2017 Multi-University Training 2 解题报告
Is Derek lying?
Time Limit: 3000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 65536/65536 K (Java/Others)
Total Submission(s): 1003 Accepted Submission(s): 548
and Alfia
are good friends.Derek
is Chinese,and Alfia
is Austrian.This summer holiday,they both participate in the summer camp of Borussia Dortmund.During the summer camp,there will be fan tests at intervals.The test consists of N
choice questions and each question is followed by three choices marked “A
” “B
” and “C
”.Each question has only one correct answer and each question is worth 1
point.It means that if your answer for this question is right,you can get 1
point.The total score of a person is the sum of marks for all questions.When the test is over,the computer will tell Derek
the total score of him and Alfia
.Then Alfia
will ask Derek
the total score of her and he will tell her: “My total score is X
,your total score is Y
.”But Derek
is naughty,sometimes he may lie to her. Here give you the answer that Derek
and Alfia
made,you should judge whether Derek
is lying.If there exists a set of standard answer satisfy the total score that Derek
said,you can consider he is not lying,otherwise he is lying.
,represents the number of test cases.
For each test case,there will be three lines.
The first line consists of three integers N
,X
,Y
,the meaning is mentioned above.
The second line consists of N
characters,each character is “A
” “B
” or “C
”,which represents the answer of Derek
for each question.
The third line consists of N
characters,the same form as the second line,which represents the answer of Alfia
for each question.
Data Range:1≤N≤80000
,0≤X,Y≤N,
∑T
i=1
N≤300000
Please print “Lying
” if you can make sure that Derek
is lying,otherwise please print “Not lying
”.
3 1 3
AAA
ABC
5 5 0
ABCBC
ACBCB
Lying
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
#define clr(x) memset(x,0,sizeof(x))
#define clrmax(x) memset(x,0,sizeof(x))
#define LL long long
#define mod 1000000007
using namespace std;
char s1[],s2[];
int min(int a,int b)
{
return a<b?a:b;
}
int main()
{
int T,same,dif,x,y,n;
scanf("%d",&T);
for(int kase=;kase<=T;kase++)
{
scanf("%d%d%d",&n,&x,&y);
cin>>s1;
cin>>s2;
same=;
for(int i=;i<n;i++)
if(s1[i]==s2[i])
same++;
dif=n-same;
if(dif>=abs(x-y) && (dif-abs(x-y))/+same>=min(x,y))
printf("Not lying\n");
else
printf("Lying\n");
}
return ;
}
Maximum Sequence
Time Limit: 4000/2000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 32768/32768 K (Java/Others)
Total Submission(s): 1405 Accepted Submission(s): 649
Given two integer sequences {ai} and {bi} with the same length n, you are to find the next n numbers of {ai}: an+1
…a
2n
. Just like always, there are some restrictions on an+1
…a
2n
: for each number ai
, you must choose a number bk
from {bi}, and it must satisfy ai
≤max{aj
-j│bk
≤j<i}, and any bk
can’t be chosen more than once. Apparently, there are a great many possibilities, so you are required to find max{∑2n
n+1
a
i
} modulo 109
+7 .
Now Steph finds it too hard to solve the problem, please help him.
For each test case, the first line consists of one integer n. The next line consists of n integers representing {ai}. And the third line consists of n integers representing {bi}.
1≤n≤250000, n≤a_i≤1500000, 1≤b_i≤n.
} modulo 109
+7。
8 11 8 5
3 1 4 2
For the first sample:
1. Choose 2 from {bi}, then a_2…a_4 are available for a_5, and you can let a_5=a_2-2=9;
2. Choose 1 from {bi}, then a_1…a_5 are available for a_6, and you can let a_6=a_2-2=9;
也是签到题。很容易想到的贪心:每次我们取当前数列中能取的数减去其位置的结果,最大的一个放到数列后面作为该位置的值。因此我们维护一个大根堆,以数-位置作为关键字,存放可取的数以及该数所在的位置。维护一个二叉搜索树,动态存取我们可以取的bi。大根堆用stl的优先队列,二叉搜索树用stl的multiset替代。那么每次加入ai时我们检查堆首的位置在multiset中有无小于他的数,有就贪心地取最近的一个作为该位置使用的bj并从multiset中去除该bi。并将该数作为该位置的值,将数-其位置 以及他的位置入堆;若没有则pop堆首直到有这样的数出现。
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
#define clr(x) memset(x,0,sizeof(x))
#define clrmax(x) memset(x,0,sizeof(x))
#define LL long long
#define mod 1000000007
using namespace std;
struct node
{
int pos,val;
bool operator < (const node &b) const
{
return val<b.val;
}
}u,v;
priority_queue<node> sta;
int n,m,t,pos,p;
int b[];
multiset<int>::iterator it;
multiset<int> posi;
LL ans;
int main()
{
while(scanf("%d",&n)!=EOF)
{
while(!sta.empty())
sta.pop();
posi.erase(posi.begin(),posi.end());
for(int i=;i<=n;i++)
{
scanf("%d",&t);
sta.push((node){i,t-i});
}
for(int i=;i<=n;i++)
{
scanf("%d",&t);
posi.insert(t);
}
ans=;
for(int i=;i<=n;i++)
{
while((it=posi.upper_bound(sta.top().pos))==posi.begin())
sta.pop();
it--;
ans=(ans+(LL)sta.top().val)%mod;
pos=i+n;
t=sta.top().val-pos;
sta.push((node){pos,t});
posi.erase(it);
}
printf("%lld\n",ans); }
return ;
}
Puzzle
Time Limit: 4000/2000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 262144/262144 K (Java/Others)
Total Submission(s): 271 Accepted Submission(s): 147
1.Sorting all the remaining jigsaws on the table in ascending order.
2.Picking out the 1st ,the P+1 th ,the 2*P+1 th,......the n*P+1 th jigsaws and put them back to the blank area in the board one by one from the top row to the bottom row,from the left column to the right column.
3.if there are jigsaws remained on the table,back to step 1.
After he arranging the board,it’s obvious that there’s only one blank area located at the bottom-right corner.
Your task is to make the numbers on jigsaws sorted with every row and every column in ascending order(From left to right,top to bottom),and the blank area should be located at the bottom-right corner in the end.Each step you can move the blank area’s neighboring jigsaws(which share a common side with the blank area) towards the blank area.It’s really a difficult question,so you need to write a program to judge whether it is possible to complete the task.

Following T lines,each line contains three integers N,M,P(2<=N,M<=1000;1<=P<=N*M-2).
3 2 3
3 2 4
999 999 1
NO
YES
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
#define clr(x) memset(x,0,sizeof(x))
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int T;
int n,m,p,q,t,ans,tot;
scanf("%d",&T);
while(T--)
{
ans=;
scanf("%d%d%d",&n,&m,&p);
tot=n*m-;
while(tot>p)
{
t=(tot-)/p+;
ans+=(p-)*t*(t-)/;
tot-=t;
}
if(ans%)
printf("NO\n");
else
printf("YES\n");
}
return ;
}
Sdjpx Is Happy
Time Limit: 6000/3000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 131072/131072 K (Java/Others)
Total Submission(s): 326 Accepted Submission(s): 124
1.He can divides soldiers into K disjoint non-empty subarrays.
2.He can sort a subarray many times untill a subarray is sorted in increasing order.
3.He can choose just two subarrays and change thier positions between themselves.
Consider A = [1 5 4 3 2] and P = 2. A possible soldiers into K = 4 disjoint subarrays is:A1 = [1],A2 = [5],A3 = [4],A4 = [3 2],After Sorting Each Subarray:A1 = [1],A2 = [5],A3 = [4],A4 = [2 3],After swapping A4 and A2:A1 = [1],A2 = [2 3],A3 = [4],A4 = [5].
But he wants to know for a fixed permutation ,what is the the maximum number of K?
Notice: every soldier has a distinct number from 1~n.There are no more than 10 cases in the input.
For every case:
Next line is n.
Next line is the number for the n soildiers.
Every case a line.
5
1 5 4 3 2
5
4 5 1 2 3
2
Test1:
Same as walk through in the statement.
Test2:
[4 5] [1 2 3]
Swap the 2 blocks: [1 2 3] [4 5].
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
#define clr(x) memset(x,0,sizeof(x))
#define clrmax(x) memset(x,0x3f3f3f3f,sizeof(x))
#define LL long long
#define mod 1000000007
#define N 3010
using namespace std;
int f[N][N],minx[N][N],maxx[N][N],last[N],num[N];
int n,m,k;
inline int max(int a,int b)
{
return a>b?a:b;
}
inline int min(int a,int b)
{
return a<b?a:b;
}
void predeal(int n)
{
for(int i=;i<=n;i++)
{
last[i]=i;
f[i][i]=;
minx[i][i]=maxx[i][i]=num[i];
for(int j=i+;j<=n;j++)
{
minx[i][j]=min(minx[i][j-],num[j]);
maxx[i][j]=max(maxx[i][j-],num[j]);
}
}
int j;
for(int l=;l<n;l++)
{
for(int i=;i<=n-l;i++)
{
j=i+l;
if(maxx[i][j]-minx[i][j]!=j-i)
f[i][j]=;
else
{
if(minx[i][j]<minx[i][last[i]])
f[i][j]=;
else
f[i][j]=f[i][last[i]]+f[last[i]+][j];
last[i]=j;
}
// cout<<i<<" "<<j<<":"<<f[i][j]<<endl;
}
}
return ;
}
int main()
{
int T,p,ans;
scanf("%d",&T);
while(T--)
{
scanf("%d",&n);
for(int i=;i<=n;i++)
scanf("%d",&num[i]);
predeal(n);//处理n^2确定i~j间不用交换情况下最多分几组
//n^2暴力,确定要交换的靠前的区间后,就能确定靠后区间的右端点,判断是否合法,合法则枚举靠后区间的左端点看是否能合法与靠前区间交换。合法则计算其分组数。在这些分组中和不交换情况下取最大值即为答案。
ans=;
for(int i=;i<=n;i++)
for(int j=i;j<=n;j++)
if(f[i][j] && (i==||(f[][i-] && minx[][j-]==)))
{
p=maxx[i][j];
if(p==n || (f[p+][n] && maxx[p+][n]==n))
{
for(int k=p;k>j;k--)
{
if(f[k][p] && minx[k][p]==i)
{
// cout<<i<<" "<<j<<" "<<k<<" "<<p<<":"<<f[1][i-1]+(k-1>=j+1?f[j+1][k-1]:0)+f[p+1][n]+2<<endl;
ans=max(ans,f[][i-]+(k->=j+?f[j+][k-]:)+f[p+][n]+);
}
}
}
}
ans=max(ans,f[][n]);
printf("%d\n",ans);
}
return ;
}
Funny Function
Time Limit: 2000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 32768/32768 K (Java/Others)
Total Submission(s): 1016 Accepted Submission(s): 491
satisfies: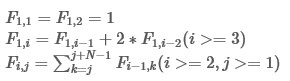
For given integers N and M,calculate Fm,1
modulo 1e9+7.
The next T lines,each line includes two integers N and M .
1<=T<=10000,1<=N,M<2^63.
2 2
3 3
33

#include<bits/stdc++.h>
#define clr(x) memset(x,0,sizeof(x))
#define mod 1000000007
#define LL long long
using namespace std;
LL n,m,ans;
LL quick_pow(LL i,LL n)
{
LL res=,mul=(i%mod+mod)%mod;
while(n)
{
if(n%==)
res=(res*mul)%mod;
mul=(mul*mul)%mod;
n/=;
}
return res;
}
void exgcd(LL a,LL b,LL &x,LL &y,LL &gcd)
{
if(!b) {gcd=a; x=; y=; }
else {exgcd(b,a%b,y,x,gcd); y-=x*(a/b); }
return ;
}
int main()
{
int T;
LL x,y,gcd;
scanf("%d",&T);
for(int kase=;kase<=T;kase++)
{
scanf("%lld%lld",&n,&m);
ans=(quick_pow((quick_pow(,n)-),m-)*%mod+(n%==?:)+mod)%mod;
exgcd(,mod,x,y,gcd);
x=(x%mod+mod)%mod;
ans=(ans*(LL)x)%mod;
printf("%lld\n",ans);
}
return ;
}
To my boyfriend
Time Limit: 2000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 32768/32768 K (Java/Others)
Total Submission(s): 630 Accepted Submission(s): 289
I never forget the moment I met with you. You carefully asked me: "I have a very difficult problem. Can you teach me?". I replied with a smile, "of course". You replied:"Given a matrix, I randomly choose a sub-matrix, what is the expectation of the number of **different numbers** it contains?"
Sincerely yours,
Guo
Each case contains two integers, n and m (1≤n, m≤100), the number of rows and the number of columns in the grid, respectively.
The next n lines each contain m integers. In particular, the j-th integer in the i-th of these rows contains g_i,j (0≤ g_i,j < n*m).
2 3
1 2 1
2 1 2
6(size = 1) + 14(size = 2) + 4(size = 3) + 4(size = 4) + 2(size = 6) = 30 / 18 = 6(size = 1) + 7(size = 2) + 2(size = 3) + 2(size = 4) + 1(size = 6)
我们不从矩阵,而从某个数字来看他对答案的贡献。对于每个数字,在每个矩阵中最上左的该数字为有效贡献的数字(先上后左)。因此我们对每个格子检查他所对应的数字对答案的贡献。做这个需要O(n)从列的位置往左和右建立两个单调栈,然后两个单调栈互弹求解,加起来是一个O(n^3)的做法。
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
#define clr(x) memset(x,0,sizeof(x))
#define LL long long
using namespace std;
int maped[][];
int last[][],inlast[];
long double ans;
stack< pair<int,int> > pushlas,by;
int max(int a,int b)
{
return a>b?a:b;
}
int main()
{
int T,n,m,t,color,inlas,ct;
LL ans;
scanf("%d",&T);
for(int kase=;kase<=T;kase++)
{
scanf("%d%d",&n,&m);
for(int i=;i<=n;i++)
for(int j=;j<=m;j++)
scanf("%d",&maped[i][j]);
clr(last);
ans=;
for(int i=;i<=n;i++)
for(int j=;j<=m;j++)
{
t=;
inlas=;
color=maped[i][j];
for(int k=m;k>=j;k--)
{
while(!by.empty() && last[color][k]>=by.top().first)
by.pop();
by.push(make_pair(last[color][k],k));
}
while(!by.empty())
{
pushlas.push(by.top());
by.pop();
}
inlas=;
for(int k=j;k>=;k--)
{
inlas=max(inlas,last[color][k]);
inlast[k]=inlas;
}
inlas=m+;
ct=;
for(int k=;k<=j;k++)
{
while(pushlas.top().first>inlast[k])
{
ans+=(LL)(ct+(i-pushlas.top().first)*(j-k+))*(LL)(inlas-pushlas.top().second)*(LL)(n-i+);
inlas=pushlas.top().second;
pushlas.pop();
}
ct+=i-inlast[k];
}
ans+=(LL)ct*(inlas-pushlas.top().second)*(LL)(n-i+);
pushlas.pop();
last[color][j]=i;
}
printf("%0.9lf\n",(double)ans/((n+)*n*(m+)*m)*);
}
return ;
}
TrickGCD
Time Limit: 5000/2500 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 262144/262144 K (Java/Others)
Total Submission(s): 1996 Accepted Submission(s): 778
, and Zhu wants to know there are how many different array B
satisfy the following conditions?
* 1≤Bi
≤A
i
* For each pair( l , r ) (1≤l≤r≤n
) , gcd(bl
,b
l+1
...b
r
)≥2
) describe the number of test cases.
Each test case begins with an integer number n describe the size of array A
.
Then a line contains n
numbers describe each element of A
You can assume that 1≤n,Ai
≤10
5
th test case , first output "Case #k: " , then output an integer as answer in a single line . because the answer may be large , so you are only need to output answer mod
109
+7
4
4 4 4 4
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
#define clr(x) memset(x,0,sizeof(x))
#define clrmax(x) memset(x,0,sizeof(x))
#define LL long long
#define mod 1000000007
using namespace std;
int inf[],mu[];
int prime[];
int a[],sum[];
int n,m,pcnt,ct,minai,maxai;
LL ans,sing;
void tooprimer(int n)
{
clr(inf);
pcnt=;
for(int i=;i<=n;i++)
{
if(!inf[i])
{
prime[++pcnt]=i;
inf[i]=;
mu[i]=;
}
for(int j=;j<=pcnt;j++)
{
if(i*prime[j]>n) break;
inf[i*prime[j]]=;
if(i%prime[j]==)
{
mu[i*prime[j]]=;
break;
}
else
mu[i*prime[j]]=-mu[i];
}
}
return ;
}
LL quick_pow(LL i,LL n)
{
LL res=,mul=(LL)i;
while(n)
{
if(n&)
res=(res*mul)%mod;
mul=(mul*mul)%mod;
n>>=;
}
return res;
} inline int min(int &a,int &b)
{
return a<b?a:b;
}
inline int max(int &a,int &b)
{
return a>b?a:b;
}
int main()
{
tooprimer();
int T,sqr;
scanf("%d",&T);
for(int kase=;kase<=T;kase++)
{
minai=0x3f3f3f3f;
maxai=;
scanf("%d",&n);
clr(sum);
for(int i=;i<=n;i++)
{
scanf("%d",&a[i]);
sum[a[i]]++;
minai=min(a[i],minai);
maxai=max(a[i],maxai);
}
for(int i=;i<=maxai;i++)
sum[i]=sum[i-]+sum[i];
ans=;
for(int i=;i<=maxai;i++)
{
sing=;
if(mu[i]==)
continue;
if(sum[i-]>)
continue;
for(int j=i;j<=maxai;j+=i)
{
sing=sing*quick_pow((LL)(j/i),(LL)(sum[(j+i->maxai?maxai:j+i-)]-sum[j-]))%mod;
}
ans=((ans+sing*(LL)mu[i])%mod+mod)%mod;
}
printf("Case #%d: %lld\n",kase,ans);
}
return ;
}
Regular polygon
Time Limit: 3000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 65536/65536 K (Java/Others)
Total Submission(s): 1959 Accepted Submission(s): 776
0 0
0 1
1 0
1 1
6
0 0
0 1
1 0
1 1
2 0
2 1
2
整数点对应的正多边形只有正方形。看透这点这题就是水题了。枚举所有边求有没有对应的正方形即可。记得去除重复的正方形。
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
#define clr(x) memset(x,0,sizeof(x))
#define clrmax(x) memset(x,0,sizeof(x))
#define LL long long
#define mod 1000000007
#define come 210
using namespace std;
bool mapped[][];
struct node
{
int x,y;
}pt[];
int main()
{
int T,n,m,k,l,maxx,ct,xi,yi,lenk,lenl,t,ans;
LL p;
while(scanf("%d",&n)!=EOF)
{
clr(mapped);
for(int i=;i<=n;i++)
{
scanf("%d%d",&pt[i].x,&pt[i].y);
pt[i].x+=come;
pt[i].y+=come;
mapped[pt[i].x][pt[i].y]=;
}
ans=;
for(int i=;i<=n;i++)
for(int j=;j<=n;j++)
if(i!=j)
{
yi=-(pt[i].x-pt[j].x);
xi=pt[i].y-pt[j].y;
if(xi+pt[i].x> && yi+pt[i].y> && mapped[xi+pt[i].x][yi+pt[i].y]== && xi+pt[j].x> && yi+pt[j].y> && mapped[xi+pt[j].x][yi+pt[j].y]==)
ans++;
xi=-xi;
yi=-yi;
if(xi+pt[i].x> && yi+pt[i].y> && mapped[xi+pt[i].x][yi+pt[i].y]== && xi+pt[j].x> && yi+pt[j].y> && mapped[xi+pt[j].x][yi+pt[j].y]==)
ans++;
}
printf("%d\n",ans/);
}
return ;
}
2017 Multi-University Training 2 解题报告的更多相关文章
- 2017 Multi-University Training 1 解题报告
Add More Zero Time Limit: 2000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 131072/131072 K (Java/Others)T ...
- 「2017 山东三轮集训 Day7 解题报告
「2017 山东三轮集训 Day7」Easy 练习一下动态点分 每个点开一个线段树维护子树到它的距离 然后随便查询一下就可以了 注意线段树开大点... Code: #include <cstdi ...
- 2015 Multi-University Training Contest 6 solutions BY ZJU(部分解题报告)
官方解题报告:http://bestcoder.hdu.edu.cn/blog/2015-multi-university-training-contest-6-solutions-by-zju/ 表 ...
- ACM-ICPC 2017 Asia HongKong 解题报告
ACM-ICPC 2017 Asia HongKong 解题报告 任意门:https://nanti.jisuanke.com/?kw=ACM-ICPC%202017%20Asia%20HongKon ...
- Mutual Training for Wannafly Union #1解题报告
---恢复内容开始--- q神等人组织的vjudge上的多校训练,题目基本上都来自于CF,#1是上周进行的,参加后感觉收获很多,因为上周准备期中比较忙,解题报告现在补上. 比赛地址(兼题目地址) A题 ...
- ZOJ_3950_How Many Nines 解题报告及如何对程序进行测试修改
The 17th Zhejiang University Programming Contest Sponsored by TuSimple Solution: #include <stdio. ...
- HDU 4303 Hourai Jeweled 解题报告
HDU 4303 Hourai Jeweled 解题报告 评测地址: http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=4303 评测地址: https://xoj. ...
- poj分类解题报告索引
图论 图论解题报告索引 DFS poj1321 - 棋盘问题 poj1416 - Shredding Company poj2676 - Sudoku poj2488 - A Knight's Jou ...
- HDU 4869 Turn the pokers (2014多校联合训练第一场1009) 解题报告(维护区间 + 组合数)
Turn the pokers Time Limit: 2000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 32768/32768 K (Java/Others) ...
随机推荐
- python学习笔记(九)之字符串
定义字符串 >>> mystring = 'Hello Python' >>> name = str('Mountain') >>> mystri ...
- 【洛谷 P4320】 道路相遇 (圆方树,LCA)
题目链接 题意:给一张无向图和\(M\)个询问,问\(u,v\)之间的路径的必经之点的个数. 对图建出圆方树,然后必经之点就是两点路径经过的原点个数,用\((dep[u]+dep[v]-dep[LCA ...
- bzoj 2440 dfs序
首先我们可以做一遍dfs,用一个队列记录每个点进出的顺序,当每个点访问的时候que[tot++]=x,记为in[x],当结束dfs的时候que[tot++]=x,记为out[x],这样处理出来的队列, ...
- js_数组去重效率对比
学习javascript已经快两年了,也不知道到了什么程度了. 说说我对javascript的理解,在电脑的世界里,只有数据. 数组,对象,字符串.对这些数据进行操作就可以完成很多业务逻辑,和页面的交 ...
- 关于js闭包官方解释庖丁解牛式理解
闭包:是一个拥有许多变量和绑定了这些变量的环境的表达式(通常是一个函数),因而这些变量也是该表达式的一部分. 变量+环境 首先按这个句子主谓宾来分解.闭包是一个表达式,通常是一个函数. 这意味着第一它 ...
- Shell脚本中引用、调用另一个脚本文件的2种方法
Shell脚本中引用.调用另一个脚本文件的2种方法 http://www.jb51.net/article/67903.htm
- Jmeter跨线程组传递变量
请求API需要授权令牌,但是授权令牌只需要获取一次,即可调用服务器上其他业务接口. 所以我想要把授权操作放在单独的一个线程,业务流放在其他线程. 这就需要我把从授权线程获取的令牌传入业务流线程. 解决 ...
- selenium遇到的一些问题,持续更新
1.今天早上运行程序的时候,发现我在循环点击一个元素的时候出现了错误 selenium.common.exceptions.StaleElementReferenceException: Messag ...
- 【LabVIEW技巧】代码块快速放置
前言 之前的文章中介绍了如何使用QuickDrop来实现快速代码放置,今天我们来详细的聊一下如何进行代码块的快速放置. 正文 LabVIWE程序设计中,我们在架构层级总是进行重复性的编写.举一个例子: ...
- DNS解析原理与Bind部署DNS服务
DNS是什么? DNS(Domain Name System,域名系统)是互联网上最核心的带层级的分布式系统,它负责把域名转换为IP地址.反查IP到域名的反向解析以及宣告邮件路由等信息,使得基于域名提 ...
