java框架之Spring(3)-JDBC模板使用&事务管理
JDBC模板使用
入门
1、导包,如要导入 Spring 的基本开发包、数据库驱动包、Spring 提供的 JDBC 模板包,如下:
2、测试:
@Test
public void test(){
// 创建连接池对象
DriverManagerDataSource driverManagerDataSource = new DriverManagerDataSource();
driverManagerDataSource.setDriverClassName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
driverManagerDataSource.setUrl("jdbc:mysql:///test");
driverManagerDataSource.setUsername("root");
driverManagerDataSource.setPassword("root");
// 创建 JDBC 模板对象
JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate = new JdbcTemplate(driverManagerDataSource);
// 通过模板对象操作数据库
jdbcTemplate.update("insert into user values(null,?,?)", "bob", 123);
}
将模板交给Spring
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<bean name="dataSource" class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DriverManagerDataSource">
<property name="driverClassName" value="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"/>
<property name="url" value="jdbc:mysql:///test"/>
<property name="username" value="root"/>
<property name="password" value="root"/>
</bean>
<bean name="jdbcTemplate" class="org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate">
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"/>
</bean>
</beans>
applicationContext.xml
package com.zze.test;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.junit.runner.RunWith;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate;
import org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DriverManagerDataSource;
import org.springframework.test.context.ContextConfiguration;
import org.springframework.test.context.junit4.SpringJUnit4ClassRunner;
@RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class)
@ContextConfiguration("classpath:applicationContext.xml")
public class Demo {
@Autowired
private JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate;
@Test
public void test() {
jdbcTemplate.update("update user set password=? where username=?", "345", "bob");
}
}
test
使用第三方连接池
DBCP配置
额外导入 jar 包:
配置:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<!--DBCP 配置-->
<bean name="dataSource" class="org.apache.commons.dbcp.BasicDataSource">
<property name="driverClassName" value="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"/>
<property name="url" value="jdbc:mysql:///test"/>
<property name="username" value="root"/>
<property name="password" value="root"/>
</bean>
<bean name="jdbcTemplate" class="org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate">
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"/>
</bean>
</beans>
applicationContext.xml
C3P0配置
额外导入 jar 包:
配置:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<!--C3P0连接池配置-->
<bean name="dataSource" class="com.mchange.v2.c3p0.ComboPooledDataSource">
<property name="driverClass" value="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"/>
<property name="jdbcUrl" value="jdbc:mysql:///test"/>
<property name="user" value="root"/>
<property name="password" value="root"/>
</bean>
<bean name="jdbcTemplate" class="org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate">
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"/>
</bean>
</beans>
applicationContext.xml
抽取JDBC配置到属性文件
有如下属性文件:
jdbc.driverClass=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver jdbc.url=jdbc:mysql:///test jdbc.username=root jdbc.password=root
jdbc.properties
方式一:
<bean class="org.springframework.beans.factory.config.PropertyPlaceholderConfigurer">
<property name="location" value="classpath:jdbc.properties"/>
</bean>
方式二:
<context:property-placeholder location="classpath:jdbc.properties"/>
接下来就可以通过如下方式引用到属性文件中的属性,例:
<bean name="dataSource" class="com.mchange.v2.c3p0.ComboPooledDataSource">
<property name="driverClass" value="${jdbc.driverClass}"/>
<property name="jdbcUrl" value="${jdbc.url}"/>
<property name="user" value="${jdbc.username}"/>
<property name="password" value="${jdbc.password}"/>
</bean>
CRUD操作
package com.zze.test;
import com.zze.bean.User;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.junit.runner.RunWith;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate;
import org.springframework.jdbc.core.RowMapper;
import org.springframework.test.context.ContextConfiguration;
import org.springframework.test.context.junit4.SpringJUnit4ClassRunner;
import java.sql.ResultSet;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import java.util.List;
@RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class)
@ContextConfiguration("classpath:applicationContext.xml")
public class Demo {
@Autowired
private JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate;
/**
* 保存
*/
@Test
public void test1() {
jdbcTemplate.update("insert into user values (null,?,?)", "bob", "123");
}
/**
* 更新
*/
@Test
public void test2() {
jdbcTemplate.update("update user set password=? where username=?", "346", "bob");
}
/**
* 删除
*/
@Test
public void test3() {
jdbcTemplate.update("delete from user where username=?", "bob");
}
/**
* 查询首行首列
*/
@Test
public void test4() {
Integer integer = jdbcTemplate.queryForObject("select COUNT(1) from user", Integer.class);
System.out.println(integer);
}
/**
* 查询一条数据封装到单个对象
*/
@Test
public void test5() {
User user = jdbcTemplate.queryForObject("select * from user where username=?", new RowMapper<User>() {
@Override
public User mapRow(ResultSet rs, int rowNum) throws SQLException {
User user = new User();
user.setId(rs.getInt("id"));
user.setUsername(rs.getString("username"));
user.setPassword(rs.getString("password"));
return user;
}
}, "bob");
System.out.println(user);
}
/**
* 查询多条记录封装到集合
*/
@Test
public void test6() {
List<User> userList = jdbcTemplate.query("select * from user", new RowMapper<User>() {
@Override
public User mapRow(ResultSet rs, int rowNum) throws SQLException {
User user = new User();
user.setId(rs.getInt("id"));
user.setUsername(rs.getString("username"));
user.setPassword(rs.getString("password"));
return user;
}
});
System.out.println(userList);
}
}
事务管理
事务回顾
参见【数据库事务了解一下】。
Spring事务管理API
- PlatformTransactionManager:平台事务管理器
接口,是 Spring 用于管理事务真正的对象。
DataSourceTransactionManager:底层使用JDBC管理事务。
HibernateTransactionManager:底层使用Hibernate管理事务。
- TransactionDefinition:事务定义信息
用于定义事务的相关的信息,隔离级别、超时信息、传播行为、是否只读。
- TransactionStatus:事务的状态
用于记录在事务管理过程中,事务的状态的对象。
Spring进行事务管理的时候,首先平台事务管理器根据事务定义信息进行事务的管理,在事务管理过程中,产生各种状态,将这些状态的信息记录到事务状态的对象中。
事务的传播行为
Spring 中提供了七种事务的传播行为,可分为如下三类:
- 保证多个操作在同一个事务中:
PROPAGATION_REQUIRED :默认值,如果A中有事务,使用A中的事务,如果A没有,创建一个新的事务,将操作包含进来
PROPAGATION_SUPPORTS :支持事务,如果A中有事务,使用A中的事务。如果A没有事务,不使用事务。
PROPAGATION_MANDATORY :如果A中有事务,使用A中的事务。如果A没有事务,抛出异常。
- 保证多个操作不在同一个事务中:
PROPAGATION_REQUIRES_NEW :如果A中有事务,将A的事务挂起(暂停),创建新事务,只包含自身操作。如果A中没有事务,创建一个新事务,包含自身操作。
PROPAGATION_NOT_SUPPORTED :如果A中有事务,将A的事务挂起。不使用事务管理。
PROPAGATION_NEVER :如果A中有事务,报异常。
- 嵌套式事务:
PROPAGATION_NESTED :嵌套事务,如果A中有事务,按照A的事务执行,执行完成后,设置一个保存点,执行B中的操作,如果没有异常,执行通过,如果有异常,可以选择回滚到最初始位置,也可以回滚到保存点。
搭建Spring的事务管理的环境
准备
创建 account 表并初始化如下数据:

下面代码模拟一个转账场景:
package com.zze.dao;
public interface AccountDao {
/**
* 转出
* @param username 转出账户的用户名
* @param money 转出金额
*/
void outMoney(String username,Double money);
/**
* 转入
* @param username 转入账户的用户名
* @param money 转入金额
*/
void inMoney(String username, Double money);
}
com.zze.dao.AccountDao
package com.zze.dao.impl;
import com.zze.dao.AccountDao;
import org.springframework.jdbc.core.support.JdbcDaoSupport;
public class AccountDaoImpl extends JdbcDaoSupport implements AccountDao {
@Override
public void outMoney(String username, Double money) {
this.getJdbcTemplate().update("update account set money=money-? where username=?", money, username);
}
@Override
public void inMoney(String username, Double money) {
this.getJdbcTemplate().update("update account set money=money+? where username=?", money, username);
}
}
com.zze.dao.impl.AccountDaoImpl
package com.zze.service;
public interface AccountService {
/**
* 转账
* @param usernameFrom 转账来源账户
* @param usernameTo 转账目标账户
* @param money 转账金额
*/
void transfer(String usernameFrom,String usernameTo,Double money);
}
com.zze.service.AccountService
package com.zze.service.impl;
import com.zze.dao.AccountDao;
import com.zze.service.AccountService;
public class AccountServiceImpl implements AccountService {
private AccountDao accountDao;
public void setAccountDao(AccountDao accountDao) {
this.accountDao = accountDao;
}
@Override
public void transfer(String usernameFrom, String usernameTo, Double money) {
accountDao.outMoney(usernameFrom, money);
accountDao.inMoney(usernameTo,money);
}
}
com.zze.service.impl.AccountServiceImpl
jdbc.driverClass=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver jdbc.url=jdbc:mysql:///test jdbc.username=root jdbc.password=root
jdbc.properties
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd">
<context:property-placeholder location="classpath:jdbc.properties"/>
<bean name="dataSource" class="com.mchange.v2.c3p0.ComboPooledDataSource">
<property name="driverClass" value="${jdbc.driverClass}"/>
<property name="jdbcUrl" value="${jdbc.url}"/>
<property name="user" value="${jdbc.username}"/>
<property name="password" value="${jdbc.password}"/>
</bean>
<!--
<bean name="jdbcTemplate" class="org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate">
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"/>
</bean>
-->
<bean name="accountDao" class="com.zze.dao.impl.AccountDaoImpl">
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"/>
<!--<property name="jdbcTemplate" ref="jdbcTemplate"/>-->
</bean>
<bean name="accountService" class="com.zze.service.impl.AccountServiceImpl">
<property name="accountDao" ref="accountDao"/>
</bean>
</beans>
applicationContext.xml
package com.zze.test;
import com.zze.service.AccountService;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.junit.runner.RunWith;
import org.springframework.test.context.ContextConfiguration;
import org.springframework.test.context.junit4.SpringJUnit4ClassRunner;
import javax.annotation.Resource;
@RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class)
@ContextConfiguration("classpath:applicationContext.xml")
public class Demo {
@Resource(name = "accountService")
private AccountService accountService;
@Test
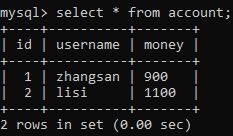
public void test(){
// zhangsan 给 lisi 转账 100
accountService.transfer("zhangsan","lisi",100d);
}
}
执行结果如下:
test
编程式事务管理
1、修改配置:
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd">
<context:property-placeholder location="classpath:jdbc.properties"/>
<!--配置 C3p0 连接池-->
<bean name="dataSource" class="com.mchange.v2.c3p0.ComboPooledDataSource">
<property name="driverClass" value="${jdbc.driverClass}"/>
<property name="jdbcUrl" value="${jdbc.url}"/>
<property name="user" value="${jdbc.username}"/>
<property name="password" value="${jdbc.password}"/>
</bean>
<!--配置事务管理器-->
<bean name="transactionManager" class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager">
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"/>
</bean>
<!--配置事务的管理的模板类-->
<bean name="transactionTemplate" class="org.springframework.transaction.support.TransactionTemplate">
<property name="transactionManager" ref="transactionManager"/>
</bean>
<bean name="accountDao" class="com.zze.dao.impl.AccountDaoImpl">
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"/>
</bean>
<bean name="accountService" class="com.zze.service.impl.AccountServiceImpl">
<property name="accountDao" ref="accountDao"/>
<!--注入事务管理模板-->
<property name="transactionTemplate" ref="transactionTemplate"/>
</bean>
</beans>
applicationContext.xml
2、修改代码模拟异常并使用事务:
package com.zze.service.impl;
import com.zze.dao.AccountDao;
import com.zze.service.AccountService;
import org.springframework.transaction.TransactionStatus;
import org.springframework.transaction.support.TransactionCallbackWithoutResult;
import org.springframework.transaction.support.TransactionTemplate;
public class AccountServiceImpl implements AccountService {
private AccountDao accountDao;
private TransactionTemplate transactionTemplate;
public void setAccountDao(AccountDao accountDao) {
this.accountDao = accountDao;
}
public void setTransactionTemplate(TransactionTemplate transactionTemplate) {
this.transactionTemplate = transactionTemplate;
}
@Override
public void transfer(String usernameFrom, String usernameTo, Double money) {
transactionTemplate.execute(new TransactionCallbackWithoutResult() {
@Override
protected void doInTransactionWithoutResult(TransactionStatus transactionStatus) {
accountDao.outMoney(usernameFrom, money);
// 模拟过程中异常
int i = 1 / 0;
accountDao.inMoney(usernameTo, money);
}
});
}
}
com.zze.service.impl.AccountServiceImpl
3、测试:
package com.zze.test;
import com.zze.service.AccountService;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.junit.runner.RunWith;
import org.springframework.test.context.ContextConfiguration;
import org.springframework.test.context.junit4.SpringJUnit4ClassRunner;
import javax.annotation.Resource;
@RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class)
@ContextConfiguration("classpath:applicationContext.xml")
public class Demo {
@Resource(name = "accountService")
private AccountService accountService;
@Test
public void test(){
// zhangsan 给 lisi 转账 100
accountService.transfer("zhangsan","lisi",100d);
// 此时表数据将不会发生变化
}
}
test
声明式事务管理-XML
1、修改配置:
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
xmlns:tx="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx"
xsi:schemaLocation="
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx/spring-tx.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd">
<context:property-placeholder location="classpath:jdbc.properties"/>
<!--配置 C3p0 连接池-->
<bean name="dataSource" class="com.mchange.v2.c3p0.ComboPooledDataSource">
<property name="driverClass" value="${jdbc.driverClass}"/>
<property name="jdbcUrl" value="${jdbc.url}"/>
<property name="user" value="${jdbc.username}"/>
<property name="password" value="${jdbc.password}"/>
</bean>
<!--配置事务管理器-->
<bean name="transactionManager" class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager">
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"/>
</bean>
<!--配置事务的通知/增强-->
<tx:advice id="txAdvice" transaction-manager="transactionManager">
<tx:attributes>
<!--事务管理规则-->
<tx:method name="save*" propagation="REQUIRED"/>
<tx:method name="update*" propagation="REQUIRED"/>
<tx:method name="delete*" propagation="REQUIRED"/>
<tx:method name="find*" read-only="true"/>
<!--
name : 匹配方法名
read-only : 为 true 时表示只做只读操作
propagation : 事务的传播行为
timeout : 事务过期时间,为 -1 时不会过期
isolation : 事务的隔离级别
-->
<tx:method name="*" propagation="REQUIRED" isolation="DEFAULT" timeout="-1"/>
</tx:attributes>
</tx:advice>
<!--AOP 配置-->
<aop:config>
<aop:pointcut id="pc_account" expression="execution(* com.zze.service.AccountService.*(..))"/>
<aop:advisor advice-ref="txAdvice" pointcut-ref="pc_account"/>
</aop:config>
<bean name="accountDao" class="com.zze.dao.impl.AccountDaoImpl">
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"/>
</bean>
<bean name="accountService" class="com.zze.service.impl.AccountServiceImpl">
<property name="accountDao" ref="accountDao"/>
</bean>
</beans>
applicationContext.xml
2、修改代码模拟异常:
package com.zze.service.impl;
import com.zze.dao.AccountDao;
import com.zze.service.AccountService;
public class AccountServiceImpl implements AccountService {
private AccountDao accountDao;
public void setAccountDao(AccountDao accountDao) {
this.accountDao = accountDao;
}
@Override
public void transfer(String usernameFrom, String usernameTo, Double money) {
accountDao.outMoney(usernameFrom, money);
// 模拟过程中异常
int i = 1 / 0;
accountDao.inMoney(usernameTo, money);
}
}
com.zze.service.impl.AccountServiceImpl
3、测试:
package com.zze.test;
import com.zze.service.AccountService;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.junit.runner.RunWith;
import org.springframework.test.context.ContextConfiguration;
import org.springframework.test.context.junit4.SpringJUnit4ClassRunner;
import javax.annotation.Resource;
@RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class)
@ContextConfiguration("classpath:applicationContext.xml")
public class Demo {
@Resource(name = "accountService")
private AccountService accountService;
@Test
public void test(){
// zhangsan 给 lisi 转账 100
accountService.transfer("zhangsan","lisi",100d);
// 此时表数据将不会发生变化
}
}
test
声明式事务管理-注解
1、修改配置:
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:tx="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx/spring-tx.xsd">
<context:property-placeholder location="classpath:jdbc.properties"/>
<!--配置 C3p0 连接池-->
<bean name="dataSource" class="com.mchange.v2.c3p0.ComboPooledDataSource">
<property name="driverClass" value="${jdbc.driverClass}"/>
<property name="jdbcUrl" value="${jdbc.url}"/>
<property name="user" value="${jdbc.username}"/>
<property name="password" value="${jdbc.password}"/>
</bean>
<!--配置事务管理器-->
<bean name="transactionManager" class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager">
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"/>
</bean>
<!--开启注解事务-->
<tx:annotation-driven transaction-manager="transactionManager"/>
<bean name="accountDao" class="com.zze.dao.impl.AccountDaoImpl">
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"/>
</bean>
<bean name="accountService" class="com.zze.service.impl.AccountServiceImpl">
<property name="accountDao" ref="accountDao"/>
</bean>
</beans>
applicationContext.xml
2、修改代码模拟异常并添加事务注解:
package com.zze.service.impl;
import com.zze.dao.AccountDao;
import com.zze.service.AccountService;
import org.springframework.transaction.annotation.Isolation;
import org.springframework.transaction.annotation.Propagation;
import org.springframework.transaction.annotation.Transactional;
// 业务类上添加注解使用事务
@Transactional(isolation=Isolation.DEFAULT,propagation = Propagation.REQUIRED)
public class AccountServiceImpl implements AccountService {
private AccountDao accountDao;
public void setAccountDao(AccountDao accountDao) {
this.accountDao = accountDao;
}
@Override
public void transfer(String usernameFrom, String usernameTo, Double money) {
accountDao.outMoney(usernameFrom, money);
// 模拟过程中异常
int i = 1 / 0;
accountDao.inMoney(usernameTo, money);
}
}
com.zze.service.impl.AccountServiceImpl
3、测试:
package com.zze.test;
import com.zze.service.AccountService;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.junit.runner.RunWith;
import org.springframework.test.context.ContextConfiguration;
import org.springframework.test.context.junit4.SpringJUnit4ClassRunner;
import javax.annotation.Resource;
@RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class)
@ContextConfiguration("classpath:applicationContext.xml")
public class Demo {
@Resource(name = "accountService")
private AccountService accountService;
@Test
public void test(){
// zhangsan 给 lisi 转账 100
accountService.transfer("zhangsan","lisi",100d);
// 此时表数据将不会发生变化
}
}
test
java框架之Spring(3)-JDBC模板使用&事务管理的更多相关文章
- 四、spring的JDBC模板和事务管理
Spring的JDBC模板 Spring是JavaEE开发的一站式框架,对各种持久化技术都提供了简单的模板 ORM持久化技术 模板类 JDBC org.springframework.jdbc.cor ...
- Java学习笔记43(Spring的jdbc模板)
在之前的学习中,我们执行sql语句,需要频繁的开流,关流比较麻烦,为了更加的简化代码,我们使用Spring 的jdbc模板jdbcTemplate来简化我们的代码量:需要导入的包有: 我们在之前的dr ...
- Java - 框架之 Spring
一. IOC 和 DI IOC : 控制反转,将对象的创建权反转给了 Spring.DI : 依赖注入,前提是必须要有 IOC 的环境,Spring 管理这个类的时候将类的依赖的属性注入(设置)进来 ...
- Spring的jdbc模板1
Spring是EE开发的一站式框架,有EE开发的每一层解决方案.Spring对持久层也提供了解决方案:ORM模块和jdbc模块,ORM模块在整合其他框架的时候使用 Spring提供了很多的模板用于简化 ...
- 创建JDBC模板简化代码、JDBC应用的事务管理以及连接池的作用
一.创建JDBC模板简化代码 一个简单的查询.要做这么一大堆事情,并且还要处理异常,我们不防来梳理一下: 1.获取connection 2.获取statement 3.获取resultset 4 ...
- 【Spring实战】—— 16 基于JDBC持久化的事务管理
前面讲解了基于JDBC驱动的Spring的持久化管理,本篇开始则着重介绍下与事务相关的操作. 通过本文你可以了解到: 1 Spring 事务管理的机制 2 基于JDBC持久化的事务管理 Spring的 ...
- Spring 简单而强大的事务管理功能
开始之前 关于本教程 本教程将深入讲解 Spring 简单而强大的事务管理功能,包括编程式事务和声明式事务.通过对本教程的学习,您将能够理解 Spring 事务管理的本质,并灵活运用之. 先决条件 本 ...
- 事务隔离级别与传播机制,spring+mybatis+atomikos实现分布式事务管理
1.事务的定义:事务是指多个操作单元组成的合集,多个单元操作是整体不可分割的,要么都操作不成功,要么都成功.其必须遵循四个原则(ACID). 原子性(Atomicity):即事务是不可分割的最小工作单 ...
- Spring事务隔离级别与传播机制详解,spring+mybatis+atomikos实现分布式事务管理
原创说明:本文为本人原创作品,绝非他处转载,转账请注明出处 1.事务的定义:事务是指多个操作单元组成的合集,多个单元操作是整体不可分割的,要么都操作不成功,要么都成功.其必须遵循四个原则(ACID). ...
随机推荐
- go 源码学习之---Tail 源码分析
已经有两个月没有写博客了,也有好几个月没有看go相关的内容了,由于工作原因最近在做java以及大数据相关的内容,导致最近工作较忙,博客停止了更新,正好想捡起之前go的东西,所以找了一个源码学习 这个也 ...
- OFTP简介
OFTP协议由欧洲汽车标准组织Odette创建,第一个版本于1986年发布,旨在用于当时可用的网络服务,主要是X.25服务.Odette还考虑到VAN(增值网络)服务可能是通信链的一部分.OFTP是汽 ...
- matplotlib绘图不显示问题解决plt.show()
最近在看<Python数据分析>这本书,而自己写代码一直用的是Pycharm,在练习的时候就碰到了plot()绘图不能显示出来的问题.网上翻了一下找到知乎上一篇回答,试了一下好像不行,而且 ...
- 程序猿必备的10款超有趣的SVG绘制动画赏析
SVG作为时下比较新颖的技术标准,已经建立了很多基于SVG的前端项目.由于SVG在绘制路径上非常灵活,我们将很多网页上的元素使用SVG来绘制而成,有各种人物.小图标.小动画等等.今天我们收集了10个非 ...
- 解决Warning Couldn't flush user prefs: java.util.prefs.BackingStoreException: Couldn't get file lock.
系统:Ubuntu 16.04 LTS 环境:vscode+java extension pack打开了一个gradle的java项目:另外,用一个terminal启动了groovysh 报错: gr ...
- 【java】[文件上传jar包]commons-fileUpload组件解决文件上传(文件名)乱码问题
response.setContentType("text/html; charset=UTF-8"); Boolean isMultipart = ServletFileUpl ...
- 100BASE-TX、100Base-FX等含义
100BASE-TX:双绞线,使用两对非屏蔽双绞线或两对1类屏蔽双绞线连接,传输距离100米 100Base-FX,是在光纤上实现的100 Mbps以太网标准,其中F指示光纤,IEEE标准为802.3 ...
- 微信jssdk常见错误及解决方法
调用config 接口的时候传入参数 debug: true 可以开启debug模式,页面会alert出错误信息.以下为常见错误及解决方法: invalid url domain当前页面所在域名与使用 ...
- 【nodejs】初识 NodeJS(三)
上节我们将 http 服务器(server.js)和请求路由模块(route.js)整合在一起了,当然这还不够,路由,顾名思义,是指我们要针对不同的 url 有不同的处理方式. 请求处理程序模块(re ...
- 给centos7.3添加中文拼音输入法输入汉字
https://jingyan.baidu.com/article/86f4a73eaa0a6337d6526985.html
