Spring AOP 五大通知类型
1.前置通知
在目标方法执行之前执行执行的通知。
前置通知方法,可以没有参数,也可以额外接收一个JoinPoint,Spring会自动将该对象传入,代表当前的连接点,通过该对象可以获取目标对象 和 目标方法相关的信息。
注意,如果接收JoinPoint,必须保证其为方法的第一个参数,否则报错。
配置方式:

<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-3.2.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-3.2.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop-3.2.xsd
"> <context:annotation-config></context:annotation-config>
<context:component-scan base-package="cn.tedu.service,cn.tedu.aop"></context:component-scan> <aop:config proxy-target-class="true">
<!-- 配置切入点 -->
<aop:pointcut
expression="execution(* cn.tedu.service.UserServiceImpl.addUser(..))"
id="pc01"/> <!-- 配置切面 -->
<aop:aspect ref="firstAspect">
<<!-- 前置通知 -->
<aop:before method="before" pointcut-ref="pc01"/> </aop:aspect>
</aop:config>
</beans>


package cn.tedu.service; import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
/**
* UserServiceImple:目标对象
*/
@Service("userService")
public class UserServiceImple implements UserService { @Override
public void addUser(String name) {
System.out.println("增加用户。。");
} @Override
public void updateUser() {
System.out.println("修改用户。。");
} @Override
public void deleteUser() {
System.out.println("删除用户。。");
} @Override
public void query() {
System.out.println("查询用户。。");
}
}


package cn.tedu.aop; import org.aspectj.lang.JoinPoint;
import org.aspectj.lang.Signature;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
/**
* FirstAspect:切面代码
*/
@Component
public class FirstAspect {
public void before(JoinPoint jp){ // 可以选择额外的传入一个JoinPoint连接点对象,必须用方法的第一个参数接收。
Class clz = jp.getTarget().getClass();
Signature signature = jp.getSignature(); // 通过JoinPoint对象获取更多信息
String name = signature.getName();
System.out.println("1 -- before...["+clz+"]...["+name+"]...");
}
}


package cn.tedu.test; import org.junit.Test;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext; import cn.tedu.service.UserService;
/**
* AOPTest:测试代码
*/
public class AOPTest {
@Test
public void test01(){
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
UserService userService = (UserService) context.getBean("userService");
userService.addUser("cjj"); // 一个连接点
}
}

执行结果:
1 -- before...[class cn.tedu.service.UserServiceImple]...[addUser]...
增加用户。。
2.环绕通知
在目标方法执行之前和之后都可以执行额外代码的通知。
在环绕通知中必须显式的调用目标方法,目标方法才会执行,这个显式调用时通过ProceedingJoinPoint来实现的,可以在环绕通知中接收一个此类型的形参,spring容器会自动将该对象传入,注意这个参数必须处在环绕通知的第一个形参位置。
**要注意,只有环绕通知可以接收ProceedingJoinPoint,而其他通知只能接收JoinPoint。
环绕通知需要返回返回值,否则真正调用者将拿不到返回值,只能得到一个null。
环绕通知有控制目标方法是否执行、有控制是否返回值、有改变返回值的能力。
环绕通知虽然有这样的能力,但一定要慎用,不是技术上不可行,而是要小心不要破坏了软件分层的“高内聚 低耦合”的目标。
配置方式:
<!-- 环绕通知 -->
<aop:around method="around" pointcut-ref="pc1"/>
public Object around(ProceedingJoinPoint jp) throws Throwable{
System.out.println("1 -- around before...");
Object obj = jp.proceed(); //--显式的调用目标方法
System.out.println("1 -- around after...");
return obj;
}
运行结果:
1 -- around before...
增加用户。。
1 -- around after...
3.后置通知
在目标方法执行之后执行的通知。
在后置通知中也可以选择性的接收一个JoinPoint来获取连接点的额外信息,但是这个参数必须处在参数列表的第一个。
配置方式:
<!-- 后置通知 -->
<aop:after-returning method="afterReturn" pointcut-ref="pc1"/>
public void afterReturn(JoinPoint jp){
Class clz = jp.getTarget().getClass();
Signature signature = jp.getSignature();
String name = signature.getName();
System.out.println("1 -- afterReturn...["+clz+"]...["+name+"]...");
}
执行结果:
1 -- before...[class cn.tedu.service.UserServiceImple]...[addUser]...
1 -- around before...
增加用户。。
1 -- around after...
1 -- afterReturn...[class cn.tedu.service.UserServiceImple]...[addUser]...
在后置通知中,还可以通过配置获取返回值
一定要保证JoinPoint处在参数列表的第一位,否则抛异常
配置方式:
<!-- 后置通知 -->
<aop:after-returning method="afterReturn" pointcut-ref="pc1" returning="msg"/>
public void afterReturn(JoinPoint jp, Object msg){
Class clz = jp.getTarget().getClass();
Signature signature = jp.getSignature();
String name = signature.getName();
System.out.println("1 -- afterReturn...["+clz+"]...["+name+"]...["+msg+"]...");
}
执行结果:
1 -- before...[class cn.tedu.service.UserServiceImple]...[addUser]...
1 -- around before...
增加用户。。
1 -- around after...
1 -- afterReturn...[class cn.tedu.service.UserServiceImple]...[addUser]...[cjj]...
4.异常通知
在目标方法抛出异常时执行的通知
可以配置传入JoinPoint获取目标对象和目标方法相关信息,但必须处在参数列表第一位
另外,还可以配置参数,让异常通知可以接收到目标方法抛出的异常对象。
配置方法:
<!-- 异常通知 -->
<aop:after-throwing method="afterThrow" pointcut-ref="pc1" throwing="e"/>
public void afterThrow(JoinPoint jp,Throwable e){
Class clz = jp.getTarget().getClass();
String name = jp.getSignature().getName();
System.out.println("1afterThrow..["+clz+"]..["+name+"].."+e.getMessage());
}
代码报异常后
执行结果:
1 -- before...[class cn.tedu.service.UserServiceImple]...[addUser]...
1 -- around before...
1 -- afterThrow..[class cn.tedu.service.UserServiceImple]..[addUser]../ by zero
5.最终通知
是在目标方法执行之后执行的通知。
和后置通知不同之处在于,后置通知是在方法正常返回后执行的通知,如果方法没有正常返-例如抛出异常,则后置通知不会执行。
而最终通知无论如何都会在目标方法调用过后执行,即使目标方法没有正常的执行完成。
另外,后置通知可以通过配置得到返回值,而最终通知无法得到。
最终通知也可以额外接收一个JoinPoint参数,来获取目标对象和目标方法相关信息,但一定要保证必须是第一个参数。
配置方式:
<!-- 最终通知 -->
<aop:after method="after" pointcut-ref="pc1" />
public void after(JoinPoint jp){
Class clz = jp.getTarget().getClass();
String name = jp.getSignature().getName();
System.out.println("1 -- after..["+clz+"]..["+name+"]...");
}
执行结果:

1 -- before...[class cn.tedu.service.UserServiceImple]...[addUser]...
1 -- around before...
增加用户。。
1 -- around after...
1 -- afterReturn...[class cn.tedu.service.UserServiceImple]...[addUser]...[cjj]...
1 -- after..[class cn.tedu.service.UserServiceImple]..[addUser]...
cjj

源码
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans
xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-3.2.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-3.2.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop-3.2.xsd "
> <context:annotation-config></context:annotation-config>
<context:component-scan base-package="cn.tedu.service,cn.tedu.aop"></context:component-scan> <!-- proxy-target-class属性值决定是基于接口的还是基于类的代理被创建 -->
<aop:config proxy-target-class="true">
<!-- 配置切入点 -->
<aop:pointcut expression="execution(* cn.tedu.service.UserServiceImple.addUser(..))" id="pc1"/> <!-- 配置切入面 -->
<aop:aspect ref="firstAspect">
<!-- 前置通知 -->
<aop:before method="before" pointcut-ref="pc1"/> <!-- 环绕通知 -->
<aop:around method="around" pointcut-ref="pc1"/> <!-- 后置通知 -->
<!-- <aop:after-returning method="afterReturn" pointcut-ref="pc1"/> -->
<aop:after-returning method="afterReturn" pointcut-ref="pc1" returning="msg"/> <!-- 异常通知 -->
<aop:after-throwing method="afterThrow" pointcut-ref="pc1" throwing="e"/> <!-- 最终通知 -->
<aop:after method="after" pointcut-ref="pc1" />
</aop:aspect> </aop:config> </beans>

<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans
xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-3.2.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-3.2.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop-3.2.xsd "
> <context:annotation-config></context:annotation-config>
<context:component-scan base-package="cn.tedu.service,cn.tedu.aop"></context:component-scan> <!-- proxy-target-class属性值决定是基于接口的还是基于类的代理被创建 -->
<aop:config proxy-target-class="true">
<!-- 配置切入点 -->
<aop:pointcut expression="execution(* cn.tedu.service.UserServiceImple.addUser(..))" id="pc1"/> <!-- 配置切入面 -->
<aop:aspect ref="firstAspect">
<!-- 前置通知 -->
<aop:before method="before" pointcut-ref="pc1"/> <!-- 环绕通知 -->
<aop:around method="around" pointcut-ref="pc1"/> <!-- 后置通知 -->
<!-- <aop:after-returning method="afterReturn" pointcut-ref="pc1"/> -->
<aop:after-returning method="afterReturn" pointcut-ref="pc1" returning="msg"/> <!-- 异常通知 -->
<aop:after-throwing method="afterThrow" pointcut-ref="pc1" throwing="e"/> <!-- 最终通知 -->
<aop:after method="after" pointcut-ref="pc1" />
</aop:aspect> </aop:config> </beans>

package cn.tedu.service;
/**
* 接口
*/
public interface UserService {
public String addUser(String name);
public void updateUser();
public void deleteUser();
public void query();
}

package cn.tedu.service;
/**
* 接口
*/
public interface UserService {
public String addUser(String name);
public void updateUser();
public void deleteUser();
public void query();
}

package cn.tedu.service; import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
/**
* UserServiceImple:目标对象
*/
@Service("userService")
public class UserServiceImple implements UserService { @Override
public String addUser(String name) {
// int i = 1/0;
System.out.println("增加用户。。");
return "cjj";
} @Override
public void updateUser() {
System.out.println("修改用户。。");
} @Override
public void deleteUser() {
System.out.println("删除用户。。");
} @Override
public void query() {
System.out.println("查询用户。。");
}
}

package cn.tedu.service; import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
/**
* UserServiceImple:目标对象
*/
@Service("userService")
public class UserServiceImple implements UserService { @Override
public String addUser(String name) {
// int i = 1/0;
System.out.println("增加用户。。");
return "cjj";
} @Override
public void updateUser() {
System.out.println("修改用户。。");
} @Override
public void deleteUser() {
System.out.println("删除用户。。");
} @Override
public void query() {
System.out.println("查询用户。。");
}
}

package cn.tedu.aop; import org.aspectj.lang.JoinPoint;
import org.aspectj.lang.ProceedingJoinPoint;
import org.aspectj.lang.Signature;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
/**
* FirstAspect:切面代码
*/
@Component
public class FirstAspect {
public void before(JoinPoint jp){ // 可以选择额外的传入一个JoinPoint连接点对象,必须用方法的第一个参数接收。
Class clz = jp.getTarget().getClass();
Signature signature = jp.getSignature(); // 通过JoinPoint对象获取更多信息
String name = signature.getName();
System.out.println("1 -- before...["+clz+"]...["+name+"]...");
} public Object around(ProceedingJoinPoint jp) throws Throwable{
System.out.println("1 -- around before...");
Object obj = jp.proceed(); //--显式的调用目标方法
System.out.println("1 -- around after...");
return obj;
} public void afterReturn(JoinPoint jp, Object msg){
Class clz = jp.getTarget().getClass();
Signature signature = jp.getSignature();
String name = signature.getName();
System.out.println("1 -- afterReturn...["+clz+"]...["+name+"]...["+msg+"]...");
} public void afterThrow(JoinPoint jp,Throwable e){
Class clz = jp.getTarget().getClass();
String name = jp.getSignature().getName();
System.out.println("1 -- afterThrow..["+clz+"]..["+name+"].."+e.getMessage());
} public void after(JoinPoint jp){
Class clz = jp.getTarget().getClass();
String name = jp.getSignature().getName();
System.out.println("1 -- after..["+clz+"]..["+name+"]...");
}
}

package cn.tedu.aop; import org.aspectj.lang.JoinPoint;
import org.aspectj.lang.ProceedingJoinPoint;
import org.aspectj.lang.Signature;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
/**
* FirstAspect:切面代码
*/
@Component
public class FirstAspect {
public void before(JoinPoint jp){ // 可以选择额外的传入一个JoinPoint连接点对象,必须用方法的第一个参数接收。
Class clz = jp.getTarget().getClass();
Signature signature = jp.getSignature(); // 通过JoinPoint对象获取更多信息
String name = signature.getName();
System.out.println("1 -- before...["+clz+"]...["+name+"]...");
} public Object around(ProceedingJoinPoint jp) throws Throwable{
System.out.println("1 -- around before...");
Object obj = jp.proceed(); //--显式的调用目标方法
System.out.println("1 -- around after...");
return obj;
} public void afterReturn(JoinPoint jp, Object msg){
Class clz = jp.getTarget().getClass();
Signature signature = jp.getSignature();
String name = signature.getName();
System.out.println("1 -- afterReturn...["+clz+"]...["+name+"]...["+msg+"]...");
} public void afterThrow(JoinPoint jp,Throwable e){
Class clz = jp.getTarget().getClass();
String name = jp.getSignature().getName();
System.out.println("1 -- afterThrow..["+clz+"]..["+name+"].."+e.getMessage());
} public void after(JoinPoint jp){
Class clz = jp.getTarget().getClass();
String name = jp.getSignature().getName();
System.out.println("1 -- after..["+clz+"]..["+name+"]...");
}
}

package cn.tedu.test; import org.junit.Test;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext; import cn.tedu.service.UserService;
/**
* AOPTest:测试代码
*/
public class AOPTest {
@Test
public void test01(){
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
UserService userService = (UserService) context.getBean("userService");
String result = userService.addUser("cjj"); // 一个连接点
System.out.println(result);
}
}

package cn.tedu.test; import org.junit.Test;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext; import cn.tedu.service.UserService;
/**
* AOPTest:测试代码
*/
public class AOPTest {
@Test
public void test01(){
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
UserService userService = (UserService) context.getBean("userService");
String result = userService.addUser("cjj"); // 一个连接点
System.out.println(result);
}
}

五种通知的执行顺序
1.在目标方法没有抛出异常的情况下
前置通知
环绕通知的调用目标方法之前的代码
目标方法
环绕通知的调用目标方法之后的代码
后置通知
最终通知
2.在目标方法抛出异常的情况下
前置通知
环绕通知的调用目标方法之前的代码
目标方法 抛出异常 异常通知
最终通知
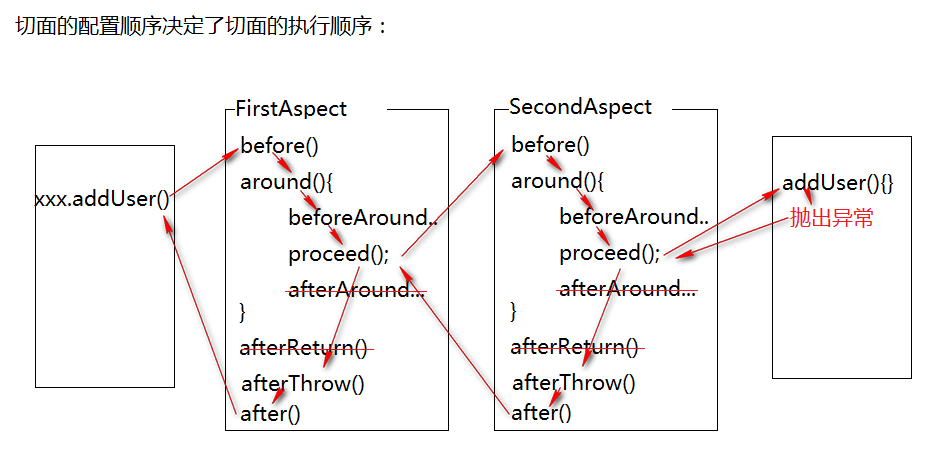
3.如果存在多个切面
多切面执行时,采用了责任链设计模式。
切面的配置顺序决定了切面的执行顺序,多个切面执行的过程,类似于方法调用的过程,在环绕通知的proceed()执行时,去执行下一个切面或如果没有下一个切面执行目标方法,从而达成了如下的执行过程:

如果目标方法抛出异常:
五种通知的常见使用场景
|
环绕通知 |
控制事务 权限控制 |
|
后置通知 |
记录日志(方法已经成功调用) |
|
异常通知 |
异常处理 控制事务 |
|
最终通知 |
记录日志(方法已经调用,但不一定成功) |
Spring AOP 五大通知类型的更多相关文章
- 利用Spring AOP的通知类型以及创建通知
写在最前端 1.SpringAOP中共有六种通知类型,只要我们自定义一个类实现对应的接口,它们全都是org.springframework.aop包中的. 2.AOP的连接点可以是方法调用.方法调用本 ...
- JAVA-Spring AOP五大通知类型
一.前置通知 在目标方法执行之前执行的通知 在前置通知方法,可以没有参数,也可以额外接收一个JoinPoint,Spring会自动将该对象传入,代表当前的连接点,通过该对象可以获取目标对象和目标方法相 ...
- Spring AOP 四大通知
Spring AOP 四大通知 Spring 3.X 以前 1.前置通知,实现 MethodBeforeAdvice 接口,重写 public void before(Method metho ...
- Spring笔记07(Spring AOP的通知advice和顾问advisor)
1.Spring AOP的通知advice 01.接口代码: package cn.pb.dao; public interface UserDao { //主业务 String add(); //主 ...
- Spring AOP前置通知和后置通知
Spring AOP AspectJ:Java社区里最完整最流行的AOP框架 在Spring2.0以上的版本中,可以使用基于AspectJ注解或基于XML配置的AOP 在Spring中启用Aspect ...
- 【Spring AOP】通知(五)
一.通知介绍 1. 前置通知(Before) 在目标方法执行之前执行的通知. 前置通知方法,可以没有参数,也可以额外接收一个JoinPoint,Spring会自动将该对象传入,代表当前的连接点,通过该 ...
- Spring AOP(通知、连接点、切点、切面)
一.AOP术语 通知(Advice) 切面的工作被称为通知.通知定义了切面是什么以及何时使用.除了描述切面要完成的工作,通知还解决了何时执行这个工作的问题.5种通知类型: 前置通知(Before): ...
- spring aop 环绕通知around和其他通知的区别
前言: spring 的环绕通知和前置通知,后置通知有着很大的区别,主要有两个重要的区别: 1) 目标方法的调用由环绕通知决定,即你可以决定是否调用目标方法,而前置和后置通知 是不能决定的,他们只 ...
- spring aop环绕通知
[Spring实战]—— 9 AOP环绕通知 假如有这么一个场景,需要统计某个方法执行的时间,如何做呢? 典型的会想到在方法执行前记录时间,方法执行后再次记录,得出运行的时间. 如果采用Sprin ...
随机推荐
- Python-将json文件写入ES数据库
1.安装Elasticsearch数据库 PS:在此之前需首先安装Java SE环境 下载elasticsearch-6.5.2版本,进入/elasticsearch-6.5.2/bin目录,双击执行 ...
- Linux下Zookeeper安装使用
1. 下载 下载地址,选择稳定的版本,比如3.4.13,beta为在测版本 2. 复制到任意的目录,解压 3. 修改配置文件 配置文件位于conf目录下,原配置文件为zoo_sample.cfg,更改 ...
- 借助Chrome和插件爬取数据
工具 Chrome浏览器 TamperMonkey ReRes Chrome浏览器 chrome浏览器是目前最受欢迎的浏览器,没有之一,它兼容大部分的w3c标准和ecma标准,对于前端工程师在开发过程 ...
- java调用python程序以及向python程序传递参数
在做项目的时候,经常会碰到这个问题,主要程序是用java写的,有些功能使用python写的,整个项目需要把java代码和python代码进行整合,在一个项目里面运行,这就涉及到java调用python ...
- ASP.NET Core中使用GraphQL - 第六章 使用EF Core作为持久化仓储
ASP.NET Core中使用GraphQL ASP.NET Core中使用GraphQL - 第一章 Hello World ASP.NET Core中使用GraphQL - 第二章 中间件 ASP ...
- [深度应用]·实战掌握PyTorch图片分类简明教程
[深度应用]·实战掌握PyTorch图片分类简明教程 个人网站--> http://www.yansongsong.cn/ 项目GitHub地址--> https://github.com ...
- C++ 编程技巧笔记记录(持续更新)
C++是博大精深的语言,特性复杂得跟北京二环一样,继承乱得跟乱伦似的. 不过它仍然是我最熟悉且必须用在游戏开发上的语言,这篇文章用于挑选出一些个人觉得重要的条款/经验/技巧进行记录总结. 文章最后列出 ...
- python ddt数据驱动(简化重复代码)
在接口自动化测试中,往往一个接口的用例需要考虑 正确的.错误的.异常的.边界值等诸多情况,然后你需要写很多个同样代码,参数不同的用例.如果测试接口很多,不但需要写大量的代码,测试数据和代码柔合在一起, ...
- Java多线程小总结
多线程 线程与进程 线程:具有完成特定任务的一条执行路径,是CPU执行的最小单位 进程:正在执行的程序 重点:CPU在某个时间刻度上只能够执行一条原子性语句 字节最小是bit位 原子性语句:不能够再次 ...
- TrieTree
学习链接:https://blog.csdn.net/lisonglisonglisong/article/details/45584721 前缀树解决字符串前缀匹配问题,查找单词是否存在,统计以如“ ...
