多模态对比语言图像预训练CLIP:打破语言与视觉的界限
多模态对比语言图像预训练CLIP:打破语言与视觉的界限
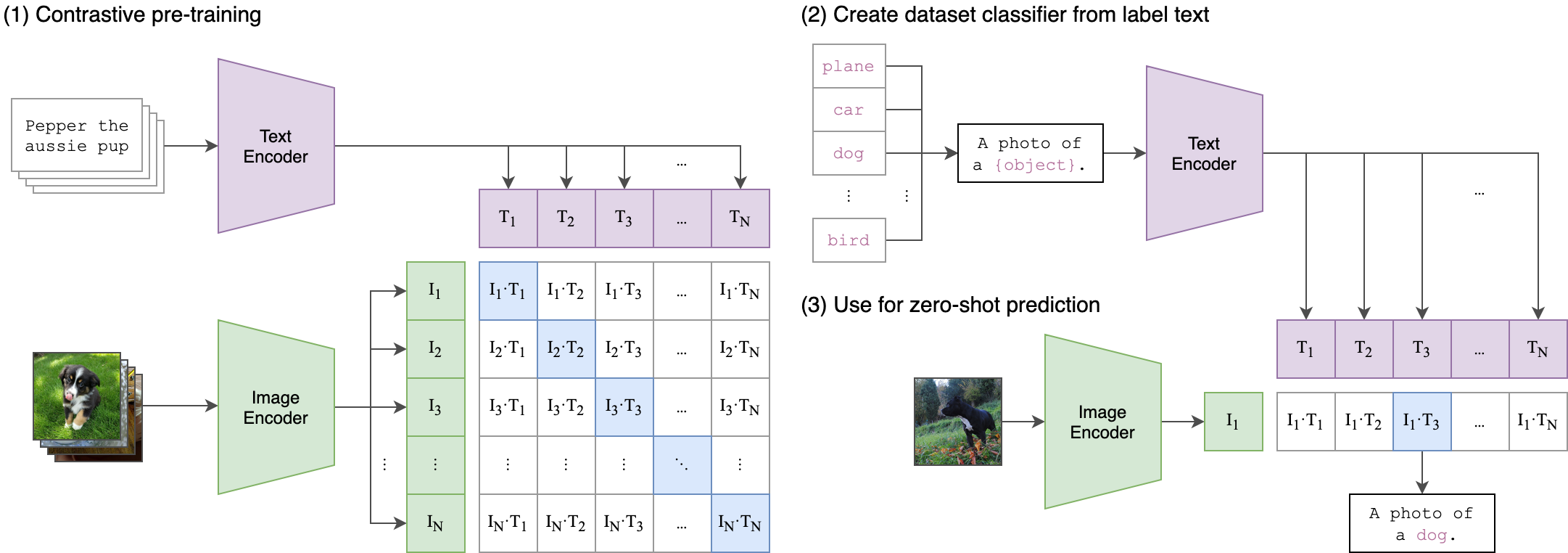
一种基于多模态(图像、文本)对比训练的神经网络。它可以在给定图像的情况下,使用自然语言来预测最相关的文本片段,而无需为特定任务进行优化。CLIP的设计类似于GPT-2和GPT-3,具备出色的零射击能力,可以应用于多种多模态任务。
多模态对比语言图像预训练(CLIP)是一种神经网络模型,它通过多模态对比训练来学习图像和文本之间的关联。与传统的单模态预训练模型不同,CLIP能够同时处理图像和文本,从而更好地理解它们之间的语义关系。
CLIP的设计类似于GPT-2和GPT-3,是一种自回归语言模型。它通过对比学习来学习图像和文本之间的映射关系。在训练过程中,CLIP会接收一张图像和一个与之相关的文本片段,并学习如何将这两个模态的信息进行关联。通过这种方式,CLIP可以学会将图像与相应的文本片段进行匹配,从而在给定图像的情况下,使用自然语言来预测最相关的文本片段。
由于CLIP采用了对比学习的方法,它可以在无需为特定任务进行优化的前提下,表现出色地完成多种多模态任务。这使得CLIP成为了一种通用的多模态预训练模型,可以广泛应用于图像标注、视觉问答、图像生成等领域。
CLIP(对比语言图像预训练)是一种基于多种(图像、文本)对进行训练的神经网络。在给定图像的情况下,它可以用自然语言来预测最相关的文本片段,而无需直接针对任务进行优化,类似于GPT-2和gpt - 3的零射击能力。我们发现CLIP在不使用任何原始的1.28M标记示例的情况下,在ImageNet“零射击”上匹配原始ResNet50的性能,克服了计算机视觉中的几个主要挑战。
1.安装
ftfy
regex
tqdm
torch
torchvision
$ conda install --yes -c pytorch pytorch=1.7.1 torchvision cudatoolkit=11.0
$ pip install ftfy regex tqdm
$ pip install git+https://github.com/openai/CLIP.git
Replace cudatoolkit=11.0 above with the appropriate CUDA version on your machine or cpuonly when installing on a machine without a GPU.
import torch
import clip
from PIL import Image
device = "cuda" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu"
model, preprocess = clip.load("ViT-B/32", device=device)
image = preprocess(Image.open("CLIP.png")).unsqueeze(0).to(device)
text = clip.tokenize(["a diagram", "a dog", "a cat"]).to(device)
with torch.no_grad():
image_features = model.encode_image(image)
text_features = model.encode_text(text)
logits_per_image, logits_per_text = model(image, text)
probs = logits_per_image.softmax(dim=-1).cpu().numpy()
print("Label probs:", probs) # prints: [[0.9927937 0.00421068 0.00299572]]
- API
The CLIP module clip provides the following methods:
clip.available_models()
Returns the names of the available CLIP models.
clip.load(name, device=..., jit=False)
返回模型和模型所需的TorchVision转换,由' clip.available_models() '返回的模型名指定。它将根据需要下载模型。' name '参数也可以是本地检查点的路径。
可以选择性地指定运行模型的设备,默认是使用第一个CUDA设备(如果有的话),否则使用CPU。当' jit '为' False '时,将加载模型的非jit版本。
clip.tokenize(text: Union[str, List[str]], context_length=77)
返回一个LongTensor,其中包含给定文本输入的标记化序列。这可以用作模型的输入
' clip.load() '返回的模型支持以下方法:
model.encode_image(image: Tensor)
给定一批图像,返回由CLIP模型的视觉部分编码的图像特征。
model.encode_text(text: Tensor)
给定一批文本tokens,返回由CLIP模型的语言部分编码的文本特征。
model(image: Tensor, text: Tensor)
给定一批图像和一批文本标记,返回两个张量,包含对应于每个图像和文本输入的logit分数。其值是对应图像和文本特征之间的相似度的余弦值,乘以100。
2.案例介绍
2.1 零样本能力
下面的代码使用CLIP执行零样本预测,如本文附录B所示。本例从CIFAR-100数据集获取图像,并在数据集的100个文本标签中预测最可能的标签。
import os
import clip
import torch
from torchvision.datasets import CIFAR100
#Load the model
device = "cuda" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu"
model, preprocess = clip.load('ViT-B/32', device)
#Download the dataset
cifar100 = CIFAR100(root=os.path.expanduser("~/.cache"), download=True, train=False)
#Prepare the inputs
image, class_id = cifar100[3637]
image_input = preprocess(image).unsqueeze(0).to(device)
text_inputs = torch.cat([clip.tokenize(f"a photo of a {c}") for c in cifar100.classes]).to(device)
#Calculate features
with torch.no_grad():
image_features = model.encode_image(image_input)
text_features = model.encode_text(text_inputs)
#Pick the top 5 most similar labels for the image
image_features /= image_features.norm(dim=-1, keepdim=True)
text_features /= text_features.norm(dim=-1, keepdim=True)
similarity = (100.0 * image_features @ text_features.T).softmax(dim=-1)
values, indices = similarity[0].topk(5)
#Print the result
print("\nTop predictions:\n")
for value, index in zip(values, indices):
print(f"{cifar100.classes[index]:>16s}: {100 * value.item():.2f}%")
输出将如下所示(具体数字可能因计算设备的不同而略有不同):
Top predictions:
snake: 65.31%
turtle: 12.29%
sweet_pepper: 3.83%
lizard: 1.88%
crocodile: 1.75%
Note that this example uses the encode_image() and encode_text() methods that return the encoded features of given inputs.
2.2 Linear-probe 评估
The example below uses scikit-learn to perform logistic regression on image features.
import os
import clip
import torch
import numpy as np
from sklearn.linear_model import LogisticRegression
from torch.utils.data import DataLoader
from torchvision.datasets import CIFAR100
from tqdm import tqdm
#Load the model
device = "cuda" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu"
model, preprocess = clip.load('ViT-B/32', device)
#Load the dataset
root = os.path.expanduser("~/.cache")
train = CIFAR100(root, download=True, train=True, transform=preprocess)
test = CIFAR100(root, download=True, train=False, transform=preprocess)
def get_features(dataset):
all_features = []
all_labels = []
with torch.no_grad():
for images, labels in tqdm(DataLoader(dataset, batch_size=100)):
features = model.encode_image(images.to(device))
all_features.append(features)
all_labels.append(labels)
return torch.cat(all_features).cpu().numpy(), torch.cat(all_labels).cpu().numpy()
#Calculate the image features
train_features, train_labels = get_features(train)
test_features, test_labels = get_features(test)
#Perform logistic regression
classifier = LogisticRegression(random_state=0, C=0.316, max_iter=1000, verbose=1)
classifier.fit(train_features, train_labels)
#Evaluate using the logistic regression classifier
predictions = classifier.predict(test_features)
accuracy = np.mean((test_labels == predictions).astype(float)) * 100.
print(f"Accuracy = {accuracy:.3f}")
Note that the C value should be determined via a hyperparameter sweep using a validation split.
3.更多资料参考:
- OpenCLIP: includes larger and independently trained CLIP models up to ViT-G/14
- Hugging Face implementation of CLIP: for easier integration with the HF ecosystem
更多优质内容请关注公号:汀丶人工智能;会提供一些相关的资源和优质文章,免费获取阅读。
多模态对比语言图像预训练CLIP:打破语言与视觉的界限的更多相关文章
- 预训练语言模型的前世今生 - 从Word Embedding到BERT
预训练语言模型的前世今生 - 从Word Embedding到BERT 本篇文章共 24619 个词,一个字一个字手码的不容易,转载请标明出处:预训练语言模型的前世今生 - 从Word Embeddi ...
- 【中文版 | 论文原文】BERT:语言理解的深度双向变换器预训练
BERT:Pre-training of Deep Bidirectional Transformers for Language Understanding 谷歌AI语言组论文<BERT:语言 ...
- 预训练中Word2vec,ELMO,GPT与BERT对比
预训练 先在某个任务(训练集A或者B)进行预先训练,即先在这个任务(训练集A或者B)学习网络参数,然后存起来以备后用.当我们在面临第三个任务时,网络可以采取相同的结构,在较浅的几层,网络参数可以直接加 ...
- CNN基础二:使用预训练网络提取图像特征
上一节中,我们采用了一个自定义的网络结构,从头开始训练猫狗大战分类器,最终在使用图像增强的方式下得到了82%的验证准确率.但是,想要将深度学习应用于小型图像数据集,通常不会贸然采用复杂网络并且从头开始 ...
- 深度学习tensorflow实战笔记 用预训练好的VGG-16模型提取图像特征
1.首先就要下载模型结构 首先要做的就是下载训练好的模型结构和预训练好的模型,结构地址是:点击打开链接 模型结构如下: 文件test_vgg16.py可以用于提取特征.其中vgg16.npy是需要单独 ...
- 从Word Embedding到Bert模型—自然语言处理中的预训练技术发展史(转载)
转载 https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/49271699 首发于深度学习前沿笔记 写文章 从Word Embedding到Bert模型—自然语言处理中的预训练技术发展史 张 ...
- 预训练语言模型整理(ELMo/GPT/BERT...)
目录 简介 预训练任务简介 自回归语言模型 自编码语言模型 预训练模型的简介与对比 ELMo 细节 ELMo的下游使用 GPT/GPT2 GPT 细节 微调 GPT2 优缺点 BERT BERT的预训 ...
- 学习AI之NLP后对预训练语言模型——心得体会总结
一.学习NLP背景介绍: 从2019年4月份开始跟着华为云ModelArts实战营同学们一起进行了6期关于图像深度学习的学习,初步了解了关于图像标注.图像分类.物体检测,图像都目标物体检测等 ...
- zz从Word Embedding到Bert模型—自然语言处理中的预训练技术发展史
从Word Embedding到Bert模型—自然语言处理中的预训练技术发展史 Bert最近很火,应该是最近最火爆的AI进展,网上的评价很高,那么Bert值得这么高的评价吗?我个人判断是值得.那为什么 ...
- 第二十四节,TensorFlow下slim库函数的使用以及使用VGG网络进行预训练、迁移学习(附代码)
在介绍这一节之前,需要你对slim模型库有一些基本了解,具体可以参考第二十二节,TensorFlow中的图片分类模型库slim的使用.数据集处理,这一节我们会详细介绍slim模型库下面的一些函数的使用 ...
随机推荐
- 多图预警,DreamBooth 微调黑客松结果发布啦!
去年 12 月底,我们面向全球的开发者举办了 DreamBooth 编程马拉松活动.通过 DreamBooth,你可以使用少量的图像对文生图模型进行微调,将你「喂给」模型的图片信息进行命名,就可以通过 ...
- 机器人多目标包围问题(MECA)新算法:基于关系图深度强化学习
摘要:中科院自动化所蒲志强教授团队,提出一种基于关系图的深度强化学习方法,应用于多目标避碰包围问题(MECA),使用NOKOV度量动作捕捉系统获取多机器人位置信息,验证了方法的有效性和适应性.研究成果 ...
- RocketMQ事务消息在订单创建和库存扣减的使用
前言 下单的过程包括订单创建,还有库存的扣减,为提高系统的性能,将库存放在redis扣减,则会涉及到Mysql和redis之间的数据同步,其中,这个过程还涉及到,必须是订单创建成功才进行库存的扣减操作 ...
- websever
1 在浏览器键入url,按下回车会经历如下行为 浏览器向 DNS 服务器请求解析该 URL 中的域名所对应的 IP 地址; 解析出 IP 地址后,根据该 IP 地址和默认端口 80,和服务器建立 TC ...
- 解决延迟有 Wi-Fi 6 就够了!
最近二狗子家里的路由器坏了,而家里的数据网络信号又非常差,失去了路由器基本上就等于和世界隔离,所以二狗子打算去附近商城随便买一个新的路由器,结果售货员张口就问:"买 Wi-Fi 6 的路由器 ...
- 【JAVA基础】数值处理
#BigDecimal处理 ##保留两位小数 https://www.cnblogs.com/jpfss/p/8072379.html /** * 保留两位小数 */ @org.junit.Test ...
- signed main 和 int main 的区别
事实上只是因为有人直接 #define int long long 了...然后int main改成signed main就行了 #define int long long ... signed ma ...
- CompletableFuture 使用详解
CompletableFuture 使用详解 1. runAsync 和 supplyAsync方法 CompletableFuture 提供了四个静态方法来创建一个异步操作. public stat ...
- 版本升级 | v3.0.0卷起来了!多种特殊情况解析轻松拿捏!
在过往发行版的基础上,结合社区用户提供的大量反馈及研发小伙伴的积极探索,项目组对OpenSCA的解析引擎做了全方位的优化,v3.0.0版本正式发布啦~ 感谢所有用户的支持和信任~是很多人的一小步聚在一 ...
- rem在手机移动端app中的兼容适配问题
这是我之前一直使用的第一种rem方案.贴代码 1 <script> 2 // 适用于750的设计稿 3 var iScale = 1; 4 // 通过页面加载的时候去获取用户设备的物理像素 ...