZDSRhRXY0QoE ...
- Failed to start component [StandardEngine[Catalina].StandardHost[localhost....
今天我用了近一天的时间研究一个错误,早上写代码是遇到一个 错误严重错误代码如下: 严重: ContainerBase.addChild: start: org.apache.catalina.Life ...
- Mysql-学习笔记(==》权限管理 十 三)
-- 用户与权限管理-- 查看当前服务器上的所有账号密码主机SELECT USER,PASSWORD,HOST FROM mysql.user; -- 设置账号密码SET PASSWORD=PASSW ...
