django rest framework用户认证
django rest framework用户认证
- 进入rest framework的Apiview
@classmethod
def as_view(cls, **initkwargs):
"""
Store the original class on the view function. This allows us to discover information about the view when we do URL
reverse lookups. Used for breadcrumb generation.
"""
if isinstance(getattr(cls, 'queryset', None), models.query.QuerySet):
def force_evaluation():
raise RuntimeError(
'Do not evaluate the `.queryset` attribute directly, '
'as the result will be cached and reused between requests. '
'Use `.all()` or call `.get_queryset()` instead.'
)
cls.queryset._fetch_all = force_evaluation view = super().as_view(**initkwargs)
view.cls = cls
view.initkwargs = initkwargs # Note: session based authentication is explicitly CSRF validated,
# all other authentication is CSRF exempt.
return csrf_exempt(view)django的类视图是调用内部的as_view方法来实现CBV,在第18行调用了父类的as_view,父类的as_view调用了dispatch方法,这里在ApiView自定义了dispatch
def dispatch(self, request, *args, **kwargs):
"""
`.dispatch()` is pretty much the same as Django's regular dispatch,
but with extra hooks for startup, finalize, and exception handling.
"""
self.args = args
self.kwargs = kwargs
request = self.initialize_request(request, *args, **kwargs)
self.request = request
self.headers = self.default_response_headers # deprecate? try:
self.initial(request, *args, **kwargs) # Get the appropriate handler method
if request.method.lower() in self.http_method_names:
handler = getattr(self, request.method.lower(),
self.http_method_not_allowed)
else:
handler = self.http_method_not_allowed response = handler(request, *args, **kwargs) except Exception as exc:
response = self.handle_exception(exc) self.response = self.finalize_response(request, response, *args, **kwargs)
return self.response和django的dispatch类似,第8,9行对request进行了封装
def initialize_request(self, request, *args, **kwargs):
"""
Returns the initial request object.
"""
parser_context = self.get_parser_context(request) return Request(
request,
parsers=self.get_parsers(),
authenticators=self.get_authenticators(),
negotiator=self.get_content_negotiator(),
parser_context=parser_context
)封装函数内部返回的是Request对象
class Request:
"""
Wrapper allowing to enhance a standard `HttpRequest` instance. Kwargs:
- request(HttpRequest). The original request instance.
- parsers_classes(list/tuple). The parsers to use for parsing the
request content.
- authentication_classes(list/tuple). The authentications used to try
authenticating the request's user.
""" def __init__(self, request, parsers=None, authenticators=None,
negotiator=None, parser_context=None):
assert isinstance(request, HttpRequest), (
'The `request` argument must be an instance of '
'`django.http.HttpRequest`, not `{}.{}`.'
.format(request.__class__.__module__, request.__class__.__name__)
) self._request = request
self.parsers = parsers or ()
self.authenticators = authenticators or ()
self.negotiator = negotiator or self._default_negotiator()
self.parser_context = parser_context
self._data = Empty
self._files = Empty
self._full_data = Empty
self._content_type = Empty
self._stream = Empty if self.parser_context is None:
self.parser_context = {}
self.parser_context['request'] = self
self.parser_context['encoding'] = request.encoding or settings.DEFAULT_CHARSET force_user = getattr(request, '_force_auth_user', None)
force_token = getattr(request, '_force_auth_token', None)
if force_user is not None or force_token is not None:
forced_auth = ForcedAuthentication(force_user, force_token)
self.authenticators = (forced_auth,)Request对象的初始化函数,它将原生django的request对象赋值给self._request,所以在ApiView视图中想使用原生的request要用request._request来使用
- 查看self.authenticators
- self.authenticators等于传进来的authenticators
- 在ApiView内部定义了get_authenticators方法,它会被authenticators来接受
def get_authenticators(self):
"""
Instantiates and returns the list of authenticators that this view can use.
"""
return [auth() for auth in self.authentication_classes]这个方法回去self.authentication_classes里面找定义好的对象再将其实例化
- 定义自定义验证类
from rest_framework.views import APIView
from django.http import HttpResponse
from rest_framework.authentication import BaseAuthentication
from rest_framework.exceptions import AuthenticationFailed class MyAuthentication(BaseAuthentication):
def authenticate(self, request):
if not request._request.GET.get('name'):
raise AuthenticationFailed
return ('user', None) def authenticate_header(self, request):
pass class MyView(APIView):
authentication_classes = [MyAuthentication] def get(self, request):
user = request.user
return HttpResponse(user)验证类继承BaseAuthentication(不继承也可以,但都要实现authenticate)方法,在authenticate里面实现用户的认证,最后返回一个元祖,第一个元素为user对象,该对象被request.user接受, 第二个元素会被request.auth捕捉
- 效果
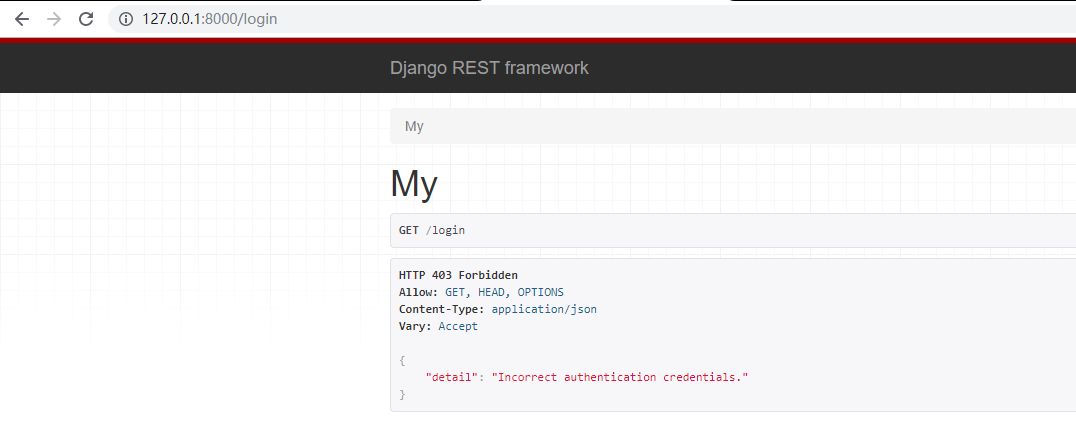
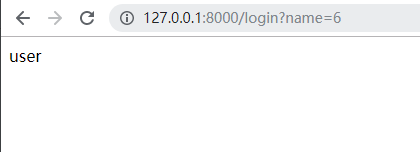
django rest framework用户认证的更多相关文章
- Django Rest framework 之 认证
django rest framework 官网 django rest framework 之 认证(一) django rest framework 之 权限(二) django rest fra ...
- Django 中的用户认证
Django 自带一个用户认证系统,这个系统处理用户帐户.组.权限和基于 cookie 的 会话.本文说明这个系统是如何工作的. 概览 认证系统由以下部分组成: 用户 权限:控制用户进否可以执行某项任 ...
- Django rest framework 的认证流程(源码分析)
一.基本流程举例: urlpatterns = [ url(r'^admin/', admin.site.urls), url(r'^users/', views.HostView.as_view() ...
- Django Rest Framework用户访问频率限制
一. REST framework的请求生命周期 基于rest-framework的请求处理,与常规的url配置不同,通常一个django的url请求对应一个视图函数,在使用rest-framewor ...
- Django组件之用户认证组件
一.auth模块 from django.contrib import auth django.contrib.auth中提供了许多方法,这里主要介绍其中的三个: 1.1 .authenticate( ...
- Django Rest Framework之认证
代码基本结构 url.py: from django.conf.urls import url, include from web.views.s1_api import TestView urlpa ...
- 使用django实现自定义用户认证
参考资料:https://docs.djangoproject.com/en/1.10/topics/auth/customizing/ 直接拉到最后看栗子啦 django自定义用户认证(使用自 ...
- 09 Django组件之用户认证组件
没有学习Django认证组件之前使用装饰器方法 from django.shortcuts import render, HttpResponse, redirect from app01.MyFor ...
- Django组件之用户认证
auth模块 1 from django.contrib import auth django.contrib.auth中提供了许多方法,这里主要介绍其中的三个: 1.1 .authenticate( ...
随机推荐
- [android]p7-1 fragment学习笔记
本文源自<android权威编程指南第3版>第7章UI fragment与fragment 第7章主要内容是实现一个记录不良行为的APP(部分实现),有列表,有具体的行为内容显示.第7章主 ...
- Java反射之成员变量的反射
上一篇介绍了Java反射之构造方法反射.这次我们在说一说如何反射类中的成员变量并用作一个简单案例. [一]Field类 Filed类代表字段,包含字段拥有的所有属性,比如修饰符,变量类型,值等等,Fi ...
- 初识JVM:(一)JVM工作原理和流程
本文主要参考:http://blog.csdn.net/CSDN_980979768/article/details/47281037?locationNum=7&fps=1 声明:主要用于个 ...
- 杂谈 | 增量思维v.s.存量思维
无挂碍故,无有恐怖,远离颠倒梦想,究竟涅槃. ——<心经> 声明在前,本文并不是要论述“存量思维”是不好的, 而是整理某些场景下需要摒弃“存量思维”,或者提倡“增量思维”. 1 ...
- GitHub 热点速览 Vol.12:不可思议的浏览器 browser-2020 周涨 star 超 3 千
作者:HelloGitHub-小鱼干 摘要:本周的 GitHub Trending 像极最近的天气,温暖如春突然来个急降温.新晋 GitHub 项目重启屈指可数的模式,好在老项目们表现甚好.比如一周就 ...
- eclipse操作快捷键
Eclipse最全快捷键,熟悉快捷键可以帮助开发事半功倍,节省更多的时间来用于做有意义的事情. Ctrl+1 快速修复(最经典的快捷键,就不用多说了) Ctrl+D: 删除当前行 Ctrl+Alt+↓ ...
- JavaScript 模式》读书笔记(4)— 函数1
从这篇开始,我们会用很长的章节来讨论函数,这个JavaScript中最重要,也是最基本的技能.本章中,我们会区分函数表达式与函数声明,并且还会学习到局部作用域和变量声明提升的工作原理.以及大量对API ...
- AAAI 2020 | 反向R?削弱显著特征为细粒度分类带来提升
论文提出了类似于dropout作用的diversification block,通过抑制特征图的高响应区域来反向提高模型的特征提取能力,在损失函数方面,提出专注于top-k类别的gradient-bo ...
- Mybatis三剑客介绍
1.MyBatis generator 利用mybatis-generator自动生成代码 下载地址: https://download.csdn.net/download/qq_36625806/ ...
- P1969 积木大赛 题解
原题链接 简要题意: 每次把一段区间 \(+1\),问得到 \(a\) 数组的最小次数. 我们可以把 \(+1\) 得到 \(a\) 换成,从 \(a\) 依次 \(-1\) 得到 \(0\). 算法 ...
