集合之TreeSet(含JDK1.8源码分析)
一、前言
前面分析了Set接口下的hashSet和linkedHashSet,下面接着来看treeSet,treeSet的底层实现是基于treeMap的。
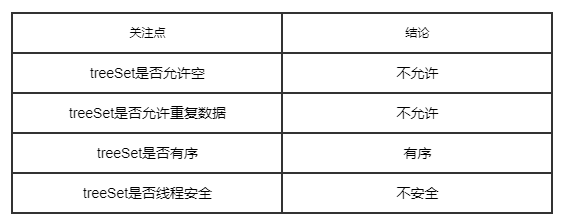
四个关注点在treeSet上的答案
二、treeSet的数据结构
因为treeSet的底层是基于treeMap的,所以treeSet的数据结构就是treeMap的数据结构:红黑树,因为前面已经分析过了treeMap的数据结构,这里不再赘述。集合之TreeMap(含JDK1.8源码分析)。
三、treeSet源码分析-属性及构造函数
3.1 类的继承关系
public class TreeSet<E> extends AbstractSet<E>
implements NavigableSet<E>, Cloneable, java.io.Serializable
说明:实现了NavigableSet接口,定义了一些共有的操作。
3.2 类的属性
/**
* The backing map.
*/
private transient NavigableMap<E,Object> m; // Dummy value to associate with an Object in the backing Map
private static final Object PRESENT = new Object(); //版本号
private static final long serialVersionUID = -2479143000061671589L;
说明:属性m为NavigableMap接口,treeSet的一些操作都是基于此map的,而前面分析treeMap的时候,发现treeMap实现了NavigableMap接口,所以hashSet中基于NavigableMap接口的操作实际上都是基于其实现类treeMap的操作,此处也是多态的概念。
treeMap的继承实现关系:
public class TreeMap<K,V>
extends AbstractMap<K,V>
implements NavigableMap<K,V>, Cloneable, java.io.Serializable
而对于Object类型的属性PRESENT,在分析hashSet的时候已经做了说明,因为map(treeSet中是NavigableMap)是存储key-value键值对的,所以PRESENT只是配一下key-value中value的位置,起个占位的作用,没有什么实际的意义,所有通过treeSet添加进来的key都对应同一个value值,PRESENT。
3.3 类的构造函数

1、TreeSet(NavigableMap<E,Object> m)型
/**
* Constructs a set backed by the specified navigable map.
*/
TreeSet(NavigableMap<E,Object> m) {
this.m = m;
}
说明:构建一个treeSet,基于navigable map(其实现类treeMap)实现的。
2、TreeSet()型
/**
* Constructs a new, empty tree set, sorted according to the
* natural ordering of its elements. All elements inserted into
* the set must implement the {@link Comparable} interface.
* Furthermore, all such elements must be <i>mutually
* comparable</i>: {@code e1.compareTo(e2)} must not throw a
* {@code ClassCastException} for any elements {@code e1} and
* {@code e2} in the set. If the user attempts to add an element
* to the set that violates this constraint (for example, the user
* attempts to add a string element to a set whose elements are
* integers), the {@code add} call will throw a
* {@code ClassCastException}.
*/
public TreeSet() {
this(new TreeMap<E,Object>());
}
说明:构建一个treeSet,排序是基于插入元素的自然顺序。
3、TreeSet(Comparator<? super E> comparator)型
/**
* Constructs a new, empty tree set, sorted according to the specified
* comparator. All elements inserted into the set must be <i>mutually
* comparable</i> by the specified comparator: {@code comparator.compare(e1,
* e2)} must not throw a {@code ClassCastException} for any elements
* {@code e1} and {@code e2} in the set. If the user attempts to add
* an element to the set that violates this constraint, the
* {@code add} call will throw a {@code ClassCastException}.
*
* @param comparator the comparator that will be used to order this set.
* If {@code null}, the {@linkplain Comparable natural
* ordering} of the elements will be used.
*/
public TreeSet(Comparator<? super E> comparator) {
this(new TreeMap<>(comparator));
}
说明:构建一个treeSet,排序是基于自定义的比较器的排序规则。
4、TreeSet(Collection<? extends E> c)型
/**
* Constructs a new tree set containing the elements in the specified
* collection, sorted according to the <i>natural ordering</i> of its
* elements. All elements inserted into the set must implement the
* {@link Comparable} interface. Furthermore, all such elements must be
* <i>mutually comparable</i>: {@code e1.compareTo(e2)} must not throw a
* {@code ClassCastException} for any elements {@code e1} and
* {@code e2} in the set.
*
* @param c collection whose elements will comprise the new set
* @throws ClassCastException if the elements in {@code c} are
* not {@link Comparable}, or are not mutually comparable
* @throws NullPointerException if the specified collection is null
*/
public TreeSet(Collection<? extends E> c) {
this();
addAll(c);
}
说明:构建一个treeSet,包含参数c中的元素,排序是基于元素的自然顺序。
5、TreeSet(SortedSet<E> s)型
/**
* Constructs a new tree set containing the same elements and
* using the same ordering as the specified sorted set.
*
* @param s sorted set whose elements will comprise the new set
* @throws NullPointerException if the specified sorted set is null
*/
public TreeSet(SortedSet<E> s) {
this(s.comparator());
addAll(s);
}
说明:构建一个treeSet,排序是基于SortedSet指定的排序规则。
四、treeSet源码分析-核心函数
4.1 增:add函数----存储元素
/**
* Adds the specified element to this set if it is not already present.
* More formally, adds the specified element {@code e} to this set if
* the set contains no element {@code e2} such that
* <tt>(e==null ? e2==null : e.equals(e2))</tt>.
* If this set already contains the element, the call leaves the set
* unchanged and returns {@code false}.
*
* @param e element to be added to this set
* @return {@code true} if this set did not already contain the specified
* element
* @throws ClassCastException if the specified object cannot be compared
* with the elements currently in this set
* @throws NullPointerException if the specified element is null
* and this set uses natural ordering, or its comparator
* does not permit null elements
*/
public boolean add(E e) {
return m.put(e, PRESENT)==null;
}
说明:添加一个原先set中未存在的元素,返回true,若是该元素已经存在,set不做改变,返回false。
可以看到其方法内部调用navigableMap的put方法,因为treeMap是其实现类,所以实际执行的时候,调用的是treeMap的put方法。可参见:集合之TreeMap(含JDK1.8源码分析)。
4.2 增:remove函数----删除元素
/**
* Removes the specified element from this set if it is present.
* More formally, removes an element {@code e} such that
* <tt>(o==null ? e==null : o.equals(e))</tt>,
* if this set contains such an element. Returns {@code true} if
* this set contained the element (or equivalently, if this set
* changed as a result of the call). (This set will not contain the
* element once the call returns.)
*
* @param o object to be removed from this set, if present
* @return {@code true} if this set contained the specified element
* @throws ClassCastException if the specified object cannot be compared
* with the elements currently in this set
* @throws NullPointerException if the specified element is null
* and this set uses natural ordering, or its comparator
* does not permit null elements
*/
public boolean remove(Object o) {
return m.remove(o)==PRESENT;
}
说明:若set中存在要删除的元素,删除,返回true,不存在,返回false。
可以看到其方法内部调用navigableMap的remove方法,因为treeMap是其实现类,所以实际执行的时候,调用的是treeMap的remove方法。可参见:集合之TreeMap(含JDK1.8源码分析)。
4.3 contains函数----是否存在该元素
/**
* Returns {@code true} if this set contains the specified element.
* More formally, returns {@code true} if and only if this set
* contains an element {@code e} such that
* <tt>(o==null ? e==null : o.equals(e))</tt>.
*
* @param o object to be checked for containment in this set
* @return {@code true} if this set contains the specified element
* @throws ClassCastException if the specified object cannot be compared
* with the elements currently in the set
* @throws NullPointerException if the specified element is null
* and this set uses natural ordering, or its comparator
* does not permit null elements
*/
public boolean contains(Object o) {
return m.containsKey(o);
}
说明:若set中存在该元素,返回true,不存在,返回false。
可以看到其方法内部调用navigableMap的containsKey方法,因为treeMap是其实现类,所以实际执行的时候,调用的是treeMap的containsKey方法。
五、总结
总之,treeSet底层是基于treeMap实现的,可以自定义比较器对元素进行排序,或是使用元素的自然顺序。
集合之TreeSet(含JDK1.8源码分析)的更多相关文章
- 集合之LinkedHashSet(含JDK1.8源码分析)
一.前言 上篇已经分析了Set接口下HashSet,我们发现其操作都是基于hashMap的,接下来看LinkedHashSet,其底层实现都是基于linkedHashMap的. 二.linkedHas ...
- 集合之HashSet(含JDK1.8源码分析)
一.前言 我们已经分析了List接口下的ArrayList和LinkedList,以及Map接口下的HashMap.LinkedHashMap.TreeMap,接下来看的是Set接口下HashSet和 ...
- 集合之HashMap(含JDK1.8源码分析)
一.前言 之前的List,讲了ArrayList.LinkedList,反映的是两种思想: (1)ArrayList以数组形式实现,顺序插入.查找快,插入.删除较慢 (2)LinkedList以链表形 ...
- 集合之LinkedList(含JDK1.8源码分析)
一.前言 LinkedList是基于链表实现的,所以先讲解一下什么是链表.链表原先是C/C++的概念,是一种线性的存储结构,意思是将要存储的数据存在一个存储单元里面,这个存储单元里面除了存放有待存储的 ...
- 集合之ArrayList(含JDK1.8源码分析)
一.ArrayList的数据结构 ArrayList底层的数据结构就是数组,数组元素类型为Object类型,即可以存放所有类型数据.我们对ArrayList类的实例的所有的操作(增删改查等),其底层都 ...
- 集合之TreeMap(含JDK1.8源码分析)
一.前言 前面所说的hashMap和linkedHashMap都不具备统计的功能,或者说它们的统计性能的时间复杂度都不是很好,要想对两者进行统计,需要遍历所有的entry,时间复杂度比较高,此时,我们 ...
- 集合之LinkedHashMap(含JDK1.8源码分析)
一.前言 大多数的情况下,只要不涉及线程安全问题,map都可以使用hashMap,不过hashMap有一个问题,hashMap的迭代顺序不是hashMap的存储顺序,即hashMap中的元素是无序的. ...
- 【集合框架】JDK1.8源码分析之HashMap(一) 转载
[集合框架]JDK1.8源码分析之HashMap(一) 一.前言 在分析jdk1.8后的HashMap源码时,发现网上好多分析都是基于之前的jdk,而Java8的HashMap对之前做了较大的优化 ...
- 【集合框架】JDK1.8源码分析之ArrayList详解(一)
[集合框架]JDK1.8源码分析之ArrayList详解(一) 一. 从ArrayList字表面推测 ArrayList类的命名是由Array和List单词组合而成,Array的中文意思是数组,Lis ...
随机推荐
- ESP8266串口和MQTT服务器消息互传(版本一) 单纯透传+保存WIFI账号信息
目标 制作一个ESP8266串口和MQTT相互透传的小WIFI,可用手机修改其连接的路由器,由此该模块可以任意加载到各种串口传输的单片机上,完成硬件到云端的传输. 1 实物图 2 MQTT网页测试客户 ...
- redis list 清空记录小技巧
redis list 清空记录小技巧 redis中的list操作命令中删除指定key中的所有记录命令: ltrim key 1 0 即 ltrim key start end 中的start要比e ...
- missing 1 required positional argument: 'on_delete'报错解决方案
最近在使用Python的Django框架开发web站点,通过models.py文件建表后,执行数据库迁移(命令行:mange.py makemigrations)时报错,下面是查看官方文档后找到的解决 ...
- python魔法方法、构造函数、序列与映射、迭代器、生成器
在Python中,所有以__双下划线包起来的方法,都统称为"魔术方法".比如我们接触最多的__init__,魔法方法也就是具有特殊功能的方法. 构造函数 构造函数不同于普通方法,将 ...
- Feature Extractor[googlenet v1]
1 - V1 google团队在模型上,更多考虑的是实用性,也就是如何能让强大的深度学习模型能够用在嵌入式或者移动设备上.传统的想增强模型的方法无非就是深度和宽度,而如果简单的增加深度和宽度,那么带来 ...
- 从零开始搭建django前后端分离项目 系列一(技术选型)
前言 最近公司要求基于公司的hadoop平台做一个关于电信移动网络的数据分析平台,整个项目需求大体分为四大功能模块:数据挖掘分析.报表数据查询.GIS地理化展示.任务监控管理.由于页面功能较复杂,所以 ...
- 2小时学会Spring Boot(IDE:eclipse)
一:安装STS插件 官网下载:点此下载STS 注意:STS版本必须与eclipse版本对应 安装教程:http://blog.csdn.net/cryhelyxx/article/details/53 ...
- iOS开发简记(6):storyboard的使用
从xib到storyboard,iOS界面开发的方式在变化. 这里记录怎么使用storyboard来完成简单的界面开发,比如实现一个“我”的简单界面. (1)新建storyboard 在新建文件向导中 ...
- public private protected default小结
public:可以被所有其他类所访问: private:只能被自己访问和修改: protected:自身.子类及同一个包中类可以访问: default:声明时没有加修饰符,同一包中的类可以访问:当子类 ...
- c++入门之const初步理解
关于const,首先建立这样的一个认识:const并不是定义了一个常量,而是定义了在某种环境下只读的变量.下面我们来区分一些东西: ; const int*p = # *p = ; i ...
