Matlab的用法总结
1. 对序列进行洗牌 randperm()
randperm()产生随机的序列
%if filepaths 是一个5*1的结构体,then cshuffle = randperm(length(filepaths)) %对filepaths进行随机的洗牌,得到了 cshuffle => [2,5,4,1,3] 洗牌后的序列
2. 图像灰度化 rgb2gray()
MyYuanLaiPic = imread('e:/image/matlab/Cluo.jpg');%读取RGB格式的图像
MyFirstGrayPic = rgb2gray(MyYuanLaiPic);%用已有的函数进行RGB到灰度图像的转换
[rows , cols , colors] = size(MyYuanLaiPic);%得到原来图像的矩阵的参数
MidGrayPic = zeros(rows , cols);%用得到的参数创建一个全零的矩阵,这个矩阵用来存储用下面的方法产生的灰度图像
MidGrayPic = uint8(MidGrayPic);%将创建的全零矩阵转化为uint8格式,因为用上面的语句创建之后图像是double型的
for i = :rows
for j = :cols
sum = ;
for k = :colors
sum = sum + MyYuanLaiPic(i , j , k) / ;%进行转化的关键公式,sum每次都因为后面的数字而不能超过255
end
MidGrayPic(i , j) = sum;
end
end
imwrite(MidGrayPic , 'E:/image/matlab/Cluo.png' , 'png');
%显示原来的RGB图像
figure();
imshow(MyYuanLaiPic);
%显示经过系统函数运算过的灰度图像
figure();
imshow(MyFirstGrayPic);
%显示转化之后的灰度图像
figure();
imshow(MidGrayPic);
3. 对图像进行旋转和翻转
function I = data_augmentation(I, K) if K ==
return;
elseif K == % flipped
I = flipud(I);
return;
elseif K == % rotation
I = rot90(I,);
return;
elseif K == % rotation & flipped
I = rot90(I,);
I = flipud(I);
return;
elseif K == % rotation
I = rot90(I,);
return;
elseif K == % rotation & flipped
I = rot90(I,);
I = flipud(I);
return;
elseif K == % rotation
I = rot90(I,);
return;
elseif K == % rotation & flipped
I = rot90(I,);
I = flipud(I);
return;
end
4. 对array进行连接 cat(dim, A, B)
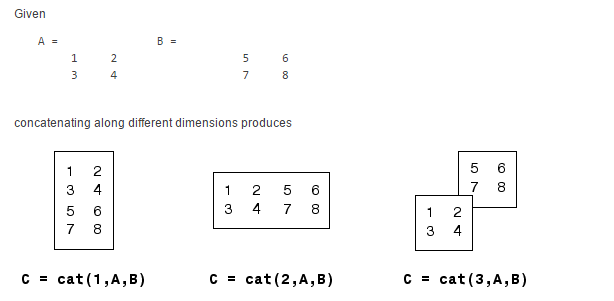
、
5.对图像进缩放,imresize()
HR_current = imresize(HR,nscales(j,i),'bicubic');
%第二个参数为缩放因子,e.g. 0.5、0.8
%第三个参数为缩放method
6.读取图像默认的数据类型uint8,最大值为255;但是在进行图形矩阵的操作和变化过程中非常容易溢出,所以需要转化为double(64为,0~1)或者single
im2double()将值0~255映射到0~1之间
7.两个循环搞定patch的获取
for x = +step1 : stride : (hei-patchsize+)
for y = +step2 : stride : (wid-patchsize+)
count = count + ;
subim_label = HR_current(x : x+patchsize-, y : y+patchsize-,:nch);
imdb.HRlabels(:, :, :, count) = subim_label;
if count<=diffPatches %不够一个patch进行填充
imdb.HRlabels(:, :, :, end-count+) = HR_current(x : x+patchsize-, y : y+patchsize-,:nch);
end
end
end
8.产生图像的patch
function [imdb] = generatepatches %% Note, set your training image set first, large dataset is prefered!
folders = {'path_of_your_training_dataset'}; % set this first! stride = ; % control the number of image patches
patchsize = ; batchSize = ; % important for BNorm
count = ;
nch = ; % for grayscale image, for color image step1 = ;
step2 = ; ext = {'*.jpg','*.png','*.bmp'};
filepaths = []; for j = :length(folders)
for i = : length(ext)
filepaths = cat(,filepaths, dir(fullfile(folders{j}, ext{i}))); %获取folder获取所有figure
end
end cshuffle = randperm(length(filepaths)); % randperm获取filepaths的随机排列
nimages = round(length(filepaths)); % control the number of image patches 去整数 ns = ;
nscales = min(,0.45 + 0.05*randi(,[ns,nimages])); %产生随机矩阵 * all values are less than
naugment = randi(,[,nimages]); %产生一个随机矩阵1* all values are form - for i = : nimages
% HR = imread(fullfile(filepaths(cshuffle(i)).folder,filepaths(cshuffle(i)).name));
HR = imread(fullfile(folders{},filepaths(cshuffle(i)).name)); %从文件夹里随机读取一张图片
HR = HR(:,:,); %如果是rgb图就获取一个通道的,如果是gray图则自然为该图像 HR = data_augmentation(HR, naugment(i)); % 数据增大data_augmentation data_augmentation(HR, ); 转到data_augmentation.m里面就将图片旋转90度
disp([i,nimages,round(count/batchSize)]) for j = : size(nscales,) % size(nscales,) 为1 HR_current = imresize(HR,nscales(j,i),'bicubic'); %对图像进行尺度的缩放
[hei,wid,~] = size(HR_current); % 得到此时的高和宽
for x = +step1 : stride : (hei-patchsize+) % 产生的patch (hei-patchsize+)这个value是一个临界值,最后放不了一个patch
for y = +step2 : stride : (wid-patchsize+)
count=count+;
end
end
end
end numPatches = ceil(count/batchSize)*batchSize; %ceil(1.2)=> ceil(0.2)=> 总共有多少个patch
diffPatches = numPatches - count; % 真实的差了多少个patch
disp([numPatches,numPatches/batchSize,diffPatches]); disp('-----------------------------'); %------------------------------------------------------------------
%------------------------------------------------------------------ count = ;
imdb.HRlabels = zeros(patchsize, patchsize, nch, numPatches,'single'); %imdb是一个结构体 *** for i = : nimages
% HR = imread(fullfile(filepaths(cshuffle(i)).folder,filepaths(cshuffle(i)).name));
HR = imread(fullfile(folders{},filepaths(cshuffle(i)).name)); %从文件夹里随机读取一张图片 if nch == && size(HR,) == %rgb2gray
HR = rgb2gray(HR);
end HR = data_augmentation(HR, naugment(i)); % 图像旋转操作
disp([i,nimages,round(count/)]) for j = : size(nscales,) HR_current = imresize(HR,nscales(j,i),'bicubic'); %图像进行随机的缩放
[hei,wid,~] = size(HR_current);
HR_current = im2single(HR_current); for x = +step1 : stride : (hei-patchsize+)
for y = +step2 : stride : (wid-patchsize+)
count = count + ;
subim_label = HR_current(x : x+patchsize-, y : y+patchsize-,:nch);
imdb.HRlabels(:, :, :, count) = subim_label;
if count<=diffPatches %不够一个patch进行填充
imdb.HRlabels(:, :, :, end-count+) = HR_current(x : x+patchsize-, y : y+patchsize-,:nch);
end
end
end
end
end imdb.set = uint8(ones(,size(imdb.HRlabels,)));
9.求某一个矩阵的指定维度的大小
size(A,dims) = value
# 如xx是一个16*401的矩阵,则求到第一维度的大小16 size(xx,1) =>16 # 如xx是一个16*401的矩阵,则求到第二维度的大小401 size(xx,2) =>401
Matlab的用法总结的更多相关文章
- matlab fscanf用法
matlab fscanf用法 matlab中的fscanf的用法如下: A=fscanf(fid,format)[A, count]=fscanf(fid,format,size) [A, coun ...
- Matlab norm 用法小记
Matlab norm 用法小记 matlab norm (a) 用法以及实例 norm(A,p)当A是向量时norm(A,p) Returns sum(abs(A).^p)^(1/p), for ...
- matlab fspecial 用法解释
Matlab 的fspecial函数用法 fspecial函数用于建立预定义的滤波算子,其语法格式为:h = fspecial(type)h = fspecial(type,para)其中type指定 ...
- Matlab基本用法
转至:http://blog.sina.com.cn/s/blog_8354dda801012dyn.html 目录: 一.说明 二.数据类型及基本输入输出 三.流程控制 四.循环 五.数组.数组运算 ...
- matlab ()的用法
经常见到标识符+(),用法比如阵列Y().函数f()..... 时机到了,会总结一下.
- MATLAB入门教程
MATLAB入门教程 1.MATLAB的基本知识 1-1.基本运算与函数 在MATLAB下进行基本数学运算,只需将运算式直接打入提示号(>>)之後,并按入Enter键即可.例如: ...
- (转)MATLAB入门教程
MATLAB入门教程 1.MATLAB的基本知识 1-1.基本运算与函数 在MATLAB下进行基本数学运算,只需将运算式直接打入提示号(>>)之後,并按入Enter键即可.例如: ...
- Matlab各种拟合
作者:Z-HE链接:https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/36103034来源:知乎著作权归作者所有.商业转载请联系作者获得授权,非商业转载请注明出处. 1) polyfit 代码 ...
- matlab代码学习_2018-7-28
1.核范数||A|| * 是指矩阵奇异值的和,英文称呼叫Nuclear Norm.matlab code:[s, u, v] = svd(A); nulear_norm = sum(diag(s)); ...
随机推荐
- OpenGL normalMap
参考zwqxin的博客 http://www.zwqxin.com/ shader 来自zwqxin,稍作修改 <-vertex-> attribute vec3 v_Pos; attr ...
- Spring-Cloud-Ribbon学习笔记(二):自定义负载均衡规则
Ribbon自定义负载均衡策略有两种方式,一是JavaConfig,一是通过配置文件(yml或properties文件). 需求 假设我有包含A和B服务在内的多个微服务,它们均注册在一个Eureka上 ...
- Qt中关于QMouseEventbuttons()和QMouseEventbutton()的使用注意
在进行QT程序开发中经常需要响应鼠标事件,在QWidget或QMainWindow的子类中可以重载如下鼠标事件实现自己需要的效果. virtual void mouseDoubleClickEvent ...
- linux telnet检测与某个端口是否开通
转自:http://blog.51cto.com/meiling/1982402 一:telnet此法常被用来检测是个远端端口是否通畅. 测试域名: # telnet baidu.com 80 Try ...
- vue使用mockjs配置步骤(无需启动node服务)
1.安装好mockjs命令行 npm install mockjs 2.在项目中引用mockjs [ 重要 ] ##在项目src目录下新建一个mock文件夹 ##在mock文件夹下新建 index.j ...
- Spring data Jpa,Mybatis,读写锁,@Lock 使用
Spring data jpa 支持注解式的读写锁(悲观锁),实际上这个东西硬编码也简单,但是基于Jpa 命名方式定义的Sql,只能用注解添加支持读写锁了, 不了解读写锁的可以点这里 mysql读写锁 ...
- chrome 浏览器之下载管理器插件
chrome默认下载器实在是不招人待见,下面插件是一个非常不错的选择: 名称:Chrono下载管理器 插件地址:https://chrome.google.com/webstore/detail/ch ...
- ES6 export
一.默认导出(default export)// 1.一个模块只能有一个默认导出, 对于默认导出, 导入的名称可以和导出的名称不一致, 这对于导出匿名函数或类非常有用. <!---- page. ...
- [Codeforces Round #221 (Div. 1)][D. Tree and Queries]
题目链接:375D - Tree and Queries 题目大意:给你一个有n个点的树,每个点都有其对应的颜色,给出m次询问(v,k),问v的子树中有多少种颜色至少出现k次 题解:先对所有的询问进行 ...
- js中的异步与同步,解决由异步引起的问题
之前在项目中遇到过好多次因为异步引起的变量没有值,所以意识到了认识js中同步与异步机制的重要性 在单线程的js中,异步代码会被放入一个事件队列,等到所有其他代码执行后再执行,而不会阻塞线程. 下面是j ...
