hdu 1890 splay树
Robotic Sort
Time Limit: 6000/2000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 32768/32768 K (Java/Others)
Total Submission(s): 3340 Accepted Submission(s): 1423
multimedia lab. But there are still others, serving to their original purposes.
In this task, you are to write software for a robot that handles samples in such a laboratory. Imagine there are material samples lined up on a running belt. The samples have different heights, which may cause troubles to the next processing unit. To eliminate
such troubles, we need to sort the samples by their height into the ascending order.
Reordering is done by a mechanical robot arm, which is able to pick up any number of consecutive samples and turn them round, such that their mutual order is reversed. In other words, one robot operation can reverse the order of samples on positions between
A and B.
A possible way to sort the samples is to find the position of the smallest one (P1) and reverse the order between positions 1 and P1, which causes the smallest sample to become first. Then we find the second one on position P and reverse the order between 2
and P2. Then the third sample is located etc.
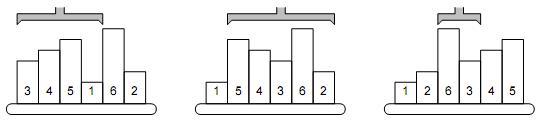
The picture shows a simple example of 6 samples. The smallest one is on the 4th position, therefore, the robot arm reverses the first 4 samples. The second smallest sample is the last one, so the next robot operation will reverse the order of five samples on
positions 2–6. The third step will be to reverse the samples 3–4, etc.
Your task is to find the correct sequence of reversal operations that will sort the samples using the above algorithm. If there are more samples with the same height, their mutual order must be preserved: the one that was given first in the initial order must
be placed before the others in the final order too.
of individual samples and their initial order.
The last scenario is followed by a line containing zero.
Each Pi must be an integer (1 ≤ Pi ≤ N ) giving the position of the i-th sample just before the i-th reversal operation.
Note that if a sample is already on its correct position Pi , you should output the number Pi anyway, indicating that the “interval between Pi and Pi ” (a single sample) should be reversed.
3 4 5 1 6 2
4
3 3 2 1
0
4 2 4 4
/*
hdu-1890 splay树g
开始是用伸展树保存的值,然后发现如果有相同的进行了交换,然后输出的值就有问题
3 3 2 1 -> 4 2 4 4 但我的是4 2 4 3,因为我每次是去找的某个值的位置,相同值的话就可能找到较小那个值去了
假设排序后b[3] = b[4]= 3,我先处理b[3],然后b[3],b[4]交换,处理b[4]时就出现了bug,然后GG
准确说是对题意的理解上出现了,果然英语弱O__O "… 后来改用数组坐标建树,对于翻转get_kth找到其中第k个位置,然后get_next找出排序后第i大的后面那个,然后打标记即可.
至于求位置,直接把这个点旋转到根,然后计算左儿子的大小即可 hhh-2016-02-21 01:10:21
*/ #include <functional>
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <cstring>
#include <algorithm>
#include <map>
#include <cmath>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
typedef long double ld;
#define key_value ch[ch[root][1]][0]
const int maxn = 300010; int ch[maxn][2];
int pre[maxn],siz[maxn],num[maxn];
int rev[maxn];
int root,tot,cnt,n;
struct Node
{
int val,id;
}node[maxn]; bool cmp(Node a,Node b)
{
if(a.val != b.val) return a.val < b.val;
else return a.id < b.id;
} void push_up(int r)
{
int lson = ch[r][0],rson = ch[r][1];
siz[r] = siz[lson] + siz[rson] + 1;
} void update_rev(int r)
{
if(!r)return ;
swap(ch[r][0],ch[r][1]);
rev[r] ^= 1;
} void push_down(int r)
{
if(rev[r])
{
update_rev(ch[r][0]);
update_rev(ch[r][1]);
rev[r] = 0;
}
} void NewNode(int &r,int far,int k)
{
r = k;
pre[r] = far;
ch[r][0] = ch[r][1] = 0;
siz[r] = 1;
rev[r] = 0;
} void rotat(int x,int kind)
{
int y = pre[x];
push_down(y);
push_down(x);
ch[y][!kind] = ch[x][kind];
pre[ch[x][kind]] = y;
if(pre[y])
ch[pre[y]][ch[pre[y]][1]==y] = x;
pre[x] = pre[y];
ch[x][kind] = y;
pre[y] = x;
push_up(y);
} void build(int &x,int l,int r,int far)
{
if(l > r) return ;
int mid = (l+r) >>1;
NewNode(x,far,mid);
build(ch[x][0],l,mid-1,x);
build(ch[x][1],mid+1,r,x);
push_up(x);
} void splay(int r,int goal)
{
push_down(r);
while(pre[r] != goal)
{
if(pre[pre[r]] == goal)
{
push_down(pre[r]);
push_down(r);
rotat(r,ch[pre[r]][0] == r);
}
else
{
push_down(pre[pre[r]]);
push_down(pre[r]);
push_down(r);
int y = pre[r];
int kind = ch[pre[y]][0] == y;
if(ch[y][kind] == r)
{
rotat(r,!kind);
rotat(r,kind);
}
else
{
rotat(y,kind);
rotat(r,kind);
}
}
}
push_up(r);
if(goal == 0)
root = r;
} int get_kth(int r,int k)
{
push_down(r);
int t = siz[ch[r][0]] + 1;
if(k == t)return r;
if(t > k) return get_kth(ch[r][0],k);
else return get_kth(ch[r][1],k-t);
} int get_next(int r)
{
push_down(r);
if(ch[r][1] == 0)return -1;
r = ch[r][1];
while(ch[r][0])
{
r = ch[r][0];
push_down(r);
}
return r;
} void ini(int n)
{
root = 0;
ch[root][0] = ch[root][1] = pre[root] = siz[root] = num[root] = 0 ;
NewNode(root,0,n+1);
NewNode(ch[root][1],root,n+2);
build(key_value,1,n,ch[root][1]); push_up(ch[root][1]);
push_up(root);
} int main()
{
int q,T;
int cas =1;
while(scanf("%d",&n) != EOF)
{
if(!n)
break;
for(int i=1; i <= n; i++)
{
scanf("%d",&node[i].val);
node[i].id = i;
}
sort(node+1,node+n+1,cmp);
ini(n);
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
splay(node[i].id,0);
printf("%d",siz[ch[root][0]]);
if(i != n) printf(" ");
else printf("\n");
splay(get_kth(root,i),0);
splay(get_next(node[i].id),root);
update_rev(key_value);
}
}
return 0;
}
hdu 1890 splay树的更多相关文章
- hdu 3436 splay树+离散化*
Queue-jumpers Time Limit: 2000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 32768/32768 K (Java/Others) To ...
- [置顶] hdu 1890 伸展树区间翻转
题意: 给你n个数,每次先输出第i大的数的位置(如果有多个,选下标小的那个),然后每次将第i个位置到第i大的数所在位置之间的数进行翻转. 思路:输入的数组可能有多个相同的值,我们可以进行两次排序把数组 ...
- hdu 1890 Robotic Sort(splay 区间反转+删点)
题目链接:hdu 1890 Robotic Sort 题意: 给你n个数,每次找到第i小的数的位置,然后输出这个位置,然后将这个位置前面的数翻转一下,然后删除这个数,这样执行n次. 题解: 典型的sp ...
- Splay树学习
首先给出一论文讲的很好: http://www.docin.com/p-63165342.html http://www.docin.com/p-62465596.html 然后给出模板胡浩大神的模板 ...
- hdu 5398 动态树LCT
GCD Tree Time Limit: 5000/2500 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 65536/65536 K (Java/Others)Total Su ...
- hdu 5002 (动态树lct)
Tree Time Limit: 16000/8000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 65536/65536 K (Java/Others)Total Submi ...
- hdu 5314 动态树
Happy King Time Limit: 10000/5000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 262144/262144 K (Java/Others)Tot ...
- hdu 3436 线段树 一顿操作
Queue-jumpers Time Limit: 2000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 32768/32768 K (Java/Others) To ...
- Splay树-Codevs 1296 营业额统计
Codevs 1296 营业额统计 题目描述 Description Tiger最近被公司升任为营业部经理,他上任后接受公司交给的第一项任务便是统计并分析公司成立以来的营业情况. Tiger拿出了公司 ...
随机推荐
- JAVA_SE基础——67.System类
System类对大家都不陌生吧! 以前经常需要打印结果时使用的都是"System.out.println()"语句,这句代码中就使用了System类.System类定义了一些与系统 ...
- TP框架关于模版的使用技巧
1.
- 第二章 初识JSP
第二章 初识JSP 一.JSP简述 1.是JSP JSP是指在HTML中嵌入Java脚本语言.全称(Java Server Pages) 当用户通过浏览器访问Web应用时,使用JSP容器对请求的J ...
- Python内置函数(25)——frozenset
英文文档: class frozenset([iterable]) Return a new frozenset object, optionally with elements taken from ...
- 电梯模拟C++
1.问题描述与要求 模拟某校九层教学楼的电梯系统.该楼有一个自动电梯,能在每层停留,其中第一层是大楼的进出层,即是电梯的"本垒层",电梯"空闲"时,将来到该层候 ...
- linux下执行java类(运行java定时器)
假如有一个定时器TimerTest.java import java.io.IOException; import java.util.Timer; public class TimerTest { ...
- 离线Chrome插件安装文件(crx)的安装方法
离线Chrome插件安装文件(crx)的安装方法 一.正常安装方法 1.开发谷歌浏览器,设置->扩展程序 在打开的谷歌浏览器的扩展管理器中用户可以看到一些已经安装程序的Chrome插件,或者一个 ...
- 刨析Maven(对pom.xml配置文件常用标签的解析)
昨天在阿里云看到了一句话,"当你Learning和Trying之后,如果能尽量把Teaching也做好,会促进我们思考".共勉! 这是关于Maven的第三篇博客,这次我们深入了解p ...
- java.lang.IllegalAccessError: tried to access method org.apache.poi.util.POILogger.log from class org.apache.poi.openxml4j.opc.ZipPackage
代码说简单也简单,说复杂那还真是寸步难行. 之前好好的excel导出功能,本地启动调试的时候突然就不行了,一直报上面的错. 一直在本地折腾了半天,去测试环境上看,又是好的,可以正常导出excel. 搜 ...
- POJ-1860 Currency Exchange---Bellman-Ford判断正环
题目链接: https://vjudge.net/problem/POJ-1860 题目大意: 我们的城市有几个货币兑换点.让我们假设每一个点都只能兑换专门的两种货币.可以有几个点,专门从事相同货币兑 ...