【DKNN】Distilling the Knowledge in a Neural Network 第一次提出神经网络的知识蒸馏概念
原文链接 小样本学习与智能前沿 。 在这个公众号后台回复“DKNN”,即可获得课件电子资源。


文章已经表明,对于将知识从整体模型或高度正则化的大型模型转换为较小的蒸馏模型,蒸馏非常有效。在MNIST上,即使用于训练蒸馏模型的迁移集缺少一个或多个类别的任何示例,蒸馏也能很好地工作。对于Android语音搜索所用模型的一种深层声学模型,我们已经表明,通过训练一组深层神经网络实现的几乎所有改进都可以提炼成相同大小的单个神经网络,部署起来容易得多。
对于非常大的神经网络,甚至训练一个完整的集成也是不可行的,但是我们已经表明,通过学习大量的专家网络,可以对经过长时间训练的单个非常大的网络的性能进行显着改善。每个网络都学会在高度易混淆的群集中区分类别。我们尚未表明我们可以将专家网络的知识提炼回单个大型网络中。
@
论文: https://arxiv.org/pdf/1503.02531.pdf
Bibtex: @misc{hinton2015distilling,
title={Distilling the Knowledge in a Neural Network},
author={Geoffrey Hinton and Oriol Vinyals and Jeff Dean},
year={2015},
eprint={1503.02531},
archivePrefix={arXiv},
primaryClass={stat.ML}
}

Abstract
We achieve some surprising results on MNIST and we show that we can significantly improve the acoustic model of a heavily used commercial system by distilling the knowledge in an ensemble of models into a single model.
We also introduce a new type of ensemble composed of one or more full models and many specialist models which learn to distinguish fine-grained classes that the full models confuse. Unlike a mixture of experts, these specialist models can be trained rapidly and in parallel.
1 Introduction
In large-scale machine learning, we typically use very similar models for the training stage and the deployment stage despite their very different requirements。
Once the cumbersome model has been trained, we can then use a different kind of training, which we call “distillation” to transfer the knowledge from the cumbersome model to a small model that is more suitable for deployment.
we tend to identify the knowledge in a trained model with the learned parameter values and this makes it hard to see how we can change the form of the model but keep the same knowledge.
A more abstract view of the knowledge, that frees it from any particular instantiation, is that it is a learned mapping from input vectors to output vectors.
When we are distilling the knowledge from a large model into a small one, however, we can train the small model to generalize in the same way as the large model.
An obvious way to transfer the generalization ability of the cumbersome model to a small model is to use the class probabilities produced by the cumbersome model as “soft targets” for training the
small model.
When the cumbersome model is a large ensemble of simpler models, we can use an arithmetic or geometric mean of their individual predictive distributions as the soft targets
When the soft targets have high entropy, they provide much more information per training case than hard targets and much less variance in the gradient between training cases, so the small model can often be trained on much less data than the original cumbersome model and using a much higher learning rate.
This is valuable information that defines a rich similarity structure over the data (i. e. it says which 2’s look like 3’s and which look like 7’s) but it has very little influence on the cross-entropy cost function during the transfer stage because the probabilities are so close to zero.
Caruana and his collaborators circumvent this problem by using the logits (the inputs to the final softmax) rather than the probabilities produced by the softmax as the targets for learning the small model and they minimize the squared difference between the logits produced by the cumbersome model and the logits produced by the small model.
Our more general solution, called “distillation”, is to raise the temperature of the final softmax until the cumbersome model produces a suitably soft set of targets. We then use the same high temperature when training the small model to match these soft targets. We show later that matching the logits of the cumbersome model is actually a special\ case of distillation.
The transfer set that is used to train the small model could consist entirely of unlabeled data [1] or we could use the original training set.
2 Distillation
Neural networks typically produce class probabilities by using a “softmax” output layer that converts the logit, \(z_i\) , computed for each class into a probability,\(q_i\), by comparing \(z_i\) with the other logits.
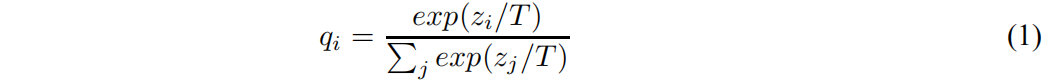
where \(T\) is a temperature that is normally set to 1. Using a higher value for \(T\) produces a softer
probability distribution over classes.
!!!! In the simplest form of distillation, knowledge is transferred to the distilled model by training it on
a transfer set and using a soft target distribution for each case in the transfer set that is produced by
using the cumbersome model with a high temperature in its softmax. The same high temperature is used when training the distilled model, but after it has been trained it uses a temperature of 1.
When the correct labels are known for all or some of the transfer set, this method can be significantly improved by also training the distilled model to produce the correct labels.
也就是半监督情况
One way to do this is to use the correct labels to modify the soft targets, but we found that a better way is to simply use a weighted average of two different objective functions.
- The first objective function is the cross entropy with the soft targets and this cross entropy is computed using the same high temperature in the softmax of the distilled model as was used for generating the soft targets from the cumbersome model.
- The second objective function is the cross entropy with the correct labels.
We found that the best results were generally obtained by using a condiderably lower weight on the second objective function.
2.1 Matching logits is a special case of distillation
The softmax of this type of specialist can be made much smaller by combining all of the classes it does not care about into a single dustbin class.
After training, we can correct for the biased training set by incrementing the logit of the dustbin class by the log of the proportion by which the specialist class is oversampled.
3 Preliminary experiments on MNIST
4 Experiments on speech recognition
4.1 Results
5 Training ensembles of specialists on very big datasets
5.1 The JFT dataset
5.2 Specialist Models
5.3 Assigning classes to specialists
5.4 Performing inference with ensembles of specialists
5.5 Results
6 Soft Targets as Regularizers
6.1 Using soft targets to prevent specialists from overfitting
7 Relationship to Mixtures of Experts
8 Discussion
We have shown that distilling works very well for transferring knowledge from an ensemble or from a large highly regularized model into a smaller, distilled model. On MNIST distillation works remarkably well even when the transfer set that is used to train the distilled model lacks any examples of one or more of the classes. For a deep acoustic model that is version of the one used by Android voice search, we have shown that nearly all of the improvement that is achieved by training an ensemble of deep neural nets can be distilled into a single neural net of the same size which is far easier to deploy.
For really big neural networks, it can be infeasible even to train a full ensemble, but we have shown that the performance of a single really big net that has been trained for a very long time can be significantly improved by learning a large number of specialist nets, each of which learns to discriminate between the classes in a highly confusable cluster. We have not yet shown that we can distill the knowledge in the specialists back into the single large net.
【DKNN】Distilling the Knowledge in a Neural Network 第一次提出神经网络的知识蒸馏概念的更多相关文章
- Distilling the Knowledge in a Neural Network
url: https://arxiv.org/abs/1503.02531 year: NIPS 2014   简介 将大模型的泛化能力转移到小模型的一种显而易见的方法是使用由大模型产生的类概率作 ...
- 【论文考古】知识蒸馏 Distilling the Knowledge in a Neural Network
论文内容 G. Hinton, O. Vinyals, and J. Dean, "Distilling the Knowledge in a Neural Network." 2 ...
- Python -- machine learning, neural network -- PyBrain 机器学习 神经网络
I am using pybrain on my Linuxmint 13 x86_64 PC. As what it is described: PyBrain is a modular Machi ...
- Recurrent Neural Network(递归神经网络)
递归神经网络(RNN),是两种人工神经网络的总称,一种是时间递归神经网络(recurrent neural network),另一种是结构递归神经网络(recursive neural network ...
- 【RS】Automatic recommendation technology for learning resources with convolutional neural network - 基于卷积神经网络的学习资源自动推荐技术
[论文标题]Automatic recommendation technology for learning resources with convolutional neural network ( ...
- 1503.02531-Distilling the Knowledge in a Neural Network.md
原来交叉熵还有一个tempature,这个tempature有如下的定义: \[ q_i=\frac{e^{z_i/T}}{\sum_j{e^{z_j/T}}} \] 其中T就是tempature,一 ...
- deep_learning_初学neural network
神经网络——最易懂最清晰的一篇文章 神经网络是一门重要的机器学习技术.它是目前最为火热的研究方向--深度学习的基础.学习神经网络不仅可以让你掌握一门强大的机器学习方法,同时也可以更好地帮助你理解深度学 ...
- 论文笔记:蒸馏网络(Distilling the Knowledge in Neural Network)
Distilling the Knowledge in Neural Network Geoffrey Hinton, Oriol Vinyals, Jeff Dean preprint arXiv: ...
- 论文笔记之:Progressive Neural Network Google DeepMind
Progressive Neural Network Google DeepMind 摘要:学习去解决任务的复杂序列 --- 结合 transfer (迁移),并且避免 catastrophic f ...
随机推荐
- 【事件中心 Azure Event Hub】Event Hub日志种发现的错误信息解读
问题描述 使用Event Hub消费事件时,出现的各种客户端错误的解读.(再后期遇见新的错误信息,会持续添加进此说明) 一:再Linux中运行Event Hub消费端程序,出现Too many ope ...
- linux 查看和设置主机名
1.设置主机名 通过编辑/etc/sysconfig/network文件中的HOSTNAME字段就可以修改主机名.如下所示: [root@zijuan /]# vim /etc/sysconfig/n ...
- R语言factor类型转numeric
R 语言中为了进行数据分析,比如回归分析,这时候对于数据表格中的factor类型的数据会带来弊端,比如对因子的每一个数据都进行一次回归,这样就显得很复杂,且违背了我们的初衷,需要把factor转换为n ...
- 剑指41和为s的连续整数序列
题目描述 小明很喜欢数学,有一天他在做数学作业时,要求计算出9~16的和,他马上就写出了正确答案是100.但是他并不满足于此,他在想究竟有多少种连续的正数序列的和为100(至少包括两个数).没多久,他 ...
- 转载:WIFI无线协议802.11a/b/g/n/ac的演变以及区别
WIFI无线协议802.11a/b/g/n/ac的演变以及区别 版权声明:版权所有,转载须注明出处. https://blog.csdn.net/Brouce__Lee/article/details ...
- tcp 拥塞控制引擎&状态机
TCP核心:流量控制 拥塞控制 流量控制:滑动窗口来实现, 防止接收方能够处理过来 拥塞控制:防止过多的包被发送到网络中,避免出现网络负载过大 说一说 拥塞控制: 拥塞控制状态机的状态有五种,分别 ...
- intelx86为何从0xFFFF0处执行
第一条指令的地址 在用户按下计算机电源开关之后,CPU会自动的将其CS寄存器设定为0xFFFF,将其IP寄存器设定为0x0000.由于CS:IP指出了下一条指令的地址[1],因此CPU会跳到0xFFF ...
- 《GNU_makefile》第七章——makefile的条件执行
条件执行即,通过变量的值,来控制make的执行和忽略. 条件执行只能控制makefile的make语法部分,不能控制shell部分 1.一个例子 - libs_for_gcc = -lgnu norm ...
- 同步FIFO学习笔记
- 二:Redis:(REmote DIctionary Server)远程字典服务器
Redis是完全开源免费的,用C语言编写的,遵循BSD协议,是一个高性能的(key-value)分布式内存数据库,基于内存运行,并支持持久化的NOSQL数据库,是当前最热门的NOSQL数据库之一,也被 ...
