《DSP using MATLAB》示例Example5.8

代码:
n = [0:1:99]; x = cos(0.48*pi*n) + cos(0.52*pi*n);
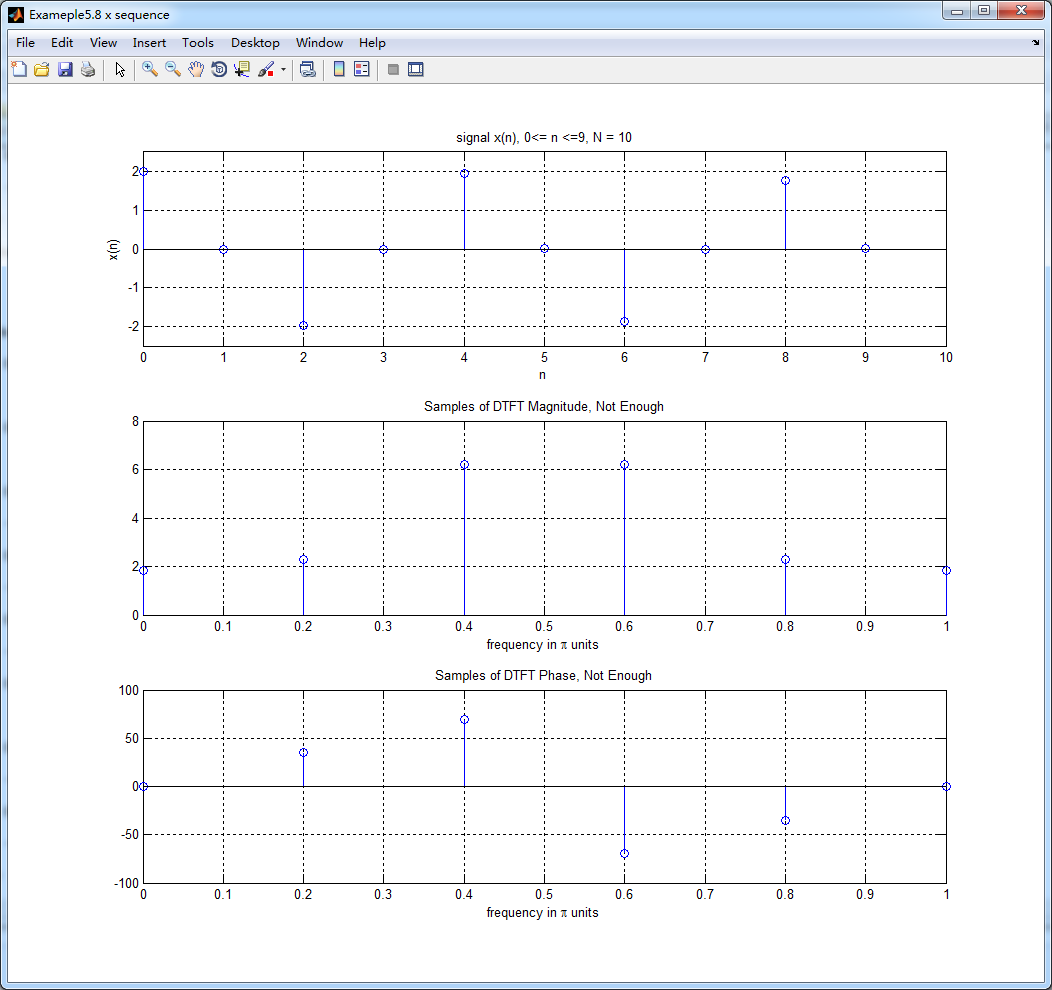
n1 = [0:1:9]; y1 = x(1:1:10); % N = 10 figure('NumberTitle', 'off', 'Name', 'Exameple5.8 x sequence')
set(gcf,'Color','white');
subplot(3,1,1); stem(n1,y1); title('signal x(n), 0<= n <=9, N = 10'); axis([0,10,-2.5,2.5]);
xlabel('n'); ylabel('x(n)'); grid on; Y1_DFT = dft(y1,10); % DFT of y1 magY1_DFT = abs(Y1_DFT(1:1:6));
%magY1_DFT = abs(Y1_DFT);
%phaY1_DFT = angle(Y1_DFT)*180/pi % degrees
phaY1_DFT = angle(Y1_DFT(1:1:6))*180/pi % degrees
%realX_DFT = real(X_DFT); imagX_DFT = imag(X_DFT);
%angX_DFT = angle(X_DFT); % radias k1 = 0:1:5; w1 = 2*pi/10*k1; % [0,2pi] axis divided into 501 points.
%k = 0:500; w = (pi/500)*k; % [0,pi] axis divided into 501 points.
%X_DTFT = x * (exp(-j*pi/500)) .^ (n'*k); % DTFT of x(n) %magX_DTFT = abs(X_DTFT); angX_DTFT = angle(X_DTFT); realX_DTFT = real(X_DTFT); imagX_DTFT = imag(X_DTFT);
subplot(3,1,2); stem(w1/pi,magY1_DFT); title('Samples of DTFT Magnitude, Not Enough'); %axis([0,N,-0.5,1.5]);
xlabel('frequency in \pi units');
%ylabel('x(n)');
grid on;
subplot(3,1,3); stem(w1/pi,phaY1_DFT); title('Samples of DTFT Phase, Not Enough'); %axis([0,N,-0.5,1.5]);
xlabel('frequency in \pi units');
%ylabel('x(n)');
grid on; %% ------------------------------------------------------
%% zero-padding coperation, Append 90 zeros
%% To obtain a dense spectrum
%% ------------------------------------------------------
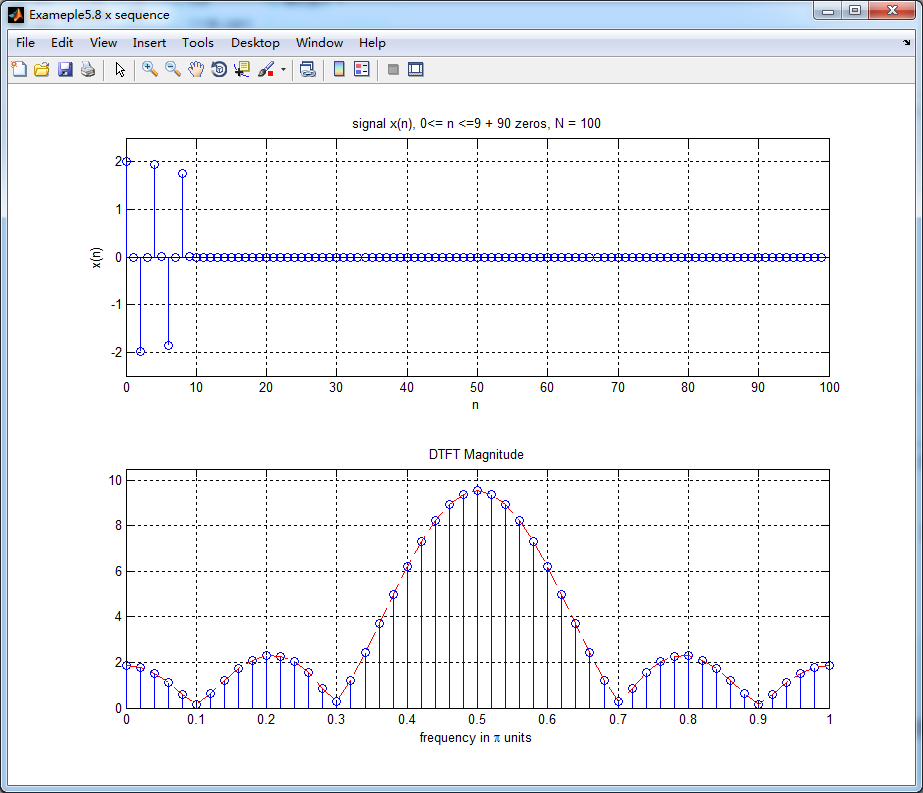
n2 = [0:1:99]; y2 = [x(1:1:10) zeros(1,90)]; % zero-padding, N = 100 figure('NumberTitle', 'off', 'Name', 'Exameple5.8 x sequence')
set(gcf,'Color','white');
subplot(2,1,1); stem(n2,y2); title('signal x(n), 0<= n <=9 + 90 zeros, N = 100'); axis([0,100,-2.5,2.5]);
xlabel('n'); ylabel('x(n)'); grid on; Y2_DFT = dft(y2,100); % DFT of y2 magY2_DFT = abs(Y2_DFT(1:1:51));
phaY2_DFT = angle(Y2_DFT)*180/pi % degrees k2 = 0:1:50; w2 = (2*pi/100)*k2; % [0,2pi] axis divided into 501 points.
subplot(2,1,2); stem(w2/pi,magY2_DFT); hold on; plot(w2/pi,magY2_DFT,'--r');
title('DTFT Magnitude'); axis([0,1,0,10.5]); hold off;
xlabel('frequency in \pi units');
%ylabel('x(n)');
grid on; %% -----------------------------------------------------------
%% Exameple5.8b take first 100 samples of x(n)
%% determine the DTFT
%% -----------------------------------------------------------
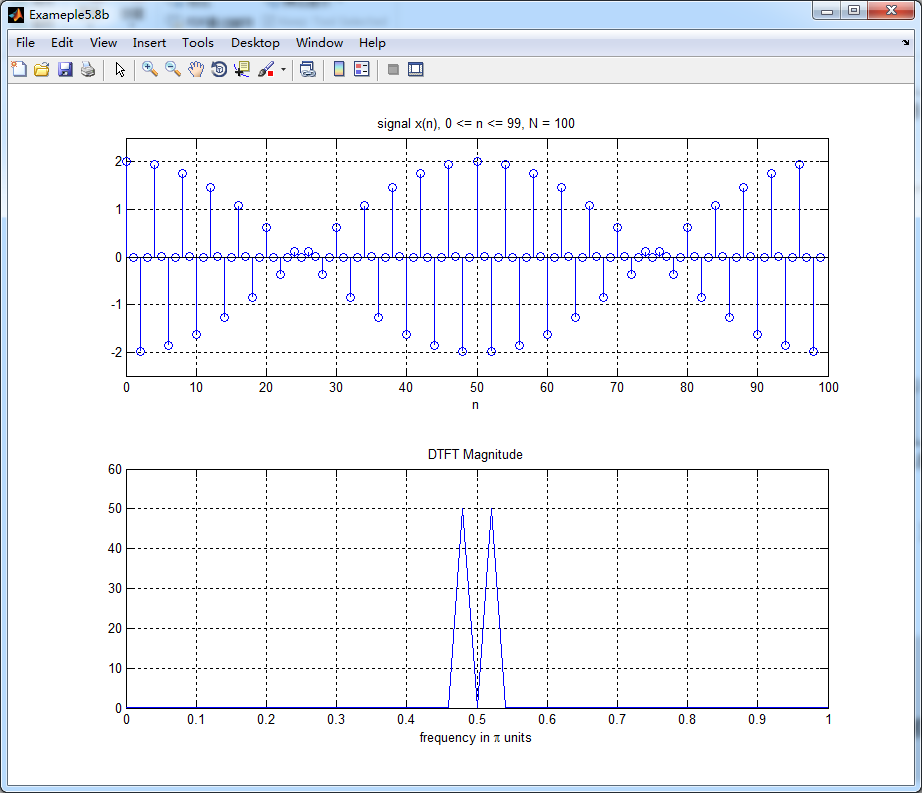
figure('NumberTitle', 'off', 'Name', 'Exameple5.8b ')
set(gcf,'Color','white');
subplot(2,1,1); stem(n,x); axis([0,100,-2.5,2.5]);
title('signal x(n), 0 <= n <= 99, N = 100'); xlabel('n'); grid on; X = dft(x,100); magX = abs(X(1:1:51));
k = 0:1:50; w = 2*pi/100*k;
subplot(2,1,2); plot(w/pi, magX); title('DTFT Magnitude');
xlabel('frequency in \pi units'); axis([0,1,0,60]); grid on;
%% -----------------------------------------------------------
%% END Exameple5.8b
%% -----------------------------------------------------------
结果:
《DSP using MATLAB》示例Example5.8的更多相关文章
- DSP using MATLAB 示例Example3.21
代码: % Discrete-time Signal x1(n) % Ts = 0.0002; n = -25:1:25; nTs = n*Ts; Fs = 1/Ts; x = exp(-1000*a ...
- DSP using MATLAB 示例 Example3.19
代码: % Analog Signal Dt = 0.00005; t = -0.005:Dt:0.005; xa = exp(-1000*abs(t)); % Discrete-time Signa ...
- DSP using MATLAB示例Example3.18
代码: % Analog Signal Dt = 0.00005; t = -0.005:Dt:0.005; xa = exp(-1000*abs(t)); % Continuous-time Fou ...
- DSP using MATLAB 示例Example3.23
代码: % Discrete-time Signal x1(n) : Ts = 0.0002 Ts = 0.0002; n = -25:1:25; nTs = n*Ts; x1 = exp(-1000 ...
- DSP using MATLAB 示例Example3.22
代码: % Discrete-time Signal x2(n) Ts = 0.001; n = -5:1:5; nTs = n*Ts; Fs = 1/Ts; x = exp(-1000*abs(nT ...
- DSP using MATLAB 示例Example3.17
- DSP using MATLAB示例Example3.16
代码: b = [0.0181, 0.0543, 0.0543, 0.0181]; % filter coefficient array b a = [1.0000, -1.7600, 1.1829, ...
- DSP using MATLAB 示例 Example3.15
上代码: subplot(1,1,1); b = 1; a = [1, -0.8]; n = [0:100]; x = cos(0.05*pi*n); y = filter(b,a,x); figur ...
- DSP using MATLAB 示例 Example3.13
上代码: w = [0:1:500]*pi/500; % freqency between 0 and +pi, [0,pi] axis divided into 501 points. H = ex ...
- DSP using MATLAB 示例 Example3.12
用到的性质 代码: n = -5:10; x = sin(pi*n/2); k = -100:100; w = (pi/100)*k; % freqency between -pi and +pi , ...
随机推荐
- mysql安装和配置
一.下载mysql mysql下载页 我用的是5.6,点击旁边的"Looking for previous GA versions?"按钮就能看到5.6版本 mysql-5.6.3 ...
- Logistic Regression - Formula Deduction
Sigmoid Function \[ \sigma(z)=\frac{1}{1+e^{(-z)}} \] feature: axial symmetry: \[ \sigma(z)+ \sigma( ...
- MySQL中日期与时间类型
http://blog.sina.com.cn/s/blog_4d8730df01014jiy.html
- 再次认识ASP.NET MVC
MVC, V,就是View.视图 M,只应该是ViewModel.视图模型 C,Controller.控制器 我们需要怎么看待并使用这三者. 从你敲入url,我们可以做为入口. 当你敲入url并按了回 ...
- CSS3实现加载中效果
代码: <!doctype html> <html> <head> <meta charset="utf-8" /> <tit ...
- Bootstrap学习------按钮
Bootstrap为我们提供了按钮组的样式,博主写了几个简单的例子,以后也许用的到. 效果如下 代码如下 <!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> ...
- visio二次开发——图纸解析
(转发请注明来源:http://www.cnblogs.com/EminemJK/) visio二次开发的案例或者教程,国内真的非常少,这个项目也是花了不少时间来研究visio的相关知识,困难之所以难 ...
- ZOJ 3699 Dakar Rally
Dakar Rally Time Limit: 2 Seconds Memory Limit: 65536 KB Description The Dakar Rally is an annu ...
- idea之resource配置
1.问题 在idea中配置springmvc项目,用hibernate管理数据库,在web.xml中作如下配置: <!--配置hibernate数据库连接--> <listener& ...
- BZOJ 4581: [Usaco2016 Open]Field Reduction
Description 有 \(n\) 个点,删掉三个点后,求最小能围住的面积. Sol 搜索. 找出 左边/右边/上边/下边 的几个点枚举就可以了. 我找了 12 个点,统计一下坐标的个数,然后找到 ...
