Feature Preprocessing on Kaggle
刚入手data science, 想着自己玩一玩kaggle,玩了新手Titanic和House Price的 项目, 觉得基本的baseline还是可以写出来,但是具体到一些细节,以至于到能拿到的出手的成绩还是需要理论分析的。
本文旨在介绍kaggle比赛到各种原理与技巧,当然一切源自于coursera,由于课程都是英文的,且都比较好理解,这里直接使用英文
Features: numeric, categorical, ordinal, datetime, coordinate, text
Numeric features
All models are divided into tree-based model and non-tree-based model. 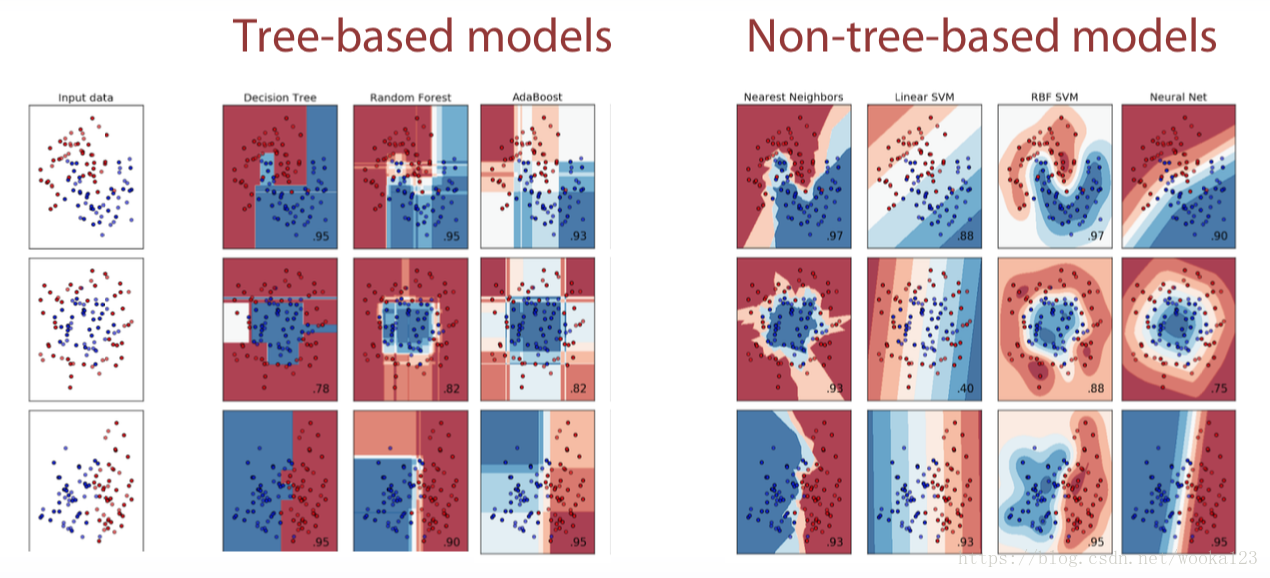
Scaling
For example: if we apply KNN algorithm to the instances below, as we see in the second row, we caculate the distance between the instance and the object. It is obvious that dimension of large scale dominates the distance.

Tree-based models doesn’t depend on scaling
Non-tree-based models hugely depend on scaling
How to do
sklearn:
- To [0,1]
sklearn.preprocessing.MinMaxScaler
X = ( X-X.min( ) )/( X.max()-X.min() ) To mean=0, std=1
sklearn.preprocessing.StandardScaler
X = ( X-X.mean( ) )/X.std()- if you want to use KNN, we can go one step ahead and recall that the bigger feature is, the more important it will be for KNN. So, we can optimize scaling parameter to boost features which seems to be more important for us and see if this helps
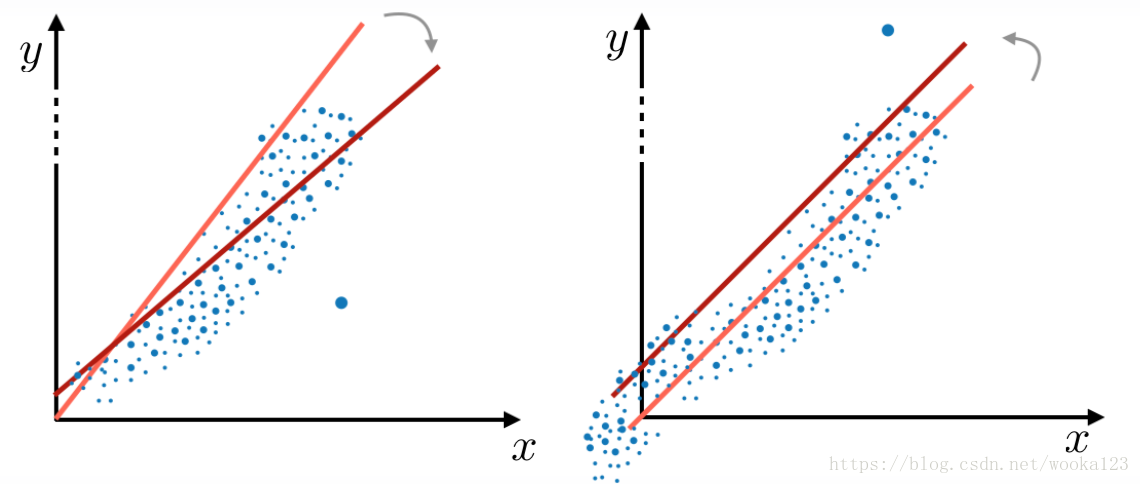
Outliers
The outliers make the model diviate like the red line.
We can clip features values between teo chosen values of lower bound and upper bound
- Rank Transformation
If we have outliers, it behaves better than scaling. It will move the outliers closer to other objects
Linear model, KNN, Neural Network will benefit from this mothod.
rank([-100, 0, 1e5]) == [0,1,2]
rank([1000,1,10]) = [2,0,1]scipy:
scipy.stats.rankdata
Other method
- Log transform: np.log(1 + x)
- Raising to the power < 1: np.sqrt(x + 2/3)
Feature Generation
Depends on
a. Prior knowledge
b. Exploratory data analysis
Ordinal features
Examples:
- Ticket class: 1,2,3
- Driver’s license: A, B, C, D
- Education: kindergarden, school, undergraduate, bachelor, master, doctoral
Processing
1.Label Encoding
* Alphabetical (sorted)
[S,C,Q] -> [2, 1, 3]
sklearn.preprocessing.LabelEncoder
- Order of appearance
[S,C,Q] -> [1, 2, 3]
Pandas.factorize
This method works fine with two ways because tree-methods can split feature, and extract most of the useful values in categories on its own. Non-tree-based-models, on the other side,usually can’t use this feature effectively.
2.Frequency Encoding
[S,C,Q] -> [0.5, 0.3, 0.2]
encoding = titanic.groupby(‘Embarked’).size()
encoding = encoding/len(titanic)
titanic[‘enc’] = titanic.Embarked.map(encoding)from scipy.stats import rankdata
For linear model, it is also helpful.
if frequency of category is correlated with target value, linear model will utilize this dependency.
3.One-hot Encoding
pandas.get_dummies
It give all the categories of one feature a new columns and often used for non-tree-based model.
It will slow down tree-based model, so we introduce sparse matric. Most of libaraies can work with these sparse matrices directly. Namely, xgboost, lightGBM
Feature generation
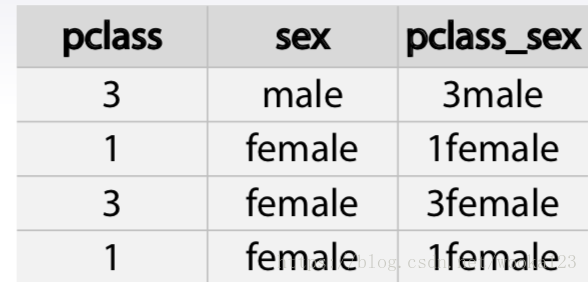
Interactions of categorical features can help linear models and KNN
By concatenating string
Datetime and Coordinates
Date and time
1.Periodicity
2.Time since
a. Row-independent moment
For example: since 00:00:00 UTC, 1 January 1970;
b. Row-dependent important moment
Number of days left until next holidays/ time passed after last holiday.
3.Difference betwenn dates
We can add date_diff feature which indicates number of days between these events
Coordicates
1.Interesting places from train/test data or additional data
Generate distance between the instance to a flat or an old building(Everything that is meanful)
2.Aggergates statistics
The price of surrounding building
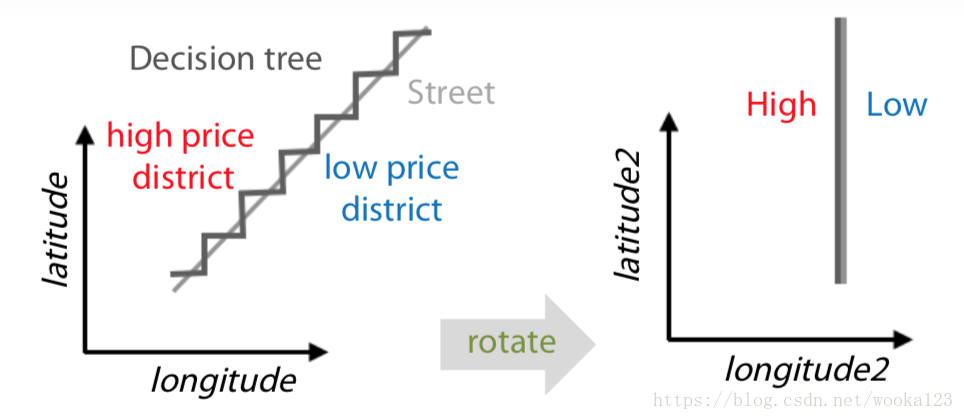
3.Rotation
Sometime it makes the model more precisely to classify the instances.
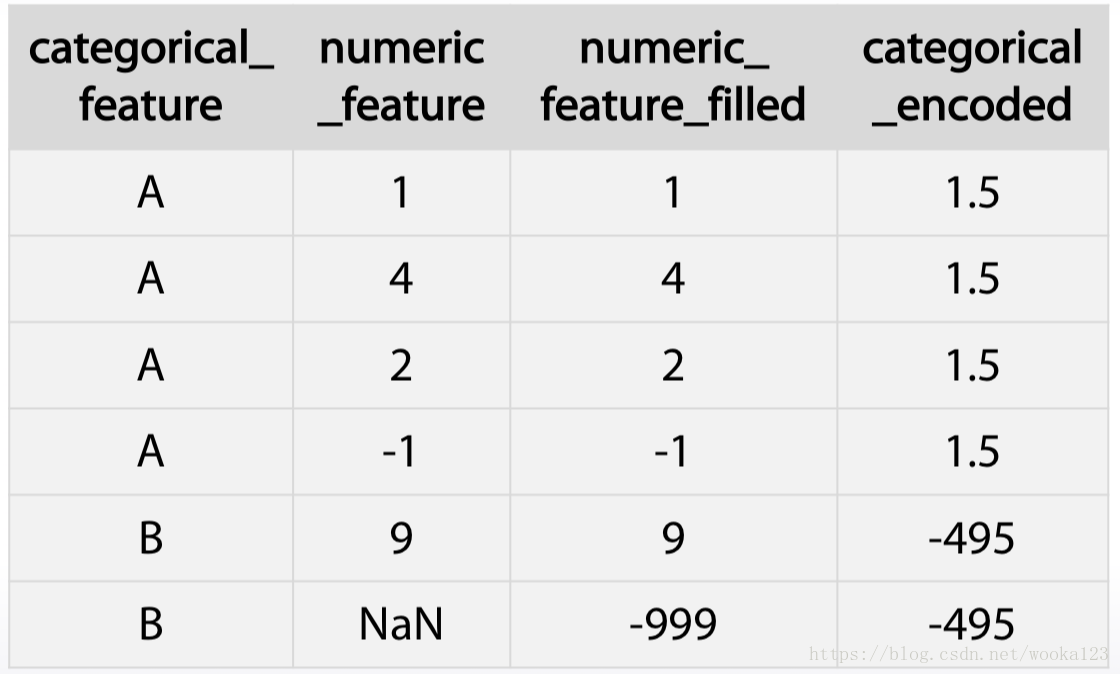
Missing data
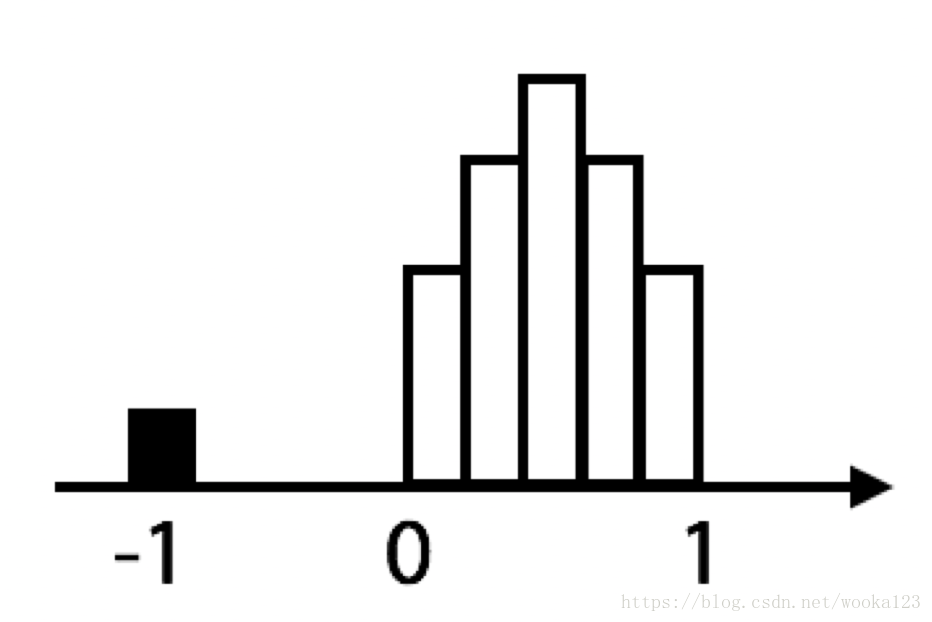
Hidden Nan, numeric
When drawing a histgram, we see the following picture:
It is obivous that -1 is a hidden Nan which is no meaning for this feature.
Fillna approaches
1.-999,-1,etc(outside the feature range)
It is useful in a way that it gives three possibility to take missing value into separate category. The downside of this is that performance of linear networks can suffer.
2.mean,median
Second method usually beneficial for simple linear models and neural networks. But again for trees it can be harder to select object which had missing values in the first place.
3.Reconstruct:
Isnull
Prediction
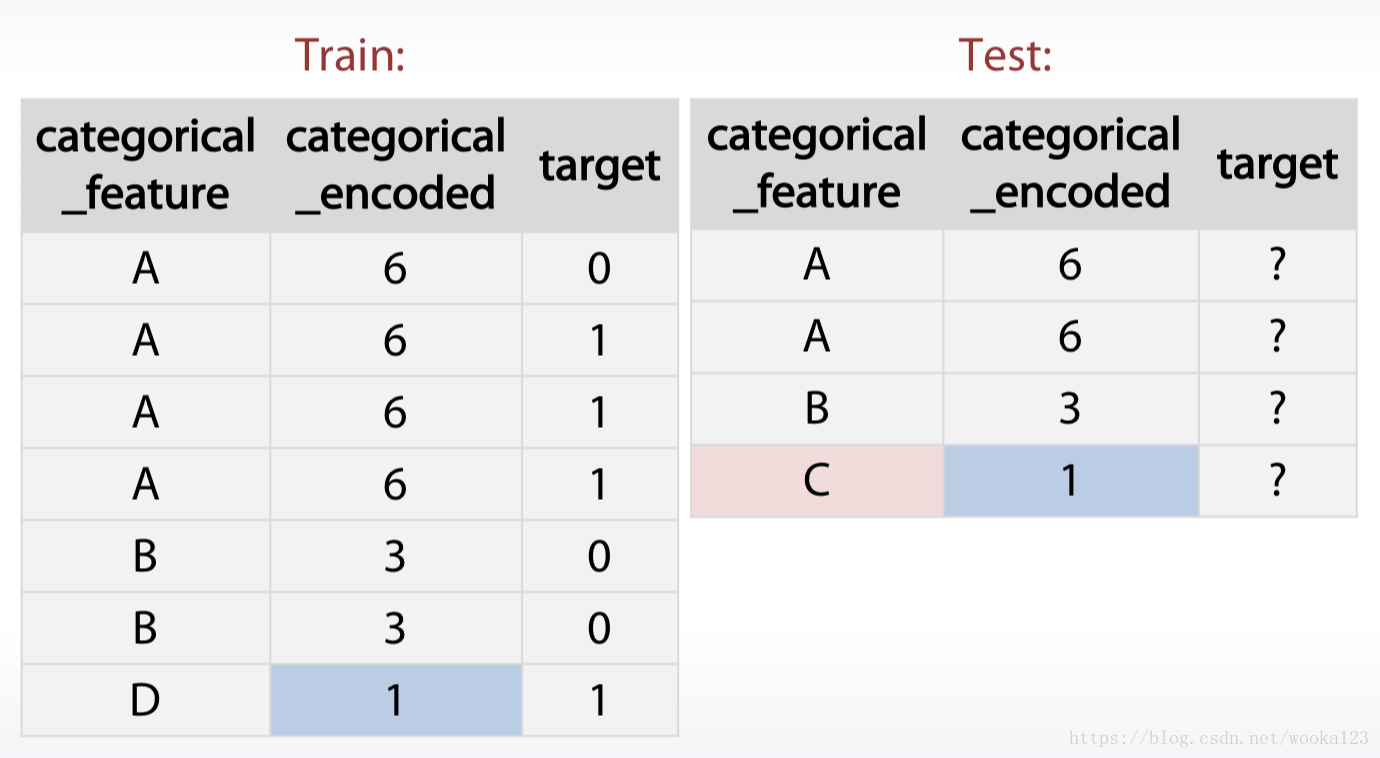
* Replace the missing data with the mean of medain grouped by another feature.
But sometimes it can be screwed up, like:
The way to handle this is to ignore missing values while calculating means for each category.
- Treating values which do not present in trian data
Just generate new feature indicating number of occurrence in the data(freqency)
- Xgboost can handle Nan
4.Remove rows with missing values
This one is possible, but it can lead to loss of important samples and a quality decrease.
Text
Bag of words
Text preprocessing
1.Lowercase
2.Lemmatization and Stemming
3.Stopwords
Examples:
1.Articles(冠词) or prepositions
2.Very common words
sklearn.feature_extraction.text.CountVectorizer:
max_df
- max_df : float in range [0.0, 1.0] or int, default=1.0
When building the vocabulary ignore terms that have a document frequency strictly higher than the given threshold (corpus-specific stop words). If float, the parameter represents a proportion of documents, integer absolute counts. This parameter is ignored if vocabulary is not None.
CountVectorizer
The number of times a term occurs in a given document
sklearn.feature_extraction.text.CountVectorizer
TFiDF
In order to re-weight the count features into floating point values suitable for usage by a classifier
Term frequency
tf = 1 / x.sum(axis=1) [:,None]
x = x * tfInverse Document Frequency
idf = np.log(x.shape[0] / (x > 0).sum(0))
x = x * idf
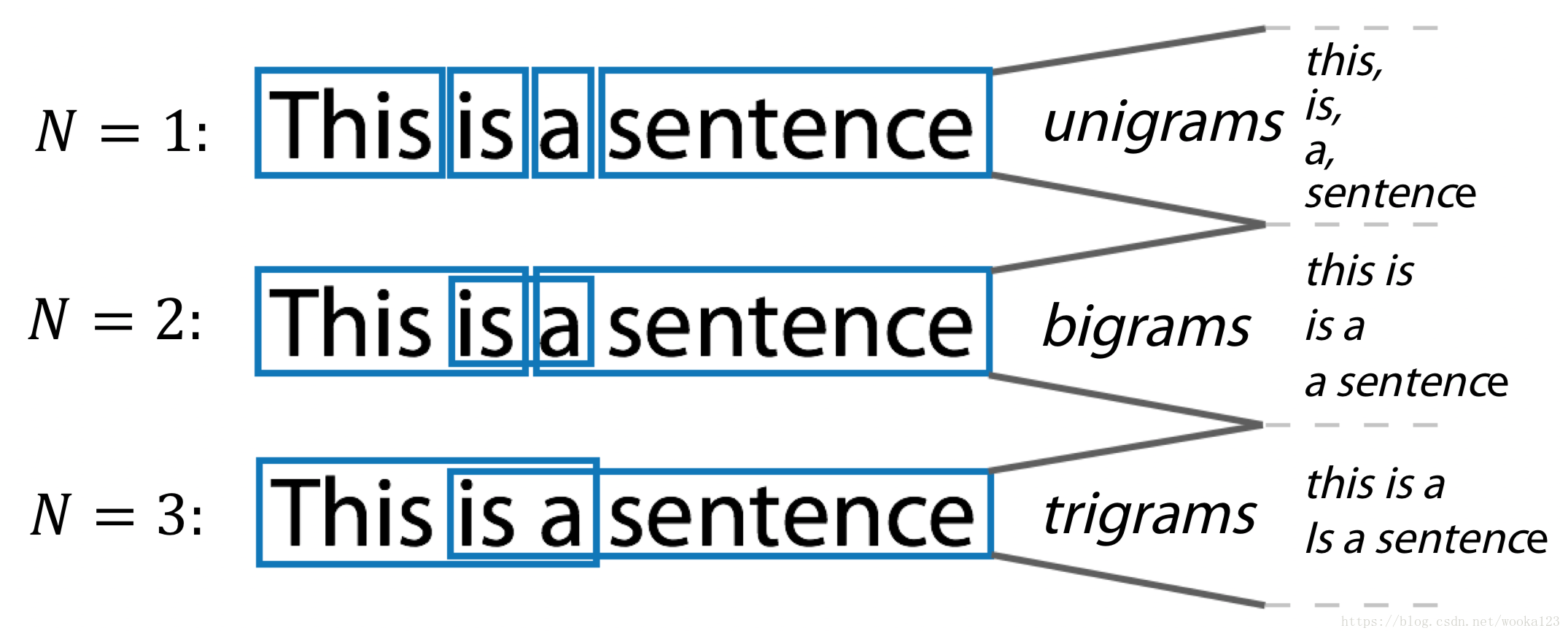
N-gram
sklearn.feature_extraction.text.CountVectorizer:
Ngram_range, analyzer
- ngram_range : tuple (min_n, max_n)
The lower and upper boundary of the range of n-values for different n-grams to be extracted. All values of n such that min_n <= n <= max_n will be used.
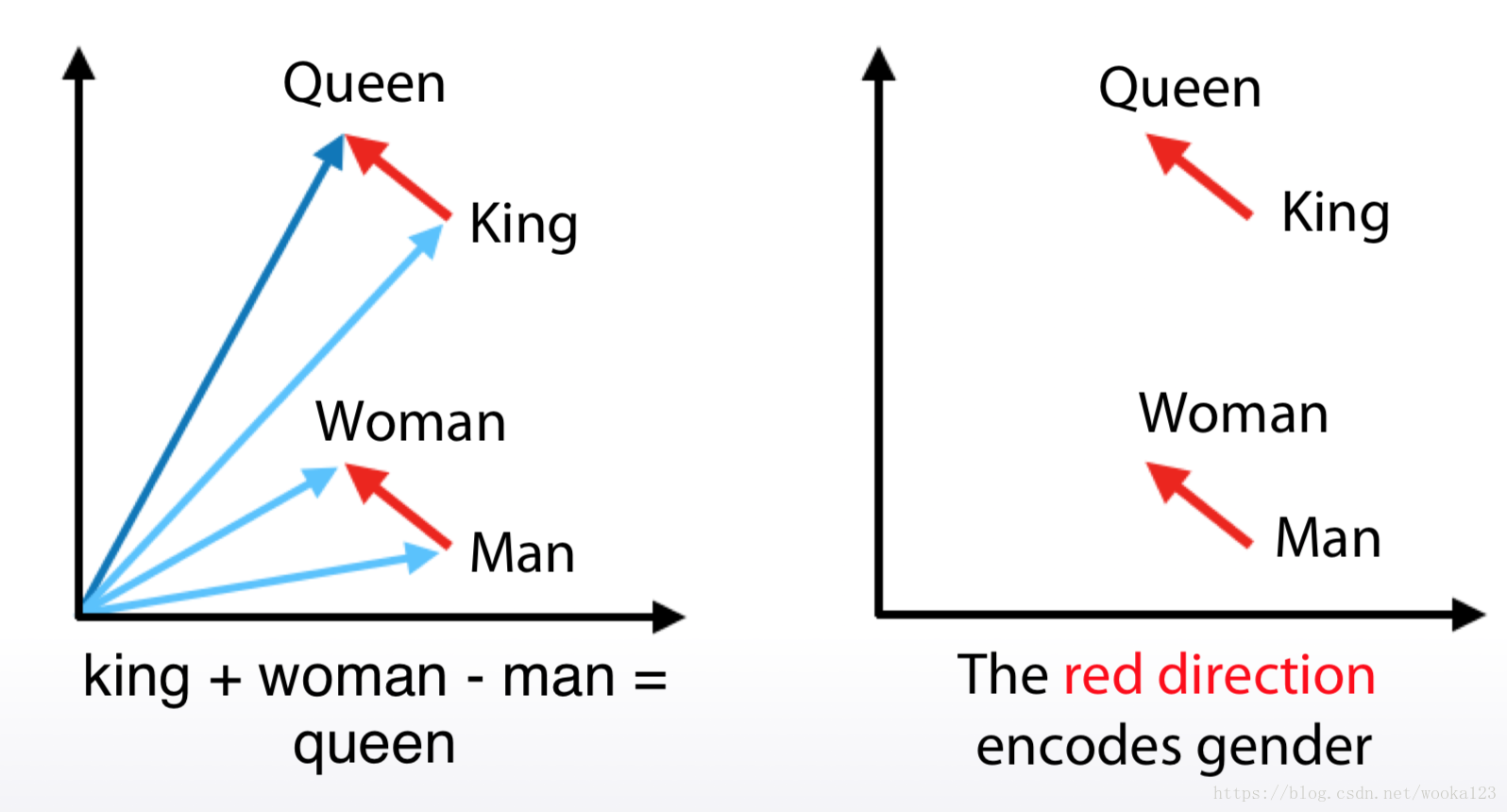
Embeddings(~word2vec)
It converts each word to some vector in some sophisticated space, which usually have several hundred dimensions
a. Relatively small vectors
b. Values in vector can be interpreted only in some cases
c. The words with similar meaning often have similar
embeddings
Example:
Feature Preprocessing on Kaggle的更多相关文章
- Kaggle教程——大神教你上分
本文记录笔者在观看Coursera上国立经济大学HLE的课程 How to win a data science competetion中的收获,和大家分享.课程的这门课的讲授人是Kaggle的大牛, ...
- [Feature] Final pipeline: custom transformers
有视频:https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=BFaadIqWlAg 有代码:https://github.com/jem1031/pandas-pipelines-cust ...
- [ML] Load and preview large scale data
Ref: [Feature] Preprocessing tutorial 主要是 “无量纲化” 之前的部分. 加载数据 一.大数据源 http://archive.ics.uci.edu/ml/ht ...
- scikit-learn:class and function reference(看看你究竟掌握了多少。。)
http://scikit-learn.org/stable/modules/classes.html#module-sklearn.decomposition Reference This is t ...
- 以股票案例入门基于SVM的机器学习
SVM是Support Vector Machine的缩写,中文叫支持向量机,通过它可以对样本数据进行分类.以股票为例,SVM能根据若干特征样本数据,把待预测的目标结果划分成“涨”和”跌”两种,从而实 ...
- Machine Learning : Pre-processing features
from:http://analyticsbot.ml/2016/10/machine-learning-pre-processing-features/ Machine Learning : Pre ...
- 逻辑回归应用之Kaggle泰坦尼克之灾(转)
正文:14pt 代码:15px 1 初探数据 先看看我们的数据,长什么样吧.在Data下我们train.csv和test.csv两个文件,分别存着官方给的训练和测试数据. import pandas ...
- kaggle Titanic心得
Titanic是kaggle上一个练手的比赛,kaggle平台提供一部分人的特征,以及是否遇难,目的是预测另一部分人是否遇难.目前抽工作之余,断断续续弄了点,成绩为0.79426.在这个比赛过程中,接 ...
- Kaggle竞赛 —— 泰坦尼克号(Titanic)
完整代码见kaggle kernel 或 NbViewer 比赛页面:https://www.kaggle.com/c/titanic Titanic大概是kaggle上最受欢迎的项目了,有7000多 ...
随机推荐
- COSO企业风险管理框架2017版发布!看看有哪些变化?
近期,COSO发布了新版(2017版)的企业风险管理框架:<企业风险管理—与战略和业绩的整合>.相较于2004年发布的上一版框架<企业风险管理—整合框架>,新框架强调了制定战略 ...
- aliyun ubuntu读取第三方源被forbidden的问题
使用下面指令添加了一个源: sudo add-apt-repository ppa:webupd8team/java 然后update的时候提示: W: Failed to fetch http:// ...
- git如何移除某文件夹的版本控制
目录结构如下 project bin lib src ...... 执行如下的操作 git add . git commit -m "add bin/ lib/ src/" git ...
- java之Spring(AOP)前奏-动态代理设计模式(下)
在上一章我们看到了,新增的三种类都能实现对原始功能类进行添加功能的事务处理,这三种类就是一个代理. 但是这种代理是写死的,怎样实现对任意接口添加自定义的代理呢? 我们先来看一下之前的代理实现: pub ...
- Vue--学习过程中遇到的坑
在这里总结一下学习Vue遇到的易错点,持续更新 1.实例化一个Vue对象: 通过new Vue({ el:'#id', data:{ a:'字符串1', b:‘字符串2’ }) 这里的Vue必须大写V ...
- python笔记:#013#高级变量类型
高级变量类型 目标 列表 元组 字典 字符串 公共方法 变量高级 知识点回顾 Python 中数据类型可以分为 数字型 和 非数字型 数字型 整型 (int) 浮点型(float) 布尔型(bool) ...
- css那些事(一)
一.内边框padding和外边框margin属性缩写 内外边框有四个属性:padding-top,padding-right,padding-bottom,padding-left;margin-to ...
- Maven分模块以及打war包
我们如何进行模块化开发呢? 我们使用上面的例子进行演示,先进行合理的优化,我们希望dao和service作为通用的底层工具来使用,把它们合并成一个核心模块(core),build成core.jar,简 ...
- servlet简介及生命周期
Servlet 简介 Servlet 是什么? Java Servlet 是运行在 Web 服务器或应用服务器上的程序,它是作为来自 Web 浏览器或其他 HTTP 客户端的请求和 HTTP 服务器上 ...
- TCP连接的建立与释放(三次握手与四次挥手)
TCP连接的建立与释放(三次握手与四次挥手) TCP是面向连接的运输层协议,它提供可靠交付的.全双工的.面向字节流的点对点服务.HTTP协议便是基于TCP协议实现的.(虽然作为应用层协议,HTTP协议 ...