Codeforces 631C. Report 模拟
Each month Blake gets the report containing main economic indicators of the company "Blake Technologies". There are n commodities produced by the company. For each of them there is exactly one integer in the final report, that denotes corresponding revenue. Before the report gets to Blake, it passes through the hands of m managers. Each of them may reorder the elements in some order. Namely, the i-th manager either sorts first ri numbers in non-descending or non-ascending order and then passes the report to the manager i + 1, or directly to Blake (if this manager has number i = m).
Employees of the "Blake Technologies" are preparing the report right now. You know the initial sequence ai of length n and the description of each manager, that is value ri and his favourite order. You are asked to speed up the process and determine how the final report will look like.
The first line of the input contains two integers n and m (1 ≤ n, m ≤ 200 000) — the number of commodities in the report and the number of managers, respectively.
The second line contains n integers ai (|ai| ≤ 109) — the initial report before it gets to the first manager.
Then follow m lines with the descriptions of the operations managers are going to perform. The i-th of these lines contains two integers ti and ri (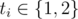 , 1 ≤ ri ≤ n), meaning that the i-th manager sorts the first ri numbers either in the non-descending (if ti = 1) or non-ascending (if ti = 2) order.
, 1 ≤ ri ≤ n), meaning that the i-th manager sorts the first ri numbers either in the non-descending (if ti = 1) or non-ascending (if ti = 2) order.
Print n integers — the final report, which will be passed to Blake by manager number m.
3 1
1 2 3
2 2
2 1 3
4 2
1 2 4 3
2 3
1 2
2 4 1 3
In the first sample, the initial report looked like: 1 2 3. After the first manager the first two numbers were transposed: 2 1 3. The report got to Blake in this form.
In the second sample the original report was like this: 1 2 4 3. After the first manager the report changed to: 4 2 1 3. After the second manager the report changed to: 2 4 1 3. This report was handed over to Blake.
题目连接:http://codeforces.com/contest/631/problem/C
题意:一个长度为n的一位数组a,有m操作,每次操作把前r个元素进行非升序或者非降序进行排列。输出最后数组a。
思路:如果后面的操作的元素个数比前面的元素个数多或者相等,前面的操作就会无效。所以优化之后的操作就是r依次递减的。将a的前max(最大的r)位进行非降序排序Q。前一次操作为ti,ri;后一次操作为tj,rj。那么数组a的后ri-rj就确定了,如果ti==1,取剩下的Q的后ri-rj位作为a,如果ti==2,取剩下的Q的前ri-rj作为a。
代码:(Q用数组模拟,标记Q的头s和尾)
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
struct reorder
{
int p,t,r;
friend bool operator < (reorder a,reorder b)
{
if(a.r!=b.r) return a.r>b.r;
else return a.p>b.p;
}
} reo[];
int a[];
deque<int>Q; ///双向队列
int main()
{
int i,j,n,m;
scanf("%d%d",&n,&m);
for(i=; i<n; i++) scanf("%d",&a[i]);
for(i=; i<m; i++)
{
scanf("%d%d",&reo[i].t,&reo[i].r);
reo[i].p=i+;
}
sort(reo,reo+m);
int cou=reo[].r,sign=reo[].p,flag=reo[].t;
sort(a,a+cou);
for(i=; i<cou; i++) Q.push_back(a[i]); ///队列尾入
reo[m].t=,reo[m].r=,reo[m].p=m+;
for(i=; i<=m; i++)
{
if(reo[i].p>sign)
{
if(flag==)
{
int gg=cou-reo[i].r;
while(gg--)
{
a[--cou]=Q.back(); ///队列尾元素
Q.pop_back(); ///尾列尾出
}
}
else
{
int gg=cou-reo[i].r;
while(gg--)
{
a[--cou]=Q.front(); ///队列头元素
Q.pop_front(); ///队列头出
}
}
sign=reo[i].p;
flag=reo[i].t;
}
}
for(i=; i<n; i++) cout<<a[i]<<" ";
cout<<endl;
return ;
}
数组模拟
关于运算符重载:传送门
关于STL:传送门
Codeforces 631C. Report 模拟的更多相关文章
- Codeforces 631C Report【其他】
题意: 给定序列,将前a个数进行逆序或正序排列,多次操作后,求最终得到的序列. 分析: 仔细分析可以想到j<i,且rj小于ri的操作是没有意义的,对于每个i把类似j的操作删去(这里可以用mult ...
- codeforces 631C. Report
题目链接 按题目给出的r, 维护一个递减的数列,然后在末尾补一个0. 比如样例给出的 4 21 2 4 32 31 2 递减的数列就是3 2 0, 操作的时候, 先变[3, 2), 然后变[2, 0) ...
- codeforces 631C C. Report
C. Report time limit per test 2 seconds memory limit per test 256 megabytes input standard input out ...
- Report CodeForces - 631C (栈)
题目链接 题目大意:给定序列, 给定若干操作, 每次操作将$[1,r]$元素升序或降序排列, 求操作完序列 首先可以发现对最后结果有影响的序列$r$一定非增, 并且是升序降序交替的 可以用单调栈维护这 ...
- Codeforces 389B(十字模拟)
Fox and Cross Time Limit: 1000MS Memory Limit: 262144KB 64bit IO Format: %I64d & %I64u Submi ...
- codeforces 591B Rebranding (模拟)
Rebranding Problem Description The name of one small but proud corporation consists of n lowercase E ...
- Codeforces 626B Cards(模拟+规律)
B. Cards time limit per test:2 seconds memory limit per test:256 megabytes input:standard input outp ...
- Codeforces 679B. Barnicle 模拟
B. Barnicle time limit per test: 1 second memory limit per test :256 megabytes input: standard input ...
- CodeForces 382C【模拟】
活生生打成了大模拟... #include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; typedef long long LL; typedef unsig ...
随机推荐
- angularjs探秘<一>认识angularjs
首先聊聊angularjs是啥. 首先AngularJS 是一个 JavaScript 框架.(PS:其实就是外部引用的js文件) 所以AngularJS的使用依然是外部引用js文件. 附上引用地址 ...
- bootstrapValidator针对设置赋值进行验证
bootstrapValidator在提交的时候可以进行验证,但是对于点击输入框进行赋值的时候验证失效. 解决方法: 然后在设置change方法方可解决.
- nodejs 获取文件夹中所有文件、图片 名
//获取项目工程里的图片 var fs = require('fs');//引用文件系统模块 var image = require("imageinfo"); //引用image ...
- session失效刷新后登录页面嵌入在iframe中的前台解决办法
在前台登录页面中加入JS代码,判断登录页面是否在iframe中,在iframe中就跳转出去 例: //判断是否在iframe中,在里面就跳出去 if (top.location.href != loc ...
- delphi Firemonkey ListBoxItem自绘
delphi Firemonkey ListBoxItem自绘 ListBoxItem1的事件ListBoxItem1Paint procedure TForm1.ListBoxItem1Paint( ...
- as2 loadClip
loadClip(url:String, target:Object) : Boolean target是直接被赋值,而不是add进去
- 【转】.net 实现 语音搜索(仅限WebKit内核浏览器)
<input type="text" class="text" name="value_2" id="value_2&quo ...
- Linux逻辑卷的拉伸和缩小
相对于普通磁盘优势是逻辑卷可以在线动态的拉伸(不用先unmount操作),只要vg中有足够的空间即可 1:首先查看vg是否有足够的空间 [root@gechong mapper]# vgdisplay ...
- sqlserver table partion
SQL SERVER 表分区实施步奏 1. 概要说明 SQL SERVER的表分区功能是为了将一个大表(表中含有非常多条数据)的数据根据某条件(仅限该表的主键)拆分成多个文件存放,以提高查询数据时 ...
- 吴裕雄 数据挖掘与分析案例实战(10)——KNN模型的应用
# 导入第三方包import pandas as pd # 导入数据Knowledge = pd.read_excel(r'F:\\python_Data_analysis_and_mining\\1 ...
