week3编程作业: Logistic Regression中一些难点的解读
%% ============ Part : Compute Cost and Gradient ============
% In this part of the exercise, you will implement the cost and gradient
% for logistic regression. You neeed to complete the code in
% costFunction.m % Setup the data matrix appropriately, and add ones for the intercept term
[m, n] = size(X); % Add intercept term to x and X_test
X = [ones(m, ) X]; % Initialize fitting parameters
initial_theta = zeros(n + , ); % Compute and display initial cost and gradient
[cost, grad] = costFunction(initial_theta, X, y);
难点1:X和theta的维度变化,怎么变得,为什么?
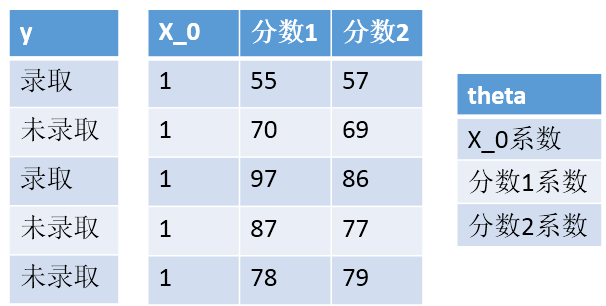
X加了一列1,θ加了一行θ0,因为最后边界是θ0+θ1X1+θ2X2,要符合矩阵运算
难点2:costFunction中grad是什么函数,有什么作用?
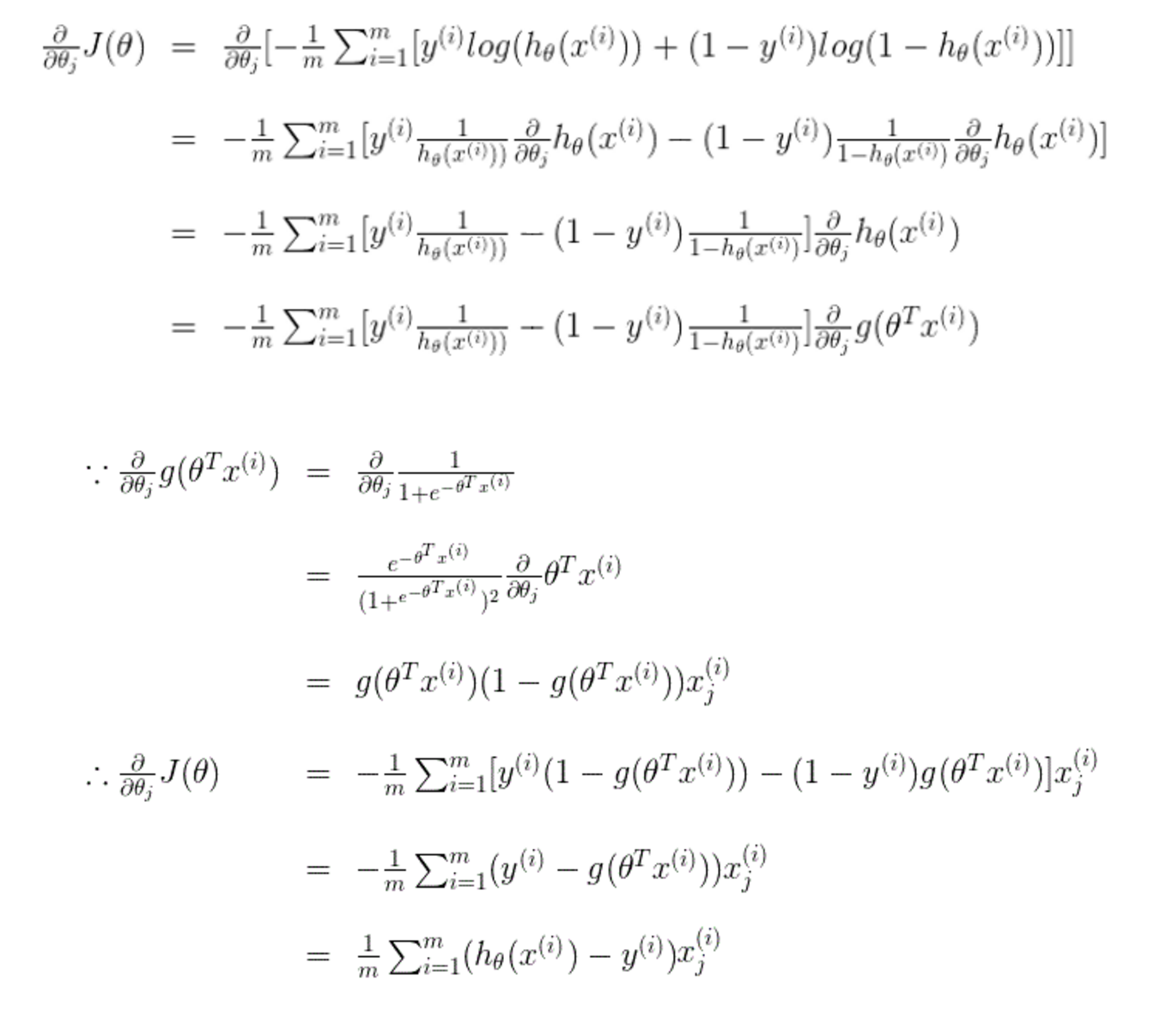
w.r.t 什么意思?
with regard to
with reference to 关于的意思
难点3:linear regression的代价函数和logistic regression的代价函数,为什么不一样?
和幂次有关,如果还用原来的代价函数,那么会有很多局部最值,没有办法梯度下降到最小值。

另一个解读角度:从最大似然函数出发考虑。
下面的文章写得很好,参考链接:
http://blog.csdn.net/lu597203933/article/details/38468303
http://blog.csdn.net/it_vitamin/article/details/45625143
%% ============= Part : Optimizing using fminunc =============
% In this exercise, you will use a built-in function (fminunc) to find the
% optimal parameters theta. % Set options for fminunc
options = optimset('GradObj', 'on', 'MaxIter', ); % Run fminunc to obtain the optimal theta
% This function will return theta and the cost
[theta, cost] = ...
fminunc(@(t)(costFunction(t, X, y)), initial_theta, options);
难点4:optimset是什么作用?
options = optimset('GradObj', 'on', 'MaxIter', 400); //
通过optimset函数设置或改变这些参数。其中有的参数适用于所有的优化算法,有的则只适用于大型优化问题,另外一些则只适用于中型问题。
LargeScale – 当设为'on'时使用大型算法,若设为'off'则使用中型问题的算法。
适用于大型和中型算法的参数:
Diagnostics – 打印最小化函数的诊断信息。
Display – 显示水平。选择'off',不显示输出;选择'iter',显示每一步迭代过程的输出;选择'final',显示最终结果。打印最小化函数的诊断信息。
GradObj – 用户定义的目标函数的梯度。对于大型问题此参数是必选的,对于中型问题则是可选项。
MaxFunEvals – 函数评价的最大次数。
MaxIter – 最大允许迭代次数。
TolFun – 函数值的终止容限。
TolX – x处的终止容限。
options = optimset('param1',value1,'param2',value2,...) %设置所有参数及其值,未设置的为默认值
options = optimset('GradObj', 'on', 'MaxIter', 400);
在使用options的函数中,参数是由用户自行定义的,最大递归次数为400
难点5:[theta, cost] = fminunc(@(t)(costFunction(t, X, y)), initial_theta, options)是怎么实现功能?
关于句柄@,参考偏文章:http://blog.csdn.net/gzp444280620/article/details/49252491
关于fiminuc,参考这篇文章:http://blog.csdn.net/gzp444280620/article/details/49272977
fminunc(@(t)(costFunction(t, X, y)), initial_theta, options); %是为了当代码里面有这样的函数的时候,fminunc(1,θ,option)第一个参数,
会传递给costFunction(t, X, y)的第一个参数里面进行计算。
function plotDecisionBoundary(theta, X, y)
%PLOTDECISIONBOUNDARY Plots the data points X and y into a new figure with
%the decision boundary defined by theta
% PLOTDECISIONBOUNDARY(theta, X,y) plots the data points with + for the
% positive examples and o for the negative examples. X is assumed to be
% a either
% ) Mx3 matrix, where the first column is an all-ones column for the
% intercept.
% ) MxN, N> matrix, where the first column is all-ones % Plot Data
plotData(X(:,:), y);
hold on if size(X, ) <=
% Only need points to define a line, so choose two endpoints
plot_x = [min(X(:,))-, max(X(:,))+]; % Calculate the decision boundary line//令theta装置乘以X等于0,即可 plot_y = (-./theta()).*(theta().*plot_x + theta()); % Plot, and adjust axes for better viewing
plot(plot_x, plot_y) % Legend, specific for the exercise
legend('Admitted', 'Not admitted', 'Decision Boundary')
axis([, , , ])
else
% Here is the grid range
u = linspace(-, 1.5, );
v = linspace(-, 1.5, ); z = zeros(length(u), length(v));
% Evaluate z = theta*x over the grid
for i = :length(u)
for j = :length(v)
z(i,j) = mapFeature(u(i), v(j))*theta;
end
end
z = z'; % important to transpose z before calling contour % Plot z =
% Notice you need to specify the range [, ]
contour(u, v, z, [, ], 'LineWidth', )
end
hold off end
难点6:这个plotDecisionBoundary函数是怎么画出边界的?
plotDecisionBoundary中的下面的两行看不懂:
plot_x = [min(X(:,2))-2, max(X(:,2))+2]; //直线的参数其实已经得到,选划线的范围,把直线画出来即可。为了美观,扩大了两个单位
% Calculate the decision boundary line//令theta装置乘以X等于0,即可 plot_y = (-1./theta(3)).*(theta(2).*plot_x + theta(1));
plot_y = (-1./theta(3)).*(theta(2).*plot_x + theta(1));
function plotData(X, y) //会按照真类和假类分类 画出输入的点
%PLOTDATA Plots the data points X and y into a new figure
% PLOTDATA(x,y) plots the data points with + for the positive examples
% and o for the negative examples. X is assumed to be a Mx2 matrix. % Create New Figure
figure; hold on; % ====================== YOUR CODE HERE ======================
% Instructions: Plot the positive and negative examples on a
% 2D plot, using the option 'k+' for the positive
% examples and 'ko' for the negative examples.
%
% Find Indices of Positive and Negative Examples //返回 y=1和y=0的位置,也就是行数
pos = find(y==); neg = find(y == ); //利用find的查找功能,把正类和负类分开,并把横纵坐标保存在pos里面
% Plot Examples
plot(X(pos, ), X(pos, ), 'k+','LineWidth', , ...
'MarkerSize', );
plot(X(neg, ), X(neg, ), 'ko', 'MarkerFaceColor', 'y', ...
'MarkerSize', ); % ========================================================================= hold off; end
%% =========== Part : Regularized Logistic Regression ============
% In this part, you are given a dataset with data points that are not
% linearly separable. However, you would still like to use logistic
% regression to classify the data points.
%
% To do so, you introduce more features to use -- in particular, you add
% polynomial features to our data matrix (similar to polynomial
% regression).
% % Add Polynomial Features % Note that mapFeature also adds a column of ones for us, so the intercept
% term is handled
X = mapFeature(X(:,), X(:,)); % Initialize fitting parameters
initial_theta = zeros(size(X, ), ); % Set regularization parameter lambda to
lambda = ; % Compute and display initial cost and gradient for regularized logistic
% regression
[cost, grad] = costFunctionReg(initial_theta, X, y, lambda);
难点7:mapFeature是怎么工作的,原理?
难点8:[cost, grad] = costFunctionReg(initial_theta, X, y, lambda);怎么工作?
%% ============= Part : Regularization and Accuracies =============
% Optional Exercise:
% In this part, you will get to try different values of lambda and
% see how regularization affects the decision coundart
%
% Try the following values of lambda (, , , ).
%
% How does the decision boundary change when you vary lambda? How does
% the training set accuracy vary?
% % Initialize fitting parameters
initial_theta = zeros(size(X, ), ); % Set regularization parameter lambda to (you should vary this)
lambda = ; % Set Options
options = optimset('GradObj', 'on', 'MaxIter', ); % Optimize
[theta, J, exit_flag] = ...
fminunc(@(t)(costFunctionReg(t, X, y, lambda)), initial_theta, options);
难点9:为什么fminunc可以返回三个变量?
ps:先把问题记录一下,稍后会一个个解决。
week3编程作业: Logistic Regression中一些难点的解读的更多相关文章
- Andrew Ng机器学习编程作业:Logistic Regression
编程作业文件: machine-learning-ex2 1. Logistic Regression (逻辑回归) 有之前学生的数据,建立逻辑回归模型预测,根据两次考试结果预测一个学生是否有资格被大 ...
- logistic regression中的cost function选择
一般的线性回归使用的cost function为: 但由于logistic function: 本身非凸函数(convex function), 如果直接使用线性回归的cost function的话, ...
- Andrew Ng机器学习编程作业: Linear Regression
编程作业有两个文件 1.machine-learning-live-scripts(此为脚本文件方便作业) 2.machine-learning-ex1(此为作业文件) 将这两个文件解压拖入matla ...
- Logistic regression中regularization失败的解决方法探索(文末附解决后code)
在matlab中做Regularized logistic regression 原理: 我的代码: function [J, grad] = costFunctionReg(theta, X, y, ...
- Coursera machine learning 第二周 编程作业 Linear Regression
必做: [*] warmUpExercise.m - Simple example function in Octave/MATLAB[*] plotData.m - Function to disp ...
- Andrew Ng 的 Machine Learning 课程学习 (week3) Logistic Regression
这学期一直在跟进 Coursera上的 Machina Learning 公开课, 老师Andrew Ng是coursera的创始人之一,Machine Learning方面的大牛.这门课程对想要了解 ...
- 逻辑回归 logistic regression(1)逻辑回归的求解和概率解释
本系列内容大部分来自Standford公开课machine learning中Andrew老师的讲解,附加自己的一些理解,编程实现和学习笔记. 第一章 Logistic regression 1.逻辑 ...
- Matlab实现线性回归和逻辑回归: Linear Regression & Logistic Regression
原文:http://blog.csdn.net/abcjennifer/article/details/7732417 本文为Maching Learning 栏目补充内容,为上几章中所提到单参数线性 ...
- Probabilistic SVM 与 Kernel Logistic Regression(KLR)
本篇讲的是SVM与logistic regression的关系. (一) SVM算法概论 首先我们从头梳理一下SVM(一般情况下,SVM指的是soft-margin SVM)这个算法. 这个算法要实现 ...
随机推荐
- AGC006C Rabbit Exercise
传送门 设 \(f_{i,j}\) 表示兔子 \(i\) 在当前 \(j\) 轮的期望位置 对于一次操作 \(f_{i,j+1}=\frac{1}{2}(2f_{i-1,j}-f_{i,j})+\fr ...
- centos 快速安装wordpress
1.两种方式得到Wordpress 首先你可以去wordpress官方网站看下最新的wordpress的下载地址多少.比如wordpress 3.9.1的下载地址是: http://cn.wordpr ...
- 无法在类...中找到资源".bmp"
在WinForm中写的一个程序,在项目中添加了一个bmp图片,然后 public void SetSubType(int SubType) { m_subType = SubType; switch ...
- leaflet 整合 esri
此 demo 通过 proj4js 将 leaflet 与 esri 整合起来,同时添加了 ClusteredFeatureLayer 的支持. 下载 <html> <head> ...
- html History API
History api 兼容性支持一下浏览器 为什么要使用History API 在AJAX给我们带来提高用户体验.减少HTTP连接数等好处的同时,也渐渐显露出一些不足之处,比如: 1.页面全是用aj ...
- Spring Boot—18Redis
pom.xml <dependency> <groupId>mysql</groupId> <artifactId>mysql-connector-ja ...
- Winform 多个窗口编辑同一条数据同步的实现
场景: 一个主窗口中,可以在列表(DataGridView)里选中一条记录编辑,打开一个编辑窗口(非模态窗口),编辑窗口保存后需要刷新父窗口,由于编辑窗口是非模态窗口,如果打开了多个窗口,并且都是编辑 ...
- Linux chkconfig命令详解
chkconfig命令检查.设置系统的各种服务.这是Red Hat公司遵循GPL规则所开发的程序,它可查询操作系统在每一个执行等级中会执行哪些系统服务,其中包括各类常驻服务.谨记chkconfig不是 ...
- 【原创】使用Java进行Clob转String字符串
背景 oracle字段类型varchar2最大长度4000,超过的怎么办 解决 使用clob类型,大字段,无长度限制 问题 使用Java的JDBC读取的RS获取的clob类型无法正常使用,封装的rs. ...
- 铁乐学Python_day03-字符串常用操作方法
文:铁乐与猫 2018-3-20 1)字符串首个字母大写,其它字母也会转换成小写: S.capitalize() -> str 记忆方法:capital(大写字母) def capitalize ...
