MINST手写数字识别(一)—— 全连接网络
这是一个简单快速入门教程——用Keras搭建神经网络实现手写数字识别,它大部分基于Keras的源代码示例 minst_mlp.py.
1、安装依赖库
首先,你需要安装最近版本的Python,再加上一些包Keras,numpy,matplotlib和jupyter.你可以安装这些报在全局,但是我建议安装它们在virtualenv虚拟环境,
这基本上封装了一个完全孤立的Python环境。
安装Python包管理器
sudo easy_install pip
安装virtualenv
pip install virtualenv
使用cd ~进入主目录,并创建一个名为kerasenv的虚拟环境
virtualenv kerasenv
再激活这个虚拟环境
source kerasenv/bin/activate
现在你可以安装前面提到的包到这个环境
pip install numpy jupyter keras matplotlib
2、搭建神经网络
以下代码都在Google Colab中运行
2.1 导入一些依赖
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
plt.rcParams['figure.figsize'] = (7,7) # Make the figures a bit bigger from keras.datasets import mnist
from keras.models import Sequential
from keras.layers.core import Dense, Dropout, Activation
from keras.utils import np_utils
2.2 装载训练数据
nb_classes = 10 # the data, shuffled and split between tran and test sets
(X_train, y_train), (X_test, y_test) = mnist.load_data()
print("X_train original shape", X_train.shape)
print("y_train original shape", y_train.shape)
结果:
Downloading data from https://s3.amazonaws.com/img-datasets/mnist.npz
11493376/11490434 [==============================] - 0s 0us/step
X_train original shape (60000, 28, 28)
y_train original shape (60000,)
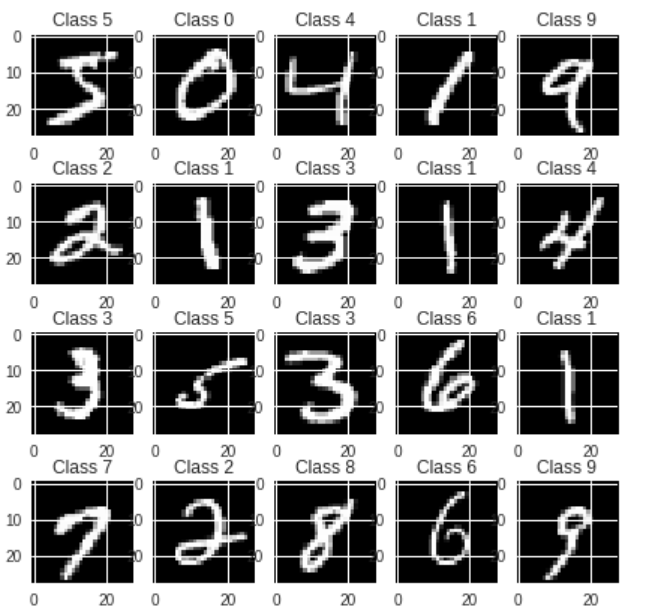
让我们看看训练集中的一些例子:
for i in range(20):
plt.subplot(4,5,i+1)
plt.imshow(X_train[i], cmap='gray', interpolation='none')
plt.title("Class {}".format(y_train[i]))
2.3 格式化训练数据
对于每一个训练样本我们的神经网络得到单个的数组,所以我们需要将28x28的图片变形成784的向量,我们还将输入从[0,255]缩到[0,1].
X_train = X_train.reshape(60000, 784)
X_test = X_test.reshape(10000, 784)
X_train = X_train.astype('float32')
X_test = X_test.astype('float32')
X_train /= 255
X_test /= 255
print("Training matrix shape", X_train.shape)
print("Testing matrix shape", X_test.shape)
结果:
Training matrix shape (60000, 784)
Testing matrix shape (10000, 784)
将目标矩阵变成one-hot格式
0 -> [1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0]
1 -> [0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0]
2 -> [0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0]
etc.
Y_train = np_utils.to_categorical(y_train, nb_classes)
Y_test = np_utils.to_categorical(y_test, nb_classes)
2.4 搭建神经网络
2.4.1 搭建三层全连接网络
我们将做一个简单的三层全连接网络,如下:
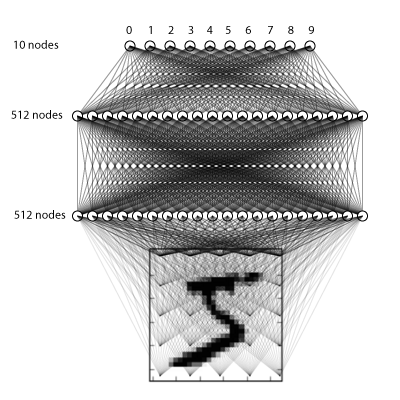
model = Sequential()
model.add(Dense(512, input_shape=(784,)))
model.add(Activation('relu')) # An "activation" is just a non-linear function applied to the output
# of the layer above. Here, with a "rectified linear unit",
# we clamp all values below 0 to 0. model.add(Dropout(0.2)) # Dropout helps protect the model from memorizing or "overfitting" the training data
model.add(Dense(512))
model.add(Activation('relu'))
model.add(Dropout(0.2))
model.add(Dense(10))
model.add(Activation('softmax')) # This special "softmax" activation among other things,
# ensures the output is a valid probaility distribution, that is
# that its values are all non-negative and sum to 1.
结果:
WARNING:tensorflow:From /usr/local/lib/python3.6/dist-packages/tensorflow/python/framework/op_def_library.py:263: colocate_with (from tensorflow.python.framework.ops) is deprecated and will be removed in a future version.
Instructions for updating:
Colocations handled automatically by placer.
WARNING:tensorflow:From /usr/local/lib/python3.6/dist-packages/keras/backend/tensorflow_backend.py:3445: calling dropout (from tensorflow.python.ops.nn_ops) with keep_prob is deprecated and will be removed in a future version.
Instructions for updating:
Please use `rate` instead of `keep_prob`. Rate should be set to `rate = 1 - keep_prob`.
2.4.2 编译模型
Keras是建立在Theano(现在TensorFlow也是),这两个包都允许你定义计算图,然后高效地在CPU或GPU上编译和运行,而没有Python解释器地开销。
当编译一个模型,Keras要求你确定损失函数和优化器,我使用的是分类交叉熵(categorical crossentropy),它是一种非常适合比较两个概率分布的函数。
在这里,我们的预测是十个不同数字的概率分布(例如,80%认为这个图片是3,10%认为是2,5%认为是1等),目标是一个概率分布,正确类别为100%,其他所有类别为0。交叉熵是度量两个概率分布差异程度的方法,详情wiki。
优化器帮助模型快速的学习,同时防止“卡住“和“爆炸”的情况,我们不讨论其太多的细节,但是“adam”是一个经常使用的好的选择。
model.compile(loss='categorical_crossentropy', optimizer='adam')
2.4.3 训练模型!
这是有趣的部分:你可以喂入之前加载好的训练集到模型,它将学习如何分类数字.
model.fit(X_train, Y_train,
batch_size=128, epochs=4,
verbose=1,
validation_data=(X_test, Y_test))
结果:
Train on 60000 samples, validate on 10000 samples
Epoch 1/4
60000/60000 [==============================] - 10s 171us/step - loss: 0.0514 - val_loss: 0.0691
Epoch 2/4
60000/60000 [==============================] - 10s 170us/step - loss: 0.0410 - val_loss: 0.0700
Epoch 3/4
60000/60000 [==============================] - 11s 177us/step - loss: 0.0349 - val_loss: 0.0750
Epoch 4/4
60000/60000 [==============================] - 11s 184us/step - loss: 0.0298 - val_loss: 0.0616
<keras.callbacks.History at 0x7f531f596fd0>
2.4.4 最后,评估其性能
score = model.evaluate(X_test, Y_test,
verbose=0)
print('Test score:', score)
效果:
Test score: 0.061617326979574866
检查输出,检查输出并确保一切看起来都很合理,这总是一个好主意。接下来,我们看一些分类正确的例子和错误的例子.
# The predict_classes function outputs the highest probability class
# according to the trained classifier for each input example.
predicted_classes = model.predict_classes(X_test) # Check which items we got right / wrong
correct_indices = np.nonzero(predicted_classes == y_test)[0]
incorrect_indices = np.nonzero(predicted_classes != y_test)[0]
plt.figure()
for i, correct in enumerate(correct_indices[:9]):
plt.subplot(3,3,i+1)
plt.imshow(X_test[correct].reshape(28,28), cmap='gray', interpolation='none')
plt.title("Predicted {}, Class {}".format(predicted_classes[correct], y_test[correct])) plt.figure()
for i, incorrect in enumerate(incorrect_indices[:9]):
plt.subplot(3,3,i+1)
plt.imshow(X_test[incorrect].reshape(28,28), cmap='gray', interpolation='none')
plt.title("Predicted {}, Class {}".format(predicted_classes[incorrect], y_test[incorrect]))
结果:


总之,这是一个完整的程序,在Keras主页http://keras.io/和githubhttps://github.com/fchollet/keras有其它许多优秀的例子。
MINST手写数字识别(一)—— 全连接网络的更多相关文章
- MINST手写数字识别(三)—— 使用antirectifier替换ReLU激活函数
这是一个来自官网的示例:https://github.com/keras-team/keras/blob/master/examples/antirectifier.py 与之前的MINST手写数字识 ...
- MINST手写数字识别(二)—— 卷积神经网络(CNN)
今天我们的主角是keras,其简洁性和易用性简直出乎David 9我的预期.大家都知道keras是在TensorFlow上又包装了一层,向简洁易用的深度学习又迈出了坚实的一步. 所以,今天就来带大家写 ...
- 深度学习之PyTorch实战(3)——实战手写数字识别
上一节,我们已经学会了基于PyTorch深度学习框架高效,快捷的搭建一个神经网络,并对模型进行训练和对参数进行优化的方法,接下来让我们牛刀小试,基于PyTorch框架使用神经网络来解决一个关于手写数字 ...
- 第三节,TensorFlow 使用CNN实现手写数字识别(卷积函数tf.nn.convd介绍)
上一节,我们已经讲解了使用全连接网络实现手写数字识别,其正确率大概能达到98%,这一节我们使用卷积神经网络来实现手写数字识别, 其准确率可以超过99%,程序主要包括以下几块内容 [1]: 导入数据,即 ...
- 第二节,TensorFlow 使用前馈神经网络实现手写数字识别
一 感知器 感知器学习笔记:https://blog.csdn.net/liyuanbhu/article/details/51622695 感知器(Perceptron)是二分类的线性分类模型,其输 ...
- 【PaddlePaddle系列】手写数字识别
最近百度为了推广自家编写对深度学习框架PaddlePaddle不断推出各种比赛.百度声称PaddlePaddle是一个“易学.易用”的开源深度学习框架,然而网上的资料少之又少.虽然百度很用心地提供 ...
- 深度学习面试题12:LeNet(手写数字识别)
目录 神经网络的卷积.池化.拉伸 LeNet网络结构 LeNet在MNIST数据集上应用 参考资料 LeNet是卷积神经网络的祖师爷LeCun在1998年提出,用于解决手写数字识别的视觉任务.自那时起 ...
- 手写数字识别——基于LeNet-5卷积网络模型
在<手写数字识别——利用Keras高层API快速搭建并优化网络模型>一文中,我们搭建了全连接层网络,准确率达到0.98,但是这种网络的参数量达到了近24万个.本文将搭建LeNet-5网络, ...
- 【百度飞桨】手写数字识别模型部署Paddle Inference
从完成一个简单的『手写数字识别任务』开始,快速了解飞桨框架 API 的使用方法. 模型开发 『手写数字识别』是深度学习里的 Hello World 任务,用于对 0 ~ 9 的十类数字进行分类,即输入 ...
随机推荐
- 基于Jenkins自动构建系统开发
1 绪论 1.1 课题的研究背景 随着IT行业的不断发展,软件开发的复杂度也随着不断提高.与此同时,软件的开发团队也越来越庞大,而如何更好地协同整个团队进行高效准确的工作,从而确保软件开发的质量已经 ...
- 20个Flutter实例视频教程-第09节: 保持页面状态-2
视频地址:https://www.bilibili.com/video/av39709290/?p=9 博客地址:https://jspang.com/post/flutterDemo.html#to ...
- msql 初识数据库
一 数据库管理软件的由来 基于我们之前所学,数据要想永久保存,都是保存于文件中, 毫无疑问, 一个文件仅仅只能存在于某一台机器上. 如果我们暂且忽略直接基于文件来存取数据的效率问题, 并且假设程序所有 ...
- YUV格式学习:YUV420P、YV12、NV12、NV21格式转换成RGB24(转载)
转自:http://www.latelee.org/my-study/yuv-learning-yuv420p-to-rgb24.html 对于YUV420的格式,网上有一大堆资料,这里就不说了.直奔 ...
- JAVA基础--JAVA API常见对象(其他API)13
一.其他API 1.System类 system类中的方法和成员变量都是静态的, 不需要创建System对象就可以直接使用. /* * 演示System的使用 */ public class Syst ...
- (3)ASP.NET Core 服务生命周期
1.前言 在ConfigureServices方法中的容器注册每个应用程序的服务,Asp.Core都可以为每个应用程序提供三种服务生命周期:●Transient(暂时):每次请求都会创建一个新的实例. ...
- 算法学习--Day6
题目描述 实现一个加法器,使其能够输出a+b的值. 输入描述: 输入包括两个数a和b,其中a和b的位数不超过1000位. 输出描述: 可能有多组测试数据,对于每组数据, 输出a+b的值. 示例1 输入 ...
- Lightoj1018 【状压DP】
题意: 给你一个坐标系,坐标系上有N个点,然后让你用最少的线,把这些点全部连起来: 思路: (1+15)*15/2=90条线: 然后线上有哪些点就可以知道: 然后按照线上点的个数排序,然后删掉这个线, ...
- 在OpenCV for Android 2.4.5中使用SURF(nonfree module)
http://blog.csdn.net/ruifdu/article/details/9120559 在OpenCV4Android中没有nonfree module,因此也就没有了SURF和SIF ...
- 构建使用SQL服务器的ASP.net Core2.0 API
web api的教程非常少,使用 core2.0的更少,微软提供了一个aspnet core2的教程,也提供了EF core中访问SQL服务器的教程,参考这些教程可以做出使用sql server的as ...
