The Instruction Set In Cortex-M3
The Cortex-M3 supports the Thumb-2 instruction set. This is one of the most important features of the Cortex-M3 processor because it allows 32-bit instructions and 16-bit instructions to be used together for high code density and high efficiency. It is flexible and powerful yet easy to use.
In previous ARM processors, the central processing unit (CPU) had two operation states: a 32-bit ARM state and a 16-bit Thumb state. In the ARM state, the instructions are 32 bits and can execute all supported instructions with very high performance. In the Thumb state, the instructions are 16 bits, so there is a much higher instruction code density, but the Thumb state does not have all the functionality of ARM instructions and may require more instructions to complete certain types of operations.
To get the best of both worlds, many applications have mixed ARM and Thumb codes. However, the mixed-code arrangement does not always work best. There is overhead (in terms of both execution time and instruction space, see Figure 2.7) to switch between the states, and ARM and Thumb codes might need to be compiled separately in different files. This increases the complexity of software develop- ment and reduces maximum efficiency of the CPU core.
With the introduction of the Thumb-2 instruction set, it is now possible to handle all process- ing requirements in one operation state. There is no need to switch between the two. In fact, the Cortex-M3 does not support the ARM code. Even interrupts are now handled with the Thumb state. (Previously, the ARM core entered interrupt handlers in the ARM state.) Since there is no need to switch between states, the Cortex-M3 processor has a number of advantages over traditional ARM processors, such as:
No state switching overhead, saving both execution time and instruction space
No need to separate ARM code and Thumb code source files, making software development and
maintenance easier
It’s easier to get the best efficiency and performance, in turn making it easier to write software, because there is no need to worry about switching code between ARM and Thumb to try to get the best density/performance
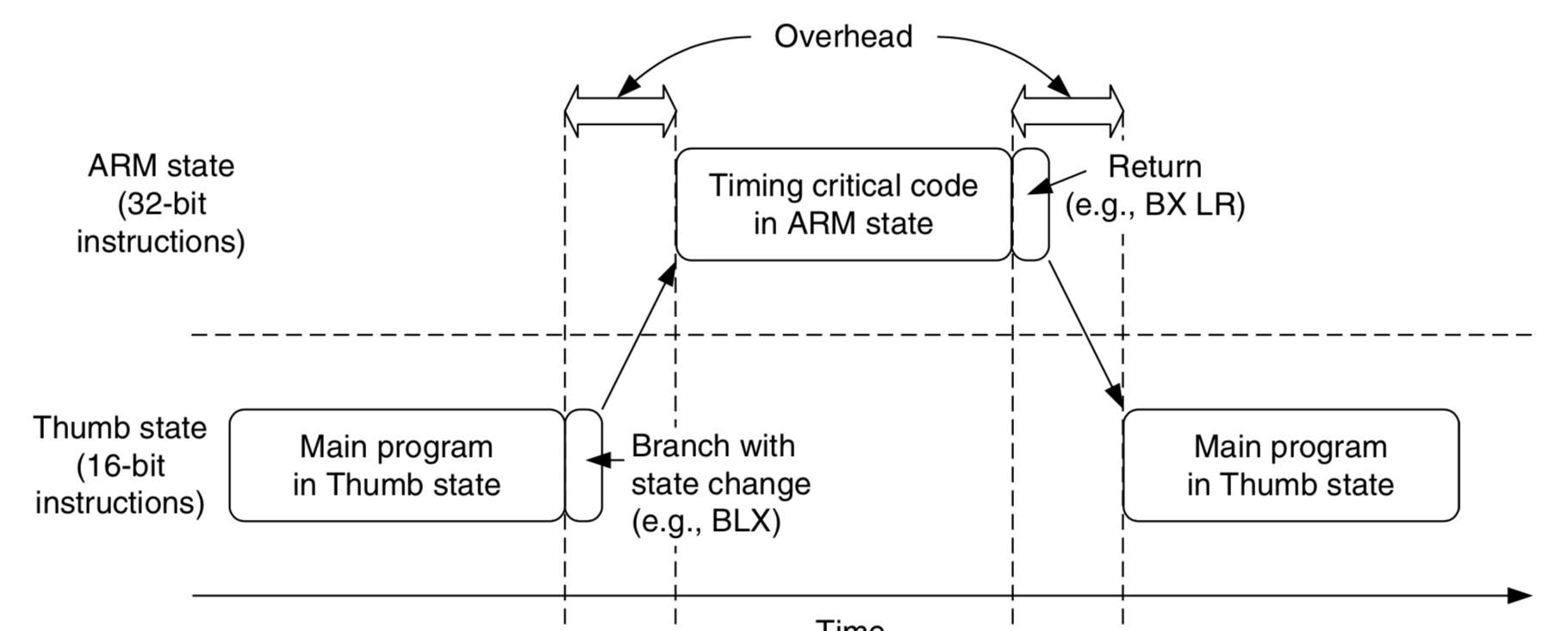
|
|
Switching between ARM Code and Thumb Code in Traditional ARM Processors Such as the ARM7. The Cortex-M3 processor has a number of interesting and powerful instructions. Here are a few examples:
Since the Cortex-M3 processor supports the Thumb-2 instruction set only, existing program code for ARM needs to be ported to the new architecture. Most C applications simply need to be recompiled using new compilers that support the Cortex-M3. Some assembler codes need modification and porting to use the new architecture and the new unified assembler framework. Note that not all the instructions in the Thumb-2 instruction set are implemented on the Cortex-M3. The ARMv7-M Architecture Application Level Reference Manual [Ref. 2] only requires a subset of the Thumb-2 instructions to be implemented. For example, coprocessor instructions are not supported on the Cortex-M3 (external data processing engines can be added), and Single Instruction–Multiple Data (SIMD) is not implemented on the Cortex-M3. In addition, a few Thumb instructions are not supported, such as Branch with Link and Exchange (BLX) with immediate (used to switch processor state from Thumb to ARM), a couple of change process state (CPS) instructions, and the SETEND (Set Endian) instructions, which were introduced in architecture v6. For a complete list of supported instructions, refer to Appendix A. 摘抄自:《The definitive guide to the ARM Cortex-M3》Second Edition. |
The Instruction Set In Cortex-M3的更多相关文章
- ARM Cortex M3(V7-M架构)硬件启动程序 一
Cortex-m3启动代码分析笔记 启动代码文件名是STM32F10X.S,它的作用先总结下,然后再分析. 启动代码作用一般是: 1)堆和栈的初始化: 2)中断向量表定义: 3)地址重映射及中断向量表 ...
- ARM Cortex M3系列GPIO口介绍(工作方式探讨)
一.Cortex M3的GPIO口特性 在介绍GPIO口功能前,有必要先说明一下M3的结构框图,这样能够更好理解总线结构和GPIO所处的位置. Cortex M3结构框图 从图中可以看出 ...
- ARM 架构、ARM7、ARM9、STM32、Cortex M3 M4 、51、AVR 之间有什么区别和联系?(转载自知乎)
ARM架构: 由英国ARM公司设计的一系列32位的RISC微处理器架构总称,现有ARMv1~ARMv8种类. ARM7: 一类采用ARMv3或ARMv4架构的,使用冯诺依曼结构的内核. ...
- STM32学习之路入门篇之指令集及cortex——m3的存储系统
STM32学习之路入门篇之指令集及cortex——m3的存储系统 一.汇编语言基础 一).汇编语言:基本语法 1.汇编指令最典型的书写模式: 标号 操作码 操作数1, 操作数2,... ...
- Implementation of Serial Wire JTAG flash programming in ARM Cortex M3 Processors
Implementation of Serial Wire JTAG flash programming in ARM Cortex M3 Processors The goal of the pro ...
- 【ARM-Linux开发】ARM7 ARM9 ARM Cortex M3 M4 有什么区别
ARM7 ARM9 ARM Cortex M3 M4 区别 arm7 arm9 可以类比386和奔腾, 不同代,arm9相比arm7指令集和性能都有所增强,arm7和arm9都有带mmu和无mmu的版 ...
- 【freertos】002-posix模拟器设计与cortex m3异常处理
目录 前言 posix 标准接口层设计 模拟器的系统心跳 模拟器的task底层实质 模拟器的任务切换原理 cortex M3/M4异常处理 双堆栈指针 双操作模式 栈帧 EXC_RETURN 前言 如 ...
- CORTEX -M3 : Registers in depth
http://www.zembedded.com/cortex-m3-registers-in-depth/ Thanks for the overwhelm response you show in ...
- ARM Cortex M3(V7-M架构)硬件启动程序 二
解析 STM32 的启动过程 解析STM32的启动过程 当前的嵌入式应用程序开发过程里,并且C语言成为了绝大部分场合的最佳选择.如此一来main函数似乎成为了理所当然的起点——因为C程序往往从main ...
- stm32和cortex M3学习内核简单总结
1.stm32综述 2.寄存器组 3.操作模式和特权级别 4.存储器映射 5.中断和异常 6.其他 Stm32综述 这可以说是我第一款认真学习的单片机了,学完这个就要开启我通往arm9的大门了,接下来 ...
随机推荐
- Maya编程——沿Curve绘制圆柱
操作流程: 1. VS运行代码,生成插件 2. 打开Maya绘制曲线,加载插件 3. 选中绘制的曲线,运行插件 Posts1.0 代码: #include <maya/MSimple.h> ...
- 定制flask-admin的主页
flask也用了很久了,一般配合flask-admin设置后台. 但是flask-admin设置的都是自己加入的,对某些model进行管理. 下面介绍如何定制flask-admin的首页. 原来我们引 ...
- WPF之图片处理系列(19/590)
https://www.cnblogs.com/Big-Head/p/12068230.html
- python数据分析2之numpy
源代码 # -*- coding: utf-8 -*- """ Spyder Editor This is a temporary script file. " ...
- centos个性化命令行提示符
为了在满屏的命令中找到用户的命令行,所以很有必要设置一种字体颜色.我就设置最实用的一种,可以用蓝色字体显示当前所在路径 命令行输入: echo "PS1='[\${debian_chroot ...
- [转帖]Proof Of Work 工作量证明
Proof Of Work 工作量证明 https://www.cnblogs.com/zhang-qc/p/10451817.html 借鉴了 哈希现金(Hashcash)-1997年 英国密码学专 ...
- Java基础---Java环境配置
java 下载:https://www.java.com/zh_CN/ 1.Java安装:jdk9 2. JAVA_HOME 环境变量的配置 在DOS命令行下使用这些工具,就要先进入到JDK的bin目 ...
- 修改 Delphi 10.3.3 IDE 字体和字体大小
Delphi 10.2.2 之前,可以通过 IDE视觉设置的系统注册表项 修改字体和字体大小,因为 Delphi 10.2.2 IDE增加了主题,主题包含了字体信息, 此方法失效了.对于高分辨率屏幕, ...
- Python之路【第二十二篇】:轮播图片CSS
轮播代码如下: <!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="U ...
- 嵌入式web服务器BOA+CGI+HTML+MySQL项目实战——Linux
准备环境操作系统: Ubuntu12.04 LTS环境搭建: 需要 BOA,Apache,CCGI,MySQL,GCC[Linux下嵌入式Web服务器BOA和CGI编程开发][数据库的相关知识——学习 ...
