Spring Cloud Gateway-自定义异常处理
前提
我们平时在用SpringMVC的时候,只要是经过DispatcherServlet处理的请求,可以通过@ControllerAdvice和@ExceptionHandler自定义不同类型异常的处理逻辑,具体可以参考ResponseEntityExceptionHandler和DefaultHandlerExceptionResolver,底层原理很简单,就是发生异常的时候搜索容器中已经存在的异常处理器并且匹配对应的异常类型,匹配成功之后使用该指定的异常处理器返回结果进行Response的渲染,如果找不到默认的异常处理器则用默认的进行兜底(个人认为,Spring在很多功能设计的时候都有这种“有则使用自定义,无则使用默认提供”这种思想十分优雅)。
SpringMVC中提供的自定义异常体系在Spring-WebFlux中并不适用,其实原因很简单,两者底层的运行容器并不相同。WebExceptionHandler是Spring-WebFlux的异常处理器顶层接口,因此追溯到子类可以追踪到DefaultErrorWebExceptionHandler是Spring Cloud Gateway的全局异常处理器,配置类是ErrorWebFluxAutoConfiguration。
为什么要自定义异常处理
先画一个假想但是贴近实际架构图,定位一下网关的作用:
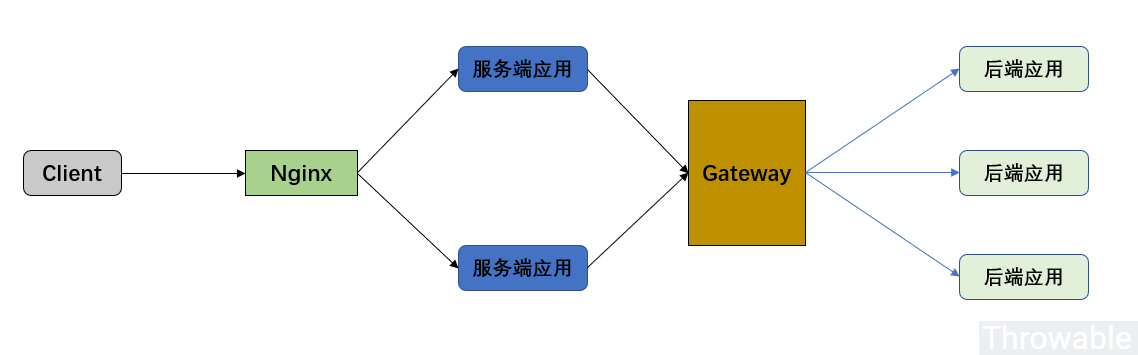
网关在整个架构中的作用是:
- 路由服务端应用的请求到后端应用。
- (聚合)后端应用的响应转发到服务端应用。
假设网关服务总是正常的前提下:
对于第1点来说,假设后端应用不能平滑无损上线,会有一定的几率出现网关路由请求到一些后端的“僵尸节点(请求路由过去的时候,应用更好在重启或者刚好停止)”,这个时候会路由会失败抛出异常,一般情况是Connection Refuse。
对于第2点来说,假设后端应用没有正确处理异常,那么应该会把异常信息经过网关转发回到服务端应用,这种情况理论上不会出现异常。
其实还有第3点隐藏的问题,网关如果不单单承担路由的功能,还包含了鉴权、限流等功能,如果这些功能开发的时候对异常捕获没有做完善的处理甚至是逻辑本身存在BUG,有可能导致异常没有被正常捕获处理,走了默认的异常处理器DefaultErrorWebExceptionHandler,默认的异常处理器的处理逻辑可能并不符合我们预期的结果。
如何自定义异常处理
我们可以先看默认的异常处理器的配置类ErrorWebFluxAutoConfiguration:
@Configuration
@ConditionalOnWebApplication(type = ConditionalOnWebApplication.Type.REACTIVE)
@ConditionalOnClass(WebFluxConfigurer.class)
@AutoConfigureBefore(WebFluxAutoConfiguration.class)
@EnableConfigurationProperties({ ServerProperties.class, ResourceProperties.class })
public class ErrorWebFluxAutoConfiguration {
private final ServerProperties serverProperties;
private final ApplicationContext applicationContext;
private final ResourceProperties resourceProperties;
private final List<ViewResolver> viewResolvers;
private final ServerCodecConfigurer serverCodecConfigurer;
public ErrorWebFluxAutoConfiguration(ServerProperties serverProperties,
ResourceProperties resourceProperties,
ObjectProvider<ViewResolver> viewResolversProvider,
ServerCodecConfigurer serverCodecConfigurer,
ApplicationContext applicationContext) {
this.serverProperties = serverProperties;
this.applicationContext = applicationContext;
this.resourceProperties = resourceProperties;
this.viewResolvers = viewResolversProvider.orderedStream()
.collect(Collectors.toList());
this.serverCodecConfigurer = serverCodecConfigurer;
}
@Bean
@ConditionalOnMissingBean(value = ErrorWebExceptionHandler.class,
search = SearchStrategy.CURRENT)
@Order(-1)
public ErrorWebExceptionHandler errorWebExceptionHandler(
ErrorAttributes errorAttributes) {
DefaultErrorWebExceptionHandler exceptionHandler = new DefaultErrorWebExceptionHandler(
errorAttributes, this.resourceProperties,
this.serverProperties.getError(), this.applicationContext);
exceptionHandler.setViewResolvers(this.viewResolvers);
exceptionHandler.setMessageWriters(this.serverCodecConfigurer.getWriters());
exceptionHandler.setMessageReaders(this.serverCodecConfigurer.getReaders());
return exceptionHandler;
}
@Bean
@ConditionalOnMissingBean(value = ErrorAttributes.class,
search = SearchStrategy.CURRENT)
public DefaultErrorAttributes errorAttributes() {
return new DefaultErrorAttributes(
this.serverProperties.getError().isIncludeException());
}
}
注意到两个Bean实例ErrorWebExceptionHandler和DefaultErrorAttributes都使用了@ConditionalOnMissingBean注解,也就是我们可以通过自定义实现去覆盖它们。先自定义一个CustomErrorWebFluxAutoConfiguration(除了ErrorWebExceptionHandler的自定义实现,其他直接拷贝ErrorWebFluxAutoConfiguration):
@Configuration
@ConditionalOnWebApplication(type = ConditionalOnWebApplication.Type.REACTIVE)
@ConditionalOnClass(WebFluxConfigurer.class)
@AutoConfigureBefore(WebFluxAutoConfiguration.class)
@EnableConfigurationProperties({ServerProperties.class, ResourceProperties.class})
public class CustomErrorWebFluxAutoConfiguration {
private final ServerProperties serverProperties;
private final ApplicationContext applicationContext;
private final ResourceProperties resourceProperties;
private final List<ViewResolver> viewResolvers;
private final ServerCodecConfigurer serverCodecConfigurer;
public CustomErrorWebFluxAutoConfiguration(ServerProperties serverProperties,
ResourceProperties resourceProperties,
ObjectProvider<ViewResolver> viewResolversProvider,
ServerCodecConfigurer serverCodecConfigurer,
ApplicationContext applicationContext) {
this.serverProperties = serverProperties;
this.applicationContext = applicationContext;
this.resourceProperties = resourceProperties;
this.viewResolvers = viewResolversProvider.orderedStream()
.collect(Collectors.toList());
this.serverCodecConfigurer = serverCodecConfigurer;
}
@Bean
@ConditionalOnMissingBean(value = ErrorWebExceptionHandler.class,
search = SearchStrategy.CURRENT)
@Order(-1)
public ErrorWebExceptionHandler errorWebExceptionHandler(ErrorAttributes errorAttributes) {
// TODO 这里完成自定义ErrorWebExceptionHandler实现逻辑
return null;
}
@Bean
@ConditionalOnMissingBean(value = ErrorAttributes.class, search = SearchStrategy.CURRENT)
public DefaultErrorAttributes errorAttributes() {
return new DefaultErrorAttributes(this.serverProperties.getError().isIncludeException());
}
}
ErrorWebExceptionHandler的实现,可以直接参考DefaultErrorWebExceptionHandler,甚至直接继承DefaultErrorWebExceptionHandler,覆盖对应的方法即可。这里直接把异常信息封装成下面格式的Response返回,最后需要渲染成JSON格式:
{
"code": 200,
"message": "描述信息",
"path" : "请求路径",
"method": "请求方法"
}
我们需要分析一下DefaultErrorWebExceptionHandler中的一些源码:
// 封装异常属性
protected Map<String, Object> getErrorAttributes(ServerRequest request, boolean includeStackTrace) {
return this.errorAttributes.getErrorAttributes(request, includeStackTrace);
}
// 渲染异常Response
protected Mono<ServerResponse> renderErrorResponse(ServerRequest request) {
boolean includeStackTrace = isIncludeStackTrace(request, MediaType.ALL);
Map<String, Object> error = getErrorAttributes(request, includeStackTrace);
return ServerResponse.status(getHttpStatus(error))
.contentType(MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON_UTF8)
.body(BodyInserters.fromObject(error));
}
// 返回路由方法基于ServerResponse的对象
@Override
protected RouterFunction<ServerResponse> getRoutingFunction(ErrorAttributes errorAttributes) {
return route(acceptsTextHtml(), this::renderErrorView).andRoute(all(), this::renderErrorResponse);
}
// HTTP响应状态码的封装,原来是基于异常属性的status属性进行解析的
protected HttpStatus getHttpStatus(Map<String, Object> errorAttributes) {
int statusCode = (int) errorAttributes.get("status");
return HttpStatus.valueOf(statusCode);
}
确定三点:
- 最后封装到响应体的对象来源于
DefaultErrorWebExceptionHandler#getErrorAttributes(),并且结果是一个Map<String, Object>实例转换成的字节序列。 - 原来的
RouterFunction实现只支持HTML格式返回,我们需要修改为JSON格式返回(或者说支持所有格式返回)。 DefaultErrorWebExceptionHandler#getHttpStatus()是响应状态码的封装,原来的逻辑是基于异常属性getErrorAttributes()的status属性进行解析的。
自定义的JsonErrorWebExceptionHandler如下:
public class JsonErrorWebExceptionHandler extends DefaultErrorWebExceptionHandler {
public JsonErrorWebExceptionHandler(ErrorAttributes errorAttributes,
ResourceProperties resourceProperties,
ErrorProperties errorProperties,
ApplicationContext applicationContext) {
super(errorAttributes, resourceProperties, errorProperties, applicationContext);
}
@Override
protected Map<String, Object> getErrorAttributes(ServerRequest request, boolean includeStackTrace) {
// 这里其实可以根据异常类型进行定制化逻辑
Throwable error = super.getError(request);
Map<String, Object> errorAttributes = new HashMap<>(8);
errorAttributes.put("message", error.getMessage());
errorAttributes.put("code", HttpStatus.INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR.value());
errorAttributes.put("method", request.methodName());
errorAttributes.put("path", request.path());
return errorAttributes;
}
@Override
protected RouterFunction<ServerResponse> getRoutingFunction(ErrorAttributes errorAttributes) {
return RouterFunctions.route(RequestPredicates.all(), this::renderErrorResponse);
}
@Override
protected HttpStatus getHttpStatus(Map<String, Object> errorAttributes) {
// 这里其实可以根据errorAttributes里面的属性定制HTTP响应码
return HttpStatus.INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR;
}
}
配置类CustomErrorWebFluxAutoConfiguration添加JsonErrorWebExceptionHandler:
@Bean
@ConditionalOnMissingBean(value = ErrorWebExceptionHandler.class, search = SearchStrategy.CURRENT)
@Order(-1)
public ErrorWebExceptionHandler errorWebExceptionHandler(ErrorAttributes errorAttributes) {
JsonErrorWebExceptionHandler exceptionHandler = new JsonErrorWebExceptionHandler(
errorAttributes,
resourceProperties,
this.serverProperties.getError(),
applicationContext);
exceptionHandler.setViewResolvers(this.viewResolvers);
exceptionHandler.setMessageWriters(this.serverCodecConfigurer.getWriters());
exceptionHandler.setMessageReaders(this.serverCodecConfigurer.getReaders());
return exceptionHandler;
}
很简单,这里把异常的HTTP响应状态码统一为HttpStatus.INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR(500),改造的东西并不多,只要了解原来异常处理的上下文逻辑即可。
测试
测试场景一:只启动网关,下游服务不启动的情况下直接调用下游服务:
curl http://localhost:9090/order/host
// 响应结果
{"path":"/order/host","code":500,"message":"Connection refused: no further information: localhost/127.0.0.1:9091","method":"GET"}
测试场景二:下游服务正常启动和调用,网关自身抛出异常。
在网关应用自定义一个全局过滤器并且故意抛出异常:
@Component
public class ErrorGlobalFilter implements GlobalFilter {
@Override
public Mono<Void> filter(ServerWebExchange exchange, GatewayFilterChain chain) {
int i = 1/0;
return chain.filter(exchange);
}
}
curl http://localhost:9090/order/host
// 响应结果
{"path":"/order/host","code":500,"message":"/ by zero","method":"GET"}
响应结果和定制的逻辑一致,并且后台的日志也打印了对应的异常堆栈。
小结
笔者一直认为,做异常分类和按照分类处理是工程里面十分重要的一环。笔者在所在公司负责的系统中,坚持实现异常分类捕获,主要是需要区分可以重试补偿以及无法重试需要及时预警的异常,这样子才能针对可恢复异常定制自愈逻辑,对不能恢复的异常及时预警和人为介入。所以,Spring Cloud Gateway这个技术栈也必须调研其自定义异常的处理逻辑。
原文链接
- GitHub Page:http://www.throwable.club/2019/05/11/spring-cloud-gateway-custom-exception-handler
- Coding Page:http://throwable.coding.me/2019/05/11/spring-cloud-gateway-custom-exception-handler
(本文完 c-1-d e-a-20190511)
Spring Cloud Gateway-自定义异常处理的更多相关文章
- Spring Cloud Gateway自定义异常处理Exception Handler
版本: Spring Cloud 2020.0.3 常见的方法有 实现自己的 DefaultErrorWebExceptionHandler 或 仅实现ErrorAttributes. 方法1: Er ...
- spring cloud gateway自定义过滤器
在API网关spring cloud gateway和负载均衡框架ribbon实战文章中,主要实现网关与负载均衡等基本功能,详见代码.本节内容将继续围绕此代码展开,主要讲解spring cloud g ...
- Spring Cloud Gateway中异常处理
最近我们的项目在考虑使用Gateway,考虑使用Spring Cloud Gateway,发现网关的异常处理和spring boot 单体应用异常处理还是有很大区别的.让我们来回顾一下异常. 关于异常 ...
- Spring Cloud Alibaba学习笔记(21) - Spring Cloud Gateway 自定义全局过滤器
在前文中,我们介绍了Spring Cloud Gateway内置了一系列的全局过滤器,本文介绍如何自定义全局过滤器. 自定义全局过滤需要实现GlobalFilter 接口,该接口和 GatewayFi ...
- Spring Cloud Alibaba学习笔记(19) - Spring Cloud Gateway 自定义过滤器工厂
在前文中,我们介绍了Spring Cloud Gateway内置了一系列的内置过滤器工厂,若Spring Cloud Gateway内置的过滤器工厂无法满足我们的业务需求,那么此时就需要自定义自己的过 ...
- Spring Cloud Alibaba学习笔记(17) - Spring Cloud Gateway 自定义路由谓词工厂
在前文中,我们介绍了Spring Cloud Gateway内置了一系列的路由谓词工厂,但是如果这些内置的路由谓词工厂不能满足业务需求的话,我们可以自定义路由谓词工厂来实现特定的需求. 例如有某个服务 ...
- Spring cloud gateway自定义filter以及负载均衡
自定义全局filter package com.example.demo; import java.nio.charset.StandardCharsets; import org.apache.co ...
- spring cloud gateway 自定义GatewayFilterFactory
spring cloud gateway提供了很多内置的过滤器,那么因为需求的关系,需要自定义实现,并且要可配置,在一番折腾之后,总算是解决了,那么久记录下来 对于自定义的factory,我们可以选择 ...
- Spring Cloud Gateway自定义过滤器实战(观测断路器状态变化)
欢迎访问我的GitHub https://github.com/zq2599/blog_demos 内容:所有原创文章分类汇总及配套源码,涉及Java.Docker.Kubernetes.DevOPS ...
- 微服务网关实战——Spring Cloud Gateway
导读 作为Netflix Zuul的替代者,Spring Cloud Gateway是一款非常实用的微服务网关,在Spring Cloud微服务架构体系中发挥非常大的作用.本文对Spring Clou ...
随机推荐
- 编译出错:must be index or base register
指令 mov ds:[dx],dx 原因:上述指令使用寄存器相对寻址方式,只能使用BX,BP,SI,DI 方括号里必须是变址(index,指SI, DI)或基址(base,指BX, BP)寄存器 正确 ...
- [译]Vulkan教程(22)创建顶点buffer
[译]Vulkan教程(22)创建顶点buffer Vertex buffer creation 创建顶点buffer Introduction 入门 Buffers in Vulkan are re ...
- IDEA生成可执行的jar文件
场景 用IDEA开发一个Java控制台程序,项目完成后,打包给客户使用. 做法 首先用IDEA打开要生成jar的项目,打开后选择File->Project Structure... 选择Arti ...
- python del和垃圾回收
1. del是删除对象 2. python中的垃圾回收是删除引用计数
- 常用类-excel转csv
public class ExcelFileHelper { public static bool SaveAsCsv(string excelFilePath, string destination ...
- 【H5最强攻略】百度人脸情绪实时识别
最近看的各位大佬都在体验百度大脑2019年全新上线的24项AI能力! (我也按耐不住了,赶紧走一波- 哈哈) 接下来要介绍的就是H5端的人脸检测攻略. 附带详细的介绍,代码,以及演示体验等 欢迎提出各 ...
- Data Management Technology(1) -- Introduction
1.Database concepts (1)Data & Information Information Is any kind of event that affects the stat ...
- Redis专题——Redis管理工具
一.安全性 1.运行环境 Redis以简洁为美,其安全性没有太多操作,要求在生产系统中外界不能直接连接Redis进行操作,而必须经过程序中转后,由程序进行操作. 即,redis要求运行在可信的环境中. ...
- Python3+Requests+Excel完整接口自动化框架
框架整体使用Python3+Requests+Excel:包含对实时token的获取 框架结构图 1.------base -------runmethond.py runmethond:对不同的请求 ...
- java8-02-再探Lambda表达式
Lambda表达式 主要作用替代匿名内部类 达到简化代码的操作 Lambda表达式 在对象中的使用 Employee类
