剪枝在pytorch中是如何实现的?
Pytorch中剪枝源码可参考:
https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/blob/master/torch/nn/utils/prune.py
可参考:
pytorch中函数接口:https://runebook.dev/zh-CN/docs/pytorch/-index-#nn
在Pytorch中的剪枝操作一文中,自定义剪枝中提到剪枝操作继承自BasePruningMethod基类 ,并且子类中需要单独实现__init__ 和 compute_mask (mask和参数所执行的逻辑操作),并指明执行哪种剪枝类型 ( global,structured, 或者 unstructured),这一讲就来看下,其中是如何实现的。
类图结构
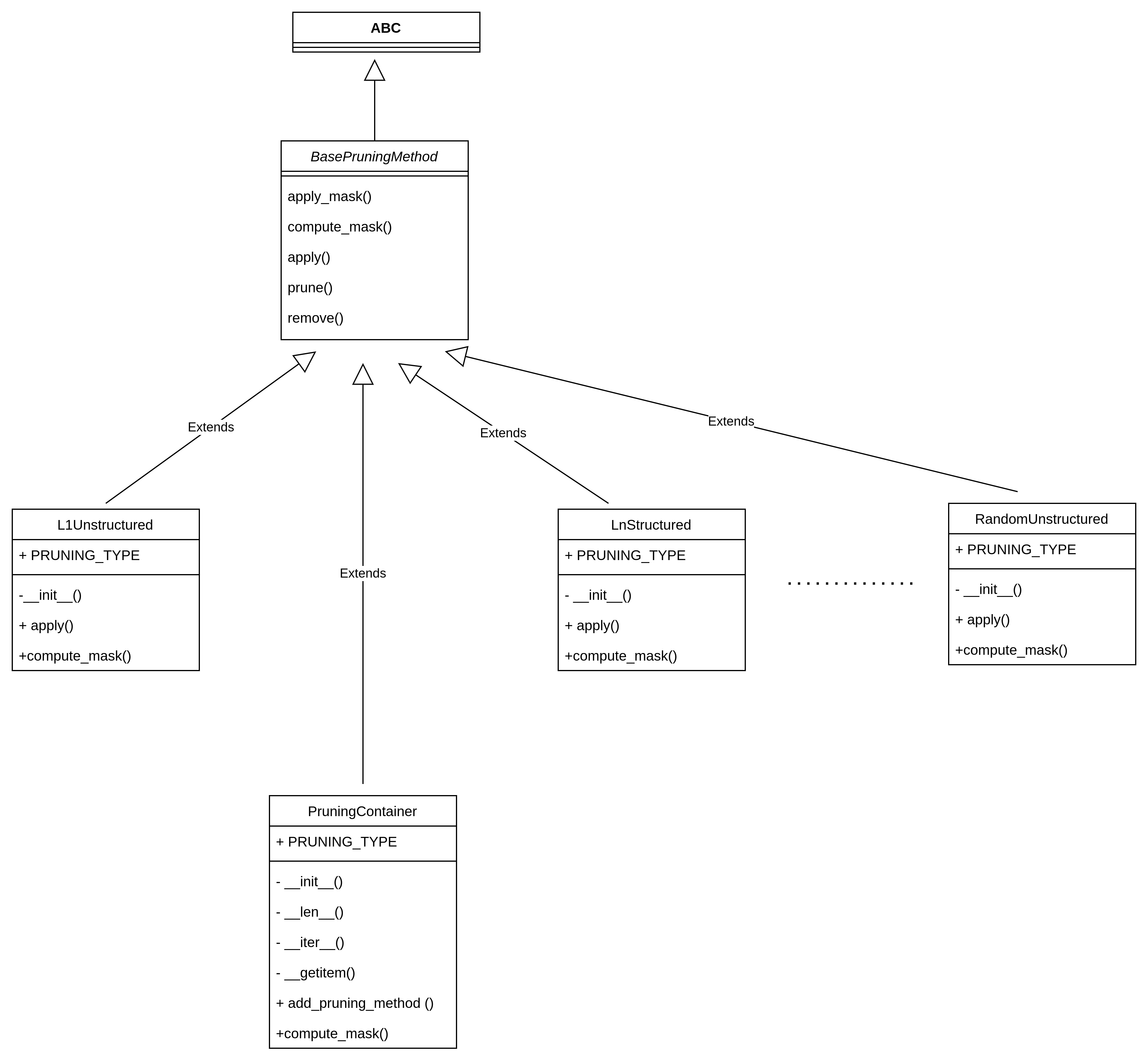
可看到裁剪策略有L1非结构化剪枝、Ln结构化剪枝、随机非结构化剪枝、自定义剪枝等等都是继承自BasePruningMethod,另还有一个非常重要的子类:PruningContainer,为迭代修剪而持有修剪方法序列的容器。跟踪应用修剪方法的顺序,并处理连续修剪调用的组合。对于同一个module使用多个剪枝策略时,pytorch通过PruningContainer来对剪枝策略进行管理。PruningContainer本身也是继承自BasePruningMethod。同时设置前向计算的回调,便于后续训练时调用。
基类 BasePruningMethod
基类BasePruningMethod为一个抽象类,提供了剪枝方法的框架
class BasePruningMethod(ABC):
r"""需要自己实现compute_mask和apply方法
"""
_tensor_name: str
def __init__(self):
pass
# 调用apply_mask
def __call__(self, module, inputs):
...
@abstractmethod
def compute_mask(self, t, default_mask):
r"""计算mask tensor,输入tensor t,输出和t相同维度的mask
"""
pass
def apply_mask(self, module):
r"""简单将待剪得parameter 和 mask相乘,输入mask和原始tensor,返回剪之后的tensor.
"""
...
pruned_tensor = mask.to(dtype=orig.dtype) * orig
return pruned_tensor
@classmethod
def apply(cls, module, name, *args, importance_scores=None, **kwargs):
r"""增加forward pre-hook 可以在forward()时完成original tensor
和 pruning mask的reparametrization
"""
def _get_composite_method(cls, module, name, *args, **kwargs):
old_method = None
found = 0
# 一个module只允许一个_forward_pre_hook
...
assert (
found <= 1
), "Avoid adding multiple pruning hooks to the\
same tensor {} of module {}. Use a PruningContainer.".format(
name, module
)
...
# 创建pruning container包含多个pruning method
# combine `methods` with `old_method`, if `old_method` exists
...
container = PruningContainer(old_method)
# Have the pruning method remember the name of its tensor
# setattr(container, '_tensor_name', name)
container.add_pruning_method(method)
method = container # rename container --> method
return method
method = _get_composite_method(cls, module, name, *args, **kwargs)
...
#
# 第一次裁剪,初始化default_mask,将原param tensor移动到一个新参数name + '_orig' 并删除原来 parameter
if not isinstance(method, PruningContainer):
# copy `module[name]` to `module[name + '_orig']`
module.register_parameter(name + "_orig", orig)
# temporarily delete `module[name]`
del module._parameters[name]
default_mask = torch.ones_like(orig) # temp
# 不是第一次裁剪
# If this is not the first time pruning is applied, all of the above
# has been done before in a previous pruning iteration, so we're good
# to go
else:
default_mask = (
getattr(module, name + "_mask")
.detach()
.clone(memory_format=torch.contiguous_format)
)
# Use try/except 避免意外来回滚
# 计算compute_mask 并register_forward_pre_hook
try:
# 依据importance_scores来compute_mask
mask = method.compute_mask(importance_scores, default_mask=default_mask)
# 保存 mask to `module[name + '_mask']` 缓存
module.register_buffer(name + "_mask", mask)
# 以及pruned tensor 存到 `module[name]` 状态
setattr(module, name, method.apply_mask(module))
# 通过hook,register_forward_pre_hook,关联module的pruning到的forward()中,这样推理时也可以做reparam
module.register_forward_pre_hook(method)
except Exception as e:
# 删除name_orig,恢复orig
if not isinstance(method, PruningContainer):
orig = getattr(module, name + "_orig")
module.register_parameter(name, orig)
del module._parameters[name + "_orig"]
raise e
return method
可以看到,BasePruningMethod基类中,抽象方法compute_mask()、__init__ 需要子类进行实现,apply()方法可以调用基类的方法即可。
L1Unstructured为例
class L1Unstructured(BasePruningMethod):
r"""非结构化,最小L1norm(绝对值)的值zero out.
amount,要裁剪参数的比率,如果是整数,则是裁剪的参数总个数
"""
PRUNING_TYPE = "unstructured" ##必须指明结构化还是非结构化
def __init__(self, amount):
# Check range of validity of pruning amount
_validate_pruning_amount_init(amount)
self.amount = amount
## 重写父类方法compute_mask
def compute_mask(self, t, default_mask):
...""" """
# 计算要裁剪的参数个数
nparams_toprune = _compute_nparams_toprune(self.amount, tensor_size)
...
# container接口里的default_mask本地拷贝一下
mask = default_mask.clone(memory_format=torch.contiguous_format)
if nparams_toprune != 0: # k=0 not supported by torch.kthvalue
# largest=True --> top k; largest=False --> bottom k
# 取出abs最小的那些权重序号,将对应的mask位置置为0
topk = torch.topk(torch.abs(t).view(-1), k=nparams_toprune, largest=False)
# topk will have .indices and .values
mask.view(-1)[topk.indices] = 0
return mask
@classmethod
def apply(cls, module, name, amount, importance_scores=None):
r"""调用父类方法,增加forward pre-hook 方便来做reparametrization ,生成 original tensor(xxx_orig)
和pruning mask(xxx_mask).
输入:module,module的参数名,要剪的比率.
"""
# 调用父类的BasePruningMethod的apply方法
return super(L1Unstructured, cls).apply(
module, name, amount=amount, importance_scores=importance_scores
)
PruningContainer
PruningContainer这个类同样也是继承自BasePruningMethod类,它的作用主要是对剪枝策略进行管理。
既然是继承自BasePruningMethod类,必然要实现__init__、compute_mask,此外,该类中单独实现了add_pruning_method用于储存裁剪策略,其中slc 存放的是非结构化剪枝的元素位置/结构化剪枝中的保留通道信息
class PruningContainer(BasePruningMethod):
"""迭代迭代pruning的方法类.
记录BasePruningMethod的序列,然后pruning时按照顺序来apply这些BasePruningMethod
输入为:BasePruningMethod继承子类对象
"""
def __init__(self, *args):
self._pruning_methods: Tuple["BasePruningMethod", ...] = tuple()
...
self.add_pruning_method(method)
def add_pruning_method(self, method):
r"""
输入为:BasePruningMethod继承子类对象
"""
...
# if all checks passed, add to _pruning_methods tuple
self._pruning_methods += (method,)
...
# 迭代多次pruning
def compute_mask(self, t, default_mask):
r""" new mask 根据 ``PRUNING_TYPE`` ,因为mask的地方在后续就不参与统计计算了嘛:
* 'unstructured', 非结构化,mask基于nonmasked位置来叠加生成;
* 'structured', 结构化,mask 根据没有zero-out的channel来叠加;
* 'global', 非结构化,全局的,所以是根据整体的所有元素来统计.
输入:t,待裁剪的parameter,和default_mask维度同
default_mask,迭代剪枝当前的mask值
返回:default_mask和对当前剪枝method获取的new_mask合成
"""
def _combine_masks(method, t, mask):
r"""
Args:
method BasePruningMethod的实例
t (torch.Tensor): 需要剪的tensor.
mask (torch.Tensor): 历史mask
Returns:
new_mask (torch.Tensor): 合并之后的新mask.
"""
new_mask = mask # start off from existing mask
new_mask = new_mask.to(dtype=t.dtype)
# slc 存放的是非结构化剪枝的元素位置/结构化剪枝中的保留通道信息
# compute a slice of t onto which the new pruning method will operate
if method.PRUNING_TYPE == "unstructured":
# mask tensor上为1的地方
# 非结构化剪枝
slc = mask == 1
# for struct pruning, exclude channels that have already been
# entirely pruned
elif method.PRUNING_TYPE == "structured":
if not hasattr(method, "dim"):
raise AttributeError(
"Pruning methods of PRUNING_TYPE "
'"structured" need to have the attribute `dim` defined.'
)
# find the channels to keep by removing the ones that have been
# zeroed out already (i.e. where sum(entries) == 0)
n_dims = t.dim() # "is this a 2D tensor? 3D? ..."
dim = method.dim
# convert negative indexing
if dim < 0:
dim = n_dims + dim
# if dim is still negative after subtracting it from n_dims
if dim < 0:
raise IndexError(
"Index is out of bounds for tensor with dimensions {}".format(
n_dims
)
)
# find channels along dim = dim that aren't already tots 0ed out
# 统计mask里是否全0,keep_channel为method设置的dim里没有全部zero-out的通道
keep_channel = mask.sum(dim=[d for d in range(n_dims) if d != dim]) != 0
# create slice to identify what to prune
slc = [slice(None)] * n_dims
slc[dim] = keep_channel
elif method.PRUNING_TYPE == "global":
# 非结构化剪枝
n_dims = len(t.shape) # "is this a 2D tensor? 3D? ..."
slc = [slice(None)] * n_dims
else:
raise ValueError(
"Unrecognized PRUNING_TYPE {}".format(method.PRUNING_TYPE)
)
# compute the new mask on the unpruned slice of the tensor t
# 具体调用每种方法的compute_mask与default_mask一起生成新的mask
partial_mask = method.compute_mask(t[slc], default_mask=mask[slc])
new_mask[slc] = partial_mask.to(dtype=new_mask.dtype)
return new_mask
# 从序列头上里取出method,_combine_masks调用该method的compute_mask
method = self._pruning_methods[-1]
mask = _combine_masks(method, t, default_mask)
return mask
在compute_mask函数的实现中,非结构化剪枝时,将mask tensor上为1 的地方保存在slc,同理,对于结构化剪枝,会通过统计mask里是否全为0,并将method设置的dim里没有全部zero-out的通道保存在keep_channel,赋值给slc,然后具体调用每种方法的compute_mask与default_mask一起生成新的mask并返回。
Pruning Method
- prune(self, t, default_mask=None, importance_scores=None)
同样,该函数也为基类BasePruningMethod的类方法,通过调用调用compute_mask,返回pruned之后的tensor
def prune(self, t, default_mask=None, importance_scores=None):
r"""调用compute_mask,返回pruned之后的tensor
"""
...
return t * self.compute_mask(importance_scores, default_mask=default_mask)
- emove(self, module)
这个类方法的作用就是将参数的缓存和mask都去掉,永久化剪枝,不可逆
def remove(self, module):
r"""将参数的缓存和mask都去掉,永久化剪枝. parameter
``name+'_orig'`` 从 parameter list顺出. ``name+'_mask'`` 从 buffers删除
不可逆
"""
# 是否已经设置过pruning
assert (
self._tensor_name is not None
), "Module {} has to be pruned\
before pruning can be removed".format(
module
) # this gets set in apply()
# to update module[name] to latest trained weights
weight = self.apply_mask(module) # masked weights
# 删除原来的weight,替换为apply_mask
if hasattr(module, self._tensor_name):
delattr(module, self._tensor_name)
orig = module._parameters[self._tensor_name + "_orig"]
orig.data = weight.data
# 删除name_orig和name_mask
del module._parameters[self._tensor_name + "_orig"]
del module._buffers[self._tensor_name + "_mask"]
setattr(module, self._tensor_name, orig)
剪枝在pytorch中是如何实现的?的更多相关文章
- 实践Pytorch中的模型剪枝方法
摘要:所谓模型剪枝,其实是一种从神经网络中移除"不必要"权重或偏差的模型压缩技术. 本文分享自华为云社区<模型压缩-pytorch 中的模型剪枝方法实践>,作者:嵌入式 ...
- PyTorch官方中文文档:PyTorch中文文档
PyTorch中文文档 PyTorch是使用GPU和CPU优化的深度学习张量库. 说明 自动求导机制 CUDA语义 扩展PyTorch 多进程最佳实践 序列化语义 Package参考 torch to ...
- PyTorch中ReLU的inplace
0 - inplace 在pytorch中,nn.ReLU(inplace=True)和nn.LeakyReLU(inplace=True)中存在inplace字段.该参数的inplace=True的 ...
- pytorch中tensorboardX的用法
在代码中改好存储Log的路径 命令行中输入 tensorboard --logdir /home/huihua/NewDisk1/PycharmProjects/pytorch-deeplab-xce ...
- Pytorch中RoI pooling layer的几种实现
Faster-RCNN论文中在RoI-Head网络中,将128个RoI区域对应的feature map进行截取,而后利用RoI pooling层输出7*7大小的feature map.在pytorch ...
- pytorch 中的重要模块化接口nn.Module
torch.nn 是专门为神经网络设计的模块化接口,nn构建于autgrad之上,可以用来定义和运行神经网络 nn.Module 是nn中重要的类,包含网络各层的定义,以及forward方法 对于自己 ...
- 对pytorch中Tensor的剖析
不是python层面Tensor的剖析,是C层面的剖析. 看pytorch下lib库中的TH好一阵子了,TH也是torch7下面的一个重要的库. 可以在torch的github上看到相关文档.看了半天 ...
- 交叉熵的数学原理及应用——pytorch中的CrossEntropyLoss()函数
分类问题中,交叉熵函数是比较常用也是比较基础的损失函数,原来就是了解,但一直搞不懂他是怎么来的?为什么交叉熵能够表征真实样本标签和预测概率之间的差值?趁着这次学习把这些概念系统学习了一下. 首先说起交 ...
- pytorch中如何使用DataLoader对数据集进行批处理
最近搞了搞minist手写数据集的神经网络搭建,一个数据集里面很多个数据,不能一次喂入,所以需要分成一小块一小块喂入搭建好的网络. pytorch中有很方便的dataloader函数来方便我们进行批处 ...
- (原)CNN中的卷积、1x1卷积及在pytorch中的验证
转载请注明处处: http://www.cnblogs.com/darkknightzh/p/9017854.html 参考网址: https://pytorch.org/docs/stable/nn ...
随机推荐
- Jupyter Notebook 一些常用的快捷键
命令模式(按 Esc 进入): A:在当前单元格上方插入新单元格. B:在当前单元格下方插入新单元格. D + D(按两次 D 键):删除当前单元格. Z:撤销单元格删除. Ctrl + Enter: ...
- Linux - 开启FTP服务
vsftpd 一.Centos6.x配置ftp 1.1.安装OpenSSH-server OpenSSH-server包含了FTP服务,通常,CentOS6.x默认已经安装了OpenSSH-serve ...
- Spark - [01] 概述
一.Spark是什么 Spark 是一种基于内存的快速.通用.可扩展的大数据分析引擎. Apache Spark is a unified analytics engine for large-sca ...
- Appflowy cloud 部署测试避坑指南
在进行 Appflowy cloud 部署测试时,我可谓是踩坑无数.下面,我想从几个关键方面来分享一下我的经验. 先给大家讲讲我的基础情况.Appflowy cloud 的部署是在 docker 环境 ...
- 腾讯云锐驰型轻量服务器搭建开源远程桌面软件RustDesk中继服务器小记
RustDesk是一个基于Rust编写的全平台开源远程桌面软件,其最大的特点为开箱即用,且数据完全自主掌控,甚至可以依托此项目定制化开发自己专属的远程桌面软件. 一.前言 由于我个人经常性出差,对远程 ...
- VirtualBox磁盘扩容
前言 虚拟机开始时设置的磁盘空间比较小,后面使用就不够了. # 查询磁盘使用情况 df -h 虚拟硬盘扩容 关闭正在运行的虚拟机 选中工具栏 选择虚拟硬盘,并选中需要扩容的磁盘 拖动进度条,设置想要扩 ...
- Golang 入门 : 变量
变量 Go语言是静态强类型语言,所以变量是有明确类型的.变量实质上就是在内存中的一小块空间,用来存储特定类型的可变数据.如果没有变量我们的程序只能将数值写死都是静态的数据,无法更改,变量可以让我们进行 ...
- SCRAPY入门学习(待完善)
Scrapy介绍 Scrapy 是用 Python 实现的一个为了爬取网站数据.提取结构性数据而编写的应用框架. Scrapy 常应用在包括数据挖掘,信息处理或存储历史数据等一系列的程序中. 通常我们 ...
- Nginx配置跨域,覆盖后端服务跨域配置
本篇文章主要介绍了,如何通过Nginx配置跨域,并覆盖后端服务跨域配置. 先看下后端代码跨域配置: 主要的目标是:不修改后端跨域配置代码,来实现Nginx跨域指定域名. @Bean public Co ...
- games101 作业4提高部分
games101 作业4提高部分 作业四中,我们按照实验步骤完成bazier曲线之后,得到的结果有一定的锯齿感: 然后pdf中给出的思路是: 对于一个曲线上的点,不只把它对应于一个像素,你需要根据到像 ...
