Saltstack_使用指南01_部署
1. 主机规划
|
服务器名称 |
操作系统版本 |
内网IP |
外网IP(模拟) |
Hostname |
部署模块 |
|
salt100 |
CentOS7.5 |
172.16.1.100 |
10.0.0.100 |
salt100 |
salt-master、salt-minion |
|
salt01 |
CentOS7.5 |
172.16.1.11 |
10.0.0.11 |
salt01 |
salt-minion |
|
salt02 |
CentOS7.5 |
172.16.1.12 |
10.0.0.12 |
salt02 |
salt-minion |
|
salt03 |
CentOS7.5 |
172.16.1.13 |
10.0.0.13 |
salt03 |
salt-minion |
Saltstack文档
https://docs.saltstack.com/en/latest/contents.html
1.1. 机器hosts文件修改
salt100、salt01、salt02、salt03的hosts文件都追加如下信息。
这样主机名相互之间可以解析。
[root@salt100 ~]# cat /etc/hosts
127.0.0.1 localhost localhost.localdomain localhost4 localhost4.localdomain4
:: localhost localhost.localdomain localhost6 localhost6.localdomain6 172.16.1.11 salt01
172.16.1.12 salt02
172.16.1.13 salt03
172.16.1.14 salt04
172.16.1.15 salt05
172.16.1.100 salt100
2. 添加用户账号
说明:
1、 运维人员使用的登录账号;
2、 所有的业务都放在 /app/ 下「yun用户的家目录」,避免业务数据乱放;
3、 该用户也可用于后期salt-ssh使用,因为几乎所有的生产环境都是禁止root远程登录的(因此进行了 sudo 提权)。
# 使用一个专门的用户,避免直接使用root用户
# 添加用户、指定家目录并指定用户密码
useradd -u -d /app yun && echo '' | /usr/bin/passwd --stdin yun
# sudo提权
echo "yun ALL=(ALL) NOPASSWD: ALL" >> /etc/sudoers
# 让其它普通用户可以进入该目录查看信息
chmod /app/
运维三板斧
监控
执行
配置管理
Saltstack四种运行方式
Local
Minion/Master C/S
Syndic 代理方式
Salt SSH
3. SaltStack部署
3.1. 镜像源安装
官方镜像源查询
https://repo.saltstack.com/
安装镜像源
在salt100、salt01、salt02、salt03机器上执行
yum install -y https://repo.saltstack.com/yum/redhat/salt-repo-latest-2.el7.noarch.rpm
3.2. saltstack安装
根据规划在salt100安装salt的master和minion,在其他机器安装salt的minion。
在salt100上操作
yum install -y salt-master salt-minion
在salt01、salt02、salt03上操作
yum install -y salt-minion
版本查看
[root@salt100 ~]# salt --version # master版本查看
salt 2018.3. (Oxygen)
[root@salt100 ~]# salt-minion --version # minion版本查看
salt-minion 2018.3. (Oxygen)
4. 服务端启动
在salt100上执行,无需任务配置修改
[root@salt100 ~]# systemctl start salt-master.service
5. 客户端启动
在salt100、salt01、salt02、salt03上操作
5.1. 修改minion配置文件
配置修改原因:
1、 minion端指向的master是哪个
2、 minion端的ID是什么
[root@salt100 salt]# pwd
/etc/salt
[root@salt100 salt]# vim minion
………………
# 可以是IP或者hostname
# 如果是hostname那么必须能够解析【最佳实践配置为 主机名】
master: salt100
………………
# Explicitly declare the id for this minion to use, if left commented the id
# will be the hostname as returned by the python call: socket.getfqdn()
# Since salt uses detached ids it is possible to run multiple minions on the
# same machine but with different ids, this can be useful for salt compute
# clusters.
# 如果id不配置,那么默认为hostname
# 如果下次要更改该配置,那么要把 /etc/salt/minion_id 也给删除掉,并重启客户端【会生成一个新的minion_id】
#id:
………………
5.2. 启动minion服务
[root@salt100 ~]# systemctl start salt-minion.service
6. 加入开机自启动
master开机自启动
systemctl enable salt-master.service
minion开机自启动
systemctl enable salt-minion.service
7. master接受minion
7.1. master和minion启动后生成的pki信息
salt100上的信息
[root@salt100 salt]# pwd
/etc/salt
[root@salt100 salt]# ll
total
-rw-r----- root root Oct : cloud
drwxr-xr-x root root Oct : cloud.conf.d
drwxr-xr-x root root Oct : cloud.deploy.d
drwxr-xr-x root root Oct : cloud.maps.d
drwxr-xr-x root root Oct : cloud.profiles.d
drwxr-xr-x root root Oct : cloud.providers.d
-rw-r----- root root Oct : master
drwxr-xr-x root root Oct : master.d
-rw-r----- root root Nov : minion
drwxr-xr-x root root Oct : minion.d
-rw-r--r-- root root Nov : minion_id
drwxr-xr-x root root Nov : pki
-rw-r----- root root Oct : proxy
drwxr-xr-x root root Oct : proxy.d
-rw-r----- root root Oct : roster
[root@salt100 salt]# tree pki/
pki/
├── master
│ ├── master.pem
│ ├── master.pub
│ ├── minions
│ ├── minions_autosign
│ ├── minions_denied
│ ├── minions_pre # master还未进一步认证【接受或拒绝】,minion的公钥都先放在这里
│ │ ├── salt01
│ │ ├── salt02
│ │ ├── salt03
│ │ └── salt100
│ └── minions_rejected
└── minion
├── minion.pem
└── minion.pub directories, files
salt03上的信息
[root@salt03 salt]# pwd
/etc/salt
[root@salt03 salt]# ll
total
-rw-r----- root root Oct : cloud
drwxr-xr-x root root Oct : cloud.conf.d
drwxr-xr-x root root Oct : cloud.deploy.d
drwxr-xr-x root root Oct : cloud.maps.d
drwxr-xr-x root root Oct : cloud.profiles.d
drwxr-xr-x root root Oct : cloud.providers.d
-rw-r----- root root Oct : master
drwxr-xr-x root root Oct : master.d
-rw-r----- root root Nov : minion
drwxr-xr-x root root Oct : minion.d
-rw-r--r-- root root Nov : minion_id
drwxr-xr-x root root Nov : pki
-rw-r----- root root Oct : proxy
drwxr-xr-x root root Oct : proxy.d
-rw-r----- root root Oct : roster
[root@salt03 salt]# tree pki/
pki/
├── master
└── minion
├── minion.pem
└── minion.pub directories, files
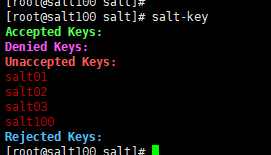
salt100上的salt-key信息
[root@salt100 salt]# salt-key
Accepted Keys:
Denied Keys:
Unaccepted Keys:
salt01
salt02
salt03
salt100
Rejected Keys:
7.2. master接受minion
7.2.1. 单个接受
[root@salt100 salt]# salt-key -a salt01 # 单个接受
The following keys are going to be accepted:
Unaccepted Keys:
salt01
Proceed? [n/Y] y
Key for minion salt01 accepted.
[root@salt100 salt]# salt-key
Accepted Keys:
salt01
Denied Keys:
Unaccepted Keys:
salt02
salt03
salt100
Rejected Keys:

7.2.2. 通配符接受
[root@salt100 salt]# salt-key -a salt0*
The following keys are going to be accepted:
Unaccepted Keys:
salt02
salt03
Proceed? [n/Y] y
Key for minion salt02 accepted.
Key for minion salt03 accepted.
[root@salt100 salt]# salt-key
Accepted Keys:
salt01
salt02
salt03
Denied Keys:
Unaccepted Keys:
salt100
Rejected Keys:

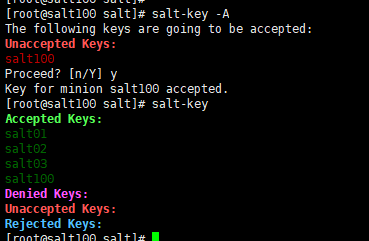
7.2.3. 接受所有minion
[root@salt100 salt]# salt-key -A
The following keys are going to be accepted:
Unaccepted Keys:
salt100
Proceed? [n/Y] y
Key for minion salt100 accepted.
[root@salt100 salt]# salt-key
Accepted Keys:
salt01
salt02
salt03
salt100
Denied Keys:
Unaccepted Keys:
Rejected Keys:
7.3. master接受minion之后的pki信息
salt100上的信息
[root@salt100 salt]# pwd
/etc/salt
[root@salt100 salt]# tree pki/
pki/
├── master
│ ├── master.pem
│ ├── master.pub
│ ├── minions # minion的公钥从minions_pre 移到了此目录
│ │ ├── salt01
│ │ ├── salt02
│ │ ├── salt03
│ │ └── salt100
│ ├── minions_autosign
│ ├── minions_denied
│ ├── minions_pre
│ └── minions_rejected
└── minion
├── minion_master.pub # 接受了来自master的公钥
├── minion.pem
└── minion.pub directories, files
salt03上的信息
[root@salt03 salt]# tree pki/
pki/
├── master
└── minion
├── minion_master.pub # 接受了来自master的公钥
├── minion.pem
└── minion.pub directories, files
8. 测试结果
[root@salt100 salt]# salt '*' test.ping # 看master可以控制哪些minion
salt02:
True
salt03:
True
salt01:
True
salt100:
True
完毕!
Saltstack_使用指南01_部署的更多相关文章
- Saltstack_实战指南01_系统规划
1. 实战项目GitHub地址 之前<Saltstack_使用指南>详细讲解了saltstack的使用.那么从这节开始实战讲解,当然不会再像之前那样详细说明了.只是讲一些系统规划之类的信息 ...
- Saltstack_使用指南17_salt-ssh
1. 主机规划 salt 版本 [root@salt100 ~]# salt --version salt (Oxygen) [root@salt100 ~]# salt-minion --versi ...
- Saltstack_使用指南16_syndic
1. 主机规划 salt 版本 [root@salt100 ~]# salt --version salt (Oxygen) [root@salt100 ~]# salt-minion --versi ...
- Saltstack_使用指南12_配置管理-jinja模板
1. 说明 下文的案例是根据上一篇文章进行的修改.因此请优先读取上一章博文内容<Saltstack_使用指南11_配置管理-状态之间依赖关系> 2. 主机规划 salt 版本 [root@ ...
- Saltstack_实战指南02_各主机Pillar信息指定
1. 实战项目GitHub地址 该项目已经放在了GitHub上,地址如下: https://github.com/zhanglianghhh/salt-example-lnmp 2. 主机规划 3. ...
- Saltstack_使用指南03_配置管理
1. 主机规划 注意事项 修改了master或者minion的配置文件,那么必须重启对应的服务. 2. 了解YAML 具体地址 https://docs.saltstack.com/en/latest ...
- Saltstack_使用指南18_API
1. 主机规划 salt 版本 [root@salt100 ~]# salt --version salt (Oxygen) [root@salt100 ~]# salt-minion --versi ...
- Saltstack_使用指南11_配置管理-状态之间依赖关系
1. 说明 下文的案例是根据上一篇文章进行的修改.因此请优先读取上一篇文章内容<Saltstack_10_配置管理-状态模块> 并且目录进行了变化,从 /srv/salt/lamp 变为了 ...
- Saltstack_使用指南10_配置管理-状态模块
1. 主机规划 salt 版本 [root@salt100 ~]# salt --version salt (Oxygen) [root@salt100 ~]# salt-minion --versi ...
随机推荐
- Echarts图标自适应问题(已解决)
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <meta charset="utf-8"> <title> ...
- c# 中的封装、继承、多态详解
面向对象有封装.继承.多态这三个特性,面向对象编程按照现实世界的特点来管理复杂的事物,把它们抽象为对象,具有自己的状态和行为,通过对消息的反应来完成任务.这种编程方法提供了非常强大的多样性,大大增加了 ...
- 【Java基础】【25多线程(下)&GUI】
25.01_多线程(单例设计模式)(掌握) 单例设计模式:保证类在内存中只有一个对象. 如何保证类在内存中只有一个对象呢? (1)控制类的创建,不让其他类来创建本类的对象.private (2)在本类 ...
- ARP欺骗攻击
一.ARP攻击概述 ARP攻击主要是存在于局域网中,通过伪造IP地址和MAC地址实现ARP欺骗,能够在网络中产生大量的ARP通信量使网络阻塞,攻击者只要持续不断的发出伪造的ARP响应包就能更改目标主机 ...
- what a fuck!这是什么鬼东西?
Topic Link http://ctf5.shiyanbar.com/DUTCTF/1.html 1) 打开链接发现一片看不懂的东西,还真是WTF? 2)分析发现是Jother编码 将其放到浏览器 ...
- Linux基础知识第三讲,拷贝文件跟移动文件命令
目录 Linux基础知识第三讲,拷贝文件跟移动文件命令 一丶常用命令 1.tree命令常用选项 2.cp复制文件命令 3.mv 命令的使用 Linux基础知识第三讲,拷贝文件跟移动文件命令 一丶常用命 ...
- Django学习笔记(4)——Django连接数据库
前言 在MVC或者MTV设计模式中,模型(M)代表对数据库的操作.那么如何操作数据库呢?本小节就认真学习一下.首先复习一下Django的整个实现流程 ,然后再实现一下使用数据库的整个流程,最后学习一下 ...
- JavaScript的事件及异常捕获
事件处理 [onClick]单击事件.[onMouseOver]鼠标经过事件.[onMouseOut]鼠标移出事件.[onChange]文本内容改变事件.[onSelect]文本被框选事件.[onFo ...
- Java GUI 单机版五子棋
前言 刚开始学java时接触到GUI,一时兴起写了个五子棋,五子棋的关键点在于判断输赢,其他的都没什么,现在翻出来整理并记录下来,不足之处还望各位路过的大佬多多指教. 代码实现 代码不多,四百多行,全 ...
- C# asp.net mvc 通过 HttpClient 访问 Web_API
//MVC 具体方法 //API地址 通过 WebConfig配置 private static string apiAdds = ConfigurationManager.AppSettings[& ...
