关于C++中vector和set使用sort方法进行排序
C++中vector和set都是非常方便的容器,
sort方法是algorithm头文件里的一个标准函数,能进行高效的排序,默认是按元素从小到大排序
将sort方法用到vector和set中能实现多种符合自己需求的排序
首先sort方法可以对静态的数组进行排序
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int main(){
int a[] = { , , , , , , , , , };
sort(a, a +);
for (int i = ; i < ; i++)
cout << a[i] << endl;
return ;
}
运行结果:
这里可以看到是sort(a,a+10),但是数组a一共只有9个元素,为什么是a+10而不是a+9呢?
因为sort方法实际上最后一位地址对应的数是不取的,
而且vector,set,map这些容器的end()取出来的值实际上并不是最后一个值,而end的前一个才是最后一个值!
需要用prev(xxx.end()),才能取出容器中最后一个元素。
对vector使用sort函数:
第一种情形:基本类型,如vector<int>,vector<double>,vector<string>也是可以的
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
int main(){
vector<int> a;
int n = ;
while (n--){
int score;
cin >> score;
a.push_back(score);
}
//cout <<" a.end()"<< *a.end() << endl; 执行这句话会报错!
cout << " prev(a.end)" << *prev(a.end()) << endl;
sort(a.begin(), a.end());
for (vector<int>::iterator it = a.begin(); it != a.end(); it++){
cout << *it << endl;
}
return ;
}
执行结果:

看到了吗,实际上end的前一个指针指向的元素才是插入时的最后一个值!
排序后从小大大。
第二种情形:用自定义的结构体进行sort算法,
这时候需要自己定义个比较函数,因为sort算法是基于容器中的元素是可以两两比较的,然后从小到大排序,所以要自定义怎么样才是小于('<')
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
#include<set>
#include<string>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
struct student{
char name[];
int score;
};
//自定义“小于”
bool comp(const student &a, const student &b){
return a.score < b.score;
}
int main(){
vector<student> vectorStudents;
int n = ;
while (n--){
student oneStudent;
string name;
int score;
cin >> name >> score;
strcpy(oneStudent.name, name.c_str());
oneStudent.score = score;
vectorStudents.push_back(oneStudent);
}
cout << "===========排序前================" << endl;
for (vector<student>::iterator it = vectorStudents.begin(); it != vectorStudents.end(); it++){
cout << "name: " << it->name << " score: " << it->score << endl;
}
sort(vectorStudents.begin(),vectorStudents.end(),comp);
cout << "===========排序后================" << endl;
for (vector<student>::iterator it = vectorStudents.begin(); it != vectorStudents.end(); it++){
cout << "name: " << it->name << " score: " << it->score << endl;
}
return ;
}
运行结果:

不过有时候一个排序条件不够,比如要求学生按分数从高到低排序,如果分数相同,则按照年龄从大到小排序
就需要在comp自定义函数里面修改一下判断了,原来是直接return a.score < b.score
现在就需要判断
if (a.score > b.score)
return true;
else if (a.score == b.score && a.age > b.age)
return true;
else
return false; 这里一定要记得else return false!!!有一次比赛的时候写到这个函数,有三个判断条件,结果忘了这茬,总是报错,
到后来有点着急了就自己手动实现了一下写了三个比较函数,调用了三次sort函数!!!!!
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
#include<set>
#include<string>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
struct student{
char name[];
int score;
int age;
};
//自定义“小于”
bool comp(const student &a, const student &b){
if (a.score > b.score)
return true;
else if (a.score == b.score && a.age > b.age)
return true;
else ///这里的else return false非常重要!!!!!
return false;
}
int main(){
vector<student> vectorStudents;
/*set<student> setStudents;*/
//int n = 5;
int n = ;
while (n--){
student oneStudent;
string name;
int score;
int age;
cin >> name >> score>>age;
strcpy(oneStudent.name, name.c_str());
oneStudent.score = score;
oneStudent.age = age;
vectorStudents.push_back(oneStudent);
}
cout << "===========排序前================" << endl;
for (vector<student>::iterator it = vectorStudents.begin(); it != vectorStudents.end(); it++){
cout << "name: " << it->name << " score: " << it->score << " age: "<<it->age<<endl;
}
sort(vectorStudents.begin(), vectorStudents.end(), comp);
//sort(setStudents.begin(), setStudents.end());
cout << "===========排序后================" << endl;
for (vector<student>::iterator it = vectorStudents.begin(); it != vectorStudents.end(); it++){
cout << "name: " << it->name << " score: " << it->score << " age: " << it->age << endl;
}
return ;
}
运行结果如下:
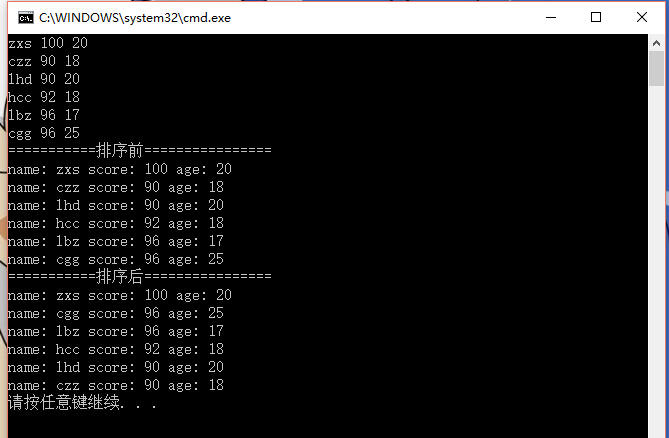
接下来,对于set做类似的操作。
set是一个集合,内部的元素不会重复,同时它会自动进行排序,也是从小到大
而且set的insert方法没有insert(a,cmp)这种重载,所以如果要把结构体插入set中,我们就要重载'<'运算符。
set方法在插入的时候也是从小到大的,那么我们重载一下<运算符让它从大到小排序
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
#include<set>
#include<string>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
struct student{
char name[];
int score;
};
//自定义“小于”
bool comp(const student &a, const student &b){
return a.score < b.score;
}
bool operator < (const student & stu1,const student &stu2){
return stu1.score > stu2.score;
}
int main(){
//vector<student> vectorStudents;
set<student> setStudents;
//int n = 5;
int n = ;
while (n--){
student oneStudent;
string name;
int score;
cin >> name >> score;
strcpy(oneStudent.name, name.c_str());
oneStudent.score = score;
setStudents.insert(oneStudent);
}
cout << "===========排序前================" << endl;
for (set<student>::iterator it = setStudents.begin(); it != setStudents.end(); it++){
cout << "name: " << it->name << " score: " << it->score << endl;
}
//sort(setStudents.begin(), setStudents.end(), comp);
//cout << "===========排序后================" << endl;
//for (set<student>::iterator it = setStudents.begin(); it != setStudents.end(); it++){
// cout << "name: " << it->name << " score: " << it->score << endl;
//}
return ;
}
运行结果:

我们可以看到,set内元素不会重复,而且它按照它所认为的“从小到大”进行了排序
关于C++中vector和set使用sort方法进行排序的更多相关文章
- 回调函数及数组中sort()方法实现排序的原理
1.回调函数:把一个方法A当一个参数值传递到另外一个函数B中,在B执行的过程当中我们随时根据需求让A方法执行: 什么是回调 :它是异步编程基本的方法,需要异步处理的时候一般采用后续传递的方式,将后 ...
- 定义一个数组,并对这个数组进行动态初始化,使用sort方法进行排序后,再将数组中的元素倒置过来。
Sort方法,生序排序 package com.fs.array; import java.util.Arrays; public class ArraySort { public static vo ...
- 论C++11 中vector的N种遍历方法
随着C++11标准的出现,C++标准添加了许多有用的特性,C++代码的写法也有比较多的变化. vector是经常要使用到的std组件,对于vector的遍历,本文罗列了若干种写法. (注:本文中代码为 ...
- C++11中vector的几种遍历方法
假设有这样的一个vector: vector<int> line={1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9}; 需要输出vector里的每个元素,主函数如下: void showvec(con ...
- Java中使用Collections.sort()方法对数字和字符串泛型的LIst进行排序
在List的排序中常用的是Collections.sort()方法,可以对String类型和Integer类型泛型的List集合进行排序. 首先演示sort()方法对Integer类型泛型的List排 ...
- .NET中string[]数组和List<string>泛型的相互转换以及Array类的Sort()方法(转)
从string[]转List<string>: " }; List<string> list = new List<string>(str); 从List ...
- 你真的会用JavaScript中的sort方法吗
在平时的业务开发中,数组(Array) 是我们经常用到的数据类型,那么对数组的排序也很常见,除去使用循环遍历数组的方法来排列数据,使用JS数组中原生的方法 sort 来排列(没错,比较崇尚JS原生 ...
- python中sort和sorted排序的相关方法
Python list内置sort()方法用来排序,也可以用python内置的全局sorted()方法来对可迭代的序列排序生成新的序列. 1)排序基础 简单的升序排序是非常容易的.只需要调用sorte ...
- Array类的Sort()方法
刚复习了Array类的sort()方法, 这里列举几个常用的,和大家一起分享. Array类实现了数组中元素的冒泡排序.Sort()方法要求数组中的元素实现IComparable接口.如System. ...
随机推荐
- 高德地图JSApi
<!DOCTYPE HTML> <html> <head> <meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content ...
- 一、js的数据类型
一.数据类型 ECMAScript中有5种简单数据类型:Undefined.Null.Boolean.Number和String.还有一种复杂数据类型--Object.ECMAScript不支持任何创 ...
- ThinkPHP中:检查Session是否过期
1.创建Session public function index(){ $sess_time=time(); session('name','andy'); session('time_stamp' ...
- struts jar包
这些错误很让我摸不着头脑,经多方查阅资料后,在Struts 2.2.x中应该导入如下7个JAR文件 1) commons-fileupload-1.2.1.jar 2) commons-io- ...
- hdu2222 ac自动机入门
Keywords Search Time Limit: 2000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 65536/32768 K (Java/Others) ...
- SQL Server XML数据解析
--5.读取XML --下面为多种方法从XML中读取EMAIL DECLARE @x XML SELECT @x = ' <People> <dongsheng> <In ...
- python装饰器 & flask 通过装饰器 实现 单点登录验证
首先介绍装饰器,以下是一段标注了特殊输出的代码.用于帮助理解装饰器的调用过程. import time def Decorator_one(arg1): info = "\033[1;31; ...
- java类加载小记
java类只有当创建实体或被调用时才会加载,加载时按 编码顺序 先加载static后加载普通的.static模块和static变量都是同一等级的,谁写前面就先加载谁. 在调用某个静态类的方法时,会按编 ...
- IOS应用FFMPEG库
1.引用资源 build-ffmpeg ffmpeg库生成 -sh开源地址: https://gist.github.com/m1entus/6983547 iFrameExtractor ffmp ...
- AspectCore中的IoC容器和依赖注入
IOC模式和依赖注入是近年来非常流行的一种模式,相信大家都不陌生了,在Asp.Net Core中提供了依赖注入作为内置的基础设施,如果仍不熟悉依赖注入的读者,可以看看由我们翻译的Asp.Net Cor ...
