HDU 1890 区间反转
http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=1890
Robotic Sort
Problem Description
In this
task, you are to write software for a robot that handles samples in such a
laboratory. Imagine there are material samples lined up on a running belt. The
samples have different heights, which may cause troubles to the next processing
unit. To eliminate such troubles, we need to sort the samples by their height
into the ascending order.
Reordering is done by a mechanical robot arm,
which is able to pick up any number of consecutive samples and turn them round,
such that their mutual order is reversed. In other words, one robot operation
can reverse the order of samples on positions between A and B.
A
possible way to sort the samples is to find the position of the smallest one
(P1) and reverse the order between positions 1 and P1, which causes the smallest
sample to become first. Then we find the second one on position P and reverse
the order between 2 and P2. Then the third sample is located etc.
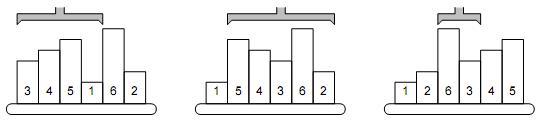
The
picture shows a simple example of 6 samples. The smallest one is on the 4th
position, therefore, the robot arm reverses the first 4 samples. The second
smallest sample is the last one, so the next robot operation will reverse the
order of five samples on positions 2–6. The third step will be to reverse the
samples 3–4, etc.
Your task is to find the correct sequence of reversal
operations that will sort the samples using the above algorithm. If there are
more samples with the same height, their mutual order must be preserved: the one
that was given first in the initial order must be placed before the others in
the final order too.
is described by two lines. The first line contains one integer number N , the
number of samples, 1 ≤ N ≤ 100 000. The second line lists exactly N
space-separated positive integers, they specify the heights of individual
samples and their initial order.
The last scenario is followed by a line
containing zero.
integers P1 , P1 , . . . PN ,separated by a space.
Each Pi must be an integer
(1 ≤ Pi ≤ N ) giving the position of the i-th sample just before the i-th
reversal operation.
Note that if a sample is already on its correct
position Pi , you should output the number Pi anyway, indicating that the
“interval between Pi and Pi ” (a single sample) should be reversed.
0
#include"stdio.h"
#include"iostream"
#include"queue"
#include"string.h"
#include"map"
#include"stdlib.h"
#include"algorithm"
#include"string"
#define M 1000005
#define inf 0x3f3f3f3f
using namespace std;
int a[M];
struct P
{
int val,pri,key;
}p[M];
int top,root;
int cmp(P a,P b)
{
if(a.val==b.val)
return a.pri<b.pri;
return a.val<b.val;
}
int son[M][],fa[M],num[M],flip[M],child[M];
struct Text
{
queue<int>q;
void init(int n)
{
top=n+;
for(int i=;i<=n+;i++)
{
num[i]=;
son[i][]=son[i][]=-;
fa[i]=-;
flip[i]=;
}
}
void Rotate(int x,int k)
{
int y=fa[x]; son[y][^k]=son[x][k];
if(son[y][^k]!=-)
fa[son[y][^k]]=y;
push_up(y);
if(son[fa[y]][]==y)
son[fa[y]][]=x;
else
son[fa[y]][]=x;
fa[x]=fa[y]; son[x][k]=y;
fa[y]=x;
}
void splay(int x,int f)
{
if(x==-)return;
while(fa[x]!=f)
{
int y=fa[x];
int z=fa[y];
if(z==f)
{
if(son[y][]==x)
Rotate(x,);
else
Rotate(x,);
}
else
{
if(son[z][]==y)
{
if(son[y][]==x)
{
Rotate(y,);
Rotate(x,);
}
else
{
Rotate(x,);
Rotate(x,);
}
}
else
{
if(son[y][]==x)
{
Rotate(y,);
Rotate(x,);
}
else
{
Rotate(x,);
Rotate(x,);
}
}
}
}
if(f==top)
root=x;
}
void RotateTo(int k,int f)
{
k++;
int x=root;
while()
{
push_down(x);
int temp=getNum(son[x][])+;
if(k==temp)break;
else if(k<temp)
x=son[x][];
else
{
k-=temp;
x=son[x][];
}
}
splay(x,f);
push_up(x);
}
int getOrder(int x)
{
int y=x;
while(fa[y]!=top)
{
int f=fa[y];
child[f]=y;
y=fa[y];
}
y=root;
while(y!=x)
{
int z=child[y];
push_down(z);
y=child[y];
}
int k=getNum(son[x][])+;
while(fa[x]!=top)
{
int y=fa[x];
int temp=getNum(son[y][])+;
if(son[y][]==x)
x=fa[x];
else
{
k+=temp;
x=fa[x];
}
}
return k-;
}
void Reversal(int x)
{
if(x==-)return;
int y=son[x][];
son[x][]=son[x][];
son[x][]=y;
}
int getNum(int x)
{
if(x==-)return ;
return num[x];
}
void push_up(int x)
{
num[x]=getNum(son[x][])+getNum(son[x][])+;
}
void push_down(int x)
{
if(x==-)return;
if(flip[x])
{
flip[x]^=;
Reversal(x);
if(son[x][]!=-)
flip[son[x][]]^=;
if(son[x][]!=-)
flip[son[x][]]^=;
}
}
void creat(int l,int r,int k,int f)
{
if(l>r)return;
int mid=(l+r)/;
if(f==top)
root=mid;
son[f][k]=mid;
fa[mid]=f;
creat(l,mid-,,mid);
creat(mid+,r,,mid);
push_up(mid);
}
void dfs(int x,int n)
{
if(x==-)return;
push_down(x);
dfs(son[x][],n);
if(x>=&&x<=n)
q.push(a[x]);
dfs(son[x][],n);
}
void output(int n)
{
dfs(root,n);
printf("%d",q.front());
q.pop();
while(!q.empty())
{
printf(" %d",q.front());
q.pop();
}
puts("");
}
}; int main()
{
int n;
while(scanf("%d",&n),n)
{
Text text;
for(int i=;i<=n;i++)
scanf("%d",&a[i]);
map<int,int>mp;
p[].val=-inf;
p[].pri=;
p[].key=;
for(int i=;i<=n;i++)
{
p[i].val=a[i];
p[i].pri=mp[a[i]];
p[i].key=i;
mp[a[i]]++;
}
p[n+].val=inf;
p[n+].pri=;
p[n+].key=n+;
sort(p,p+n+,cmp);
text.init(n);
text.creat(,n+,,top);
for(int i=;i<=n;i++)
{
int l=i-;
int key=p[i].key;
int r=text.getOrder(key)+;
text.RotateTo(l,top);
text.RotateTo(r,root);
flip[son[son[root][]][]]^=;
//text.output(n);
if(i==)
printf("%d",r-);
else
printf(" %d",r-);
}
puts("");
}
return ;
}
HDU 1890 区间反转的更多相关文章
- hdu 1890 Robotic Sort(splay 区间反转+删点)
题目链接:hdu 1890 Robotic Sort 题意: 给你n个数,每次找到第i小的数的位置,然后输出这个位置,然后将这个位置前面的数翻转一下,然后删除这个数,这样执行n次. 题解: 典型的sp ...
- hdu1890 伸展树(区间反转)
对于大神来说这题是水题.我搞这题花了快2天. 伸展树的优点有什么,就是树不管你怎么旋转序列是不会改变得,并且你要使区间反转,只要把第k大的点转到根结点,那么它的左子树就是要交换的区间[l,r),然后交 ...
- 算法模板——splay区间反转 2
实现功能:同splay区间反转 1(基于BZOJ3223 文艺平衡树) 这次改用了一个全新的模板(HansBug:琢磨了我大半天啊有木有),大大简化了程序,同时对于splay的功能也有所完善 这里面没 ...
- 算法模板——splay区间反转 1
实现的功能:将序列区间反转,并维护 详见BZOJ3223 var i,j,k,l,m,n,head,a1,a2:longint; s1:ansistring; a,b,c,d,fat,lef,rig: ...
- hdu 5869 区间不同GCD个数(树状数组)
Different GCD Subarray Query Time Limit: 6000/3000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 65536/65536 K ( ...
- hdu 4283 区间dp
You Are the One Time Limit: 2000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 32768/32768 K (Java/Others)T ...
- hdu 5700区间交(线段树)
区间交 Time Limit: 8000/4000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 65536/65536 K (Java/Others)Total Submiss ...
- HDU 2829 区间DP & 前缀和优化 & 四边形不等式优化
HDU 2829 区间DP & 前缀和优化 & 四边形不等式优化 n个节点n-1条线性边,炸掉M条边也就是分为m+1个区间 问你各个区间的总策略值最少的炸法 就题目本身而言,中规中矩的 ...
- 2018牛客网暑期ACM多校训练营(第三场) H - Shuffle Cards - [splay伸展树][区间移动][区间反转]
题目链接:https://www.nowcoder.com/acm/contest/141/C 时间限制:C/C++ 1秒,其他语言2秒 空间限制:C/C++ 262144K,其他语言524288K ...
随机推荐
- 灰度图像 Grayscale Binary_image
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Grayscale https://zh.wikipedia.org/wiki/灰度图像 In photography and comput ...
- mysql和oracle 分页查询(转)
最近简单的对oracle,mysql,sqlserver2005的数据分页查询作了研究,把各自的查询的语句贴出来供大家学习..... (一). mysql的分页查询 mysql的分页查询是最简单的,借 ...
- android ArrayAdapter 如何动态更改数据
在android开发中ListView是比较常用的组件,它以列表的形式展示具体内容,并且能够根据数据的长度自适应显示,使用adpater与listview捆绑后,有时希望在程序使用过程中能动态的更改l ...
- 【转】Warning: mysql_connect(): mysqlnd cannot connect to MySQL 4.1+ using the old insecure authenticat
Warning: mysql_connect(): mysqlnd cannot connect to MySQL 4.1+ using the old insecure authenticat 当m ...
- SHELL 八大扩展
最近在梳理bash知识的的过程中,有幸阅读了man bash文档,一时间犹如醍醐灌顶一般,很多当初不明白的地方都豁然开朗,现在就其中的一点做一分享,同时也为man bash做一下广告,当你面对bash ...
- 使用JetBrains dotMemory 4.0分析内存
安装下载地址:http://www.jetbrains.com/profiler/ 1.在本地启动web应用后,打开dotMemory,附加进程 2.附加后会看到集中颜色得粗条,不断往左边走动,这是内 ...
- C#中扩展方法
什么是扩展方法? 扩展方法顾名思义,就是允许向现有的“类型”添加方法,而无需创建派生类.重新编译或以其他方式修改原来类型. 扩展方法是一种特殊的静态方法,但可以像扩展类型上的实例方法一样进行调用. 扩 ...
- 【转载】拒绝平庸——浅谈WEB登录页面设计
用户活跃度是检验产品成功与否的重要指标之一,传统行业的商家极为重视门面的装潢,因为一个好的门面可以聚集人气,招揽更多的顾客.古时候的大户人家院子门口的石狮子或其他的摆件的摆放极为讲究,有一定的风水学说 ...
- ASP.NET中身份验证
ASP.NET中身份验证有三种方式:Windows.Forms和Passport. 1.Windows验证,基于窗体验证,需要每个页面写上验证身份代码,相对灵活,但操作过于复杂: 2.Passport ...
- mongoDB 读书笔记(初级命令)
关于mongoDB的相关知识,读书笔记,便于自己查阅用,不定期更新(纯手打) <mongoDB权威指南> 一.创建更新和删除 1.创建 //批量插入一个集合可以节省时间,只用 ...