Spring boot 官网学习笔记 - logging
- commons-logging和slf4j是java中的日志门面,即它们提供了一套通用的接口,具体的实现可以由开发者自由选择。log4j和logback则是具体的日志实现方案。
- 比较常用的搭配是commons-logging+log4j,slf4j+logback
为什么要用SLF4J+Logback 替换commons-logging+log4j?
- SLF4J是编译时绑定到具体的日志框架,性能优于采用运行时搜寻的方式的commons-logging
- 不需要使用logger.isDebugEnabled()来解决日志因为字符拼接产生的性能问题
logger.info("my name is {}", "medusar");
logger.info("my name is " + "medusar");-
在效率上,第一行比第二行更高,因为如果当前日志级别是ERROR,第一行不会进行字符串拼接,而第二行,无论日志级别是什么,都会先进行字符串拼接。
- 所以为了解决这个问题,commons-logging等框架提供了下面的方式:
if (log.isDebugEnabled()){
log.debug("dddd"+"eee");
}
- 基于commons-logging的日志使用
import org.apache.commons.logging.Log;
import org.apache.commons.logging.LogFactory;
public class XXXService {
private static final Log log = LogFactory.getLog(XXXService.class);
public void doSomething(){
log.info("begin dosomething....");
}
}
基于slf4j的日志使用
import org.slf4j.Logger;
import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory;
public class XXXService {
private static final Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(XXXService.class);
public void doSomething() {
logger.info("begin dosomething...");
}
}
- SpringBoot底层也是使用slf4j+logback的方式进行日志记录;
- SpringBoot也把其他的日志都替换成了slf4j;
- Spring Boot能自动适配所有的日志,而且底层使用slf4j+logback的方式记录日志,引入其他框架的时候,只需要把这个框架依赖的日志框架排除掉。
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-core</artifactId>
<exclusions>
<exclusion>
<groupId>commons-logging</groupId>
<artifactId>commons-logging</artifactId>
</exclusion>
</exclusions>
</dependency>- 以后开发的时候,日志记录方法的调用,不应该直接调用日志的实现类,而是调用日志抽象层里面的方法;给系统里面导入slf4j的jar和logback的实现jar
import org.slf4j.Logger;
import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory;
public class HelloWorld {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(HelloWorld.class);
logger.info("Hello World"); }
}
指定文件中日志输出的格式# 在控制台输出的日志格式 logging.pattern.console=%d{yyyy-MM-dd} [%thread] %-5level %logger{} - %msg%n
# 指定文件中日志输出的格式 logging.pattern.file=%d{yyyy-MM-dd} === [%thread] === %-5level === %logger{} === - %msg%n- <!-- 日志输出格式:
- %d表示日期时间,
- %thread表示线程名,
- %-5level:级别从左显示5个字符宽度
- %logger{50} 表示logger名字最长50个字符,否则按照句点分割。
- %msg:日志消息,
- %n是换行符-->
切换日志框架(无意义,slf4j+logback已经是最佳实现)
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
<!--排除转换包-->
<exclusions>
<exclusion>
<artifactId>logback-classic</artifactId>
<groupId>ch.qos.logback</groupId>
</exclusion>
<exclusion>
<artifactId>log4j-over-slf4j</artifactId>
<groupId>org.slf4j</groupId> </exclusion>
</exclusions>
</dependency>
<!--添加slf4j依赖-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.slf4j</groupId>
<artifactId>slf4j-log4j12</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
- 调整日志级别
- Log Level:
ERROR,WARN,INFO,DEBUG, orTRACE. - Logback does not have a
FATALlevel. It is mapped toERROR. - The default log configuration echoes messages to the console as they are written. By default,
ERROR-level,WARN-level, andINFO-level messages are logged. You can also enable a “debug” mode by starting your application with a--debugflag. $ java -jar myapp.jar --debug
- Alternatively, you can enable a “trace” mode by starting your application with a
--traceflag (ortrace=truein yourapplication.properties). All the supported logging systems can have the logger levels set in the Spring
Environment(for example, inapplication.properties) by usinglogging.level.<logger-name>=<level>wherelevelis one of TRACE, DEBUG, INFO, WARN, ERROR, FATAL, or OFF. Therootlogger can be configured by usinglogging.level.root.The following example shows potential logging settings in
application.properties:logging.level.root=WARN
logging.level.org.springframework.web=DEBUG
logging.level.org.hibernate=ERROR
- Log Level:
- 日志文件
- By default, Spring Boot logs only to the console and does not write log files. If you want to write log files in addition to the console output, you need to set a
logging.fileorlogging.pathproperty (for example, in yourapplication.properties). - Log files rotate when they reach 10 MB and, as with console output,
ERROR-level,WARN-level, andINFO-level messages are logged by default. Size limits can be changed using thelogging.file.max-sizeproperty. Previously rotated files are archived indefinitely unless thelogging.file.max-historyproperty has been set. - Logging properties are independent of the actual logging infrastructure. As a result, specific configuration keys (such as
logback.configurationFilefor Logback) are not managed by spring Boot. 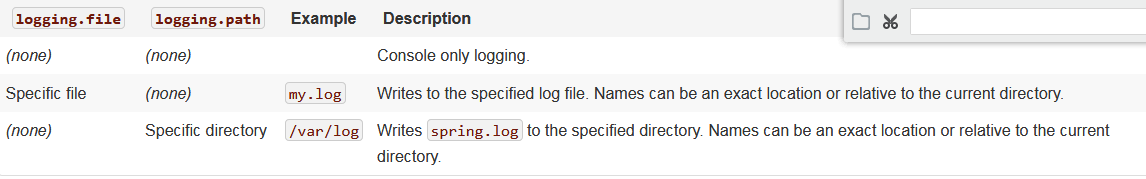
- By default, Spring Boot logs only to the console and does not write log files. If you want to write log files in addition to the console output, you need to set a
Log Groups
It’s often useful to be able to group related loggers together so that they can all be configured at the same time. For example, you might commonly change the logging levels for all Tomcat related loggers, but you can’t easily remember top level packages.
To help with this, Spring Boot allows you to define logging groups in your Spring
Environment. For example, here’s how you could define a “tomcat” group by adding it to yourapplication.properties:logging.group.tomcat=org.apache.catalina, org.apache.coyote, org.apache.tomcat
Once defined, you can change the level for all the loggers in the group with a single line:
logging.level.tomcat=TRACE
Spring Boot includes the following pre-defined logging groups that can be used out-of-the-box:
Name Loggers web
org.springframework.core.codec,org.springframework.http,org.springframework.websql
org.springframework.jdbc.core,org.hibernate.SQL
Custom Log Configuration
- The various logging systems can be activated by including the appropriate libraries on the classpath and can be further customized by providing a suitable configuration file in the root of the classpath or in a location specified by the following Spring
Environmentproperty:logging.config. - Since logging is initialized before the
ApplicationContextis created, it is not possible to control logging from@PropertySourcesin Spring@Configurationfiles. The only way to change the logging system or disable it entirely is via System properties. - Depending on your logging system, the following files are loaded:
Logging System Customization Logback
logback-spring.xml,logback-spring.groovy,logback.xml, orlogback.groovyLog4j2
log4j2-spring.xmlorlog4j2.xmlJDK (Java Util Logging)
logging.properties- When possible, we recommend that you use the
-springvariants for your logging configuration (for example,logback-spring.xmlrather thanlogback.xml). If you use standard configuration locations, Spring cannot completely control log initialization. To help with the customization, some other properties are transferred from the Spring
Environmentto System properties, as described in the following table:Spring Environment System Property Comments logging.exception-conversion-wordLOG_EXCEPTION_CONVERSION_WORDThe conversion word used when logging exceptions.
logging.fileLOG_FILEIf defined, it is used in the default log configuration.
logging.file.max-sizeLOG_FILE_MAX_SIZEMaximum log file size (if LOG_FILE enabled). (Only supported with the default Logback setup.)
logging.file.max-historyLOG_FILE_MAX_HISTORYMaximum number of archive log files to keep (if LOG_FILE enabled). (Only supported with the default Logback setup.)
logging.pathLOG_PATHIf defined, it is used in the default log configuration.
logging.pattern.consoleCONSOLE_LOG_PATTERNThe log pattern to use on the console (stdout). (Only supported with the default Logback setup.)
logging.pattern.dateformatLOG_DATEFORMAT_PATTERNAppender pattern for log date format. (Only supported with the default Logback setup.)
logging.pattern.fileFILE_LOG_PATTERNThe log pattern to use in a file (if
LOG_FILEis enabled). (Only supported with the default Logback setup.)logging.pattern.levelLOG_LEVEL_PATTERNThe format to use when rendering the log level (default
%5p). (Only supported with the default Logback setup.)PIDPIDThe current process ID (discovered if possible and when not already defined as an OS environment variable).
- The various logging systems can be activated by including the appropriate libraries on the classpath and can be further customized by providing a suitable configuration file in the root of the classpath or in a location specified by the following Spring
- xx
Spring boot 官网学习笔记 - logging的更多相关文章
- Spring boot 官网学习笔记 - Spring Boot 属性配置和使用(转)-application.properties
Spring Boot uses a very particular PropertySource order that is designed to allow sensible overridin ...
- Spring boot 官网学习笔记 - Spring DevTools 介绍
想要使用devtools支持,只需使用dependencies将模块依赖关系添加到你的构建中 运行打包的应用程序时,开发人员工具会自动禁用.如果你通过 java -jar或者其他特殊的类加载器进行启动 ...
- Spring boot 官网学习笔记 - Auto-configuration(@SpringBootApplication、@EnableAutoConfiguration、@Configuration)
Spring Boot auto-configuration attempts to automatically configure your Spring application based on ...
- Spring boot 官网学习笔记 - Using Spring Boot without the Parent POM,但是还要使用Parent POM提供的便利
If you do not want to use the spring-boot-starter-parent, you can still keep the benefit of the depe ...
- Spring boot 官网学习笔记 - 开发第一个Spring boot web应用程序(使用mvn执行、使用jar执行)
Creating the POM <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <project xmlns= ...
- Spring boot 官网学习笔记 - Spring Boot CLI 入门案例
安装CLI https://repo.spring.io/release/org/springframework/boot/spring-boot-cli/2.1.1.RELEASE/spring-b ...
- Spring boot 官网学习笔记 - Configuration Class(@import)
推荐使用 Java-based configuration ,也可以使用xml we generally recommend that your primary source be a single ...
- Spring Boot的学习之路(02):和你一起阅读Spring Boot官网
官网是我们学习的第一手资料,我们不能忽视它.却往往因为是英文版的,我们选择了逃避它,打开了又关闭. 我们平常开发学习中,很少去官网上看.也许学完以后,我们连官网长什么样子,都不是很清楚.所以,我们在开 ...
- (五)Spring Boot官网文档学习
文章目录 SpringApplication SpringApplication 事件 `ApplicationContext ` 类型 访问传递给 `SpringApplication` 的参数 A ...
随机推荐
- Python+Selenium - Web自动化测试(二):元素定位
前言 前面已经把环境搭建好了,现在开始使用 Selenium 中的 Webdriver 框架编写自动化代码脚本,我们常见的在浏览器中的操作都会有相对应的类方法,这些方法需要定位才能操作元素,不同网页的 ...
- 一 安装docker(详解)
一.安装docker 1 Docker 要求 CentOS 系统的内核版本高于 3.10 执行命令:uname -r 2 添加yum源: yum-config-manager --add-repo h ...
- 模板列传值到子窗体中,子窗体中多选gridview中checkbox保存数据多项到数据库中
<html xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml"> <head runat="server"> &l ...
- SpringMVC整合Apache Shiro
关于什么是Shiro,可以查看这篇文章http://www.cnblogs.com/Laymen/articles/6117751.html 一.添加maven依赖 <dependency> ...
- python控制窗口缩放
import win32gui import win32con import time # 使用之前先打开一个记事本 notepad = win32gui.FindWindow("Notep ...
- springmvc使用JSR-303对复杂对象进行校验
JSR-303 是JAVA EE 6 中的一项子规范,叫做Bean Validation,官方参考实现是Hibernate Validator.此实现与Hibernate ORM 没有任何关系.JSR ...
- 运行sudo apt-get install nginx时报错有几个软件包无法下载,要不运行 apt-get update 或者加上 --fix-missing 的选项再试试?解决
运行sudo apt-get install nginx时报错有几个软件包无法下载,要不运行 apt-get update 或者加上 --fix-missing 的选项再试试?解决办法 第一步:运行s ...
- GIT常见问题及其解决方案
问题: remote: Permission to beijing01/learn_github.git denied to liuhongyang02. fatal: unable to acces ...
- 聊聊 Python 的单元测试框架(二):nose 和它的继任者 nose2
作者:HelloGitHub-Prodesire HelloGitHub 的<讲解开源项目>系列,项目地址:https://github.com/HelloGitHub-Team/Arti ...
- Python集训营45天—Day02
目录 变量和运算符 1.1 初步介绍 1.2 使用案例 1.3 知识点梳理 1.4 练习 序言:这一章我们将学习变量以及常见的类型,我们将以案例和代码相结合的方式进行梳理,但是其中所有的案例和知识点 ...
