ML | SVM
What's xxx
An SVM model is a representation of the examples as points in space, mapped so that the examples of the separate categories are divided by a clear gap that is as wide as possible. New examples are then mapped into that same space and predicted to belong to a category based on which side of the gap they fall on.
In addition to performing linear classification, SVMs can efficiently perform a non-linear classification using what is called the kernel trick, implicitly mapping their inputs into high-dimensional feature spaces. The transformation may be nonlinear and the transformed space high dimensional; thus though the classifier is a hyperplane in the high-dimensional feature space, it may be nonlinear in the original input space.
Classifying data is a common task in machine learning. Suppose some given data points each belong to one of two classes, and the goal is to decide which class a new data point will be in. In the case of support vector machines, a data point is viewed as a p-dimensional vector (a list of p numbers), and we want to know whether we can separate such points with a (p − 1)-dimensional hyperplane. This is called a linear classifier. We choose the hyperplane so that the distance from it to the nearest data point on each side is maximized. If such a hyperplane exists, it is known as the maximum-margin hyperplane and the linear classifier it defines is known as a maximum margin classifier.
Any hyperplane can be written as the set of points $\mathbf{x}$ satisfying
$\mathbf{w}\cdot\mathbf{x} - b=0,\,$
where $\cdot$ denotes the dot product and ${\mathbf{w}}$ the (not necessarily normalized) normal vector to the hyperplane.
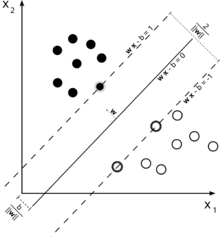
Maximum-margin hyperplane and margins for an SVM trained with samples from two classes. Samples on the margin are called the support vectors.
It was converted into a quadratic programming optimization problem. The solution can be expressed as a linear combination of the training vectors
$\mathbf{w} = \sum_{i=1}^n{\alpha_i y_i\mathbf{x_i}}.$
Only a few $\alpha_i$ will be greater than zero. The corresponding $\mathbf{x_i}$ are exactly the support vectors, which lie on the margin and satisfy $y_i(\mathbf{w}\cdot\mathbf{x_i} - b) = 1$. From this one can derive that the support vectors also satisfy
$\mathbf{w}\cdot\mathbf{x_i} - b = 1 / y_i = y_i \iff b = \mathbf{w}\cdot\mathbf{x_i} - y_i$
which allows one to define the offset b. In practice, it is more robust to average over all $N_{SV}$ support vectors:
$b = \frac{1}{N_{SV}} \sum_{i=1}^{N_{SV}}{(\mathbf{w}\cdot\mathbf{x_i} - y_i)}$
Writing the classification rule in its unconstrained dual form reveals that the maximum-margin hyperplane and therefore the classification task is only a function of the support vectors, the subset of the training data that lie on the margin.
Using the fact that $\|\mathbf{w}\|^2 = \mathbf{w}\cdot \mathbf{w}$ and substituting $\mathbf{w} = \sum_{i=1}^n{\alpha_i y_i\mathbf{x_i}}$, one can show that the dual of the SVM reduces to the following optimization problem:
Maximize (in $\alpha_i$ )
$\tilde{L}(\mathbf{\alpha})=\sum_{i=1}^n \alpha_i - \frac{1}{2}\sum_{i, j} \alpha_i \alpha_j y_i y_j \mathbf{x}_i^T \mathbf{x}_j=\sum_{i=1}^n \alpha_i - \frac{1}{2}\sum_{i, j} \alpha_i \alpha_j y_i y_j k(\mathbf{x}_i, \mathbf{x}_j)$
subject to (for any $i = 1, \dots, n$)
$\alpha_i \geq 0,\, $
and to the constraint from the minimization in $b$
$\sum_{i=1}^n \alpha_i y_i = 0.$
Here the kernel is defined by $k(\mathbf{x}_i,\mathbf{x}_j)=\mathbf{x}_i\cdot\mathbf{x}_j.$
$W$ can be computed thanks to the $\alpha$ terms:
$\mathbf{w} = \sum_i \alpha_i y_i \mathbf{x}_i.$
ML | SVM的更多相关文章
- OpenCV3 Ref SVM : cv::ml::SVM Class Reference
OpenCV3 Ref SVM : cv::ml::SVM Class Reference OpenCV2: #include <opencv2/core/core.hpp>#inclu ...
- Unknown/unsupported SVM type in function 'cv::ml::SVMImpl::checkParams'
1.在使用PYTHON[Python 3.6.8]训练样本时报错如下: Traceback (most recent call last): File "I:\Eclipse\Python\ ...
- 【OpenCV】opencv3.0中的SVM训练 mnist 手写字体识别
前言: SVM(支持向量机)一种训练分类器的学习方法 mnist 是一个手写字体图像数据库,训练样本有60000个,测试样本有10000个 LibSVM 一个常用的SVM框架 OpenCV3.0 中的 ...
- SVM+HOG特征训练分类器
#1,概念 在机器学习领域,支持向量机SVM(Support Vector Machine)是一个有监督的学习模型,通常用来进行模式识别.分类.以及回归分析. SVM的主要思想可以概括为两点:⑴它是针 ...
- [code segments] OpenCV3.0 SVM with C++ interface
talk is cheap, show you the code: /***************************************************************** ...
- EasyPR源码剖析(7):车牌判断之SVM
前面的文章中我们主要介绍了车牌定位的相关技术,但是定位出来的相关区域可能并非是真实的车牌区域,EasyPR通过SVM支持向量机,一种机器学习算法来判定截取的图块是否是真的“车牌”,本节主要对相关的技术 ...
- opencv3.1线性可分svm例子及函数分析
https://www.cnblogs.com/qinguoyi/p/7272218.html //摘自:http://docs.opencv.org/2.4/doc/tutorials/ml/int ...
- 简单HOG+SVM mnist手写数字分类
使用工具 :VS2013 + OpenCV 3.1 数据集:minst 训练数据:60000张 测试数据:10000张 输出模型:HOG_SVM_DATA.xml 数据准备 train-images- ...
- opencv 视觉项目学习笔记(二): 基于 svm 和 knn 车牌识别
车牌识别的属于常见的 模式识别 ,其基本流程为下面三个步骤: 1) 分割: 检测并检测图像中感兴趣区域: 2)特征提取: 对字符图像集中的每个部分进行提取: 3)分类: 判断图像快是不是车牌或者 每个 ...
随机推荐
- 【mysql】[Err]1267 - Illegal mix of collations(utf8_general_ci,IMPLICIT) and (utf8_unicode_ci,IMPLICIT) for operation ‘=
ALTER TABLE table_name CONVERT TO CHARACTER SET utf8 COLLATE utf8_unicode_ci;
- Java Web系统常用的第三方接口
1. Web Service 接口 1.1 接口方式说明和优点 在笔者的开发生涯中,当作为接口提供商给第三方提供接口时,以及作为客户端去调用第三方提供的接口时,大部分时候都是使用 Web Se ...
- leetcode-12-stack
409. Longest Palindrome Given a string which consists of lowercase or uppercase letters, find the le ...
- solr7.7.1完整教程
安装 上传solr-7.7.1.tgz至服务器 opt文件加下 解压 tar -zxvf solr-7.7.1.tgz 运行 进入到加压后的文件夹/opt/solr-7.7.1,执行一下命令启动sol ...
- poj 2236 网络连接问题 并查集
题意:n台电脑,当两台之间的距离小于d的时候可以连接. 题目会进行操作“修复”还有“查询是否已经连接”.只要在查询的时候输出YES或者ON 思路: 把可以相互连接的 即两者之间的距离小于 d q[i ...
- 常用C/C++预处理指令详解
预处理是在编译之前的处理,而编译工作的任务之一就是语法检查,预处理不做语法检查.预处理命令以符号“#”开头. 常用的预处理指令包括: 宏定义:#define 文件包含:#include 条件编译:#i ...
- luogu1233 木棍加工
先排个序然后做最长上升子序列就行了. #include <algorithm> #include <iostream> #include <cstdio> usin ...
- 安装python包
开始--cmd pip install pymongo 直到最后给出提示successfull install pymongo-**(版本号,最新的)
- python学习--python 连接SQLServer数据库(两种方法)
1. python 学习.安装教程参照: http://www.runoob.com/python/python-tutorial.html 2. 集成开发环境 JetBrains PyCharm C ...
- 2017"百度之星"程序设计大赛 - 资格赛
度度熊与邪恶大魔王 Accepts: 3666 Submissions: 22474 Time Limit: 2000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: ...
