支持不同Android设备,包括:不同尺寸屏幕、不同屏幕密度、不同系统设置
Some of the important variations that you should consider include different languages, screen sizes, and versions of the Android platform.
This class teaches you how to use basic platform features that leverage alternative resources and other features so your app can provide an optimized user experience on a variety of Android-compatible devices, using a single application package (APK).
主题一:支持不同语言
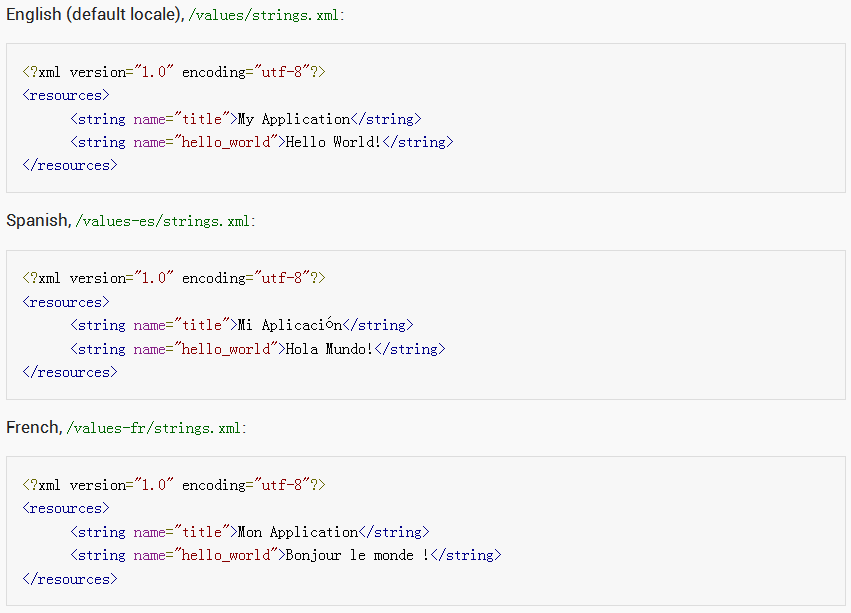
It’s always a good practice to extract UI strings from your app code and keep them in an external file. Within this res/ directory are subdirectories for various resource types. There are also a few default files such as res/values/strings.xml, which holds your string values.
步骤一:Create Locale Directories and String Files
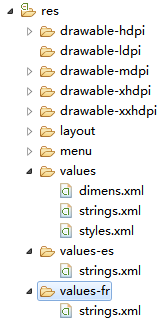
To add support for more languages, create additional values directories inside res/ that include a hyphen and the ISO language code at the end of the directory name. For example, values-es/ is the directory containing simple resources for the Locales with the language code "es". Android loads the appropriate resources according to the locale settings of the device at run time.
res/ --> values/ --> strings.xml
res/ --> values-es/ --> strings.xml
res/ --> values-fr/ --> strings.xml
At runtime, the Android system uses the appropriate set of string resources based on the locale currently set for the user's device.
根据当前设备的设置,获取对应的系统资源。
在代码中引用字符串资源:
// Get a string resource from your app's Resources
String hello = getResources().getString(R.string.hello_world);
或者使用这种方式:
TextView mTvInfo = (TextView) findViewById(R.id.tv_info);
mTvInfo.setText(R.string.hello_world);
在其他.xml文件中使用如下方式引用字符串资源:
<TextView
android:id="@+id/tv_info"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="@string/hello_world" />
主题二:支持不同设备(特别是不同屏幕大小和密度)
Android categorizes device screens using two general properties: size and density. 因此,一般希望应用程序会被安装在分辨率和密度在一定范围的设备上。为了这个目的,需要在应用程序中包含一些可用资源,用于不同设备上(分辨率和密度)。
四种普遍使用的设备分辨率:small/normal/large/xlarge;
四种普遍使用的设备密度:low(ldpi)/medium(mdpi)/high(hdpi)/extra high(xhdpi);
此外,设备屏幕方向同样需要被考虑。
To optimize your user experience on different screen sizes, you should create a unique layout XML file for each screen size you want to support. Each layout should be saved into the appropriate resources directory, named with a -<screen_size> suffix.
比如: res/ --> layout/ --> main.xml res/ --> layout-large/ --> main.xml 不同文件夹下的文件,必须同名;但其内容会依据不同分辨率和密度设置不同的值。
在代码中引用布局.xml文件,如下:
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
initView();
}
The system loads the layout file from the appropriate layout directory based on screen size of the device on which your app is running.
又比如:res/ --> layout/ --> main.xml res/ --> layout-land/ --> main.xml
默认情况下,前者用于“纵向屏幕”;后者 layout-land 用于“横向屏幕”
再比如:
res/ --> layout/ --> main.xml default(portrait)
res/ --> layout-land/ --> main.xml landscape
res/ --> layout-large/ --> main.xml large(portrait)
res/ --> layout-large-land/ --> main.xml large landscape
对于图片的处理,主要应用于不同的屏幕密度。
ldpi --> 0.75; mdpi --> 1.0(baseline); hdpi --> 1.5; xhdpi --> 2.0
This means that if you generate a 200x200 image for xhdpi devices, you should generate the same resource in 150x150 for hdpi, 100x100 for mdpi, and 75x75 for ldpi devices.
自己提供?还是系统自动生成的?
res/ --> drawable-xhdpi/ for xhdpi
res/ --> drawable-hdpi/ for hdpi
res/ --> drawable-mdpi/ for mdpi
res/ --> drawable-ldpi/ for ldpi
Any time you reference @drawable/awesomeimage, the system selects the appropriate bitmap based on the screen's density.
Note: Low-density (ldpi) resources aren’t always necessary. When you provide hdpi assets, the system scales them down by one half to properly fit ldpi screens.
主题三:支持不同Android版本
While the latest versions of Android often provide great APIs for your app, you should continue to support older versions of Android until more devices get updated. This lesson shows you how to take advantage of the latest APIs while continuing to support older versions as well. 不仅使用到最新API的强大功能,还需要兼顾低版本的系统。
Generally, it’s a good practice to support about 90% of the active devices, while targeting your app to the latest version. 一般需要让自己的应用兼容市场上90%的设备。
Tip: In order to provide the best features and functionality across several Android versions, you should use the Android Support Library in your app, which allows you to use several recent platform APIs on older versions. 使用支持包,比如:android-support-v4.jar,用于在低版本中使用较高版本才提供的API。
Specifically, the minSdkVersion and targetSdkVersion attributes for the <uses-sdk element identify the lowest API level with which your app is compatible and the highest API level against which you’ve designed and tested your app.
<uses-sdk android:minSdkVersion="20" />
As new versions of Android are released, some style and behaviors may change. To allow your app to take advantage of these changes and ensure that your app fits the style of each user's device, you should set the targetSdkVersion value to match the latest Android version available.
需要在系统运行时,确认当前系统版本,以使用最新的API。
系统中的Build类描述当前系统版本:Build.VERSION 用于描述获取到的系统版本
/** Various version strings. */
public static class VERSION {
/**
* The internal value used by the underlying source control to
* represent this build. E.g., a perforce changelist number
* or a git hash.
*/
public static final String INCREMENTAL = getString("ro.build.version.incremental");
/**
* The user-visible version string. E.g., "1.0" or "3.4b5".
*/
public static final String RELEASE = getString("ro.build.version.release");
/**
* The user-visible SDK version of the framework in its raw String
* representation; use {@link #SDK_INT} instead.
*
* @deprecated Use {@link #SDK_INT} to easily get this as an integer.
*/
@Deprecated
public static final String SDK = getString("ro.build.version.sdk");
/**
* The user-visible SDK version of the framework; its possible
* values are defined in {@link Build.VERSION_CODES}.
*/
public static final int SDK_INT = SystemProperties.getInt(
"ro.build.version.sdk", 0);
/**
* The current development codename, or the string "REL" if this is
* a release build.
*/
public static final String CODENAME = getString("ro.build.version.codename");
private static final String[] ALL_CODENAMES
= getStringList("ro.build.version.all_codenames", ",");
/**
* @hide
*/
public static final String[] ACTIVE_CODENAMES = "REL".equals(ALL_CODENAMES[0])
? new String[0] : ALL_CODENAMES;
/**
* The SDK version to use when accessing resources.
* Use the current SDK version code. For every active development codename
* we are operating under, we bump the assumed resource platform version by 1.
* @hide
*/
public static final int RESOURCES_SDK_INT = SDK_INT + ACTIVE_CODENAMES.length;
}
Build.VERSION_CODES类用于描述当前不同版本字段:
/**
* Enumeration of the currently known SDK version codes. These are the
* values that can be found in {@link VERSION#SDK}. Version numbers
* increment monotonically with each official platform release.
*/
public static class VERSION_CODES {
/**
* Magic version number for a current development build, which has
* not yet turned into an official release.
*/
public static final int CUR_DEVELOPMENT = 10000; /**
* October 2008: The original, first, version of Android. Yay!
*/
public static final int BASE = 1; /**
* February 2009: First Android update, officially called 1.1.
*/
public static final int BASE_1_1 = 2; /**
* May 2009: Android 1.5.
*/
public static final int CUPCAKE = 3; /**
* September 2009: Android 1.6.
*
* <p>Applications targeting this or a later release will get these
* new changes in behavior:</p>
* <ul>
* <li> They must explicitly request the
* {@link android.Manifest.permission#WRITE_EXTERNAL_STORAGE} permission to be
* able to modify the contents of the SD card. (Apps targeting
* earlier versions will always request the permission.)
* <li> They must explicitly request the
* {@link android.Manifest.permission#READ_PHONE_STATE} permission to be
* able to be able to retrieve phone state info. (Apps targeting
* earlier versions will always request the permission.)
* <li> They are assumed to support different screen densities and
* sizes. (Apps targeting earlier versions are assumed to only support
* medium density normal size screens unless otherwise indicated).
* They can still explicitly specify screen support either way with the
* supports-screens manifest tag.
* <li> {@link android.widget.TabHost} will use the new dark tab
* background design.
* </ul>
*/
public static final int DONUT = 4; /**
* November 2009: Android 2.0
*
* <p>Applications targeting this or a later release will get these
* new changes in behavior:</p>
* <ul>
* <li> The {@link android.app.Service#onStartCommand
* Service.onStartCommand} function will return the new
* {@link android.app.Service#START_STICKY} behavior instead of the
* old compatibility {@link android.app.Service#START_STICKY_COMPATIBILITY}.
* <li> The {@link android.app.Activity} class will now execute back
* key presses on the key up instead of key down, to be able to detect
* canceled presses from virtual keys.
* <li> The {@link android.widget.TabWidget} class will use a new color scheme
* for tabs. In the new scheme, the foreground tab has a medium gray background
* the background tabs have a dark gray background.
* </ul>
*/
public static final int ECLAIR = 5; /**
* December 2009: Android 2.0.1
*/
public static final int ECLAIR_0_1 = 6; /**
* January 2010: Android 2.1
*/
public static final int ECLAIR_MR1 = 7; /**
* June 2010: Android 2.2
*/
public static final int FROYO = 8; /**
* November 2010: Android 2.3
*
* <p>Applications targeting this or a later release will get these
* new changes in behavior:</p>
* <ul>
* <li> The application's notification icons will be shown on the new
* dark status bar background, so must be visible in this situation.
* </ul>
*/
public static final int GINGERBREAD = 9; /**
* February 2011: Android 2.3.3.
*/
public static final int GINGERBREAD_MR1 = 10;
/**
* February 2011: Android 3.0.
*
* <p>Applications targeting this or a later release will get these
* new changes in behavior:</p>
* <ul>
* <li> The default theme for applications is now dark holographic:
* {@link android.R.style#Theme_Holo}.
* <li> On large screen devices that do not have a physical menu
* button, the soft (compatibility) menu is disabled.
* <li> The activity lifecycle has changed slightly as per
* {@link android.app.Activity}.
* <li> An application will crash if it does not call through
* to the super implementation of its
* {@link android.app.Activity#onPause Activity.onPause()} method.
* <li> When an application requires a permission to access one of
* its components (activity, receiver, service, provider), this
* permission is no longer enforced when the application wants to
* access its own component. This means it can require a permission
* on a component that it does not itself hold and still access that
* component.
* <li> {@link android.content.Context#getSharedPreferences
* Context.getSharedPreferences()} will not automatically reload
* the preferences if they have changed on storage, unless
* {@link android.content.Context#MODE_MULTI_PROCESS} is used.
* <li> {@link android.view.ViewGroup#setMotionEventSplittingEnabled}
* will default to true.
* <li> {@link android.view.WindowManager.LayoutParams#FLAG_SPLIT_TOUCH}
* is enabled by default on windows.
* <li> {@link android.widget.PopupWindow#isSplitTouchEnabled()
* PopupWindow.isSplitTouchEnabled()} will return true by default.
* <li> {@link android.widget.GridView} and {@link android.widget.ListView}
* will use {@link android.view.View#setActivated View.setActivated}
* for selected items if they do not implement {@link android.widget.Checkable}.
* <li> {@link android.widget.Scroller} will be constructed with
* "flywheel" behavior enabled by default.
* </ul>
*/
public static final int HONEYCOMB = 11; /**
* May 2011: Android 3.1.
*/
public static final int HONEYCOMB_MR1 = 12; /**
* June 2011: Android 3.2.
*
* <p>Update to Honeycomb MR1 to support 7 inch tablets, improve
* screen compatibility mode, etc.</p>
*
* <p>As of this version, applications that don't say whether they
* support XLARGE screens will be assumed to do so only if they target
* {@link #HONEYCOMB} or later; it had been {@link #GINGERBREAD} or
* later. Applications that don't support a screen size at least as
* large as the current screen will provide the user with a UI to
* switch them in to screen size compatibility mode.</p>
*
* <p>This version introduces new screen size resource qualifiers
* based on the screen size in dp: see
* {@link android.content.res.Configuration#screenWidthDp},
* {@link android.content.res.Configuration#screenHeightDp}, and
* {@link android.content.res.Configuration#smallestScreenWidthDp}.
* Supplying these in <supports-screens> as per
* {@link android.content.pm.ApplicationInfo#requiresSmallestWidthDp},
* {@link android.content.pm.ApplicationInfo#compatibleWidthLimitDp}, and
* {@link android.content.pm.ApplicationInfo#largestWidthLimitDp} is
* preferred over the older screen size buckets and for older devices
* the appropriate buckets will be inferred from them.</p>
*
* <p>Applications targeting this or a later release will get these
* new changes in behavior:</p>
* <ul>
* <li><p>New {@link android.content.pm.PackageManager#FEATURE_SCREEN_PORTRAIT}
* and {@link android.content.pm.PackageManager#FEATURE_SCREEN_LANDSCAPE}
* features were introduced in this release. Applications that target
* previous platform versions are assumed to require both portrait and
* landscape support in the device; when targeting Honeycomb MR1 or
* greater the application is responsible for specifying any specific
* orientation it requires.</p>
* <li><p>{@link android.os.AsyncTask} will use the serial executor
* by default when calling {@link android.os.AsyncTask#execute}.</p>
* <li><p>{@link android.content.pm.ActivityInfo#configChanges
* ActivityInfo.configChanges} will have the
* {@link android.content.pm.ActivityInfo#CONFIG_SCREEN_SIZE} and
* {@link android.content.pm.ActivityInfo#CONFIG_SMALLEST_SCREEN_SIZE}
* bits set; these need to be cleared for older applications because
* some developers have done absolute comparisons against this value
* instead of correctly masking the bits they are interested in.
* </ul>
*/
public static final int HONEYCOMB_MR2 = 13;
/**
* October 2011: Android 4.0.
*
* <p>Applications targeting this or a later release will get these
* new changes in behavior:</p>
* <ul>
* <li> For devices without a dedicated menu key, the software compatibility
* menu key will not be shown even on phones. By targeting Ice Cream Sandwich
* or later, your UI must always have its own menu UI affordance if needed,
* on both tablets and phones. The ActionBar will take care of this for you.
* <li> 2d drawing hardware acceleration is now turned on by default.
* You can use
* {@link android.R.attr#hardwareAccelerated android:hardwareAccelerated}
* to turn it off if needed, although this is strongly discouraged since
* it will result in poor performance on larger screen devices.
* <li> The default theme for applications is now the "device default" theme:
* {@link android.R.style#Theme_DeviceDefault}. This may be the
* holo dark theme or a different dark theme defined by the specific device.
* The {@link android.R.style#Theme_Holo} family must not be modified
* for a device to be considered compatible. Applications that explicitly
* request a theme from the Holo family will be guaranteed that these themes
* will not change character within the same platform version. Applications
* that wish to blend in with the device should use a theme from the
* {@link android.R.style#Theme_DeviceDefault} family.
* <li> Managed cursors can now throw an exception if you directly close
* the cursor yourself without stopping the management of it; previously failures
* would be silently ignored.
* <li> The fadingEdge attribute on views will be ignored (fading edges is no
* longer a standard part of the UI). A new requiresFadingEdge attribute allows
* applications to still force fading edges on for special cases.
* <li> {@link android.content.Context#bindService Context.bindService()}
* will not automatically add in {@link android.content.Context#BIND_WAIVE_PRIORITY}.
* <li> App Widgets will have standard padding automatically added around
* them, rather than relying on the padding being baked into the widget itself.
* <li> An exception will be thrown if you try to change the type of a
* window after it has been added to the window manager. Previously this
* would result in random incorrect behavior.
* <li> {@link android.view.animation.AnimationSet} will parse out
* the duration, fillBefore, fillAfter, repeatMode, and startOffset
* XML attributes that are defined.
* <li> {@link android.app.ActionBar#setHomeButtonEnabled
* ActionBar.setHomeButtonEnabled()} is false by default.
* </ul>
*/
public static final int ICE_CREAM_SANDWICH = 14;
/**
* December 2011: Android 4.0.3.
*/
public static final int ICE_CREAM_SANDWICH_MR1 = 15;
/**
* June 2012: Android 4.1.
*
* <p>Applications targeting this or a later release will get these
* new changes in behavior:</p>
* <ul>
* <li> You must explicitly request the {@link android.Manifest.permission#READ_CALL_LOG}
* and/or {@link android.Manifest.permission#WRITE_CALL_LOG} permissions;
* access to the call log is no longer implicitly provided through
* {@link android.Manifest.permission#READ_CONTACTS} and
* {@link android.Manifest.permission#WRITE_CONTACTS}.
* <li> {@link android.widget.RemoteViews} will throw an exception if
* setting an onClick handler for views being generated by a
* {@link android.widget.RemoteViewsService} for a collection container;
* previously this just resulted in a warning log message.
* <li> New {@link android.app.ActionBar} policy for embedded tabs:
* embedded tabs are now always stacked in the action bar when in portrait
* mode, regardless of the size of the screen.
* <li> {@link android.webkit.WebSettings#setAllowFileAccessFromFileURLs(boolean)
* WebSettings.setAllowFileAccessFromFileURLs} and
* {@link android.webkit.WebSettings#setAllowUniversalAccessFromFileURLs(boolean)
* WebSettings.setAllowUniversalAccessFromFileURLs} default to false.
* <li> Calls to {@link android.content.pm.PackageManager#setComponentEnabledSetting
* PackageManager.setComponentEnabledSetting} will now throw an
* IllegalArgumentException if the given component class name does not
* exist in the application's manifest.
* <li> {@link android.nfc.NfcAdapter#setNdefPushMessage
* NfcAdapter.setNdefPushMessage},
* {@link android.nfc.NfcAdapter#setNdefPushMessageCallback
* NfcAdapter.setNdefPushMessageCallback} and
* {@link android.nfc.NfcAdapter#setOnNdefPushCompleteCallback
* NfcAdapter.setOnNdefPushCompleteCallback} will throw
* IllegalStateException if called after the Activity has been destroyed.
* <li> Accessibility services must require the new
* {@link android.Manifest.permission#BIND_ACCESSIBILITY_SERVICE} permission or
* they will not be available for use.
* <li> {@link android.accessibilityservice.AccessibilityServiceInfo#FLAG_INCLUDE_NOT_IMPORTANT_VIEWS
* AccessibilityServiceInfo.FLAG_INCLUDE_NOT_IMPORTANT_VIEWS} must be set
* for unimportant views to be included in queries.
* </ul>
*/
public static final int JELLY_BEAN = 16;
/**
* November 2012: Android 4.2, Moar jelly beans!
*
* <p>Applications targeting this or a later release will get these
* new changes in behavior:</p>
* <ul>
* <li>Content Providers: The default value of {@code android:exported} is now
* {@code false}. See
* <a href="{@docRoot}guide/topics/manifest/provider-element.html#exported">
* the android:exported section</a> in the provider documentation for more details.</li>
* <li>{@link android.view.View#getLayoutDirection() View.getLayoutDirection()}
* can return different values than {@link android.view.View#LAYOUT_DIRECTION_LTR}
* based on the locale etc.
* <li> {@link android.webkit.WebView#addJavascriptInterface(Object, String)
* WebView.addJavascriptInterface} requires explicit annotations on methods
* for them to be accessible from Javascript.
* </ul>
*/
public static final int JELLY_BEAN_MR1 = 17;
/**
* July 2013: Android 4.3, the revenge of the beans.
*/
public static final int JELLY_BEAN_MR2 = 18;
/**
* October 2013: Android 4.4, KitKat, another tasty treat.
*
* <p>Applications targeting this or a later release will get these
* new changes in behavior:</p>
* <ul>
* <li> The default result of {android.preference.PreferenceActivity#isValidFragment
* PreferenceActivity.isValueFragment} becomes false instead of true.</li>
* <li> In {@link android.webkit.WebView}, apps targeting earlier versions will have
* JS URLs evaluated directly and any result of the evaluation will not replace
* the current page content. Apps targetting KITKAT or later that load a JS URL will
* have the result of that URL replace the content of the current page</li>
* <li> {@link android.app.AlarmManager#set AlarmManager.set} becomes interpreted as
* an inexact value, to give the system more flexibility in scheduling alarms.</li>
* <li> {@link android.content.Context#getSharedPreferences(String, int)
* Context.getSharedPreferences} no longer allows a null name.</li>
* <li> {@link android.widget.RelativeLayout} changes to compute wrapped content
* margins correctly.</li>
* <li> {@link android.app.ActionBar}'s window content overlay is allowed to be
* drawn.</li>
* <li>The {@link android.Manifest.permission#READ_EXTERNAL_STORAGE}
* permission is now always enforced.</li>
* <li>Access to package-specific external storage directories belonging
* to the calling app no longer requires the
* {@link android.Manifest.permission#READ_EXTERNAL_STORAGE} or
* {@link android.Manifest.permission#WRITE_EXTERNAL_STORAGE}
* permissions.</li>
* </ul>
*/
public static final int KITKAT = 19;
/**
* Android 4.4W: KitKat for watches, snacks on the run.
*
* <p>Applications targeting this or a later release will get these
* new changes in behavior:</p>
* <ul>
* <li>{@link android.app.AlertDialog} might not have a default background if the theme does
* not specify one.</li>
* </ul>
*/
public static final int KITKAT_WATCH = 20;
/**
* Temporary until we completely switch to {@link #LOLLIPOP}.
*/
public static final int L = 21;
/**
* Lollipop. A flat one with beautiful shadows. But still tasty.
*
* <p>Applications targeting this or a later release will get these
* new changes in behavior:</p>
* <ul>
* <li> {@link android.content.Context#bindService Context.bindService} now
* requires an explicit Intent, and will throw an exception if given an implicit
* Intent.</li>
* </ul>
*/
public static final int LOLLIPOP = 21;
}
LogUtil.d(TAG, "onCreate::Build.VERSION.SDK_INT="
+ Build.VERSION.SDK_INT);
输出:22 --> Android API 5.1
支持不同Android设备,包括:不同尺寸屏幕、不同屏幕密度、不同系统设置的更多相关文章
- GooglePlay发布应用后,支持的 Android 设备 0 台设备
这个问题主要是权限问题: android.hardware.camera2.full #把这个权限去掉,注里能功里就不会有这一项了android.hardware.camera2.full 然后重新打 ...
- Android设备各种使用尺寸整理
// 获取屏幕的宽度.高度 Display defDip = getWindowManager().getDefaultDisplay(); int disWidth = defDip.getWidt ...
- python Windows下的android设备截图工具
目录 界面版 命令行版 界面版 利用python的wx库写个ui界面,用来把android设备的截图输出到电脑屏幕,前提需要安装adb,涉及到的python库也要安装.代码如下: #!/usr/bin ...
- Python写一个Windows下的android设备截图工具
界面版 利用python的wx库写个ui界面,用来把android设备的截图输出到电脑屏幕,前提需要安装adb,涉及到的python库也要安装.代码如下: import wx,subprocess,o ...
- Android - 支持不同的设备 - 支持不同的屏幕
Android整体上按照两大类来分类设备屏幕:尺寸和分辨率.app在设备上运行应该考虑大小和分辨率.同样的,你应该包含不同的资源来让app适应不同的屏幕大小和分辨率. 整体上有四种尺寸:小的,正常的, ...
- Android设备网络、屏幕尺寸、SD卡、本地IP、存储空间等信息获取工具类
Android设备网络.屏幕尺寸.SD卡.本地IP.存储空间.服务.进程.应用包名等信息获取的整合工具类. package com.qiyu.ddb.util; import android.anno ...
- Android屏幕适配全攻略(最权威的官方适配指导)屏幕尺寸 屏幕分辨率 屏幕像素密度 dpdipdpisppx mdpihdpixdpixxdpi
Android屏幕适配全攻略(最权威的官方适配指导)原创赵凯强 发布于2015-05-19 11:34:17 阅读数 153734 收藏展开 转载请注明出处:http://blog.csdn.net/ ...
- Android - 支持不同的设备 - 支持不同的语言
把app的字符串放到另外一个文件中是一个好习惯.Android用android工程中的资源文件夹让这件事变的很简单. 如果使用Android SDK Tools创建工程,这个工具会在工程的根目录下创建 ...
- Android - 支持不同的设备
世界上有各种不一样形状和大小的Android设备.由于有各种不同类型的设备,你的app可能在各种设备上运行.为了在Android上尽可能的成功,你的app需要使配各种不同的设备.最重要的几点需要考虑的 ...
随机推荐
- mysql将表数据导出为txt或csv文件
语法:select 字段 from 表名 into outfile 路径 示例txt:select * from stu_class into outfile './stu_class.text'; ...
- 关于dfs
DFS 关于dfs,我的理解就是深度搜索,找到所有与入口相连的路径,可以用于迷宫求出口,利用递归的思想,进行搜索返回所有值. 比如,给你两个值分别表示迷宫的长和宽,迷宫有一个入口,一个出口,判断能否从 ...
- js下载后台返回的docx(返回格式:文档流)文件
原文地址: https://www.jianshu.com/p/a81c68c15fbd PS需要指定responseType类型,不然文件内容会乱码哦 咦?文件名乱码?需要手动设置文件名哦↓ 呀,文 ...
- Visual studio 2017添加引用时报错未能正确加载ReferenceManagerPackage包的解决方法
vs2017添加引用时报错未能正确加载“ReferenceManagerPackage”包. - AusonSir - 博客园https://www.cnblogs.com/-bao/p/674941 ...
- C# 用Serializer.ToXml()方法转换成两种格式的XML
常见XML格式两种: 这种是属性的格式,实体的Model属性上面加上这个特性 [XmlAttribute] <AAA aa="/> 这种是标签的格式,实体的Model属性上面加上 ...
- Oracle GoldenGate微服务架构的服务Shell脚本
Oracle GoldenGate微服务架构的/etc/init.d下的OracleGoldenGate服务Shell脚本: #!/bin/sh # # Oracle GoldenGate Servi ...
- python笔记06-10
作者:Vamei 出处:http://www.cnblogs.com/vamei 基础06 循环 for循环 举例: range的用法 这个函数的功能是新建一个表.这个表的元素都是整数,从0开始,下 ...
- dijistra
#include<bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; ,maxm = ; int begin[maxn],to[maxm],next[maxm],v[m ...
- Python——类与对象,异常处理
类 class C1: def setdata(self,value): self.data = value def display(self): print(self.data) class C2( ...
- asp.net core 的 razor pages 如何使用ajax调用后台方法
Razor 是一种允许您向网页中嵌入基于服务器的代码(Visual Basic 和 C#)的标记语法. 当网页被写入浏览器时,基于服务器的代码能够创建动态内容. 在网页加载时,服务器在向浏览器返回页面 ...
