OpenCV 之 空间刚体变换
刚体就是 "刚性物体",它在运动过程中,内部各质点间的相对位置不会改变,也即 每两个质点间的距离 保持不变
假设刚体内任意两个质点,坐标分别为 $(x_1, y_1, z_1)$ 和 $(x_2, y_2, z_2)$,则在刚体运动过程中,这两个质点满足如下条件:
$\quad \left( (x_1 - x_2)^2 + (y_1 - y_2)^2 + (z_1 - z_2)^2 \right) |_t = l^2$
例如:影视剧《西游记》中的法宝金刚琢、玉净瓶是刚体;而幌金绳、芭蕉扇等,则不是刚体
1 刚体变换
1.1 矩阵形式
OpenCV 之 图像几何变换 中的等距变换,实际是二维刚体变换
$\quad \begin{bmatrix} x^{\prime} \\ y^{\prime} \\ 1 \end{bmatrix} = \begin{bmatrix} \cos \theta & -\sin \theta & t_x \\ \sin \theta & \cos \theta & t_y \\ 0&0&1 \end{bmatrix} \begin{bmatrix} x \\ y \\ 1\end{bmatrix}$
从平面推及空间,三维刚体变换的矩阵形式为
$\quad \begin{bmatrix}x' \\ y' \\ z' \\ 1 \end{bmatrix}=\begin{bmatrix} r_{11} & r_{12} & r_{13} & t_x \\ r_{21} & r_{22} & r_{23} & t_y \\ r_{31} & r_{32} & r_{33} &t_z \\ 0 & 0 & 0 & 1 \end{bmatrix} \begin{bmatrix} x \\ y \\z \\ 1\end{bmatrix} $
例如:空间任一点,在相机坐标系中为 $P_{c}(x, y, z)$,世界坐标系中为 $P_{w}(X, Y, Z)$ ,则 $P_c$ -> $P_w$ 就是一个刚体变换
1.2 约束分析
R 和 T 共有 12 个未知数,但 R 是标准正交矩阵,自带 6 个约束方程,则刚体变换有 12 - 6 = 6 个自由度 (和直观的感受一致)
表面上看,似乎只需两组空间对应点,联立 6 个方程,便可求得 6 个未知数,但这 6 个方程是有冗余的 (因为这两组对应点,在各自的坐标系下,两点之间的距离是相等的)
因此,第二组对应点,只是提供了 2 个约束方程,加上第一组对应点的 3 个约束,共有 5 个独立的方程
显然,还需要第三组对应点,提供 1 个独立的方程,才能求出 R 和 T
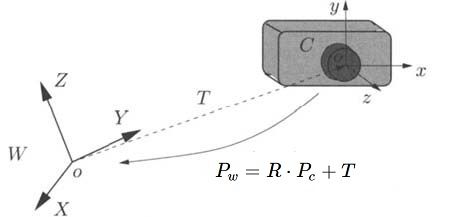
如图所示,两个刚体之间:1个点重合 => 3个自由度;2个点重合 => 1个自由度;3个点重合=> 0个自由度
1.3 直观理解
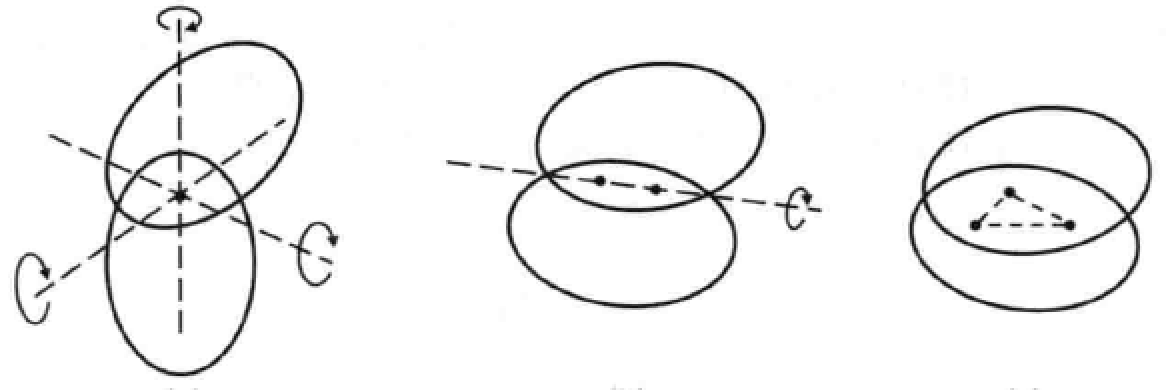
一个单位立方体,可在 X-Y-Z 坐标系中自由运动,则二者之间的转换关系,可视为刚体变换
单点重合:当立方体的角点 0 和 X-Y-Z 坐标系的原点 O 重合时,立方体还能自由的旋转 (X 轴 -> Y 轴 -> Z 轴)
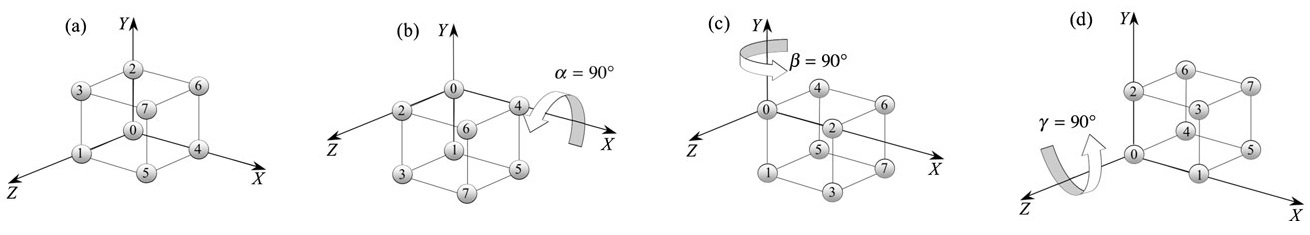
两点重合:除了立方体的角点 0 和坐标系的 原点 O 重合外,再令角点 4 和 X 轴上的某点重合,则此时立方体只能 绕 X 轴旋转
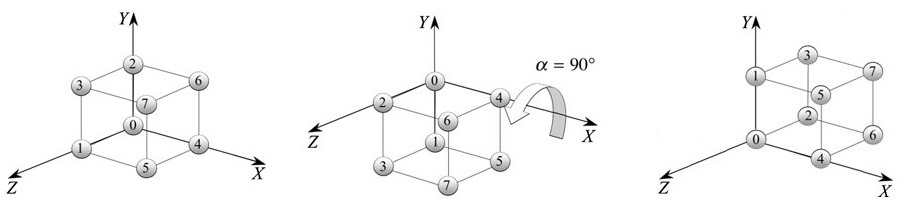
三点重合:除了以上两个角点 0 和 4,如果再使角点 1 和 Z 轴上的某点重合,则立方体就会和 X-Y-Z 坐标系 牢牢的连接在一起
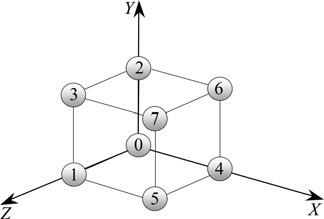
因此,选取不共面的三组对应点,联立方程组,便可求得 R 和 T
2 旋转向量
任意的旋转,都可用一个旋转轴 (axis) 和 绕轴旋转角 (angle) 来描述,简称“轴角”
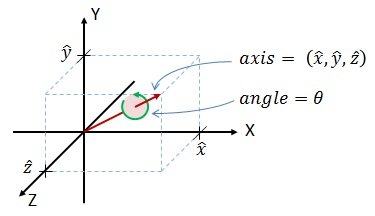
因此,可用一个方向和旋转轴一致,长度等于旋转角的向量来表示旋转,这个向量称为旋转向量 (或“旋量”)
假定旋转轴 $\mathbf{n} = [r_{x}, r_{y}, r_{z}]$,旋转角为 $\theta$,则旋转向量可记为 $\theta \mathbf{n}$
旋转向量到旋转矩阵的转换,可由罗德里格斯公式来实现,如下:
$\quad R = cos(\theta) I + (1 - cos \theta) \mathbf{nn^T} + sin \theta \begin{bmatrix} 0&-r_z&r_y \\ r_z&0&-r_x \\ -r_y&r_x&0 \end{bmatrix}$
反之,从旋转矩阵到旋量,公式如下:
$\quad \sin \theta \begin{bmatrix}0 &-r_z&r_y \\r_z&0&-r_x \\-r_y & r_x &0 \end{bmatrix} = \dfrac{R - R^T}{2} $
OpenCV 中有一个 Rodrigues() 函数,可实现二者的相互转换
void Rodrigues (
InputArray src, // 输入旋转向量 n(3x1 或 1x3) 或 旋转矩阵 R(3x3)
OutputArray dst, // 输出旋转矩阵 R 或 旋转向量 n
OutputArray jacobian = noArray() // 可选,输出 Jacobian 矩阵(3x9 或 9x3)
)
3 欧拉角
3.1 定义
假定 X-Y 平面内有一点 P, 旋转 $\theta$ 角到 $P^{\prime}$ 位置,如下图:
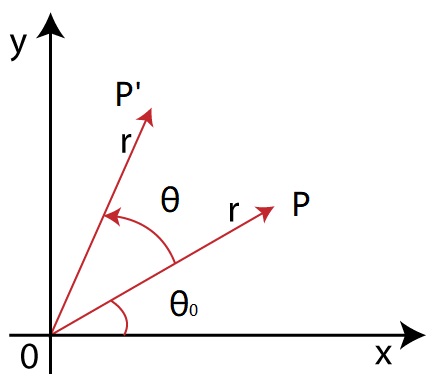
取 $\angle$POX = $\theta_0$,列方程组得
$\quad x^{\prime} = r \cos (\theta_0 + \theta) = r \cos \theta_0 \cos\theta - r \sin \theta_0 \sin\theta = x \cos\theta - y \sin \theta $
$\quad y^{\prime} = r \sin(\theta_0+ \theta) = r \sin\theta_0 cos \theta + r \cos \theta_0 \sin\theta = x \sin \theta + y \cos \theta $
转化为矩阵形式 $ \begin{bmatrix} x' \\ y' \end{bmatrix} = \begin{bmatrix} cos \theta & -sin \theta \\ sin \theta & cos \theta \end{bmatrix} \begin{bmatrix} x \\ y \end{bmatrix}$
3.2 欧拉角
将二维旋转矩阵 $R_{2 \times 2}$ 扩展到三维空间
1)绕 Z 轴旋转 roll,则添加 z 坐标 $\pmb{R_z} = \begin{bmatrix} cos \theta_z & -sin \theta_z & 0 \\ sin \theta_z & cos \theta_z & 0 \\ 0&0&1 \end{bmatrix}$

2)绕 Y 轴旋转 yaw,则添加 y 坐标 $\pmb{R_y} = \begin{bmatrix} cos \theta_y & 0 & \color{blue}{sin \theta_y} \\ 0 & 1 & 0 \\ \color{blue}{-sin \theta_y} & 0 & cos \theta_y \end{bmatrix}$
3)绕 X 轴旋转 pitch,则添加 x 坐标 $\pmb{R_x} = \begin{bmatrix} 1 & 0 & 0 \\ 0 &cos \theta_x & -sin \theta_x \\ 0 & sin \theta_x & cos \theta_x \end{bmatrix}$
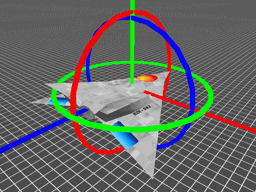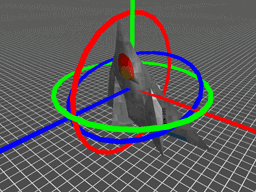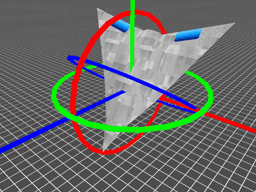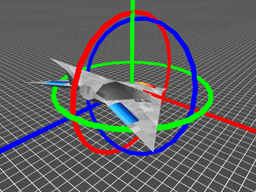
因此,当按 Z-Y-X 的顺序旋转时,一个旋转矩阵就被分解成了绕不同轴的三次旋转,旋转角称为 "欧拉角"
$\quad R = R_z \cdot R_y \cdot R_x = \begin{bmatrix} cos \theta_y cos \theta_z & sin \theta_x sin \theta_y cos \theta_z - cos \theta_x sin \theta_z & sin \theta_x sin \theta_z + cos \theta_x sin \theta_y cos \theta_z \\ cos \theta_y sin \theta_z & cos \theta_x cos \theta_z + sin \theta_x sin \theta_y sin \theta_z & cos \theta_x sin \theta_y sin \theta_z - sin \theta_x cos \theta_z \\ -sin \theta_y & sin \theta_x cos \theta_y & cos \theta_x cos \theta_y \end{bmatrix} $,
注意:在使用欧拉角时,要先指明旋转的顺序,因为绕不同的轴旋转时得到的欧拉角也不同
反之,由旋转矩阵求解欧拉角,则有:
$\quad \theta_x = tan^{-1} (\dfrac{r_{32}}{r_{33}})$
$\quad \theta_y = sin^{-1} (-r_{33})$
$\quad \theta_z = tan^{-1} (\dfrac{r_{21}}{r_{11}})$
3.3 代码实现
已知绕三个轴旋转的欧拉角,要转换为旋转矩阵,直接套用公式
Mat eulerAnglesToRotationMatrix(Vec3f &theta)
{
// Calculate rotation about x axis
Mat R_x = (Mat_<double>(3,3) <<
1, 0, 0,
0, cos(theta[0]), -sin(theta[0]),
0, sin(theta[0]), cos(theta[0]) ); // Calculate rotation about y axis
Mat R_y = (Mat_<double>(3,3) <<
cos(theta[1]), 0, sin(theta[1]),
0, 1, 0,
-sin(theta[1]), 0, cos(theta[1]) ); // Calculate rotation about z axis
Mat R_z = (Mat_<double>(3,3) <<
cos(theta[2]), -sin(theta[2]), 0,
sin(theta[2]), cos(theta[2]), 0,
0, 0, 1 ); // Combined rotation matrix
Mat R = R_z * R_y * R_x; return R;
}
旋转矩阵到欧拉角的转换,要指明旋转顺序 (Z-Y-X 或 X-Y-Z 等 6 种),下面代码实现了和 MATLAB 中 rotm2euler 一样的功能,只是旋转顺序不同 (X-Y-Z)
// Checks if a matrix is a valid rotation matrix.
bool isRotationMatrix(Mat &R)
{
Mat Rt;
transpose(R, Rt);
Mat shouldBeIdentity = Rt * R;
Mat I = Mat::eye(3,3, shouldBeIdentity.type()); return norm(I, shouldBeIdentity) < 1e-6;
} // The result is the same as MATLAB except the order of the euler angles ( x and z are swapped ).
Vec3f rotationMatrixToEulerAngles(Mat &R)
{
assert(isRotationMatrix(R));
float sy = sqrt(R.at<double>(0,0) * R.at<double>(0,0) + R.at<double>(1,0) * R.at<double>(1,0) );
bool singular = sy < 1e-6; // If float x, y, z;
if (!singular) {
x = atan2(R.at<double>(2,1) , R.at<double>(2,2));
y = atan2(-R.at<double>(2,0), sy);
z = atan2(R.at<double>(1,0), R.at<double>(0,0));
} else {
x = atan2(-R.at<double>(1,2), R.at<double>(1,1));
y = atan2(-R.at<double>(2,0), sy);
z = 0;
}
return Vec3f(x, y, z);
}
4 四元数
4.1 定义
四元数本质是一种高阶的复数,普通复数有一个实部和一个虚部,而四元数有一个实部和三个虚部
$\quad q = s + x \mathbf{i} + y \mathbf{j} + z \mathbf{k}$,其中 $\mathbf{i}^2=\mathbf{j}^2=\mathbf{k}^2=\mathbf{ijk}=-1$
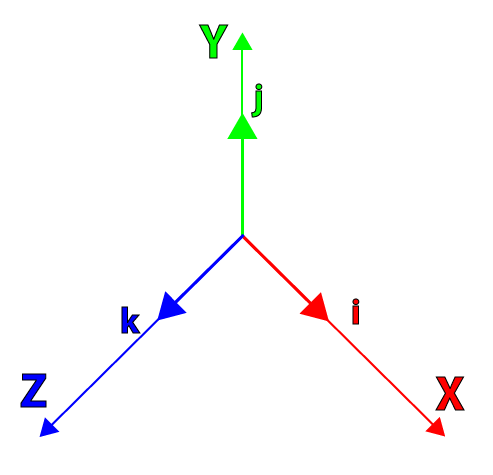
平面中任一点的旋转,可通过“左乘” 旋转向量来表示,如下:
$\quad p = a + b \mathbf{i} $,$q = cos \theta + \mathbf{i} sin \theta$
$\quad p^{\prime} = qp = a\cos\theta-b\sin\theta+(a\sin\theta+b\cos\theta)i $
推及空间中任一点的旋转,可通过“左乘”四元数来表示,如下:
$\quad p = [0, a \mathbf{i} + b \mathbf{j} + c \mathbf{k}]$,$q = [cos \theta, sin \theta \mathbf{v} ]$,其中 $\mathbf{v}$ 由 $\mathbf{i}, \mathbf{j}, \mathbf{k}$ 组合而成
$\quad p^{\prime} = qp$
4.2 实例
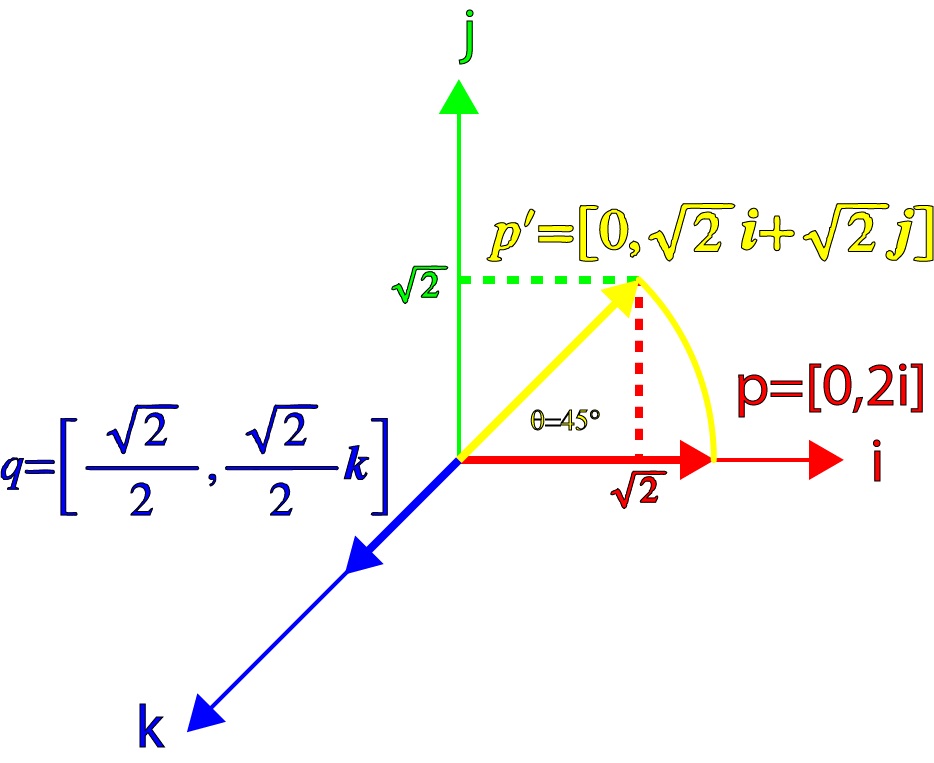
例1:当向量 p 围绕 k 轴在 i-j 平面内旋转 45°,表示该旋转的四元数为
$\quad q = \left[\dfrac{\sqrt{2}}{2}, \dfrac{\sqrt{2}}{2} \mathbf{k} \right] $
取 $p = [0, 2 \mathbf{i}]$,则 $p^{\prime} = qp = [0, \sqrt{2}\mathbf{i} + \sqrt{2} \mathbf{j}] $,如下图 p' 确实是 p 围绕 $\mathbf{k}$ 轴旋转 45° 得到的
例2:当向量 p 围绕 q 旋转 45°,且 q 中的向量 v 在 i-k 平面内和 p 成 45° 时,表示该旋转的四元数为
$\quad q = \left[ \dfrac{\sqrt{2}}{2}, \dfrac{\sqrt{2}}{2} \left(\dfrac{\sqrt{2}}{2} \mathbf{i} + \dfrac{\sqrt{2}}{2} \mathbf{k} \right) \right]$
取 $p = [0, 2 \mathbf{i}]$,则 $p^{\prime} = qp = [-1,\sqrt{2}\mathbf{i}+\mathbf{j}]$,可看出 $p^{\prime}$ 中向量模长为 $\sqrt{3}$,这不再是一个纯旋转的变换

但如果再“右乘” $q^{-1}$,则 $p^{\prime} = qpq^{-1} = [0,\mathbf{i}+\sqrt{2}\mathbf{j}+\mathbf{k} ]$
如下图,这又变成了一个纯旋转,但是旋转的角度是 90°,不是 45°

综上所述,向量 p 围绕任一轴 $\mathbf{v}$ 旋转 $\theta$,则表示该旋转的四元数形式为
$\quad q=\left[\cos\dfrac{\theta}{2},\sin\dfrac{\theta}{2} \mathbf{v}\right] $
4.3 转换关系
假定四元数 $q = s + x \mathbf{i} + y \mathbf{j} + z \mathbf{k}$,则旋转矩阵为
$\quad R = \begin{bmatrix}1-2(y^{2}+z^{2})&2(xy-sz)&2(xz+sy)\\2(xy+sz)&1-2(x^{2}+z^{2})&2(yz-sx)\\2(xz-sy)&2(yz+sx)&1-2(x^{2}+y^{2})\end{bmatrix} $
或另一种形式
$\quad R = \begin{bmatrix} s^2 + x^2 - y^2 -z^2 & 2(xy - sz) & 2(xz + sy) \\ 2(xy +sz) & s^2-x^2+y^2-z^2 & 2(yz - sx) \\ 2(xz-sy) & 2(yz+sx) & s^2-x^2-y^2+z^2 \end{bmatrix}$
附 - 欧拉角可视化
一个欧拉角的可视化链接 Euler Angle Visualization Tool,输入欧拉角可实时显示位姿变化
参考资料
《An Invitaton to 3D Vision》 ch2
《Robot Vision》ch13
OpenCV - 3D rigid/afine transforamtion
Rotation Matrix To Euler Angles
An Orge compatible class for euler angles
OpenCV 之 空间刚体变换的更多相关文章
- 在python3下使用OpenCV做离散余弦变换DCT及其反变换IDCT
对图像处理经常用到DCT, Python下有很多带有DCT算法包, 这里使用OpenCV的DCT做变换, 并简单置0部分数据, 再查看反变换图像的效果. import numpy as np impo ...
- 【几何/数学】概念的理解 —— (非)刚体变换((non-)rigid transformation)
1. 刚体变换与非刚体变换 What is a non-rigid transformation? 刚体变换(rigid transformation)一般分为如下几种: 平移对象,而不改变形状和大小 ...
- 在python3下对数据分块(8x8大小)使用OpenCV的离散余弦变换DCT
在MATLAB中有blkproc (blockproc)对数据处理, 在python下没找到对应的Function, 这里利用numpy 的split(hsplit和vsplit) 对数据分块处理成8 ...
- OpenCV——Sobel和拉普拉斯变换
Sobel变换和拉普拉斯变换都是高通滤波器. 什么是高通滤波器呢?就是保留图像的高频分量(变化剧烈的部分),抑制图像的低频分量(变化缓慢的部分).而图像变化剧烈的部分,往往反应的就是图像的边沿信息了. ...
- opencv利用hough概率变换拟合得到直线后,利用DDA算法得到直线上的像素点坐标
图片霍夫变换拟合得到直线后,怎样获得直线上的像素点坐标? 这是我今天在图像处理学习中遇到的问题,霍夫变换采用的概率霍夫变换,所以拟合得到的直线信息其实是直线的两个端点的坐标,这样一个比较直接的思路就是 ...
- opencv图像处理之gamma变换
import cv2 import numpy as np img=cv2.imread('4.jpg') def adjust_gamma(image, gamma=1.0): invGamma = ...
- OpenCV 霍夫线变换
#include "opencv2/highgui/highgui.hpp" #include "opencv2/imgproc/imgproc.hpp" #i ...
- 空间向量变换,以及OpenGL的glm库简单应用
测试项目请查看GitHub库 GLBIproject2/GLBIProject2_2
- OpenCV计算机视觉学习(11)——图像空间几何变换(图像缩放,图像旋转,图像翻转,图像平移,仿射变换,镜像变换)
如果需要处理的原图及代码,请移步小编的GitHub地址 传送门:请点击我 如果点击有误:https://github.com/LeBron-Jian/ComputerVisionPractice 图像 ...
随机推荐
- JVisualVM监控JVM-外网服务器
环境说明: a:阿里云服务器Centos8.2 b:JDK1.8 1:增加JMV运行参数 java -jar 启动时添加一下参数: -Djava.rmi.server.hostname=外网IP地址 ...
- spring boot的 yml和properties的对比
Spring Boot 虽然做了大量的工作来简化配置,但其配置依然是相当的复杂!支持的外部配置方式就有很多种,笔者没有去统计,也许是为了灵活使用吧. application.yml 和 appli ...
- elasticsearch如何设计集群
本文为博客园作者所写: 一寸HUI,个人博客地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/zsql/ 在写本文时就在想,如果让你负责一个elasticsearch集群,从零开始,你会从哪些方面 ...
- SpringBoot利用spring.profiles.active=@spring.active@不同环境下灵活切换配置文件
一.创建配置文件 配置文件结构:这里建三个配置文件,application.yml作为主配置文件配置所有共同的配置:-dev和-local分别配置两种环境下的不同配置内容,如数据库地址等. appli ...
- PAT-1147(Heaps)最大堆和最小堆的判断+构建树
Heaps PAT-1147 #include<iostream> #include<cstring> #include<string> #include<a ...
- Kubernetes 实战 —— 02. 开始使用 Kubernetes 和 Docker
创建.运行及共享容器镜像 P23 运行容器 P24 运行 P24 可以运行 Docker 客户端可执行文件来执行各种 Docker 命令.例如:可以试着从 Docker Hub 的公共镜像仓库拉取.运 ...
- [LeetCode 279.] Perfect Squres
LeetCode 279. Perfect Squres DP 是笨办法中的高效办法,又是一道可以被好办法打败的 DP 题. 题目描述 Given a positive integer n, find ...
- innerHTML,innerText
文本替换 <p id="p1">Hello World!</p><div>神经</div><h3 class="hh ...
- 字符串匹配-BF算法和KMP算法
声明:图片及内容基于https://www.bilibili.com/video/av95949609 BF算法 原理分析 Brute Force 暴力算法 用来在主串中查找模式串是否存以及出现位置 ...
- HDU_3333 Turing Tree 【线段树 + 离散化】
一.题目 Turing Tree 二.分析 这题主要还是在区间的处理上. 为了保证区间内的数没有重复的,那么可以对区间按右端点从小到大排序,这样对原数组处理时,尽量保证不重复的元素靠右(可以假设右端点 ...
