PAT006 Tree Traversals Again
题目:
An inorder binary tree traversal can be implemented in a non-recursive way with a stack. For example, suppose that when a 6-node binary tree (with the keys numbered from 1 to 6) is traversed, the stack operations are: push(1); push(2); push(3); pop(); pop(); push(4); pop(); pop(); push(5); push(6); pop(); pop(). Then a unique binary tree (shown in Figure 1) can be generated from this sequence of operations. Your task is to give the postorder traversal sequence of this tree.

Figure 1
Input Specification:
Each input file contains one test case. For each case, the first line contains a positive integer N (<=30) which is the total number of nodes in a tree (and hence the nodes are numbered from 1 to N). Then 2N lines follow, each describes a stack operation in the format: "Push X" where X is the index of the node being pushed onto the stack; or "Pop" meaning to pop one node from the stack.
Output Specification:
For each test case, print the postorder traversal sequence of the corresponding tree in one line. A solution is guaranteed to exist. All the numbers must be separated by exactly one space, and there must be no extra space at the end of the line.
Sample Input:
6
Push 1
Push 2
Push 3
Pop
Pop
Push 4
Pop
Pop
Push 5
Push 6
Pop
Pop
Sample Output:
3 4 2 6 5 1
分析: 主要是根据输入创建一个二叉树,然后进行后续遍历
代码:
#pragma mark -Tree Traversals Again
#include <stdio.h> typedef struct traversalTreeNode {
int value;
struct traversalTreeNode *left;
struct traversalTreeNode *right;
} TraversalTreeNode; int flag; TraversalTreeNode *createTraversalTreeNode(int value)
{
TraversalTreeNode *node = (TraversalTreeNode *)malloc(sizeof(TraversalTreeNode));
node->value = value;
node->left = NULL;
node->right = NULL;
return node;
} void postorderTraversal(TraversalTreeNode *head)
{
if (head) {
postorderTraversal(head->left);
postorderTraversal(head->right); if (flag == ) {
printf("%d", head->value);
flag = ;
} else {
printf(" %d", head->value);
}
}
} int main()
{
int nodeNum = ;
scanf("%d", &nodeNum); int operationCount = * nodeNum;
TraversalTreeNode *a[]; int top = -;
// 第一个节点肯定是PUSH
int index = -;
scanf("%*s %d", &index);
TraversalTreeNode *head = createTraversalTreeNode(index);
a[] = head;
top = ; TraversalTreeNode *popItem = NULL;
for (int i = ; i < operationCount; i++) {
int index = -;
char str[];
scanf("%s", str);
unsigned long len = strlen(str);
if (len >= ) {
scanf("%d", &index);
TraversalTreeNode *newNode = createTraversalTreeNode(index);
if (popItem) {
if (!popItem->left) {
popItem->left = newNode;
} else {
popItem->right = newNode;
}
} else {
if (!a[top]->left) {
a[top]->left = newNode;
} else {
a[top]->right = newNode;
}
} top++;
a[top] = newNode;
popItem = NULL;
} else {
popItem = a[top];
a[top] = NULL;
top--;
}
} flag = ;
postorderTraversal(head);
}
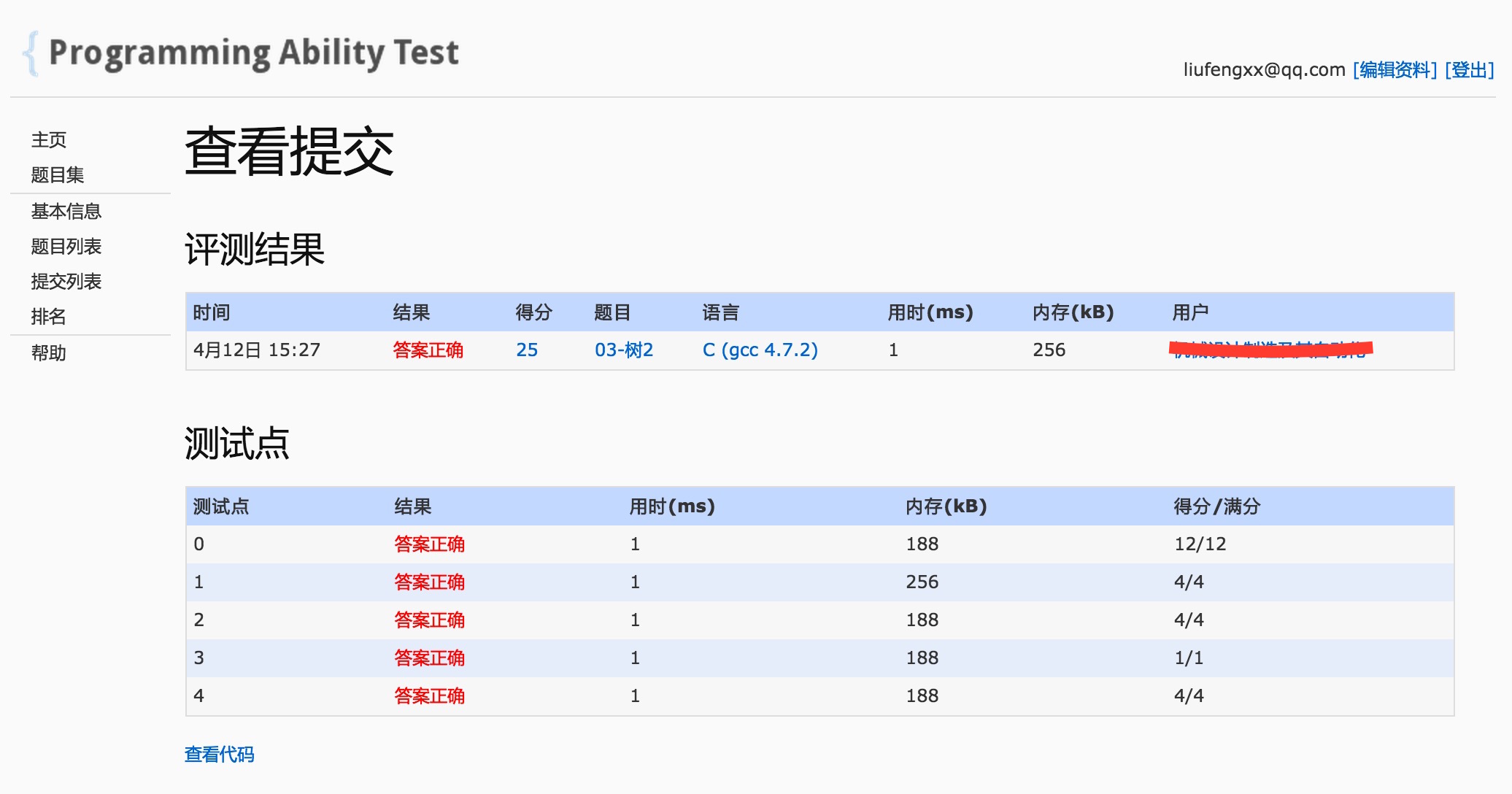
运行结果:
PAT006 Tree Traversals Again的更多相关文章
- Tree Traversals
Tree Traversals 原题链接 常见的二叉树遍历的题目,根据后序遍历和中序遍历求层次遍历. 通过后序遍历和中序遍历建立起一棵二叉树,然后层序遍历一下,主要难点在于树的建立,通过中序遍历和后序 ...
- HDU 1710 二叉树的遍历 Binary Tree Traversals
Binary Tree Traversals Time Limit: 1000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 32768/32768 K (Java/O ...
- hdu1710(Binary Tree Traversals)(二叉树遍历)
Binary Tree Traversals Time Limit: 1000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 32768/32768 K (Java/O ...
- HDU1710Binary Tree Traversals
HDU1710Binary Tree Traversals 题目大意:给一个树的前序遍历和中序遍历,要求输出后序遍历. (半年前做这道题做了两天没看懂,今天学了二叉树,回来AC了^ ^) 首先介绍一下 ...
- HDU-1701 Binary Tree Traversals
http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=1710 已知先序和中序遍历,求后序遍历二叉树. 思路:先递归建树的过程,后后序遍历. Binary Tree Tr ...
- 03-树2. Tree Traversals Again (25)
03-树2. Tree Traversals Again (25) 时间限制 200 ms 内存限制 65536 kB 代码长度限制 8000 B 判题程序 Standard 作者 CHEN, Yue ...
- HDU 1710-Binary Tree Traversals(二进制重建)
Binary Tree Traversals Time Limit: 1000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 32768/32768 K (Java/O ...
- PAT1086:Tree Traversals Again
1086. Tree Traversals Again (25) 时间限制 200 ms 内存限制 65536 kB 代码长度限制 16000 B 判题程序 Standard 作者 CHEN, Yue ...
- Binary Tree Traversals(HDU1710)二叉树的简单应用
Binary Tree Traversals Time Limit: 1000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 32768/32768 K (Java/O ...
随机推荐
- STL_算法_区间的比較(equal、mismatch、 lexicographical_compare)
C++ Primer 学习中.. . 简单记录下我的学习过程 (代码为主) //全部容器适用 equal(b,e,b2) //用来比較第一个容器[b,e)和第二个容器b2开头,是否相等 e ...
- mac本地搭建wordpress
1 下载安装最新的xampp 2 安装完成后,使用下面的命令开始运行 XAMPP.在终端下以系统管理员 root 的身份登录 管理员root身份登录 sudo su 使用命令启动XAMPP /Appl ...
- 常用class 总结
清除浮动 // Clearfix @mixin clearfix { &:before, &:after { content: " "; // 1 display: ...
- Win7如何设置标准账号无法访问我的D盘
1 右击对应的盘符,选择属性 2 设置对应的权限,比如是否可读,是否可写 3 之后再用这种用户登录就可以知道相应的权限了
- Fedora 28 设置yum代理
编辑 vi /etc/dnf/dnf.conf 文件 添加一行代理设置:proxy=http://****:****
- POJ1125 Stockbroker Grapevine 多源最短路
题目大意 给定一个图,问从某一个顶点出发,到其它顶点的最短路的最大距离最短的情况下,是从哪个顶点出发?须要多久? (假设有人一直没有联络,输出disjoint) 解题思路 Floyd不解释 代码 #i ...
- [Objective-C A]-知识点锦集
1.@autoreleasepool why1 2.retain O-C内存管理和点语法 1>OC内存管理正常情况要使用大量的retain和relrese操作 2>点语法可以减少使用re ...
- Oracle中查询某字段不为空或者为空的SQL语句怎么写
比如 insert into table a (a1,b1)values("a1",''); 对于这种情况,因为表里存的是'',其实是没有内容的,要查询这个字段,不能直接使用 se ...
- hibernate 关系映射之 双向外键关联一对一
在上一篇博客内容的基础上做了以下修改,即可实现. 注解方式: package com.bjsxt.hibernate; import javax.persistence.Entity; imp ...
- 【微信小程序】退款功能教程(含申请退款和退款回调)
1.一定要区分小程序和公众号的退款,唯一的区别就是 appid不一样,其他的都是一样的. 不废话,直接写代码了啊. 放大招!!! 然后,需要注意的:最好是把证书放在下面的php的同级或者下级. 证书的 ...
