Service生命周期以及应用
Service概念及用途:
Android中的服务,它与Activity不同,它是不能与用户交互的,不能自己启动的,运行在后台的程序,如果我们退出应用时,Service进程并没有结束,它仍然在后台运行,那 我们什么时候会用到Service呢?比如我们播放音乐的时候,有可能想边听音乐边干些其他事情,当我们退出播放音乐的应用,如果不用Service,我 们就听不到歌了,所以这时候就得用到Service了,又比如当我们一个应用的数据是通过网络获取的,不同时间(一段时间)的数据是不同的这时候我们可以 用Service在后台定时更新,而不用每打开应用的时候在去获取。
Service生命周期 :
Android Service的生命周期并不像Activity那么复杂,它只继承了onCreate(),onStart(),onDestroy()三个方法,当我 们第一次启动Service时,先后调用了onCreate(),onStart()这两个方法,当停止Service时,则执行onDestroy()方法,这里需要注意的是,如果Service已经启动了,当我们再次启动Service时,不会在执行onCreate()方法,而是直接执行onStart()方法,具体的可以看下面的实例。
Service与Activity通信:
Service后端的数据最终还是要呈现在前端Activity之上的,因为启动Service时,系统会重新开启一个新 的进程,这就涉及到不同进程间通信的问题了(AIDL)这一节我不作过多描述,当我们想获取启动的Service实例时,我们可以用到 bindService和onBindService方法,它们分别执行了Service中IBinder()和onUnbind()方法。
为了让大家 更容易理解,我写了一个简单的Demo,大家可以模仿着我,一步一步的来。
第一步:新建一个Android工程,我这里命名为ServiceDemo.
第二步:修改main.xml代码,我这里增加了四个按钮,代码如下:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:orientation="vertical"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="fill_parent"
>
<TextView
android:id="@+id/text"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="@string/hello"
/>
<Button
android:id="@+id/startservice"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="startService"
/>
<Button
android:id="@+id/stopservice"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="stopService"
/>
<Button
android:id="@+id/bindservice"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="bindService"
/>
<Button
android:id="@+id/unbindservice"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="unbindService"
/>
</LinearLayout>
第三步:新建一个Service,命名为MyService.java代码如下:
import android.app.Service;
import android.content.Intent;
import android.os.Binder;
import android.os.IBinder;
import android.text.format.Time;
import android.util.Log;
public class MyService extends Service {
//定义个一个Tag标签
private static final String TAG = "MyService";
//这里定义吧一个Binder类,用在onBind()有方法里,这样Activity那边可以获取到
private MyBinder mBinder = new MyBinder();
@Override
public IBinder onBind(Intent intent) {
Log.e(TAG, "start IBinder~~~");
return mBinder;
}
@Override
public void onCreate() {
Log.e(TAG, "start onCreate~~~");
super.onCreate();
}
@Override
public void onStart(Intent intent, int startId) {
Log.e(TAG, "start onStart~~~");
super.onStart(intent, startId);
}
@Override
public void onDestroy() {
Log.e(TAG, "start onDestroy~~~");
super.onDestroy();
}
@Override
public boolean onUnbind(Intent intent) {
Log.e(TAG, "start onUnbind~~~");
return super.onUnbind(intent);
}
//这里我写了一个获取当前时间的函数,不过没有格式化就先这么着吧
public String getSystemTime(){
Time t = new Time();
t.setToNow();
return t.toString();
}
public class MyBinder extends Binder{
MyService getService()
{
return MyService.this;
}
}
}
第四步:修改ServiceDemo.java,代码如下:
package com.tutor.servicedemo;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.content.ComponentName;
import android.content.Context;
import android.content.Intent;
import android.content.ServiceConnection;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.os.IBinder;
import android.view.View;
import android.view.View.OnClickListener;
import android.widget.Button;
import android.widget.TextView;
public class ServiceDemo extends Activity implements OnClickListener{ private MyService mMyService;
private TextView mTextView;
private Button startServiceButton;
private Button stopServiceButton;
private Button bindServiceButton;
private Button unbindServiceButton;
private Context mContext; //这里需要用到ServiceConnection在Context.bindService和context.unBindService()里用到
private ServiceConnection mServiceConnection = new ServiceConnection() {
//当我bindService时,让TextView显示MyService里getSystemTime()方法的返回值
public void onServiceConnected(ComponentName name, IBinder service) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
mMyService = ((MyService.MyBinder)service).getService();
mTextView.setText("I am frome Service :" + mMyService.getSystemTime());
} public void onServiceDisconnected(ComponentName name) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub }
};
public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.main);
setupViews();
} public void setupViews(){ mContext = ServiceDemo.this;
mTextView = (TextView)findViewById(R.id.text); startServiceButton = (Button)findViewById(R.id.startservice);
stopServiceButton = (Button)findViewById(R.id.stopservice);
bindServiceButton = (Button)findViewById(R.id.bindservice);
unbindServiceButton = (Button)findViewById(R.id.unbindservice); startServiceButton.setOnClickListener(this);
stopServiceButton.setOnClickListener(this);
bindServiceButton.setOnClickListener(this);
unbindServiceButton.setOnClickListener(this);
} public void onClick(View v) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
if(v == startServiceButton){
Intent i = new Intent();
i.setClass(ServiceDemo.this, MyService.class);
mContext.startService(i);
}else if(v == stopServiceButton){
Intent i = new Intent();
i.setClass(ServiceDemo.this, MyService.class);
mContext.stopService(i);
}else if(v == bindServiceButton){
Intent i = new Intent();
i.setClass(ServiceDemo.this, MyService.class);
mContext.bindService(i, mServiceConnection, BIND_AUTO_CREATE);
}else{
mContext.unbindService(mServiceConnection);
}
} }
第五步:修改AndroidManifest.xml代码(将我们新建的MyService注册进去如下代码第14行:)
第六步:执行上述工程,效果图如下:
点击startServie按钮时先后执行了Service中onCreate()->onStart()这两个方法,打开Logcat视窗效果如下图:

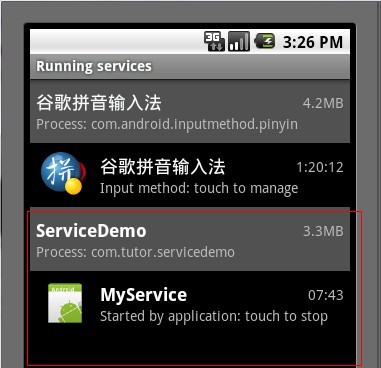
我们这时可以按HOME键进入Settings(设置)->Applications(应用)->Running Services(正在运行的服务)看一下我们新启动了一个服务,效果如下:
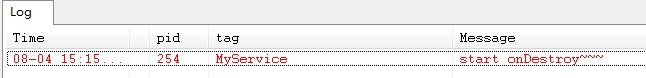
点击stopService按钮时,Service则执行了onDestroy()方法,效果图如下所示:
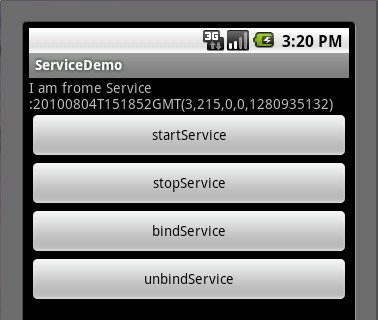
这时候我们再次点击startService按钮,然后点击bindService按钮(通常bindService都是bind已经启动的
Service),我们看一下Service执行了IBinder()方法,以及TextView的值也有所变化了,如下两张图所示:

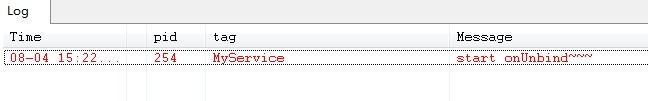
最后点击unbindService按钮,则Service执行了onUnbind()方法,如下图所示:
转载:http://blog.csdn.net/android_tutor/article/details/5789203
Service生命周期以及应用的更多相关文章
- Android生命周期和Service生命周期
android生命周期 运行:oncreate → onstart → onresume暂停:onresume → onpause:再次运行:onresume停止:onpause → onstop → ...
- Android(java)学习笔记171:Service生命周期
1.Service的生命周期 Android中的Service(服务)与Activity不同,它是不能和用户交互,不能自己启动的,运行在后台的程序,如果我们退出应用的时候,Servic ...
- Android Service生命周期及用法
Service概念及用途:Android中的服务,它与Activity不同,它是不能与用户交互的,不能自己启动的,运行在后台的程序,如果我们退出应用时,Service进程并没有结束,它仍然在后台运行, ...
- Service具体解释(二):Service生命周期
< Service具体解释(一):什么是Service> < Service具体解释(二):Service生命周期> <Service具体解释(三):Service的使用 ...
- Android中startService的使用及Service生命周期
Android中有两种主要方式使用Service,通过调用Context的startService方法或调用Context的bindService方法.本文仅仅探讨纯startService的使用.不 ...
- Service 生命周期
有了 Service 类我们如何启动他呢,有两种方法: • Context.startService() • Context.bindService() 1. 在同一个应用任何地方调用 start ...
- Android Service 生命周期
Service概念及用途: Android中的服务,它与Activity不同,它是不能与用户交互的,不能自己启动的,运行在后台的程序,如果我们退出应用时,Service进程并没有结束,它仍然在后台运行 ...
- Android(java)学习笔记114:Service生命周期
1.Service的生命周期 Android中的Service(服务)与Activity不同,它是不能和用户交互,不能自己启动的,运行在后台的程序,如果我们退出应用的时候,Servic ...
- Android 中Service生命周期
使用context.startService() 启动Service 其生命周期为context.startService() ->onCreate()- >onStart()->S ...
随机推荐
- Day 22 面向对象知识.
https://www.cnblogs.com/bigberg/p/7252349.html #类方法,静态方法, 属性方法. 类有两种作用:属性引用 和实例化.属性引用(类名.属性)class pe ...
- JAVA 定时器时间格式
格式: [秒] [分] [小时] [日] [月] [周] [年] 通配符说明: \*:表示所有值.例如:在分的字段上设置"\*",表示每一分钟都会触发. ?:表示不指定值.使用的场 ...
- 如何在Qt资源文件中包含和释放exe等各种类型文件?
操作系统:Windows 10 X64 企业版 Qt: 5.8.0 QtCreater: 4.2.1 刚刚开始学习Qt,不断遇到困难和挑战,前几天在各个QQ群里询问如何在Qt的资源文件中包含和释放ex ...
- 守护进程与Supervisor
博客链接:http://www.cnblogs.com/zhenghongxin/p/8676565.html 消息队列处理后台任务带来的问题 在系统稍微大些的时候,我们经常会用到消息队列(实现的方式 ...
- XCode10.0遇到的问题
1:编译时报info.plist冲突. 解决方法,XCode上 File -> Workspace Settings ... 将Build System改为 Legacy Build Syste ...
- Vue 部署单页应用,刷新页面 404/502 报错
在 Vue 项目中,可以选择 hash或者 history.pushState() 实现路由跳转.如果在路由中使用history模式: export default new Router({ mode ...
- Centos之文件搜索命令find
find [搜索范围] [搜索条件] #搜索文件 find / -name install.log #避免大范围搜索,会非常耗费系统资源 #find是在系统当中搜索符合条件的文件名.如果需要匹配, 使 ...
- 如何通过Python暴力破解网站登陆密码
首先申明,该文章只可以用于交流学习,不可以用于其他用途,否则后果自负. 现在国家对网络安全的管理,越来越严,但是还是有一些不法网站逍遥法外,受限于国内的人力.物力,无法对这些网站进行取缔. 今天演示的 ...
- day 47 Django 4的简单应用 创建简单的图书管理 (单表的增删改查)
前情提要 Django 已经学了大半.. 很多东西已经能够使用在生产环境当中 一:模糊查询 二:单表删除 三:单表修改 四:图书管理 图书管理操作 视图结构 A:路由层 A :配置路由文件 参数解 ...
- C#获取获取北京时间多种方法
#region 获取网络时间 ///<summary> /// 获取中国国家授时中心网络服务器时间发布的当前时间 ///</summary> ///<returns> ...
