How to Use Rsync to Sync New or Changed/Modified Files in Linux
As a system administrator or Linux power user, you may have probably come across or even on several occasions, used the versatile Linux Rsync tool, which enables users to expeditiously copy or synchronize files locally and remotely. It is as well a great tool popularly used for backup operations and mirroring.
Some of its eminent features and advantages include; it is exceptionally versatile in that, it can copy locally, to/from a remote shell or remote rsync, it is also remarkably flexible, allowing users to specify any number of files to copy.
Suggested Read: 10 Practical Examples of Rsync Command in Linux
Furthermore, it permits copying of links, devices, file or directory owner, groups and the permissions. It also supports usage without root privileges coupled with many more.
One imperative differential of rsync in comparison to other file-coying commands in Linux is its use of the remote-update protocol, to transfer only the difference between files or directory content.
Therefore, in this article, we shall examine how rsync can help us only sync new or changed files or directory content while making backups and beyond in Linux.
To start with, you need remember that the conventional and simplest form of using rsync is as follows:
# rsync options source destination
That said, let us dive into some examples to uncover how the concept above actually works.
Syncing Files Locally Using Rsync
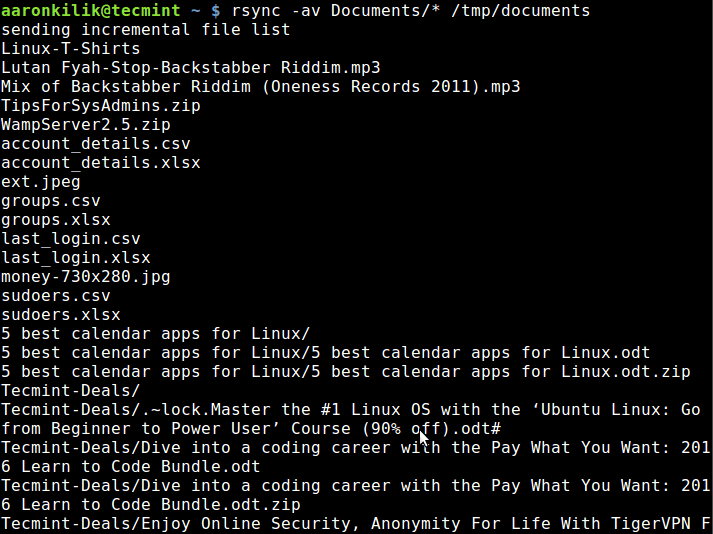
Using the command below, am able to copy files from my Documents directory to /tmp/documentsdirectory locally:
$ rsync -av Documents/* /tmp/documents
In the command above, the option:
-a– means archive mode-v– means verbose, showing details of ongoing operations
Sync Files Locally
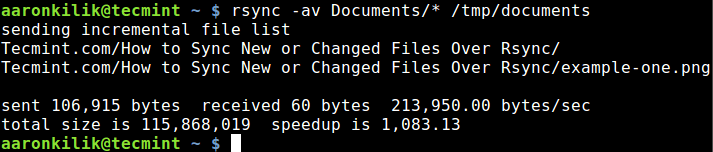
By default, rsync only copies new or changed files from a source to destination, when I add a new file into myDocuments directory, this is what happens after running the same command second time:
$ rsync -av Documents/* /tmp/documents
Sync New Updated Files
As you can observe and notice from the output of the command, only the new file is copied to the destination directory.
Suggested Read: How to Sync Two Apache Web Servers/Websites Using Rsync
The --update or -u option allows rsync to skip files that are still new in the destination directory, and one important option, --dry-run or -n enables us to execute a test operation without making any changes. It shows us what files are to be copied.
$ rsync -aunv Documents/* /tmp/documents

Dry Run Rsync Before Syncing Files
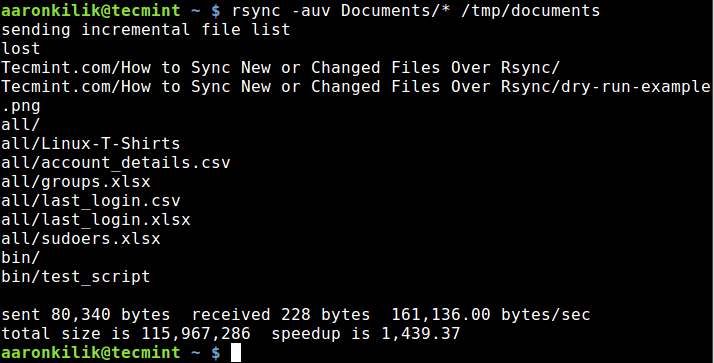
After executing a test run, we can then do away with the -n and perform a real operation:
$ rsync -auv Documents/* /tmp/documents
Sync Updated Files
Syncing Files From Local to Remote Linux
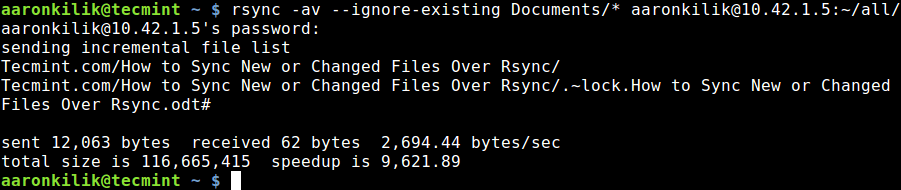
In the example below, I am copying files from my local machine to a remote sever with the IP address –10.42.1.5. So as to only sync new files on the local machine, that do not exist on the remote machine, we can include the --ignore-existing option:
$ rsync -av --ignore-existing Documents/* aaronkilik@10.42.1.5:~/all/
Sync Files Local to Remote Linux
Subsequently, to sync only updated or modified files on the remote machine that have changed on the local machine, we can perform a dry run before copying files as below:
$ rsync -av --dry-run --update Documents/* aaronkilik@10.42.1.5:~/all/
$ rsync -av --update Documents/* aaronkilik@10.42.1.5:~/all/
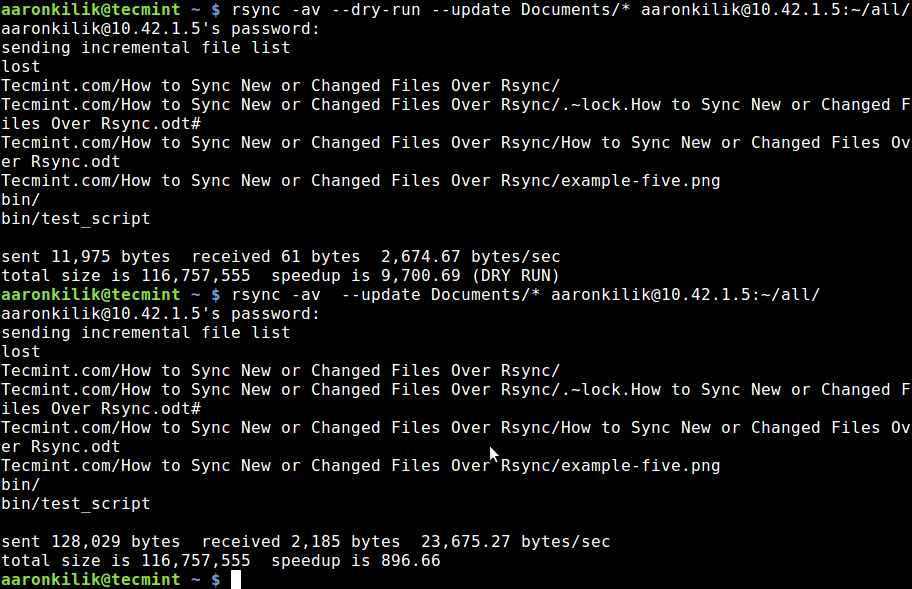
Check Sync Only Updated Files
To update existing files and prevent creation of new files in the destination, we utilize the --existing option.
You can run through the rsync man page to discover additionally useful options for advanced usage, as I had mentioned earlier on, rsync is a very powerful and versatile Linux tool and many System Administrator and Linux power users know just how advantageous it is.
Most importantly, you can as well share your view on the examples we have covered here or even better still, offer us valuable tips on using this vital command line tool through the comment section below.
How to Use Rsync to Sync New or Changed/Modified Files in Linux的更多相关文章
- External file changes sync may be slow: Project files cannot be watched (are they under network mount?)
if some files are on a mounted disk: go to Settings | Notifications | File Watcher Messages and tune ...
- Linux命令——rsync
参考:Rsync (Remote Sync): 10 Practical Examples of Rsync Command in Linux How to Sync Files/Directorie ...
- 【转载】CentOS 6.3下rsync服务器的安装与配置
一.rsync 简介 Rsync(remote synchronize)是一个远程数据同步工具,可通过LAN/WAN快速同步多台主机间的文件,也可以使用 Rsync 同步本地硬盘中的不同目录. Rsy ...
- CentOS 6.3下rsync服务器的安装与配置
一.rsync 简介 Rsync(remote synchronize)是一个远程数据同步工具,可通过LAN/WAN快速同步多台主机间的文件,也可以使用 Rsync 同步本地硬盘中的不同目录. Rsy ...
- CentOS6 下rsync服务器配置
一.rsync 简介 Rsync(remote synchronize)是一个远程数据同步工具,可通过LAN/WAN快速同步多台主机间的文件,也可以使用 Rsync 同步本地硬盘中的不同目录. Rsy ...
- Server Data Synchronization Via Linux rsync、rsync+inotify Between Load Balance Server
目录 . 远程文件同步的应用场景 . rsync+crontab . rsync+inotify 1. 远程文件同步的应用场景 在负载均衡集群的应用场景中,往往在多台web server的前端有一个提 ...
- rsync 使用示例
导读 Rsync(remote sync) 是用于同步某一位置文件和目录到另一位置的有效方法.备份的位置可以在本地服务器或远程服务器.本站之前亦有介绍rsync的安装配置和教程,详看<rsync ...
- linux服务之rsync
http://www.cnblogs.com/itech/archive/2010/06/13/1757952.html rsync与mfs好像有点类似,都是传输块的chunk,chunk的 1)软件 ...
- rsync常用命令及格式
rsync在同步文件夹内容这个工作上应用非常广泛,但是rsync本身命令还是比较复杂,本文总结一下: rsync = remote sync的简称 ,它 被用于在linux/unix系统中执行备份操作 ...
随机推荐
- WCF再学习小结
http://www.cnblogs.com/jillzhang/archive/2010/04/04/1704388.html http://leelei.blog.51cto.com/856755 ...
- Mes首检确认统计的存储过程
USE [ChiefmesNEW]GO/****** Object: StoredProcedure [dbo].[st_MES_RptInspectFirstCollect] Script Date ...
- [转载]NoSQL数据库的基础知识
关系型数据库和NoSQL数据库 什么是NoSQL 大家有没有听说过“NoSQL”呢?近年,这个词极受关注.看到“NoSQL”这个词,大家可能会误以为是“No!SQL”的缩写,并深感愤怒:“SQL怎么会 ...
- AVR 定点数运算程序设计及数制转换
AVR 单片机有加法和减法指令,可以直接调用相关指令来达到目的. 这里列出了16位加法.16位带立即数加法. 16位减法.16位带立即数减法. 16位比较.16位带立即数比较程序和16位取补程序. a ...
- C++ Primer 学习笔记_67_面向对象编程 --转换与继承、复制控制与继承
面向对象编程 --转换与继承.复制控制与继承 I.转换与继承 引言: 由于每一个派生类对象都包括一个基类部分,因此能够像使用基类对象一样在派生类对象上执行操作. 对于指针/引用,能够将派生类对象的指针 ...
- tomcat配置文件server.xml具体解释
元素名 属性 解释 server port 指定一个port,这个port负责监听关闭tomcat 的请求 shutdown 指定向port发送的命令字符串 service name 指定servic ...
- jQuery hover事件鼠标滑过图片半透明标题文字滑动显示隐藏
1.效果及功能说明 hover事件制作产品图片鼠标滑过图片半透明,标题文字从左到右滑动动画移动显示隐藏 2.实现原理 首先把效果都隐藏,然后定义一个伪类来触发所有的效果,接下来当触发伪类后会有一个遍历 ...
- iframe自适应高度的多种方法小结
转自:http://www.jb51.net/article/15780.htm 不带边框的iframe因为能和网页无缝的结合从而不刷新页面的情况下更新页面的部分数据成为可能,可是 iframe的大小 ...
- apache2.2 虚拟主机配置
一.改动httpd.conf 打开appserv的安装文件夹,找到httpd.conf文件,分别去掉以下两行文字前面的#号. #LoadModule vhost_alias_module module ...
- 表ADT
表一般不用简单数组来实现,通常将其实现为链表.在链表中要不要使用表头则属于个人兴趣问题.在下面的例程中我们都使用表头. 按照C的约定,作为类型的List(表)和Position(位置)以及函数的原型都 ...
