java学习笔记之原型模式及深浅拷贝
一、原型模式的基本介绍
在聊原型模式之前,我们来思考一个小问题,传统的方式我们是如何克隆对象呢?
那我们以多利羊(Sheep)为例,来说明上述这个问题,具体代码见下面:
多利羊(Sheep)
public class Sheep {
private String sname;
private Date birthday;
public Sheep(String sname, Date birthday) {
this.sname = sname;
this.birthday = birthday;
}
public String getSname() {
return sname;
}
public void setSname(String sname) {
this.sname = sname;
}
public Date getBirthday() {
return birthday;
}
public void setBirthday(Date birthday) {
this.birthday = birthday;
}
}
测试类(Client)
public class Client {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Sheep sheep=new Sheep("多利",new Date());
Sheep sheep2=new Sheep(sheep.getSname(),sheep.getBirthday());
System.out.println("sheep:"+sheep.getSname()+sheep.getBirthday());
System.out.println("sheep2:"+sheep2.getSname()+sheep2.getBirthday());
}
}
那我们来分析一下:
1、在创建新对象时,总是需要获取原始对象的属性,如果我们在实际项目中创建的对象复杂的话,效率是很低的。
2、总是需要重新初始化对象,而不是动态地获取对象运行时的状态,不够灵活。
有什么方法可以改进吗?,原型模式闪亮登场
大家都知道在Java中有一个Object类,这个类提供了一个clone()方法,该方法可以将Java对象复制一份,前提是该类实现一个Cloneable接口,这就是原型模式的源头。
什么是原型模式:
用原型实例指定创建对象的种类,并且通过拷贝这些原型来创建新的对象。
看了这个定义可能有的小伙伴们比较蒙,那我们来撸一把代码来说明(多利羊克隆):
多利羊(Sheep)实现Cloneable
public class Sheep implements Cloneable {
private String sname;
private Date birthday;
private Sheep mother;
public Sheep getMother() {
return mother;
}
public void setMother(Sheep mother) {
this.mother = mother;
}
public Sheep(String sname, Date birthday) {
this.sname = sname;
this.birthday = birthday;
}
public String getSname() {
return sname;
}
public void setSname(String sname) {
this.sname = sname;
}
public Date getBirthday() {
return birthday;
}
public void setBirthday(Date birthday) {
this.birthday = birthday;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Sheep{" +
"sname='" + sname + '\'' +
", birthday=" + birthday +
'}';
}
@Override
protected Object clone() throws CloneNotSupportedException {
Sheep sheep=null;
try {
sheep=(Sheep) super.clone();
}catch (Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
return sheep;
}
}
克隆方法的测试(Client)
public class Client {
public static void main(String[] args) throws CloneNotSupportedException {
Sheep sheep=new Sheep("多利",new Date());
Sheep mother=new Sheep("多利的妈妈",new Date());
sheep.setMother(mother);
Sheep sheep1=(Sheep) sheep.clone();
System.out.println("sheep:"+sheep);
System.out.println("sheep1:"+sheep1);
System.out.println("sheep:"+sheep.getMother().hashCode());
System.out.println("sheep1:"+sheep1.getMother().hashCode());
}
}
运行结果:hashcode 的值一样
sheep:Sheep{sname='多利', birthday=Sun May 17 11:56:58 CST 2020}
sheep1:Sheep{sname='多利', birthday=Sun May 17 11:56:58 CST 2020}
sheephashcode:2061475679
sheep1hashcode:2061475679
二、原型模式实现浅克隆和深克隆
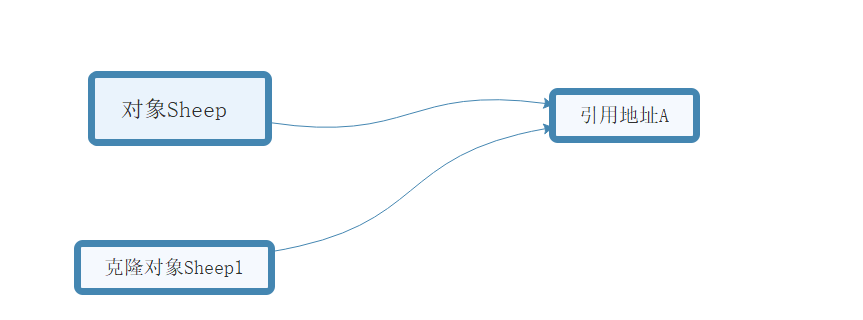
浅克隆的介绍:
对于数据类型是基本数据类型的成员变量,浅拷贝会直接进行值传递,也就是将该属性值复制一份给新的对象。
对于数据类型是引用数据类型的成员变量(数组,对象),浅拷贝会进行引用传递,也就是将成员变量的引用值(内存地址)复制一份给新的对象,因为实际上两个对象的该成员变量都指向同一个实例(前面克隆羊就是浅拷贝,使用clone()方法实现)。
再次说明:其实就是克隆多利羊之后,克隆的对象没有被真正的复制一份,而是引用指向第一个对象的属性空间。
画图说明:
具体代码如下见上面(多利羊克隆)
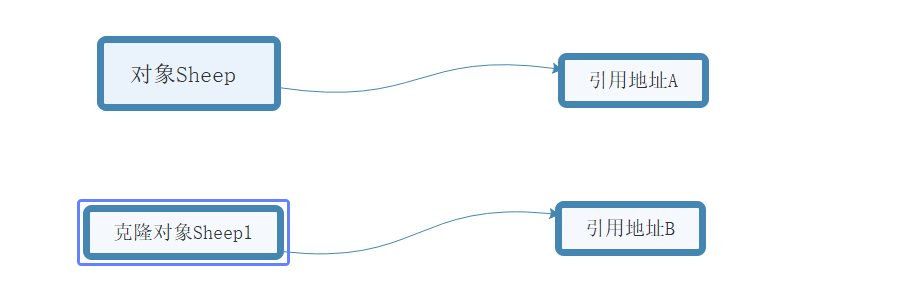
深克隆的介绍:
1、对对象进行深拷贝要对整个对象(包括对象的引用类型)进行拷贝。
深克隆实现的方式:
1、重写clone()方法实现深克隆
2、通过对象序列化实现深克隆
第一种方式:重写clone()方法实现深克隆,参考下面代码实现:
public class Sheep implements Cloneable {
private String sname;
private Date birthday;
public Mother mother;
public Sheep() {
}
public Sheep(String sname, Date birthday,Mother mother ) {
this.sname = sname;
this.birthday = birthday;
this.mother=mother;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Sheep{" +
"sname='" + sname + '\'' +
", birthday=" + birthday +
", mother=" + mother +
'}';
}
@Override
protected Object clone() throws CloneNotSupportedException {
Sheep sheep=null;
try {
Object obj= super.clone();
sheep=(Sheep) obj;
sheep.mother=(Mother) mother.clone();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return sheep;
}
}
多利的妈咪
public class Mother implements Cloneable {
private int age;
private String name;
public Mother(int age, String name) {
this.age = age;
this.name = name;
}
@Override
protected Object clone() throws CloneNotSupportedException {
return super.clone();
}
}
客户端测试:
public class Client {
public static void main(String[] args) throws CloneNotSupportedException {
Sheep sheep=new Sheep("多利",new Date(),new Mother(12,"多利的妈妈"));
Sheep sheep1=(Sheep) sheep.clone();
System.out.println("sheep:"+sheep);
System.out.println("sheep1:"+sheep1);
System.out.println("sheephashcode:"+sheep.mother.hashCode());
System.out.println("sheep1hashcode:"+sheep1.mother.hashCode());
}
}
运行结果:hashcode 的值不一样
sheep:Sheep{sname='多利', birthday=Sun May 17 13:20:51 CST 2020, mother=com.designpattern.pattern.prototypepattern.sprototype.Mother@7adf9f5f}
sheep1:Sheep{sname='多利', birthday=Sun May 17 13:20:51 CST 2020, mother=com.designpattern.pattern.prototypepattern.sprototype.Mother@85ede7b}
sheephashcode:2061475679
sheep1hashcode:140435067
第二种方式:序列化和反序列化
需要在Sheep ,Mother 类实现一个序列化 Serializable,具体代码和上面第一种方式的代码一样,就是这Sheep代码中增加以下这段核心代码:
// 通过对象的序列化实现
public Object deepClone() throws Exception {
ByteArrayOutputStream bos=new ByteArrayOutputStream();
ObjectOutputStream oos=new ObjectOutputStream(bos);
oos.writeObject(this);
ObjectInputStream ois=new ObjectInputStream(new ByteArrayInputStream(bos.toByteArray()));
Sheep sheep=(Sheep) ois.readObject();
return sheep;
}
运行结果:
sheep:Sheep{sname='多利', birthday=Sun May 17 13:51:23 CST 2020, mother=com.designpattern.pattern.prototypepattern.sprototype.Mother@72ea2f77}
sheep1:Sheep{sname='多利', birthday=Sun May 17 13:51:23 CST 2020, mother=com.designpattern.pattern.prototypepattern.sprototype.Mother@17f052a3}
sheephashcode:1927950199
sheep1hashcode:401625763
三、原型模式的应用场景
Spring 中bean 的scope 属性的声明:
<bean id="student" class="com.Student" scope="prototype"/>
public class ProtoType {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("beans.xml");
// 获取monster[通过id获取monster]
Object bean = applicationContext.getBean("student");
System.out.println("bean:" + bean);
Object bean2 = applicationContext.getBean("student");
System.out.println("bean1" + bean2);
System.out.println(bean == bean2);
}
}
运行结果
bean:com.atguigu.spring.bean.Student@52bf72b5
bean1com.atguigu.spring.bean.Student@37afeb11
false
四、小结
优点:
1、创建新的对象比较复杂时,可以利用原型模式创建新的对象,不用重新初始化对象,而是动态地获得对象运行时的状态。
2、如果原始对象发生变化,其克隆的对象也会发生响应的变化,不需要修改代码来实现
缺点:
需要为每一个类配置一个克隆方法,需要器修改源代码,不符合OCP原则。
技术之路还很长,慢慢来吧,时间会证明一切。
java学习笔记之原型模式及深浅拷贝的更多相关文章
- python学习笔记:第7天 深浅拷贝
目录 1. 基础数据类型补充 2. set集合 3. 深浅拷贝 1. 基础数据类型补充 (1)join方法 join方法是把一个列表中的数据进行拼接,拼接成字符串(与split方法相反,split方法 ...
- 设计模式学习笔记——Prototype原型模式
原型模型就是克隆. 还有深克隆.浅克隆,一切听上去都那么耳熟能详.
- 《Java学习笔记(第8版)》学习指导
<Java学习笔记(第8版)>学习指导 目录 图书简况 学习指导 第一章 Java平台概论 第二章 从JDK到IDE 第三章 基础语法 第四章 认识对象 第五章 对象封装 第六章 继承与多 ...
- 20145330《Java学习笔记》第一章课后练习8知识总结以及IDEA初次尝试
20145330<Java学习笔记>第一章课后练习8知识总结以及IDEA初次尝试 题目: 如果C:\workspace\Hello\src中有Main.java如下: package cc ...
- Java学习笔记4
Java学习笔记4 1. JDK.JRE和JVM分别是什么,区别是什么? 答: ①.JDK 是整个Java的核心,包括了Java运行环境.Java工具和Java基础类库. ②.JRE(Java Run ...
- java学习笔记13--反射机制与动态代理
本文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/archimedes/p/java-study-note13.html,转载请注明源地址. Java的反射机制 在Java运行时环境中,对于任意 ...
- Java学习笔记之---方法和数组
Java学习笔记之---方法与数组 (一)方法 (1)什么是方法? 方法是解决一类问题的步骤的有序组合 方法包含于类或对象中 方法在程序中被创建,在其他地方被引用 (2)方法的优点 使程序变得更简短而 ...
- java学习笔记之基础篇
java选择语句之switch //switch可以用于等值判断 switch (e) //int ,或则可以自动转化成int 的类型,(byte char short)枚举jdk 7中可以防止字 ...
- java学习笔记(1)java的基础介绍 、JDK下载、配置环境变量、运行java程序
java工程师是开发软件的 什么是软件呢? 计算机包括两部分: 硬件: 鼠标.键盘.显示器.主机箱内部的cpu.内存条.硬盘等 软件: 软件包括:系统软件和应用软件 系统软件:直接和硬件交互的软件:w ...
随机推荐
- Canvas(3)---绘制饼状图
Canvas(3)---绘制饼状图 有关canvas之前有写过两篇文章 1.Canvas(1)---概述+简单示例 2.Canvas(2)---绘制折线图 在绘制饼状图之前,我们先要理解什么是圆弧,如 ...
- ASP.Net内置对象之网页之间传参(一)
Response对象 主要运用于数据从服务器发送到浏览器,可以输出数据.页面跳转.各个网页之间传参数等操作. 以下讲解几个常用例子: 在页面中输出数据 主要通过Write .WriteFile方法输出 ...
- windows 系统使用技巧
1 自定义发送到C:\Users\adm\AppData\Roaming\Microsoft\Windows\SendTo 2 自定义关机shutdown -s -t time,可写在快捷方式中shu ...
- mybatis源码学习:基于动态代理实现查询全过程
前文传送门: mybatis源码学习:从SqlSessionFactory到代理对象的生成 mybatis源码学习:一级缓存和二级缓存分析 下面这条语句,将会调用代理对象的方法,并执行查询过程,我们一 ...
- C#线程学习笔记
本笔记摘抄自:https://www.cnblogs.com/zhili/archive/2012/07/18/Thread.html,记录一下学习,方便后面资料查找 一.线程的介绍 进程(Proce ...
- js 一维数组,转成嵌套数组
// 情况一: // 数据源var egs = [ {name_1: 'name_1...'}, {name_2: 'name_4...'}, {name_3: 'name_3...'}, {name ...
- HTTP 前世今生
HTTP 协议在我们身边随处可见,只要上网就离不开它.不论是用浏览器还是 App,不论是看新闻.短视频还是听音乐.玩游戏,后面总会有 HTTP 在默默为你服务. Http 协议是怎么来的?最开始是什么 ...
- Linux 日常操作
Linux 日常操作 */--> Linux 日常操作 Table of Contents 1. 查看硬件信息 1.1. 服务器型号序列号 1.2. 主板型号 1.3. 查看BIOS信息 1.4 ...
- How to permit SSH root Login in Ubuntu 18.04
https://www.ubuntu18.com/ssh-permitrootlogin/ SSH root login is disabled by default in Ubuntu 18.04. ...
- [Inno Setup] 退出安装程序的两种方式
1. 完全静默的退出 procedure ExitProcess(exitCode:integer); external 'ExitProcess@kernel32.dll stdcall'; ... ...
