WPF:如何高速更新Model中的属性
原文:[WPF/MVVM] How to deal with fast changing properties
In this article, I will describe a problem which happens in a WPF/MVVM application when the Model is updated at a very high frequency.
It happened to me while implementing a Model handling a lot of values coming from instruments and I wanted to display the current values, even if they were changing very quickly.
The test case
All my test are based on this simple Model class:
public class Model
{
const long MAX_DURATION = 20000;
public double Progress { get; private set; }
public event EventHandler<double> ProgressChanged;
public double Frequency { get; private set; }
public event EventHandler<double> FrequencyChanged;
public Model()
{
Task.Run((Action)LongRunningBackgroundTask);
}
void LongRunningBackgroundTask()
{
long loopCount = 0;
long elapsed = 0;
var chrono = new Stopwatch();
chrono.Start();
while (elapsed < MAX_DURATION)
{
elapsed = chrono.ElapsedMilliseconds;
SetProgress(100.0 * elapsed / MAX_DURATION);
SetFrequency(1.0 * loopCount / elapsed);
loopCount++;
}
}
void SetProgress(double value)
{
Progress = value;
if (ProgressChanged != null)
ProgressChanged(this, value);
}
void SetFrequency(double value)
{
Frequency = value;
if (FrequencyChanged != null)
FrequencyChanged(this, value);
}
}
As you can see, it’s very straightforward. The Model class contains two public properties Progressand Frequency and their associated events. During 20 seconds, it runs a loop in a background task and updates the properties as fast as it can:
Progresswill go from0.0to100.0.Frequencywill contains the average loop frequency so far.
The problem with the classic MVVM approach
In the classic MVVM approach, the ViewModel is attached to the Model’s events, so as to be updated on every change.
Usually, the ViewModel’s event handler calls Dispatcher.BeginInvoke() to ensure the eventPropertyChanged is raised in the UI thread.
public ViewModel()
{
dispatcher = Dispatcher.CurrentDispatcher;
model = new Model();
model.ProgressChanged += OnModelProgressChanged;
// ... then the same for the Frequency
}
void OnModelProgressChanged(double newValue)
{
dispatcher.BeginInvoke((Action)delegate() { Progress = newValue; });
}
public double Progress
{
get { return progress; }
set
{
if( progress == value ) return;
progress = value;
RaisePropertyChanged("Progress");
}
}
// ... then the same pattern for the Frequency property
However, this approach wont be able to work with the Model class defined earlier. The GUI is completely frozen and sometimes even throws an OutOfMemoryException.
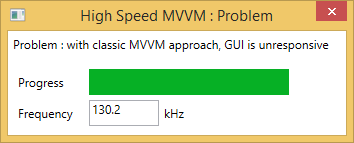
Here is why: Each time a Model’s property changes, the ViewModel calls BeginInvoke() and therefore appends a message in the dispatcher’s event queue. But the messages are dequeued way slower than they are added, so the queue will grow over and over until the memory is full.
Also, you can see that the execution speed of the Model’s task is really affected : only 130 kHz on average.
Solution 1 : Ignore events that are too close
The first solution that usualy comes in mind is:
Hmmm… I get too many events…
I’ll just slow them down !
OK, let’s try…
public ViewModel()
{
var dispatcher = Dispatcher.CurrentDispatcher;
var model = new Model();
Observable.FromEventPattern<double>(model, "ProgressChanged")
.Sample(TimeSpan.FromMilliseconds(5))
.ObserveOn(dispatcher)
.Subscribe(x => Progress = x.EventArgs);
}
Here, I used Reactive Framework because it offers the Sample() method which limits the rate of the events.
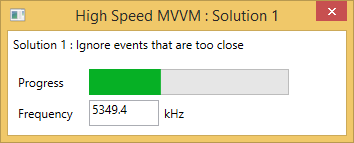
In this case the GUI is perfectly responsive and the Task execution speed is better but still low.
I think it’s a viable if you already use Reactive Framework, but I wouldn’t use it in my project: it’s too complicated and the performance is not good enough.
Solution 2 : Poll with a DispatcherTimer
Let’s look a this problem from a different angle. Why don’t we loose the “push” approach and use “pull” approach instead ?
In other words, instead of attaching to the event of the Model, the ViewModel could periodically read the values.
The most common way to implement polling in MVVM is to instanciate a DispatcherTimer in the ViewModel.
public ViewModel()
{
model = new Model();
var timer = new DispatcherTimer();
timer.Interval = TimeSpan.FromMilliseconds(5);
timer.Tick += OnTimerTick;
timer.Start();
}
void OnTimerTick(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
Progress = model.Progress;
Frequency = model.Frequency;
}
// ...the remaining is identical to the original ViewModel
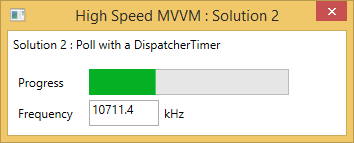
Here you go ! No only the GUI is perfectly responsive, the execution speed of the Task is way better: 10 MHz
Solution 3 : Poll on CompositionTarget.Rendering
To make it even simpler, we can move the timer from the ViewModel to the View. From that place, we can use the CompositionTarget.Rendering event and completely get rid of the DispatcherTimer. (As a reminder this event is raised by WPF each time an animation frame is rendered, 30 or 60 times per seconds)
View’s code behind:
public MainWindow()
{
InitializeComponent();
DataContext = new ViewModel();
CompositionTarget.Rendering += OnRendering;
}
void OnRendering(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
if (DataContext is IRefresh)
((IRefresh)DataContext).Refresh();
}
ViewModel:
class ViewModel : INotifyPropertyChanged, IRefresh
{
public ViewModel()
{
model = new Model();
}
public void Refresh()
{
Progress = model.Progress;
Frequency = model.Frequency;
}
// ...the remaining is identical to the original ViewModel
}
You get almost the same result as Solution 1, and even a slightly faster execution speed.
Conclusion
I like simple solutions, that why I really prefer the last one.
Whether it respects or not the MVVM pattern is really a matter of opinion. I really like the idea of theView being responsible of the timer logic and the ViewModel being responsible of updating its value.
One thing I really appreciate on the polling approach is that it really decouples the Model’s and theViewModel’s execution threads. We can even get rid of the Model’s events.
To conclude, here is a comparison of the memory consumptions: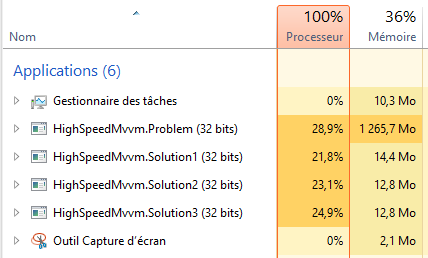
PS: A word about concurrency
When using the polling technique, you should take a special care of the concurrency.
Since the properties of the Model are accessed from several threads, you may need to add lock blocks if the type is bigger than a processor word (in my examples I used a int so that’s OK).
If you have a lot of changing properties in your model, you should group them in a class, likeModelState. That way, the ViewModel will only have one property to monitor and only this class needs to be thread safe.
WPF:如何高速更新Model中的属性的更多相关文章
- 在Asp.Net MVC中实现RequiredIf标签对Model中的属性进行验证
在Asp.Net MVC中可以用继承ValidationAttribute的方式,自定制实现RequiredIf标签对Model中的属性进行验证 具体场景为:某一属性是否允许为null的验证,要根据另 ...
- CompareValues标签对Model中的属性进行验证
在Asp.Net MVC中实现CompareValues标签对Model中的属性进行验证 在Asp.Net MVC中可以用继承ValidationAttribute的方式,自定制实现Model两个 ...
- 在.Net MVC中自定义ValidationAttribute标签对Model中的属性做验证
写一个继承与ValidationAttribute类的自定义的验证方法 MVC中传递数据时,大多数都会用Model承载数据,并且在传到控制器后,对Model进行一系列的验证. 我平时经常使用的判断方法 ...
- 将DataRow赋值给model中同名属性
/// <summary> /// 将DataRow赋值给model中同名属性 /// </summary> /// <typeparam name="T&qu ...
- MVVM Light 新手入门(2) :ViewModel / Model 中定义“属性” ,并在View中调用
今天学习MVVM架构中“属性”的添加并调用,特记录如下,学习资料均来自于网络,特别感谢翁智华的利刃 MVVMLight系列. 一个窗口的基本模型如下: View(视图) -> ViewModel ...
- 在Asp.Net MVC中实现CompareValues标签对Model中的属性进行验证
在Asp.Net MVC中可以用继承ValidationAttribute的方式,自定制实现Model两个中两个属性值的比较验证 具体应用场景为:要对两个属性值的大小进行验证 代码如下所示: /// ...
- iOS开发之遍历Model类的属性并完善使用Runtime给Model类赋值
在上篇博客<iOS开发之使用Runtime给Model类赋值>中介绍了如何使用运行时在实体类的基类中添加给实体类的属性赋值的方法,这个方法的前提是字典的Key必须和实体类的Property ...
- Model中的验证规则
一.能够使用Model的Attribute进行服务端数据验证 本文目录 一.概述 二.MVC提供的常用上下文 三.自定义正则表达式验证 一.概述 为了确保数据的安全性,由Client发送到服务端的每一 ...
- Js和Thymeleaf如何获取model中的值
一.Jquery获取Model中的数据 1.将model中的值赋给hidden,然后Js获取隐藏域的值. 后台的实现: @RequestMapping("/QEditorMod1" ...
随机推荐
- 海马玩模拟器——搭建React Native环境
Visual Studio Emulator for Android 模拟器国内这网络环境不太用,所以使用海马玩模拟器,给大家推荐一下! 下面开始配置环境: 1)下载1.8+JDK,配置JDK环境参考 ...
- mac技巧之常用的快键键
1.修改文件名 选中文件按return键即可修改文件名. 2.文件预览 选中文件按照空格键即可实现文件的预览(并不是打开文件) 3.任务之间进行切换 command+tab 4.复制文件 推动文件按照 ...
- shell监控自动备份是否成功(判断文件是否存在)
作者:邓聪聪 在自动打包生成备份sql文件后,对运行情况做一个监控! 命令前加time,查看命令执行完成所用时间! FILE_DIR=/root/ DATE=$(date +%F) FILE_NAM ...
- NOI2019 SX 模拟赛 no.5
Mas 的童年 题目描述:不知道传送门有没有用? 反正就是对于每个前缀序列求一个断点,使得断点左右两个区间的 分别的异或和 的和最大 分析 jzoj 原题? 但是我 TM 代码没存账号也过期了啊! 然 ...
- ubuntu14.04上源码安装openssl1.0.2k
卸载自带openssl sudo apt-get remove openssl 解压文件tar -xzf openssl-1.0.2k.tar.gz 配置 sudo ./config shared - ...
- $Django cookies与session--解决无连接无状态问题, session配置
session作用: 会话保持,记住用户的登录状态(WEB网站,分布式架构) 作用(和cookie的区别) 避免了敏感信息保存在客户端,防止客户端修改cookie信息! -cookie:存储在客户端浏 ...
- h5 右下角浮动按钮, 纯css实现
2017年11月22日19:00:22 效果: 代码: /** 右下角跳转按钮 跳转到列表 */ #list_note_icon { position: fixed; ...
- oracle:10g下载地址(转载)
转载地址:http://www.veryhuo.com/a/view/177074.html Oracle 10g Database和Client多平台官方下载地址 http://www.veryhu ...
- Light OJ 1012
经典搜索水题...... #include<bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; const int maxn = 20 + 13; const int ...
- python第13天
装饰器 装饰器本质上就是一个python函数,他可以让其他函数在不需要做任何改动的前提下,增加额外的功能,装饰器的返回值也是一个函数对象. 装饰器的应用场景:比如插入日志,性能测试,事务处理,缓存等等 ...
