Refresh Tokens: When to Use Them and How They Interact with JWTs
In this post we will explore the concept of refresh tokens as defined by OAuth2. We will learn why they came to be and how they compare to other types of tokens. We will also learn how to use them with a simple example. Read on!
Update: at the moment this article was written Auth0 had not gone through OpenID Connect certification. Some of the terms used in this article such as access token do not conform to this spec but do conform to the OAuth2 specification. OpenID Connect establishes a clear distinction between access tokens (used to access the API of the authorization server) and the id token(used for client authentication against a resource server).
Introduction
Modern authentication and/or authorization solutions have introduced the concept of tokens into their protocols. Tokens are specially crafted pieces of data that carry just enough information to either authorize the user to perform an action, or allow a client to get additional information about the authorization process (to then complete it). In other words, tokens are pieces of information that allow the authorization process to be performed. Whether this information is readable or parsable by the client (or any party other than the authorization server) is defined by the implementation. The important thing is: the client gets this information, and then uses it to get access to a resource. The JSON Web Token (JWT) spec defines a way in which common token information may be represented by an implementation.
A short JWT recap
JWT defines a way in which certain common information pertaining to the process of authentication/authorization may be represented. As the name implies, the data format is JSON. JWTs carry certain common fields such as subject, issuer, expiration time, etc. JWTs become really useful when combined with other specs such as JSON Web Signature (JWS) and JSON Web Encryption (JWE). Together these specs provide not only all the information usually needed for an authorization token, but also a means to validate the content of the token so that it cannot be tampered with (JWS) and a way to encrypt information so that it remains opaque to the client (JWE). The simplicity of the data format (and its other virtues) have helped JWTs become one of the most common types of tokens. If you are interested in learning how to implement JWTs in your web apps, check this excellent post by Ryan Chenkie.
Token types
For the purposes of this post, we will focus on the two most common types of tokens: access tokens and refresh tokens.
- Access tokens carry the necessary information to access a resource directly. In other words, when a client passes an access token to a server managing a resource, that server can use the information contained in the token to decide whether the client is authorized or not. Access tokens usually have an expiration date and are short-lived.
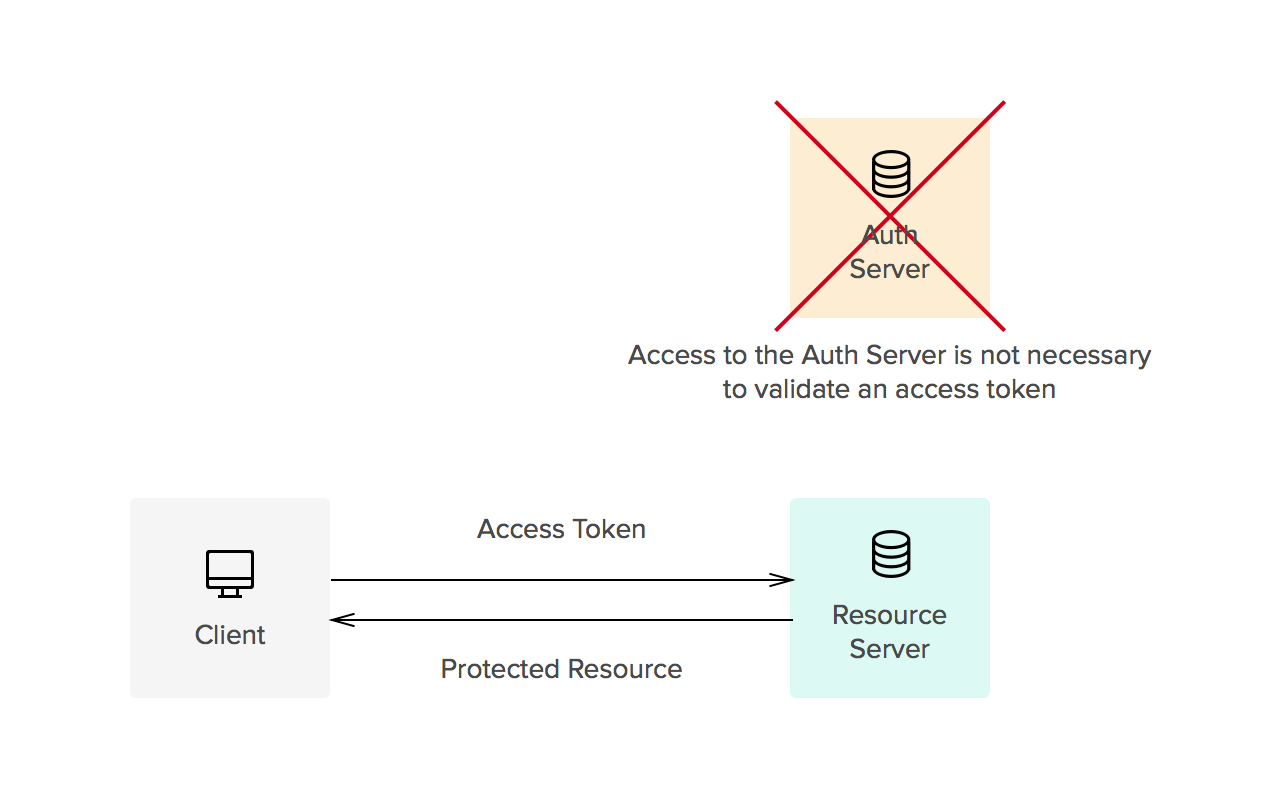
- Refresh tokens carry the information necessary to get a new access token. In other words, whenever an access token is required to access a specific resource, a client may use a refresh token to get a new access token issued by the authentication server. Common use cases include getting new access tokens after old ones have expired, or getting access to a new resource for the first time. Refresh tokens can also expire but are rather long-lived. Refresh tokens are usually subject to strict storage requirements to ensure they are not leaked. They can also be blacklisted by the authorization server.
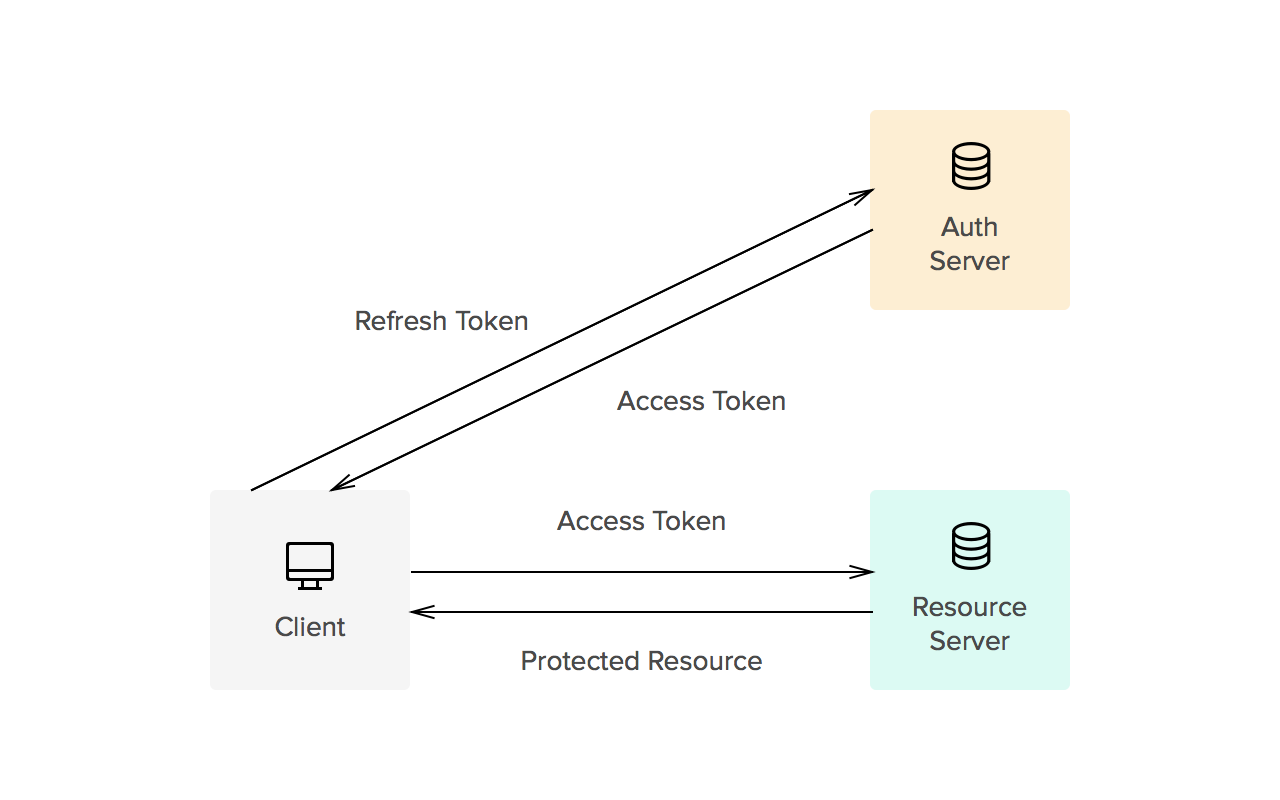
Whether tokens are opaque or not is usually defined by the implementation. Common implementations allow for direct authorization checks against an access token. That is, when an access token is passed to a server managing a resource, the server can read the information contained in the token and decide itself whether the user is authorized or not (no checks against an authorization server are needed). This is one of the reasons tokens must be signed (using JWS, for instance). On the other hand, refresh tokens usually require a check against the authorization server. This split way of handling authorization checks allows for three things:
- Improved access patterns against the authorization server (lower load, faster checks)
- Shorter windows of access for leaked access tokens (these expire quickly, reducing the chance of a leaked token allowing access to a protected resource)
- Sliding-sessions (see below)
Sliding-sessions
Sliding-sessions are sessions that expire after a period of inactivity. As you can imagine, this is easily implemented using access tokens and refresh tokens. When a user performs an action, a new access token is issued. If the user uses an expired access token, the session is considered inactive and a new access token is required. Whether this token can be obtained with a refresh token or a new authentication round is required is defined by the requirements of the development team.
Security considerations
Refresh tokens are long-lived. This means when a client gets a refresh token from a server, this token must be stored securely to keep it from being used by potential attackers. If a refresh token is leaked, it may be used to obtain new access tokens (and access protected resources) until it is either blacklisted or it expires (which may take a long time). Refresh tokens must be issued to a single authenticated client to prevent use of leaked tokens by other parties. Access tokens must be kept secret, but as you may imagine, security considerations are less strict due to their shorter life.
"Access tokens must be kept secret, security considerations are less strict due to their shorter life."
TWEET THIS
Example: a refresh-token issuing server
For the purposes of this example we will use a simple server based on node-oauth2-server that will issue access and refresh tokens. Access tokens will be required to access a protected resource. The client will be a simple CURL command. The code from this example is based on the examples from node-oauth2-server. We have modified the base examples to use JWT for access tokens.
Node-oauth2-server uses a predefined API for the model. You can find the docs here. The following code shows how to implement the model for JWT access tokens.
DISCLAIMER: Please note the code in the following example is not production ready.
model.generateToken = function(type, req, callback) {
//Use the default implementation for refresh tokens
console.log('generateToken: ' + type);
if(type === 'refreshToken') {
callback(null, null);
return;
}
//Use JWT for access tokens
var token = jwt.sign({
user: req.user.id
}, secretKey, {
expiresIn: model.accessTokenLifetime,
subject: req.client.clientId
});
callback(null, token);
}
model.getAccessToken = function (bearerToken, callback) {
console.log('in getAccessToken (bearerToken: ' + bearerToken + ')');
try {
var decoded = jwt.verify(bearerToken, secretKey, {
ignoreExpiration: true //handled by OAuth2 server implementation
});
callback(null, {
accessToken: bearerToken,
clientId: decoded.sub,
userId: decoded.user,
expires: new Date(decoded.exp * 1000)
});
} catch(e) {
callback(e);
}
};
model.saveAccessToken = function (token, clientId, expires, userId, callback) {
console.log('in saveAccessToken (token: ' + token +
', clientId: ' + clientId + ', userId: ' + userId.id +
', expires: ' + expires + ')');
//No need to store JWT tokens.
console.log(jwt.decode(token, secretKey));
callback(null);
};
The OAuth2 token endpoint (/oauth/token) handles issuing of all types of grants (password and refresh tokens). All other endpoints are protected by the OAuth2 middleware that checks for the access token.
// Handle token grant requests
app.all('/oauth/token', app.oauth.grant()); app.get('/secret', app.oauth.authorise(), function (req, res) {
// Will require a valid access_token
res.send('Secret area');
});
So, for instance, assuming there is a user 'test' with password 'test' and a client 'testclient' with a client secret 'secret', one could request a new access token/refresh token pair as follows:
$ curl -X POST -H 'Authorization: Basic dGVzdGNsaWVudDpzZWNyZXQ=' -d 'grant_type=password&username=test&password=test' localhost:3000/oauth/token
{
"token_type":"bearer",
"access_token":"eyJ0eXAiOiJKV1QiLCJhbGciOiJIUzI1NiJ9.eyJ1c2VyIjoiVlx1MDAxNcKbwoNUwoonbFPCu8KhwrYiLCJpYXQiOjE0NDQyNjI1NDMsImV4cCI6MTQ0NDI2MjU2M30.MldruS1PvZaRZIJR4legQaauQ3_DYKxxP2rFnD37Ip4",
"expires_in":20,
"refresh_token":"fdb8fdbecf1d03ce5e6125c067733c0d51de209c"
}
The authorization header contains the client id and secret encoded as BASE64 (testclient:secret).
To access a protected resource with that access token:
$ curl 'localhost:3000/secret?access_token=eyJ0eXAiOiJKV1QiLCJhbGciOiJIUzI1NiJ9.eyJ1c2VyIjoiVlx1MDAxNcKbwoNUwoonbFPCu8KhwrYiLCJpYXQiOjE0NDQyNjI1NDMsImV4cCI6MTQ0NDI2MjU2M30.MldruS1PvZaRZIJR4legQaauQ3_DYKxxP2rFnD37Ip4' Secret area
Access to the "secret area" will not cause a database lookup to validate the access token thanks to JWT.
Once the token has expired:
$ curl 'localhost:3000/secret?access_token=eyJ0eXAiOiJKV1QiLCJhbGciOiJIUzI1NiJ9.eyJ1c2VyIjoiVlx1MDAxNcKbwoNUwoonbFPCu8KhwrYiLCJpYXQiOjE0NDQyNjI2MTEsImV4cCI6MTQ0NDI2MjYzMX0.KkHI8KkF4nmi9z6rAQu9uffJjiJuNnsMg1DC3CnmEV0'
{
"code":401,
"error":"invalid_token",
"error_description":"The access token provided has expired."
}
Now we can use the refresh token to get a new access token by hitting the token endpoint like so:
curl -X POST -H 'Authorization: Basic dGVzdGNsaWVudDpzZWNyZXQ=' -d 'refresh_token=fdb8fdbecf1d03ce5e6125c067733c0d51de209c&grant_type=refresh_token' localhost:3000/oauth/token
{
"token_type":"bearer",
"access_token":"eyJ0eXAiOiJKV1QiLCJhbGciOiJIUzI1NiJ9.eyJ1c2VyIjoiVlx1MDAxNcKbwoNUwoonbFPCu8KhwrYiLCJpYXQiOjE0NDQyNjI4NjYsImV4cCI6MTQ0NDI2Mjg4Nn0.Dww7TC-d0teDAgsmKHw7bhF2THNichsE6rVJq9xu_2s",
"expires_in":20,
"refresh_token":"7fd15938c823cf58e78019bea2af142f9449696a"
}
DISCLAIMER: Please note the code in the previous example is not production ready.
See the full code here.
Aside: use refresh tokens in your Auth0 apps
At Auth0 we do the hard part of authentication for you. Refresh tokens are not an exception. Once you have setup your app with us, follow the docs here to learn how to get a refresh token.
Conclusion
Refresh tokens improve security and allow for reduced latency and better access patterns to authorization servers. Implementations can be simple using tools such as JWT + JWS. If you are interested in learning more about tokens (and cookies), check our article here.
You can also check the Refresh Tokens landing page for more information.
可以参考:http://www.haomou.net/2014/08/13/2014_web_token/ 对于使用json web token
Refresh Tokens: When to Use Them and How They Interact with JWTs的更多相关文章
- ASP.NET OWIN OAuth:refresh token的持久化
在前一篇博文中,我们初步地了解了refresh token的用途——它是用于刷新access token的一种token,并且用简单的示例代码体验了一下获取refresh token并且用它刷新acc ...
- Web API与OAuth:既生access token,何生refresh token
在前一篇博文中,我们基于 ASP.NET Web API 与 OWIN OAuth 以 Resource Owner Password Credentials Grant 的授权方式( grant_t ...
- Implement JSON Web Tokens Authentication in ASP.NET Web API and Identity 2.1 Part 3 (by TAISEER)
http://bitoftech.net/2015/02/16/implement-oauth-json-web-tokens-authentication-in-asp-net-web-api-an ...
- [转]An introduction to OAuth 2.0 using Facebook in ASP.NET Core
本文转自:http://andrewlock.net/an-introduction-to-oauth-2-using-facebook-in-asp-net-core/ This is the ne ...
- OAuth 2.0 Threat Model and Security Considerations (rfc6819)
Authorization server The following data elements are stored or accessible on the authorization serve ...
- 基于OWIN WebAPI 使用OAuth授权服务【客户端验证授权(Resource Owner Password Credentials Grant)】
适用范围 前面介绍了Client Credentials Grant ,只适合客户端的模式来使用,不涉及用户相关.而Resource Owner Password Credentials Grant模 ...
- NodeJS路径的小问题
今天从新过了一边node的基础知识,自己写了一个小例子: foo.js exports.setSome = function (x) {return x }; saveData.js /** * Cr ...
- The OAuth 2.0 Authorization Framework-摘自https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc6749
Internet Engineering T ...
- 为Web Api 2认证服务器增加令牌刷新功能
Refresh tokens can potentially improve the situation but also increase complexity. A refresh token i ...
随机推荐
- 一些值得学习的Unity教程 (很实用的包括源码)
***********************项目源码******************************** 1. 降临 2. 沉睡缤纷乐 3. 千炮捕鱼 4. Photon官方FSP示例 ...
- SpringMVC整合fastjson、easyui 乱码问题
一.框架版本 SpringMVC:3.1.1.RELEASE fastjson:1.2.7 easyui :1.4.5 二.乱码现象 Action中使用@ResponseBody返回Json数据 ...
- Andorid之Annotation框架初使用(二)
Fragment: @EActivity(R.layout.fragments) public class MyFragmentActivity extends FragmentActivity { ...
- C++ Primer 学习笔记_91_用于大型程序的工具 --命名空间
用于大型程序的工具 --命名空间 引言: 在一个给定作用域中定义的每一个名字在该作用域中必须是唯一的,对庞大.复杂的应用程序而言,这个要求可能难以满足.这样的应用程序的全局作用域中一般有很多名字定义. ...
- 解决win8/8.1系统安装.net framework 3.5出现0x800F0906代码错误
解决方案一. 首先打开windows更新,检查是否有系统更新要安装,因为这个问题可能是导致.net 3.5无法安装的罪魁祸首,要检查windows更新,可以右键“这台电脑”点击“属性”,打开后,点击左 ...
- python的单元测试框架
1.unittest是Python内置的标准类库.它的API跟Java的JUnit..net的NUnit,C++的CppUnit很相似. 通过继承unittest.TestCase来创建一个测试用 ...
- Servlet Filter 示例
1. CityQuery.java package com.xxx.servlet; import com.google.common.collect.Lists; import com.xxx.da ...
- Android宝典入门篇-进阶
学习Android前后有快有1个月了,本着不耍流氓,谈恋爱就要结婚的信念(其实AD开发也挺有趣的),做了自己的第一个Android小应用.本来准备今天和大家分享的,考虑到在不同屏幕上的效果没测试和本着 ...
- SMTP用户枚举原理简介及相关工具
前言 SMTP是安全测试中比较常见的服务类型,其不安全的配置(未禁用某些命令)会导致用户枚举的问题,这主要是通过SMTP命令进行的.本文将介绍SMTP用户枚举原理以及相关工具. SMTP SMTP命令 ...
- metal2的四个新features
https://developer.apple.com/documentation/metal/mtldevice/ios_and_tvos_devices/about_gpu_family_4 Im ...

