Spring系列15:Environment抽象
本文内容
- Environment抽象的2个重要概念
- @Profile 的使用
- @PropertySource 的使用
Environment抽象的2个重要概念
Environment 接口表示当前应用程序运行环境的接口。对应用程序环境的两个关键方面进行建模:配置文件( profiles )和属性(properties)。与属性访问相关的方法通过 PropertyResolver 超接口公开。环境对象的配置必须通过 ConfigurableEnvironment 接口完成,该接口从所有 AbstractApplicationContext 子类 getEnvironment() 方法返回
环境与配置文件
配置文件是一个命名的、逻辑的 bean 定义组,仅当给定的配置文件处于活动状态时才向容器注册。可以将 Bean 分配给配置文件,无论是在 XML 中定义还是通过注释 @Profile 定义;与配置文件相关的环境对象的作用是确定哪些配置文件(如果有)当前处于活动状态,以及哪些配置文件(如果有)默认应该是活动的。
环境与属性
属性在几乎所有应用程序中都发挥着重要作用,并且可能源自多种来源:属性文件、JVM 系统属性、系统环境变量、JNDI、servlet 上下文参数、属性对象、map等。与属性相关的环境对象的作用是为用户提供一个方便的服务接口,用于配置属性源并从中解析属性。
在 ApplicationContext 中管理的 Bean 可以注册为 EnvironmentAware 或 @Inject Environment,以便直接查询配置文件状态或解析属性。然而,在大多数情况下,应用程序级别的 bean 不需要直接与 Environment 交互,而是可能必须将 ${...} 属性值替换为属性占位符配置器,例如 PropertySourcesPlaceholderConfigurer,它本身是 EnvironmentAware 并且从 Spring 3.1 开始使用 context:property-placeholder 时默认注册 ,或是通过java bean的方式注册到容器中。
PropertySourcesPlaceholderConfigurer 分析可以阅读上一篇: Spring系列14:IoC容器的扩展点
接口源码粗览
接口继承关系
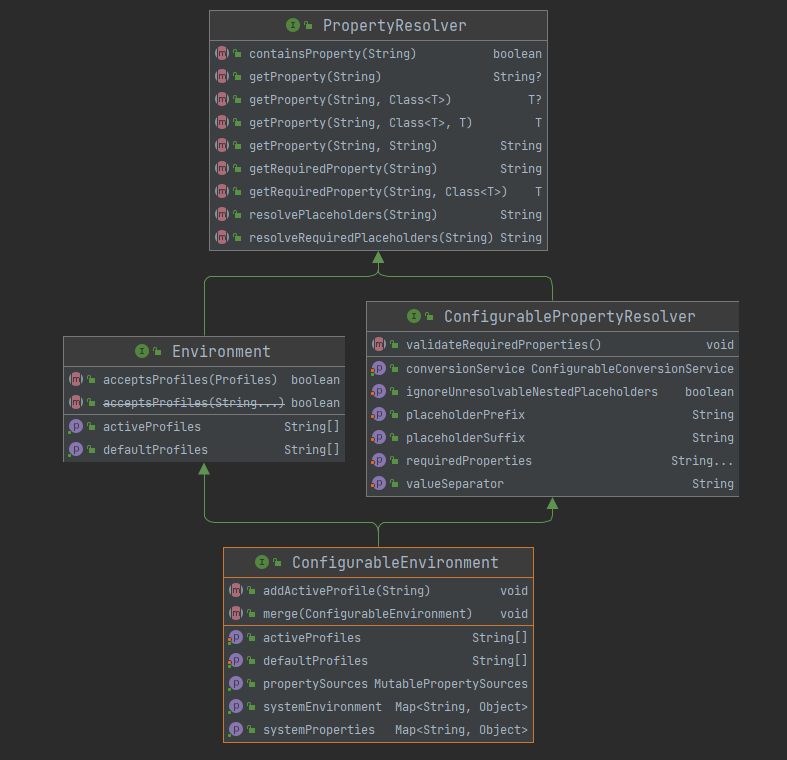
接口源码如下提供配置文件相关的接口方法,其继承的 PropertyResolver 提供属性相关的接口。
public interface Environment extends PropertyResolver {
// 当前激活的配置文件列表
// 设置系统属性值 spring.profiles.active=xxx 可激活
// 或是调用 ConfigurableEnvironment#setActiveProfiles(String...)激活
String[] getActiveProfiles();
// 当没有明确设置活动配置文件时,默认配置文件集返回为活动状态。
String[] getDefaultProfiles();
// 返回活动配置文件是否与给定的 Profiles 匹配
boolean acceptsProfiles(Profiles profiles);
}
PropertyResolver 是针对任何底层源解析属性的接口,主要接口方法如下。有一个非常重要的实现类是 PropertySourcesPlaceholderConfigurer 。
public interface PropertyResolver {
// 是否包含属性
boolean containsProperty(String key);
// 获取属性值
String getProperty(String key);
// 获取属性值带默认值
String getProperty(String key, String defaultValue);
// 获取属性值
<T> T getProperty(String key, Class<T> targetType);
// 获取属性值带默认值
<T> T getProperty(String key, Class<T> targetType, T defaultValue);
// 获取属性值
String getRequiredProperty(String key) throws IllegalStateException;
// 获取属性值
<T> T getRequiredProperty(String key, Class<T> targetType) throws IllegalStateException;
// 解析给定文本中的 ${...} 占位符
String resolvePlaceholders(String text);
// 解析给定文本中的 ${...} 占位符
String resolveRequiredPlaceholders(String text) throws IllegalArgumentException;
}
ConfigurablePropertyResolver 是大多数 PropertyResolver 类型都将实现的配置接口。提供用于访问和自定义将属性值从一种类型转换为另一种类型时使用的 ConversionService 的工具。
public interface ConfigurablePropertyResolver extends PropertyResolver {
ConfigurableConversionService getConversionService();
void setConversionService(ConfigurableConversionService conversionService);
// 设置占位符前缀 默认的 "${"怎么来的
void setPlaceholderPrefix(String placeholderPrefix);
// 设置占位符后缀 默认的 "}"怎么来的
void setPlaceholderSuffix(String placeholderSuffix);
// 设置占位符值分分隔符 默认的 ":"怎么来的
void setValueSeparator(@Nullable String valueSeparator);
void setIgnoreUnresolvableNestedPlaceholders(boolean ignoreUnresolvableNestedPlaceholders);
void setRequiredProperties(String... requiredProperties);
void validateRequiredProperties() throws MissingRequiredPropertiesException;
}
ConfigurableEnvironment是大多数环境类型都将实现的配置接口。提供用于设置活动和默认配置文件以及操作基础属性源的工具。允许客户端通过 ConfigurablePropertyResolver 超级接口设置和验证所需属性、自定义转换服务等。
public interface ConfigurableEnvironment extends Environment, ConfigurablePropertyResolver {
void setActiveProfiles(String... profiles);
void addActiveProfile(String profile);
void setDefaultProfiles(String... profiles);
MutablePropertySources getPropertySources();
// 关键的系统属性 System#getProperties()
Map<String, Object> getSystemProperties();
// 关键的系统环境 System#getenv()
Map<String, Object> getSystemEnvironment();
void merge(ConfigurableEnvironment parent);
}
@Profile 的使用
@Profile 表示当一个或多个profiles处于活动状态时,组件有资格注册。可以通过以下的方式设置活跃的一个或是多个配置文件:
- 编程方式:ConfigurableEnvironment#setActiveProfiles(String...)
- 启动参数: -Dspring.profiles.active="profile1,profile2"
- xml配置方式:
使用案例
来看一个实际场景:不同环境要求在容器中注入不同类型的的数据源,dev环境使用H2,生产环境prod使用Mysql,default环境使用 HSQL。
定义不同环境的数据源,并标识 @Profile
@Configuration
@ComponentScan
public class AppConfig {
// 测试环境数据源H2
@Profile("dev")
@Bean
public DataSource devDataSource() {
DataSource dataSource = new DataSource();
dataSource.setType("H2");
dataSource.setUrl("jdbc:h2:xxxxxx");
return dataSource;
}
// 生产环境数据源mysql
@Profile("prod")
@Bean
public DataSource prodDataSource() {
DataSource dataSource = new DataSource();
dataSource.setType("mysql");
dataSource.setUrl("jdbc:mysql:xxxxxx");
return dataSource;
}
// default 环境的 HSQL
@Profile("default")
@Bean
public DataSource defaultDataSource() {
DataSource dataSource = new DataSource();
dataSource.setType("HSQL");
dataSource.setUrl("jdbc:HSQL:xxxxxx");
return dataSource;
}
}
测试程序,首先不指定 profile
@org.junit.Test
public void test_profile() {
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext context =
new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext();
// context.getEnvironment().setActiveProfiles("prod");
context.register(AppConfig.class);
context.refresh();
DataSource dataSource = context.getBean(DataSource.class);
System.out.println(dataSource.getType());
context.close();
}
// 输出结果
HSQL
从结果可知,注册到容器中的 default 环境对应的 HSQL
指定 profile 为 prod ,观察输出
context.getEnvironment().setActiveProfiles("prod")
// 结果
mysql
从结果可知,注册到容器中的 prod 环境对应的 mysql 。
支持逻辑操作符
支持与或非操作组合
- !
- &
- |
组合&和|必须使用小括号
反例:production & us-east | eu-central
正例:production & (us-east | eu-central)
使用 @Profile 自定义组合注解
定义组合注解
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Profile("production")
public @interface Production {
}
使用
@Configuration
@Production
public class MyConfiguration {
}
如果@Configuration 类用@Profile 标记,则与该类关联的所有@Bean 方法和@Import 注释都将被绕过,除非一个或多个指定的配置文件处于活动状态。
使用xml指定 profile
标签中的 profile元素的可以指定配置文件。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans profile="prod"
xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<bean class="com.crab.spring.ioc.demo13.DataSource" id="dataSource">
<property name="type" value="mysql"/>
<property name="url" value="jdbc:mysql/xxxxx"/>
</bean>
</beans>
PropertySource 抽象
Spring 的 Environment 抽象在可配置的属性源层次结构上提供搜索操作。来看下案例如何从Spring 容器获取属性。
@org.junit.Test
public void test_property_source() {
ApplicationContext ctx = new GenericApplicationContext();
Environment env = ctx.getEnvironment();
boolean containsMyProperty = env.containsProperty("my-property");
System.out.println("Does my environment contain the 'my-property' property? " + containsMyProperty);
}
PropertySource 是对任何键值对源的简单抽象。Spring 的 StandardEnvironment 配置了两个 PropertySource 对象:
一个表示一组 JVM 系统属性 (System.getProperties())
一个表示一组系统环境变量 (System.getenv())
public class StandardEnvironment extends AbstractEnvironment {
/** System environment property source name: {@value}. */
public static final String SYSTEM_ENVIRONMENT_PROPERTY_SOURCE_NAME = "systemEnvironment";
/** JVM system properties property source name: {@value}. */
public static final String SYSTEM_PROPERTIES_PROPERTY_SOURCE_NAME = "systemProperties";
// 自定义适合任何标准的属性源自定义一组属性源
@Override
protected void customizePropertySources(MutablePropertySources propertySources) {
propertySources.addLast(
new PropertiesPropertySource(SYSTEM_PROPERTIES_PROPERTY_SOURCE_NAME, getSystemProperties()));
propertySources.addLast(
new SystemEnvironmentPropertySource(SYSTEM_ENVIRONMENT_PROPERTY_SOURCE_NAME, getSystemEnvironment()));
}
}
在属性源中查找属性是否存在的优先级顺序如下,从高到低:
- ServletConfig parameters (web上下文)
- ServletContext parameters (web.xml context-param entries)
- JNDI environment variables (
java:comp/env/entries) - JVM system properties (
-Dcommand-line arguments) - JVM system environment (operating system environment variables)
自定义 PropertySource
自定义 MyPropertySource 实现 Property 提供基于 Map 属性键值对的属性源
/**
* 自定义 PropertySource
* @author zfd
* @version v1.0
* @date 2022/1/22 22:13
* @关于我 请关注公众号 螃蟹的Java笔记 获取更多技术系列
*/
public class MyPropertySource extends PropertySource<Map<String, Object>> {
public MyPropertySource(String name, Map<String, Object> source) {
super(name, source);
}
public MyPropertySource(String name) {
super(name);
}
@Override
public Object getProperty(String name) {
return this.source.get(name);
}
}
添加到Spring 容器环境中,优先级最高
@org.junit.Test
public void test_custom_property_source() {
ConfigurableApplicationContext ctx = new GenericApplicationContext();
MutablePropertySources sources = ctx.getEnvironment().getPropertySources();
Map<String, Object> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("my-property", "xxx");
sources.addFirst(new MyPropertySource("myPropertySource",map));
// true
boolean containsMyProperty = ctx.getEnvironment().containsProperty("my-property");
System.out.println("Does my environment contain the 'my-property' property? " + containsMyProperty);
}
@PropertySource 使用
相比上面的编程式添加 PropertySource,@PropertySource 注解为将 PropertySource 添加到 Spring 的环境中提供了一种方便且声明性的机制。直接看案例。
app.properties配置
testBean.name=xxx
配置类
@Configuration
// 注入配置文件
@PropertySource("classpath:demo13/app.properties")
public class AppConfig3 {
@Autowired
private Environment env;
@Bean
public TestBean testBean() {
TestBean testBean = new TestBean();
testBean.setName(env.getProperty("testBean.name"));
return testBean;
}
}
测试结果观察
@org.junit.Test
public void test_property_source_annotation() {
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext context =
new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(AppConfig3.class);
TestBean testBean = context.getBean(TestBean.class);
System.out.println(testBean.getName());
}
// 结果
xxx
@PropertySource 中指定配置文件也是可以使用占位符${...}的。如果环境中属性值my.config.path已经存在则进行解析,否则使用默认值demo13。
@Configuration
// 注入配置文件
@PropertySource("classpath:${my.config.path:demo13}/app.properties")
public class AppConfig3 {}
总结
本文介绍了Spring中的Environment抽象的2个重要概念:Bean定义配置文件和属性源。同时介绍了@Profile使用和@PropertySource 的使用。
本篇源码地址: https://github.com/kongxubihai/pdf-spring-series/tree/main/spring-series-ioc/src/main/java/com/crab/spring/ioc/demo13
知识分享,转载请注明出处。学无先后,达者为先!
Spring系列15:Environment抽象的更多相关文章
- Spring Environment抽象
1:概述 Spring中Environment是Spring3.1版本引入的,是Spring核心框架定义的一个接口,用来表示整个应用运行时环境.该环境模型只接受两种应用环境profiles(配置文件) ...
- Spring系列之JDBC对不同数据库异常如何抽象的?
前言 使用Spring-Jdbc的情况下,在有些场景中,我们需要根据数据库报的异常类型的不同,来编写我们的业务代码.比如说,我们有这样一段逻辑,如果我们新插入的记录,存在唯一约束冲突,就会返回给客户端 ...
- Spring系列.Environment接口
Environment 接口介绍 在 Spring 中,Environment 接口主要管理应用程序两个方面的内容:profile 和 properties. profile 可以简单的等同于环境,比 ...
- Spring系列(零) Spring Framework 文档中文翻译
Spring 框架文档(核心篇1和2) Version 5.1.3.RELEASE 最新的, 更新的笔记, 支持的版本和其他主题,独立的发布版本等, 是在Github Wiki 项目维护的. 总览 历 ...
- 朱晔和你聊Spring系列S1E2:SpringBoot并不神秘
朱晔和你聊Spring系列S1E2:SpringBoot并不神秘 [编辑器丢失了所有代码的高亮,建议查看PDF格式文档] 文本我们会一步一步做一个例子来看看SpringBoot的自动配置是如何实现的, ...
- Spring 系列: Spring 框架简介 -7个部分
Spring 系列: Spring 框架简介 Spring AOP 和 IOC 容器入门 在这由三部分组成的介绍 Spring 框架的系列文章的第一期中,将开始学习如何用 Spring 技术构建轻量级 ...
- Java 集合系列 15 Map总结
java 集合系列目录: Java 集合系列 01 总体框架 Java 集合系列 02 Collection架构 Java 集合系列 03 ArrayList详细介绍(源码解析)和使用示例 Java ...
- Spring 系列: Spring 框架简介(转载)
Spring 系列: Spring 框架简介 http://www.ibm.com/developerworks/cn/java/wa-spring1/ Spring AOP 和 IOC 容器入门 在 ...
- Spring系列
Spring系列之访问数据库 阅读目录 一.概述 二.JDBC API的最佳实践 三.Spring对ORM的集成 回到顶部 一.概述 Spring的数据访问层是以统一的数据访问异常层体系为核心,结 ...
随机推荐
- Java 递归 常见24道题目 总结
1.N个台阶的走法递归[这里设为10个台阶] /** * N个台阶的走法递归 * <p> * 有个楼梯,台阶有10个,每次可以跳上1阶 或者 2阶 ,那么台阶的走法一共有多少种 */ @T ...
- 利用quake捡洞
quake一开漏洞全靠捡 定位资产 通过主域名定位子域名资产 domain:"target.com" 通过C段定位资产 ip: "1.1.1.1/24" 通过证 ...
- 关于包装类Integer,Long比较用==和equals的问题
所有整型包装类对象之间值的比较,全部使用 equals 方法比较. 说明:对于 Integer var = ? 在-128 至 127 之间的赋值,Integer 对象是在 IntegerCache. ...
- Android一句话 | ViewGroup事件分发
ViewGroup中可重写的关于事件分发的事件有dispatchTouchEvent,onTouchEvent,onInterceptTouchEvent和requestDisallowInterce ...
- Hybrid App(混合开发) 移动端开发调试
1.下载项目,npm install安装依赖 本地运行 npm run dev(根据具体packjson配 置而定) 2.局域网访问:http://172.20.9.35:8080/ 3.手机端访问: ...
- 【刷题-LeetCode】165 Compare Version Numbers
Compare Version Numbers Compare two version numbers version1 and version2. If *version1* > *versi ...
- Docker 实操
---恢复内容开始--- 一.简介 Linux容器作为一类操作系统层面的虚拟化技术成果,旨在立足于单一Linux主机交付多套隔离性Linux环境.与虚拟机不同,容器系统并不需要运行特定的访客操作系统. ...
- IoC容器-Bean管理(bean作用域)
IoC操作Bean管理(bean作用域) 1,在Spring里面,设置创建bean实例是单实例还是多实例 2,在Spring里面,默认情况下,bean是单实例对象 3,如何设置单实例还是多实例 (1) ...
- C++ 反汇编:关于Switch语句的优化措施
流程控制语句是C语言中最基本的判断语句,通常我们可以使用IF来构建多分支结构,但同样可以使用Switch语句构建,Switch语句针对多分支的优化措施有4种形式,分别是,IF-ELSE优化,有序线性优 ...
- python关于一些地址存储问题的知识
在一个类型进行转换后不能马上进行操作.要先进行存储否则操作无效 原理一个类型转换后成为一个新的类型但是没有人接受它属于空值所以做任何操作都无效 li=[] print(li.append) 也是报错的 ...
