POJ 2528 区间染色,求染色数目,离散化
| Time Limit: 1000MS | Memory Limit: 65536K | |
| Total Submissions: 47905 | Accepted: 13903 |
Description
- Every candidate can place exactly one poster on the wall.
- All posters are of the same height equal to the height of the wall; the width of a poster can be any integer number of bytes (byte is the unit of length in Bytetown).
- The wall is divided into segments and the width of each segment is one byte.
- Each poster must completely cover a contiguous number of wall segments.
They have built a wall 10000000 bytes long (such that there is enough place for all candidates). When the electoral campaign was restarted, the candidates were placing their posters on the wall and their posters differed widely in width. Moreover, the candidates started placing their posters on wall segments already occupied by other posters. Everyone in Bytetown was curious whose posters will be visible (entirely or in part) on the last day before elections.
Your task is to find the number of visible posters when all the posters are placed given the information about posters' size, their place and order of placement on the electoral wall.
Input
Output
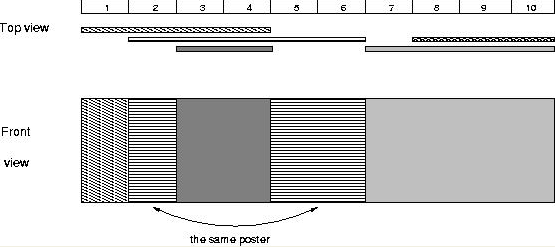
The picture below illustrates the case of the sample input.
Sample Input
1
5
1 4
2 6
8 10
3 4
7 10
Sample Output
4
Source
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
#include <algorithm>
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <queue>
#include <cmath>
#include <set>
using namespace std; #define N 40005
#define ll root<<1
#define rr root<<1|1
#define mid (a[root].l+a[root].r)/2 int max(int x,int y){return x>y?x:y;}
int min(int x,int y){return x<y?x:y;}
int abs(int x,int y){return x<?-x:x;} int n;
int x[N];
int m; int bin_s(int key){
int l=, r=m-;
while(l<=r){
int mm=(l+r)/;
if(x[mm]==key) return mm;
if(x[mm]>key) r=mm-;
else if(x[mm]<key) l=mm+;
}
} struct Line{
int l, r;
}line[N]; struct node{
int l, r, val;
bool f;
}a[N*]; void build(int l,int r,int root){
a[root].l=l;
a[root].r=r;
a[root].val=-;
if(l==r) return;
build(l,mid,ll);
build(mid+,r,rr);
} void down(int root){
if(a[root].val>&&a[root].l!=a[root].r){
a[ll].val=a[rr].val=a[root].val;
a[root].val=-;
}
} void update(int l,int r,int val,int root){
if(a[root].val==val) return;
if(a[root].l==l&&a[root].r==r){
a[root].val=val;
return;
}
down(root);
if(r<=a[ll].r) update(l,r,val,ll);
else if(l>=a[rr].l) update(l,r,val,rr);
else{
update(l,mid,val,ll);
update(mid+,r,val,rr);
}
if(a[ll].val==a[rr].val&&a[ll].val>) a[root].val=a[ll].val;
} bool visited[N];
int ans; void query(int root){
if(a[root].val!=-&&!visited[a[root].val]) {
ans++;
visited[a[root].val]=true;
return;
}
if(a[root].l==a[root].r)return ;
down(root);
query(ll);
query(rr);
} void out(int root){
if(a[root].l==a[root].r) {
printf("%d ",a[root].val);
return;
}
down(root);
out(ll);
out(rr);
} main()
{
int t, i, j, k; cin>>t;
while(t--){
scanf("%d",&n);
k=;
for(i=;i<n;i++) {
scanf("%d %d",&line[i].l,&line[i].r);
x[++k]=line[i].l;
x[++k]=line[i].r;
}
sort(x+,x+k);
k=unique(x+,x+k+)-x;
m=k;
for(i=;i<k;i++){
if(x[i]-x[i-]>) x[m++]=x[i]-;
}
sort(x,x+m);
build(,m,);
for(i=;i<n;i++){
int l=bin_s(line[i].l);
int r=bin_s(line[i].r);
update(l,r,i+,); }
memset(visited,false,sizeof(visited));
ans=;
query();
printf("%d\n",ans);
//out(1);
}
}
POJ 2528 区间染色,求染色数目,离散化的更多相关文章
- poj 2528 Mayor's posters 线段树+离散化技巧
poj 2528 Mayor's posters 题目链接: http://poj.org/problem?id=2528 思路: 线段树+离散化技巧(这里的离散化需要注意一下啊,题目数据弱看不出来) ...
- zoj 1610 Count the Colors 【区间覆盖 求染色段】
Count the Colors Time Limit: 2 Seconds Memory Limit: 65536 KB Painting some colored segments on ...
- POJ - 2528 区间离散化,线段树区间修改,区间询问
这个题非常有意思的地方是,我们发现区间[1,4]和[5,8]是紧挨着的,因为这个的数代表的是一段区间,原本我们对于普通的离散, a[1]=1,a[2]=5,a[3]=6,a[4]=8;数组下标就是重新 ...
- poj 2528(区间改动+离散化)
题意:有一个黑板上贴海报.给出每一个海报在黑板上的覆盖区间为l r,问最后多少个海报是可见的. 题解:由于l r取值到1e7,肯定是要离散化的,但普通的离散化会出问题.比方[1,10],[1,4],[ ...
- POJ 2528 Mayor's posters(线段树+离散化)
Mayor's posters 转载自:http://blog.csdn.net/winddreams/article/details/38443761 [题目链接]Mayor's posters [ ...
- poj 2528 Mayor's posters 线段树+离散化 || hihocode #1079 离散化
Mayor's posters Description The citizens of Bytetown, AB, could not stand that the candidates in the ...
- POJ 2528 Mayor‘s poster 线段树+离散化
给一块最大为10^8单位宽的墙面,贴poster,每个poster都会给出数据 a,b,表示该poster将从第a单位占据到b单位,新贴的poster会覆盖旧的,最多有10^4张poster,求最后贴 ...
- POJ 2528 Mayor's posters (线段树+离散化)
Mayor's posters Time Limit: 1000MS Memory Limit: 65536K Total Submissions:75394 Accepted: 21747 ...
- poj 2528 poster经典线段树+lazy+离散化
#include<cstdio> #include<cstring> #include<algorithm> using namespace std; ; #def ...
随机推荐
- bootstrap 图片轮播效果
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <link rel="stylesheet" href="http: ...
- (四)802.1Q VLAN
- Hostapd
Hostapd 一.基本概念 hostapd is an application used to setup your wireless interface as an access-point (m ...
- Android最佳性能实践(一)——合理管理内存
有不少朋友都问过我,怎样才能写出高性能的应用程序,如何避免程序出现OOM,或者当程序内存占用过高的时候该怎么样去排查.确实,一个优秀的应用程序,不仅仅要功能完成得好,性能问题也应该处理得恰到好处.为此 ...
- JS重要知识点(转载 学习中。。。)
这里列出了一些JS重要知识点(不全面,但自己感觉很重要).彻底理解并掌握这些知识点,对于每个想要深入学习JS的朋友应该都是必须的. 讲解还是以示例代码搭配注释的形式,这里做个小目录: JS代码预解析原 ...
- QBC用法
方法 说明 Restrictions.eq = Restrictions.allEq 利用Map来进行多个等于的限制 Restrictions.gt > Restrictions.ge > ...
- 转载:最大子段和问题(Maximum Interval Sum)
一.问题描述 给定长度为n的整数序列,a[1...n], 求[1,n]某个子区间[i , j]使得a[i]+…+a[j]和最大.或者求出最大的这个和. 例如(-2,11,- ...
- Sqlerver_各类函数
SQL Aggregate 函数 SQL Aggregate 函数计算从列中取得的值,返回一个单一的值. 有用的 Aggregate 函数: AVG() - 返回平均值-SELECT AVG(colu ...
- jQuery中对属性的增删改查
获取元素的属性 $('input').attr('type') .attr() 可以获取和设置自定义属性 .prop() 只能获取和设置固有属性 在设置属性值时 建议不要修改type属性,有的浏览 ...
- VC++全局变量初始化
目录 第1章说明 2 1.1 程序启动 2 1.2 强符号.弱符号 2 1.3 动态初始化顺序 3 1.4 exe调用dll 4 1.5 禁用动态初始化 4 1.6 ...
