【LeetCode】133. Clone Graph 解题报告(Python & C++)
作者: 负雪明烛
id: fuxuemingzhu
个人博客: http://fuxuemingzhu.cn/
题目地址:https://leetcode.com/problems/clone-graph/
题目描述
Given a reference of a node in a connected undirected graph, return a deep copy (clone) of the graph. Each node in the graph contains a val (int) and a list (List[Node]) of its neighbors.
Example:
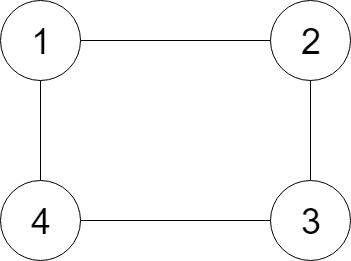
Input:
{"$id":"1","neighbors":[{"$id":"2","neighbors":[{"$ref":"1"},{"$id":"3","neighbors":[{"$ref":"2"},{"$id":"4","neighbors":[{"$ref":"3"},{"$ref":"1"}],"val":4}],"val":3}],"val":2},{"$ref":"4"}],"val":1}
Explanation:
Node 1's value is 1, and it has two neighbors: Node 2 and 4.
Node 2's value is 2, and it has two neighbors: Node 1 and 3.
Node 3's value is 3, and it has two neighbors: Node 2 and 4.
Node 4's value is 4, and it has two neighbors: Node 1 and 3.
Note:
- The number of nodes will be between 1 and 100.
- The undirected graph is a simple graph, which means no repeated edges and no self-loops in the graph.
- Since the graph is undirected, if node p has node q as neighbor, then node q must have node p as neighbor too.
- You must return the copy of the given node as a reference to the cloned graph.
题目大意
完全复制一个图结构。返回新的起始节点。
解题方法
DFS
这个题和138. Copy List with Random Pointer比较类似。至于图结构,我们可以使用DFS和BFS两种结构进行遍历。
一般的遍历只需要保存是否遍历过这个节点即可,但是由于这个题需要把neighboors对应复制过来。那么需要进行改进,改进的方式是把set改成dict,保存每个老节点对应的新节点是多少。在Python中,字典直接保存对象(指针)之间的映射。所以,我们直接把遍历过的对象和复制出来的对象一一对应即可。当我们遍历到一个新的节点的时候,需要判断这个节点是否在字典中出现过,如果出现过就把它对应的复制出来的对象放到其neighboors里,若没有出现过,那么就重新构造该节点,并把原节点和该节点放到字典中保存。
Python代码如下:
"""
# Definition for a Node.
class Node(object):
def __init__(self, val, neighbors):
self.val = val
self.neighbors = neighbors
"""
class Solution(object):
def cloneGraph(self, node):
"""
:type node: Node
:rtype: Node
"""
node_copy = self.dfs(node, dict())
return node_copy
def dfs(self, node, hashd):
if not node: return None
if node in hashd: return hashd[node]
node_copy = Node(node.val, [])
hashd[node] = node_copy
for n in node.neighbors:
n_copy = self.dfs(n, hashd)
if n_copy:
node_copy.neighbors.append(n_copy)
return node_copy
C++代码如下:
/*
// Definition for a Node.
class Node {
public:
int val;
vector<Node*> neighbors;
Node() {}
Node(int _val, vector<Node*> _neighbors) {
val = _val;
neighbors = _neighbors;
}
};
*/
class Solution {
public:
Node* cloneGraph(Node* node) {
if (!node) return nullptr;
if (m_.count(node))
return m_[node];
Node* node_copy = new Node(node->val, {});
m_[node] = node_copy;
for (Node* n : node->neighbors) {
node_copy->neighbors.push_back(cloneGraph(n));
}
return node_copy;
}
private:
unordered_map<Node*, Node*> m_;
};
BFS
这个题同样也可以使用BFS解决。方法也是使用了字典保存每一个对应关系。当新构造出一个节点之后,必须同时把它放到字典中保存,这个很重要。另外就是每遍历到一个节点时,都要把它的所有邻居放到队列中。
python代码如下:
"""
# Definition for a Node.
class Node(object):
def __init__(self, val, neighbors):
self.val = val
self.neighbors = neighbors
"""
class Solution(object):
def cloneGraph(self, node):
"""
:type node: Node
:rtype: Node
"""
que = collections.deque()
hashd = dict()
que.append(node)
node_copy = Node(node.val, [])
hashd[node] = node_copy
while que:
t = que.popleft()
if not t: continue
for n in t.neighbors:
if n not in hashd:
hashd[n] = Node(n.val, [])
que.append(n)
hashd[t].neighbors.append(hashd[n])
return node_copy
C++代码如下:
/*
// Definition for a Node.
class Node {
public:
int val;
vector<Node*> neighbors;
Node() {}
Node(int _val, vector<Node*> _neighbors) {
val = _val;
neighbors = _neighbors;
}
};
*/
class Solution {
public:
Node* cloneGraph(Node* node) {
queue<Node*> q;
q.push(node);
unordered_map<Node*, Node*> m_;
Node* node_copy = new Node(node->val, {});
m_[node] = node_copy;
while (!q.empty()) {
Node* t = q.front(); q.pop();
if (!t) continue;
for (Node* n : t->neighbors) {
if (!m_.count(n)) {
m_[n] = new Node(n->val, {});
q.push(n);
}
m_[t]->neighbors.push_back(m_[n]);
}
}
return node_copy;
}
};
日期
2019 年 3 月 9 日 —— 妇女节快乐
【LeetCode】133. Clone Graph 解题报告(Python & C++)的更多相关文章
- LeetCode: Clone Graph 解题报告
Clone GraphClone an undirected graph. Each node in the graph contains a label and a list of its neig ...
- [LeetCode] 133. Clone Graph 克隆无向图
Clone an undirected graph. Each node in the graph contains a label and a list of its neighbors. OJ's ...
- Java for LeetCode 133 Clone Graph
Clone an undirected graph. Each node in the graph contains a label and a list of its neighbors. OJ's ...
- leetcode 133. Clone Graph ----- java
Clone an undirected graph. Each node in the graph contains a label and a list of its neighbors. OJ's ...
- [leetcode]133. Clone Graph 克隆图
题目 给定一个无向图的节点,克隆能克隆的一切 思路 1--2 | 3--5 以上图为例, node neighbor 1 2, 3 2 1 3 1 ...
- Leetcode#133 Clone Graph
原题地址 方法I,DFS 一边遍历一边复制 借助辅助map保存已经复制好了的节点 对于原图中每个节点,如果已经复制过了,直接返回新节点的地址,如果没复制过,则复制并加入map中,接着依次递归复制其兄弟 ...
- 【LeetCode】120. Triangle 解题报告(Python)
[LeetCode]120. Triangle 解题报告(Python) 作者: 负雪明烛 id: fuxuemingzhu 个人博客: http://fuxuemingzhu.cn/ 题目地址htt ...
- LeetCode 1 Two Sum 解题报告
LeetCode 1 Two Sum 解题报告 偶然间听见leetcode这个平台,这里面题量也不是很多200多题,打算平时有空在研究生期间就刷完,跟跟多的练习算法的人进行交流思想,一定的ACM算法积 ...
- 133. Clone Graph 138. Copy List with Random Pointer 拷贝图和链表
133. Clone Graph Clone an undirected graph. Each node in the graph contains a label and a list of it ...
随机推荐
- composer设置阿里云镜像源
composer设置阿里云镜像源 1. 首先把默认的源给禁用掉 composer config -g secure-http false 2. 再修改镜像源 这里我使用阿里的源 composer co ...
- Oracle-判断一个表的一列是否在另一张表的一列存在
select * from A where exists(select 1 from B where A.a = B.b)
- tensorboard 拒绝连接无法打开相应页面
启动tensorboard时没有报错,但打开页面却拒绝连接. 解决方法:tensorboard --logdir=TEC4FN --host=127.0.0.1 在命令最后添加 --host=127. ...
- 日常Java 2021/10/1
正则表达式 \cx匹配由x指明的控制字符.例如,lcM匹配一个Control-M或回车符.x的值必须为A-Z或a-z之一.否则,将c视为一个原义的'℃'字符.\f匹配--个换页符.等价于\xOc和\c ...
- Spark基础:(四)Spark 数据读取与保存
1.文件格式 Spark对很多种文件格式的读取和保存方式都很简单. (1)文本文件 读取: 将一个文本文件读取为一个RDD时,输入的每一行都将成为RDD的一个元素. val input=sc.text ...
- 对于Linq关键字和await,async异步关键字的扩展使用
最近在看neuecc大佬写的一些库:https://neuecc.medium.com/,其中对await,async以及linq一些关键字实现了自定义化使用, 使其不需要引用对应命名空间,不需要多线 ...
- map和forEach的区别
总结 forEach()可以做到的东西,map()也同样可以.反过来也是如此. map()会分配内存空间存储新数组并返回,forEach()不会返回数据. forEach()允许callback更改原 ...
- c学习 - 算法
简介: 一个程序包括两方面内容:数据结构.算法 数据结构:对数据的描述,包括数据的类型和数据的组织形式 算法:对操作的描述,即操作步骤 (程序=算法+数据结构) 算法是灵魂,数据结构是加工对象,语言是 ...
- 【Linux】【Services】【SaaS】Docker+kubernetes(11. 构建复杂的高可用网络)
1. 简介 flannel在实战阶段貌似不能胜任在灾难恢复时候异地的网络,打算用openvswith试试
- 【Linux】【Basis】进程及作业管理
进程及作业管理 内核的功用:进程管理.文件系统.网络功能.内存管理.驱动程序.安全功能 Process: 运行中的程序的一个副本: 存在生命周期 L ...
