openresty开发系列38--通过Lua+Redis 实现动态封禁IP
openresty开发系列38--通过Lua+Redis 实现动态封禁IP 一)需求背景
为了封禁某些爬虫或者恶意用户对服务器的请求,我们需要建立一个动态的 IP 黑名单。
对于黑名单之内的 IP ,拒绝提供服务。 二)设计方案
实现 IP 黑名单的功能有很多途径:
1、在操作系统层面,配置 iptables,拒绝指定 IP 的网络请求;
2、在 Web Server 层面,通过 Nginx 自身的 deny 选项 或者 lua 插件 配置 IP 黑名单;
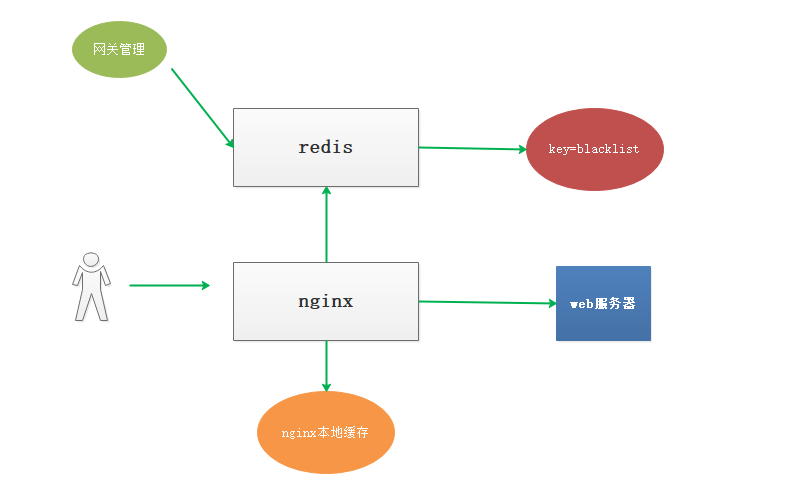
3、在应用层面,在请求服务之前检查一遍客户端 IP 是否在黑名单。 为了方便管理和共享,我们通过 Nginx+Lua+Redis 的架构实现 IP 黑名单的功能 如图
配置nginx.conf
在http部分,配置本地缓存,来缓存redis中的数据,避免每次都请求redis lua_shared_dict shared_ip_blacklist 8m; #定义ip_blacklist 本地缓存变量 location /ipblacklist {
access_by_lua_file /usr/local/lua/access_by_limit_ip.lua;
echo "ipblacklist";
}
# 编辑 /usr/local/lua/access_by_limit_ip.lua local function close_redis(red)
if not red then
return
end
--释放连接(连接池实现)
local pool_max_idle_time = --毫秒
local pool_size = --连接池大小
local ok, err = red:set_keepalive(pool_max_idle_time, pool_size)
if not ok then
ngx.say("set keepalive error : ", err)
end
end local function errlog(...)
ngx.log(ngx.ERR, "redis: ", ...)
end local function duglog(...)
ngx.log(ngx.DEBUG, "redis: ", ...)
end local function getIp()
local myIP = ngx.req.get_headers()["X-Real-IP"]
if myIP == nil then
myIP = ngx.req.get_headers()["x_forwarded_for"]
end
if myIP == nil then
myIP = ngx.var.remote_addr
end
return myIP;
end local key = "limit:ip:blacklist"
local ip = getIp();
local shared_ip_blacklist = ngx.shared.shared_ip_blacklist --获得本地缓存的最新刷新时间
local last_update_time = shared_ip_blacklist:get("last_update_time"); if last_update_time ~= nil then
local dif_time = ngx.now() - last_update_time
if dif_time < then --缓存1分钟,没有过期
if shared_ip_blacklist:get(ip) then
return ngx.exit(ngx.HTTP_FORBIDDEN) --直接返回403
end
return
end
end local redis = require "resty.redis" --引入redis模块
local red = redis:new() --创建一个对象,注意是用冒号调用的 --设置超时(毫秒)
red:set_timeout()
--建立连接
local ip = "10.11.0.215"
local port =
local ok, err = red:connect(ip, port)
if not ok then
close_redis(red)
errlog("limit ip cannot connect redis");
else
local ip_blacklist, err = red:smembers(key); if err then
errlog("limit ip smembers");
else
--刷新本地缓存,重新设置
shared_ip_blacklist:flush_all(); --同步redis黑名单 到 本地缓存
for i,bip in ipairs(ip_blacklist) do
--本地缓存redis中的黑名单
shared_ip_blacklist:set(bip,true);
end
--设置本地缓存的最新更新时间
shared_ip_blacklist:set("last_update_time",ngx.now());
end
end if shared_ip_blacklist:get(ip) then
return ngx.exit(ngx.HTTP_FORBIDDEN) --直接返回403
end
当redis设置了密码时代码如下:
[root@node5 lua]# cat /usr/local/lua/access_by_limit_ip.lua
local function close_reis(red)
if not red then
return
end
local pool_max_idle_time =
local pool_size =
local ok, err = red:set_keepalive(pool_max_idle_time, pool_size)
if not ok then
ngx.say("set keepalive error :", err)
end
end local function errlog(...)
ngx.log(ngx.ERR, "redis: ", ...)
end local function duglog(...)
ngx.log(ngx.DEBUG, "redis: ",...)
end local function getIp()
local myip = ngx.req.get_headers()["X-Real-IP"]
if myip == nil then
myip = ngx.req.get_headers()["x_forwarded_for"]
end
if myip == nil then
myip = ngx.var.remote_addr
end
return myip
end local key = "limit:ip:blacklist"
local ip = getIp();
local shared_ip_blacklist = ngx.shared.shared_ip_blacklist local last_update_time = shared_ip_blacklist:get("last_update_time"); if last_update_time ~= nil then
local dif_time = ngx.now() - last_update_time
if dif_time < then
if shared_ip_blacklist:get(ip) then
return ngx.exit(ngx.HTTP_FORBIDDEN)
end
return
end
end local redis = require "resty.redis"
local red = redis:new() red:set_timeout()
local ip = "10.11.0.215"
local port =
local ok, err = red:connect(ip,port) local count, err = red:get_reused_times()
if == count then ----新建连接,需要认证密码
ok, err = red:auth("redis123")
if not ok then
ngx.say("failed to auth: ", err)
return
end
elseif err then ----从连接池中获取连接,无需再次认证密码
ngx.say("failed to get reused times: ", err)
return
end if not ok then
close_redis(red)
errlog("limit ip cannot connect redis");
else
local ip_blacklist, err = red:smembers(key) if err then
errlog("limit ip smembers")
else
shared_ip_blacklist:flush_all(); for i,bip in ipairs(ip_blacklist) do
shared_ip_blacklist:set(bip, true);
end shared_ip_blacklist:set("last_update_time", ngx.now());
end
end if shared_ip_blacklist:get(ip) then
return ngx.exit(ngx.HTTP_FORBIDDEN)
end
用户redis客户端设置:
添加黑名单IP:
sadd limit:ip:blacklist 10.11.0.148
获取黑名单IP:
smembers limit:ip:blacklist
10.11.0.215:6379> sadd limit:ip:blacklist 10.11.0.148
10.11.0.215:6379> sadd limit:ip:blacklist 10.11.0.215
10.11.0.215:6379> smembers limit:ip:blacklist
1) "10.11.0.215"
2) "10.11.0.148"
10.11.0.215:6379> smembers limit:ip:blacklist
1) "10.11.0.215"
2) "10.11.0.148"
此方法目前只能实现手动添加黑名单IP进行IP封禁,在某些场景如:半夜如果有人恶意爬取网站服务器可能导致服务器资源耗尽崩溃或者影响业务
下面是改进后的代码,可以实现自动将访问频次过高的IP地址加入黑名单封禁一段时间
nginx.conf配置部分:
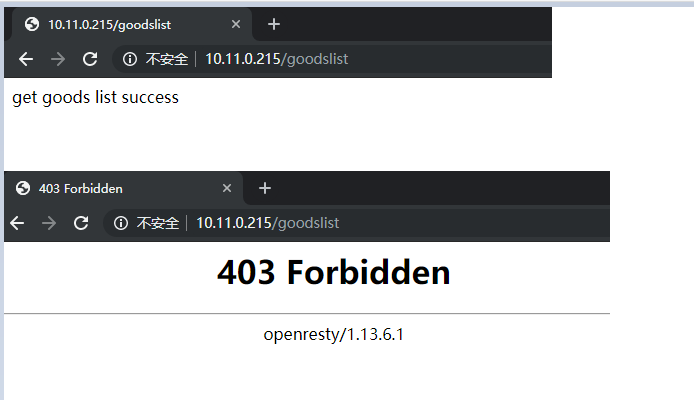
location /goodslist {
set $business "USER";
access_by_lua_file /usr/local/lua/access_count_limit.lua;
echo "get goods list success";
}
lua代码:
[root@node5 lua]# cat /usr/local/luaaccess_count_limit.lua
local function close_redis(red)
if not red then
return
end local pool_max_idle_time =
local pool_size =
local ok, err = red:set_keepalive(pool_max_idle_tme, pool_size)
if not ok then
ngx.say("set keepalive err : ", err)
end
end local ip_block_time= --封禁IP时间(秒)
local ip_time_out= --指定ip访问频率时间段(秒)
local ip_max_count= --指定ip访问频率计数最大值(秒)
local BUSINESS = ngx.var.business --nginx的location中定义的业务标识符 --连接redis
local redis = require "resty.redis"
local conn = redis:new()
ok, err = conn:connect("10.11.0.215", )
conn:set_timeout() --超时时间2秒 --如果连接失败,跳转到脚本结尾
if not ok then
--goto FLAG
close_redis(conn)
end local count, err = conn:get_reused_times()
if == count then ----新建连接,需要认证密码
ok, err = conn:auth("redis123")
if not ok then
ngx.say("failed to auth: ", err)
return
end
elseif err then ----从连接池中获取连接,无需再次认证密码
ngx.say("failed to get reused times: ", err)
return
end --查询ip是否被禁止访问,如果存在则返回403错误代码
is_block, err = conn:get(BUSINESS.."-BLOCK-"..ngx.var.remote_addr)
if is_block == '' then
ngx.exit()
close_redis(conn)
end --查询redis中保存的ip的计数器
ip_count, err = conn:get(BUSINESS.."-COUNT-"..ngx.var.remote_addr) if ip_count == ngx.null then --如果不存在,则将该IP存入redis,并将计数器设置为1、该KEY的超时时间为ip_time_out
res, err = conn:set(BUSINESS.."-COUNT-"..ngx.var.remote_addr, )
res, err = conn:expire(BUSINESS.."-COUNT-"..ngx.var.remote_addr, ip_time_out)
else
ip_count = ip_count + --存在则将单位时间内的访问次数加1 if ip_count >= ip_max_count then --如果超过单位时间限制的访问次数,则添加限制访问标识,限制时间为ip_block_time
res, err = conn:set(BUSINESS.."-BLOCK-"..ngx.var.remote_addr, )
res, err = conn:expire(BUSINESS.."-BLOCK-"..ngx.var.remote_addr, ip_block_time)
else
res, err = conn:set(BUSINESS.."-COUNT-"..ngx.var.remote_addr,ip_count)
res, err = conn:expire(BUSINESS.."-COUNT-"..ngx.var.remote_addr, ip_time_out)
end
end -- 结束标记
local ok, err = conn:close()
# redis的数据
10.11.0.215:6379> get USER-COUNT-10.11.0.148
"16"
10.11.0.215:6379> get USER-BLOCK-10.11.0.148
(nil)
四、总结 以上,便是 Nginx+Lua+Redis 实现的 IP 黑名单功能,具有如下优点: 1、配置简单、轻量,几乎对服务器性能不产生影响; 2、多台服务器可以通过Redis实例共享黑名单; 3、动态配置,可以手工或者通过某种自动化的方式设置 Redis 中的黑名单。
openresty开发系列38--通过Lua+Redis 实现动态封禁IP的更多相关文章
- Nginx 通过 Lua + Redis 实现动态封禁 IP
一.背景 为了封禁某些爬虫或者恶意用户对服务器的请求,我们需要建立一个动态的 IP 黑名单.对于黑名单之内的 IP ,拒绝提供服务. 二.架构 实现 IP 黑名单的功能有很多途径: 1.在操作系统层面 ...
- openresty开发系列27--openresty中封装redis操作
openresty开发系列27--openresty中封装redis操作 在关于web+lua+openresty开发中,项目中会大量操作redis, 重复创建连接-->数据操作-->关闭 ...
- openresty开发系列26--openresty中使用redis模块
openresty开发系列26--openresty中使用redis模块 在一些高并发的场景中,我们常常会用到缓存技术,现在我们常用的分布式缓存redis是最知名的, 操作redis,我们需要引入re ...
- openresty开发系列24--openresty中lua的引入及使用
openresty开发系列24--openresty中lua的引入及使用 openresty 引入 lua 一)openresty中nginx引入lua方式 1)xxx_by_lua ---> ...
- openresty开发系列40--nginx+lua实现获取客户端ip所在的国家信息
openresty开发系列40--nginx+lua实现获取客户端ip所在的国家信息 为了实现业务系统针对不同地区IP访问,展示包含不同地区信息的业务交互界面.很多情况下系统需要根据用户访问的IP信息 ...
- openresty开发系列37--nginx-lua-redis实现访问频率控制
openresty开发系列37--nginx-lua-redis实现访问频率控制 一)需求背景 在高并发场景下为了防止某个访问ip访问的频率过高,有时候会需要控制用户的访问频次在openresty中, ...
- openresty开发系列28--openresty中操作mysql
openresty开发系列28--openresty中操作mysql Mysql客户端 应用中最常使用的就是数据库了,尤其mysql数据库,那openresty lua如何操作mysql呢? ...
- openresty开发系列10--openresty的简单介绍及安装
openresty开发系列10--openresty的简单介绍及安装 一.Nginx优点 十几年前,互联网没有这么火,软件外包开发,信息化建设,帮助企业做无纸化办公,收银系统,工厂erp,c/s架构偏 ...
- openresty开发系列36--openresty执行流程之6日志模块处理阶段
openresty开发系列36--openresty执行流程之6日志模块处理阶段 一)header_filter_by_lua 语法:header_filter_by_lua <lua-scri ...
随机推荐
- Python 软件安装
安装Python解释器 Python目前已支持所有主流操作系统,在Linux,Unix,Mac系统上自带Python环境,在Windows系统上需要安装一下,超简单 打开官网https://www.p ...
- BZOJ2523/LOJ2646 聪明的学生
BZOJ2523/LOJ2646 聪明的学生 第一道CTSC的题. 因为是思维题,所以思路就不写了.直接看代码吧. #include<bits/stdc++.h> #define M 30 ...
- The Tower(HDU6559+2018年吉林站+数学)
题目链接 传送门 题意 告诉你圆锥的底部圆的半径和圆锥的高,再给你一个点的坐标及其运动向量,问你这个点什么时候会与这个圆锥相撞. 思路 比赛场上二分一直没过但是有人二分过了,今天再写这题想再试下二分, ...
- python笔记36-装饰器之wraps
前言 前面一篇对python装饰器有了初步的了解了,但是还不够完美,领导看了后又提出了新的需求,希望运行的日志能显示出具体运行的哪个函数. __name__和doc __name__用于获取函数的名称 ...
- 51nod 1115 最大M子段和 V3
环形最大M子段和,N个整数组成的序列排成一个环,a[1],a[2],a[3],…,a[n](a[n-1], a[n], a[1]也可以算作1段),将这N个数划分为互不相交的M个子段,并且这M个子段的和 ...
- word2vec中的subsampling
http://d0evi1.com/word2vec-subsampling/ 为了度量这种罕见词与高频词间存在不平衡现象,我们使用一个简单的subsampling方法:训练集中的每个词wiwi,以下 ...
- Python爬虫爬企查查数据
因为制作B2b网站需要,需要入库企业信息数据.所以目光锁定企查查数据,废话不多说,开干! #-*- coding-8 -*- import requests import lxml import sy ...
- javascript Object and new object() object --构造函数
- c#3.0 Lambda 表达式
使用c# 2.0 中的匿名方法查找“内部包含abc子串的所有字符串”: list.FindAll( delegate(string s) { renturn s.indexof("abc&q ...
- Linux安装部署项目实例
本次安装jdk,mysql,maven,redis,nginx,tomcat 安装之前先升级系统 使用命令:/bin/yum - y update 1.安装jdk 先建立一个项目的目录-jiaoton ...