05: 配置yum源
1.1 将镜像复制到本地创建yum源
1、将准备好的系统镜像放到指定的目录,本次目录指定在:/dawnfs/sourcecode
2、创建挂载目录:mkdir /mnt/yum
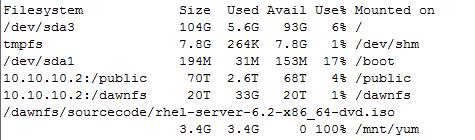
3、挂载镜像: mount -o loop /dawnfs/sourcecode/rhel-server-6.2-x86_64-dvd.iso /mnt/yum挂载完成后,使用 df -h来检查挂载是否成功:
4、修改/etc/yum.repos.d/local.repo文件
[local]
name = Red Hat Yum Name
baseurl=file:///aaa/CentOS-7.3-x86_64-DVD-1611
enabled=1
gpgcheck=0
local.repo
ps:原文件中enabled=0,gpgcheck=1.修改成enable=1,gpgcheck=0。否则输入 yum grouplist 命令时会报错
5、清除原来的yum: yum clean all
6、检查软件列表:yum list
7、查看yum组:yum grouplist
8、安装yum组,以安装Desktop为例: yum install -y "Desktop"
1.2 将windows共享挂载到centos 7.3中并配置yum源
1、临时挂载windows共享
mount.cifs //1.1.1.100/share /aaa -o user=tom,pass=1
2、配置yum源文件
[local]
name = Red Hat Yum Name
baseurl=file:///aaa/CentOS-7.3-x86_64-DVD-1611
enabled=1
gpgcheck=0
local.repo
1.3 配置centos网路yum源
cd /etc/yum.repos.d
# CentOS-Base.repo
#
# The mirror system uses the connecting IP address of the client and the
# update status of each mirror to pick mirrors that are updated to and
# geographically close to the client. You should use this for CentOS updates
# unless you are manually picking other mirrors.
#
# If the mirrorlist= does not work for you, as a fall back you can try the
# remarked out baseurl= line instead.
#
# [base]
name=CentOS-$releasever - Base - mirrors.ustc.edu.cn
baseurl=http://mirrors.ustc.edu.cn/centos/$releasever/os/$basearch/
#mirrorlist=http://mirrorlist.centos.org/?release=$releasever&arch=$basearch&repo=os
gpgcheck=1
gpgkey=http://mirrors.ustc.edu.cn/centos/RPM-GPG-KEY-CentOS-5 #released updates
[updates]
name=CentOS-$releasever - Updates - mirrors.ustc.edu.cn
baseurl=http://mirrors.ustc.edu.cn/centos/$releasever/updates/$basearch/
#mirrorlist=http://mirrorlist.centos.org/?release=$releasever&arch=$basearch&repo=updates
gpgcheck=1
gpgkey=http://mirrors.ustc.edu.cn/centos/RPM-GPG-KEY-CentOS-5 #additional packages that may be useful
[extras]
name=CentOS-$releasever - Extras - mirrors.ustc.edu.cn
baseurl=http://mirrors.ustc.edu.cn/centos/$releasever/extras/$basearch/
#mirrorlist=http://mirrorlist.centos.org/?release=$releasever&arch=$basearch&repo=extras
gpgcheck=1
gpgkey=http://mirrors.ustc.edu.cn/centos/RPM-GPG-KEY-CentOS-5 #packages used/produced in the build but not released
[addons]
name=CentOS-$releasever - Addons - mirrors.ustc.edu.cn
baseurl=http://mirrors.ustc.edu.cn/centos/$releasever/addons/$basearch/
#mirrorlist=http://mirrorlist.centos.org/?release=$releasever&arch=$basearch&repo=addons
gpgcheck=1
gpgkey=http://mirror.centos.org/centos/RPM-GPG-KEY-CentOS-5 #additional packages that extend functionality of existing packages
[centosplus]
name=CentOS-$releasever - Plus - mirrors.ustc.edu.cn
baseurl=http://mirrors.ustc.edu.cn/centos/$releasever/centosplus/$basearch/
#mirrorlist=http://mirrorlist.centos.org/?release=$releasever&arch=$basearch&repo=centosplus
gpgcheck=1
enabled=0
gpgkey=http://mirrors.ustc.edu.cn/centos/RPM-GPG-KEY-CentOS-5 #contrib - packages by Centos Users
[contrib]
name=CentOS-$releasever - Contrib - mirrors.ustc.edu.cn
baseurl=http://mirrors.ustc.edu.cn/centos/$releasever/contrib/$basearch/
#mirrorlist=http://mirrorlist.centos.org/?release=$releasever&arch=$basearch&repo=contrib
gpgcheck=1
enabled=0
gpgkey=http://mirrors.ustc.edu.cn/centos/RPM-GPG-KEY-CentOS-5
CentOS5-Base.repo
# CentOS-Base.repo
#
# The mirror system uses the connecting IP address of the client and the
# update status of each mirror to pick mirrors that are updated to and
# geographically close to the client. You should use this for CentOS updates
# unless you are manually picking other mirrors.
#
# If the mirrorlist= does not work for you, as a fall back you can try the
# remarked out baseurl= line instead.
#
# [base]
name=CentOS-$releasever - Base - mirrors.ustc.edu.cn
baseurl=http://mirrors.ustc.edu.cn/centos/$releasever/os/$basearch/
#mirrorlist=http://mirrorlist.centos.org/?release=$releasever&arch=$basearch&repo=os
gpgcheck=1
gpgkey=http://mirrors.ustc.edu.cn/centos/RPM-GPG-KEY-CentOS-6 #released updates
[updates]
name=CentOS-$releasever - Updates - mirrors.ustc.edu.cn
baseurl=http://mirrors.ustc.edu.cn/centos/$releasever/updates/$basearch/
#mirrorlist=http://mirrorlist.centos.org/?release=$releasever&arch=$basearch&repo=updates
gpgcheck=1
gpgkey=http://mirrors.ustc.edu.cn/centos/RPM-GPG-KEY-CentOS-6 #additional packages that may be useful
[extras]
name=CentOS-$releasever - Extras - mirrors.ustc.edu.cn
baseurl=http://mirrors.ustc.edu.cn/centos/$releasever/extras/$basearch/
#mirrorlist=http://mirrorlist.centos.org/?release=$releasever&arch=$basearch&repo=extras
gpgcheck=1
gpgkey=http://mirrors.ustc.edu.cn/centos/RPM-GPG-KEY-CentOS-6 #additional packages that extend functionality of existing packages
[centosplus]
name=CentOS-$releasever - Plus - mirrors.ustc.edu.cn
baseurl=http://mirrors.ustc.edu.cn/centos/$releasever/centosplus/$basearch/
#mirrorlist=http://mirrorlist.centos.org/?release=$releasever&arch=$basearch&repo=centosplus
gpgcheck=1
enabled=0
gpgkey=http://mirrors.ustc.edu.cn/centos/RPM-GPG-KEY-CentOS-6 #contrib - packages by Centos Users
[contrib]
name=CentOS-$releasever - Contrib - mirrors.ustc.edu.cn
baseurl=http://mirrors.ustc.edu.cn/centos/$releasever/contrib/$basearch/
#mirrorlist=http://mirrorlist.centos.org/?release=$releasever&arch=$basearch&repo=contrib
gpgcheck=1
enabled=0
gpgkey=http://mirrors.ustc.edu.cn/centos/RPM-GPG-KEY-CentOS-6
CentOS6-Base.repo
# CentOS-Base.repo
#
# The mirror system uses the connecting IP address of the client and the
# update status of each mirror to pick mirrors that are updated to and
# geographically close to the client. You should use this for CentOS updates
# unless you are manually picking other mirrors.
#
# If the mirrorlist= does not work for you, as a fall back you can try the
# remarked out baseurl= line instead.
#
# [base]
name=CentOS-$releasever - Base
#mirrorlist=http://mirrorlist.centos.org/?release=$releasever&arch=$basearch&repo=os
baseurl=http://mirrors.ustc.edu.cn/centos/$releasever/os/$basearch/
gpgcheck=1
gpgkey=file:///etc/pki/rpm-gpg/RPM-GPG-KEY-CentOS-7 #released updates
[updates]
name=CentOS-$releasever - Updates
# mirrorlist=http://mirrorlist.centos.org/?release=$releasever&arch=$basearch&repo=updates
baseurl=http://mirrors.ustc.edu.cn/centos/$releasever/updates/$basearch/
gpgcheck=1
gpgkey=file:///etc/pki/rpm-gpg/RPM-GPG-KEY-CentOS-7 #additional packages that may be useful
[extras]
name=CentOS-$releasever - Extras
# mirrorlist=http://mirrorlist.centos.org/?release=$releasever&arch=$basearch&repo=extras
baseurl=http://mirrors.ustc.edu.cn/centos/$releasever/extras/$basearch/
gpgcheck=1
gpgkey=file:///etc/pki/rpm-gpg/RPM-GPG-KEY-CentOS-7 #additional packages that extend functionality of existing packages
[centosplus]
name=CentOS-$releasever - Plus
# mirrorlist=http://mirrorlist.centos.org/?release=$releasever&arch=$basearch&repo=centosplus
baseurl=http://mirrors.ustc.edu.cn/centos/$releasever/centosplus/$basearch/
gpgcheck=1
enabled=0
gpgkey=file:///etc/pki/rpm-gpg/RPM-GPG-KEY-CentOS-7
CentOS7-Base.repo
1.4 yum常用命令
yum provides */kinit # 列出kinit命令使用哪个安装包
05: 配置yum源的更多相关文章
- linux配置yum源、mount及yum命令
配置yum源: 在/mnt目录下新建一个空的目录,名为rhel. [root@localhost mnt]# mkdir rhel 然后 [root@localhost Packages]# cd ...
- RHEL 7.0 本地配置yum源
RHEL 7.0 本地配置yum源 yum简介 yum = Yellow dog Updater, Modified 主要功能是更方便的添加/删除/更新RPM包. 它能自动解决包的倚赖性问题. 它 ...
- CentOS7.1 JDK安装 和 CentOS7.1配置yum源
1.卸载自带OPENJDK #查看自身jdk java -verson #查看自身安装的java rpm -qa | grep java #显示如下 python-javapackages-3.4. ...
- linux配置yum源
yum(全称为 Yellow dog Updater, Modified)是一个在Fedora和RedHat以及SUSE中的Shell前端软件包管理器.基於RPM包管理,能够从指定的服务器自动下载RP ...
- RedHat 6配置yum源为网易镜像(转)
概述 由于版权的问题,RedHat6不能直接使用yum一些指令,需要配置yum源为网易镜像,但是网上谈到很多:整理一下,将有用的信息整理如下,以便于能够为其他的配置服务配置使用:需要卸载掉原理系统自带 ...
- Linux 配置yum源.
Linux 配置yum源. 环境:虚拟机中安装了RedHat ,在进行安装mariadb的时候,出现如下错误.是因为yum源的问题,需要进行配置yum源.本教程是配置本地yum源. [root@loc ...
- redhat 配置yum源(配置163 yum repo)
一般安装好redhat后,不能注册的话,不能使用系统自带的yum源.但是我们可以自己配置yum源来解决这一问题.下面介绍下redhat配置163yum源. 1) 查看版本号和系统类别: cat /et ...
- 克隆虚拟机及配置yum源的步骤及讲解(Hadoop基础)
1.克隆虚拟机 找一台需要克隆的虚拟机但虚拟机必须在关机下进行,(建议将前期Linux环境 配置完成) 在VMware中右键虚拟机找到克隆的选项. 点击克隆 可以克隆他的快照(提前做快照)或者是克 ...
- centos 配置yum源
1.yum配置 yum的配置文件在 /etc/yum.conf [root@mini ~]# cat /etc/yum.conf [main] cachedir=/var/cache/yum/$ba ...
随机推荐
- opencv学习之PyImageSearch
Practical Python and OpenCV+ Case Studies 是一本opencv的入门书籍 强烈推荐一个老外的网站,pyimagesearch 网址:https://www.py ...
- (面试)Hash表算法十道海量数据处理面试题
Hash表算法处理海量数据处理面试题 主要针对遇到的海量数据处理问题进行分析,参考互联网上的面试题及相关处理方法,归纳为三种问题 (1)数据量大,内存小情况处理方式(分而治之+Hash映射) (2)判 ...
- CCCC L2 部落 L3社交集群
https://www.patest.cn/contests/gplt/L2-024 题解:部落是并查集模板题. 社交集群用并查集暴力有23分 坑:写了半天,发现自己并查集没怎么学明白,现在才搞懂: ...
- 算术平均数 print('arithmeticAverageSingleCompressionRatio:', sum(singleCompressionRatio)/len(singleCompressionRatio))
print('arithmeticAverageSingleCompressionRatio:', sum(singleCompressionRatio)/len(singleCompressionR ...
- 理解SQL SERVER中的逻辑读,预读和物理读
转自:https://www.cnblogs.com/CareySon/archive/2011/12/23/2299127.html 在我的上一篇关于SQL SERVER索引的博文,有圆友问道关于逻 ...
- 订阅号助手App发布 手机也能管理公众号了
盼着许久的微信订阅号助手app终于发布了!“ 微信团队发布「订阅号助手」App,支持公众号运营者在手机上发表内容.查看和回复消息.管理已关注用户和帐号.暂时只支持iOS平台,Android平台敬请期待 ...
- 关于微信小程序,你想知道的他们都问了
微信公开课深圳站小程序专场刚刚结束,大家通过"微信公开课+"互动小程序提出了许多问题.我们筛选了后台问得最多的九个问题进行解答,快来看看这里有没有你想要的答案吧! @谢杨:小程序是 ...
- Qt计算器开发(三):执行效果及项目总结
版权声明:本文为博主原创文章,未经博主同意不得转载. https://blog.csdn.net/guodongxiaren/article/details/26046543 执行效果 project ...
- 开源的挖矿软件,sha256
http://cryptomining-blog.com/tag/sha-256d-miner/ https://github.com/cbuchner1/CudaMiner/blob/master/ ...
- iOS开发需要学习哪些内容?
看图:
